

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 846.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160758
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
JIANG Tingting*( ), WANG Yuanfang, LIU Peilong, TIAN Yixia, LI Hao, HU Yongguo
), WANG Yuanfang, LIU Peilong, TIAN Yixia, LI Hao, HU Yongguo
Received:2016-11-01
Online:2017-05-10
Published:2017-04-20
Contact:
JIANG Tingting
E-mail:jiangtingting@ldu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
JIANG Tingting, WANG Yuanfang, LIU Peilong, TIAN Yixia, LI Hao, HU Yongguo. Vancomycin Derivative Modified Silica-coated Silver Nanoplate for Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering Imaging and Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy of Vancomycin Resistant Bacterial Strains†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5): 846.
| Sample | MIC/(μmol·L-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| B. Subtilis | E. Faecium | E. Faecalis | |
| Van | 1 | >88 | 44 |
| Por-Van | 3 | >15* | >15* |
| AgNPl@SiO2-Por-Van | 0.005 | >0.010* | >0.010* |
Table 1 Minimum inhibition concentration(MIC) of AgNPl@SiO2-Por-Van and relative moieties towards Vancomycin sensitive and resistant bacterial strains
| Sample | MIC/(μmol·L-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| B. Subtilis | E. Faecium | E. Faecalis | |
| Van | 1 | >88 | 44 |
| Por-Van | 3 | >15* | >15* |
| AgNPl@SiO2-Por-Van | 0.005 | >0.010* | >0.010* |
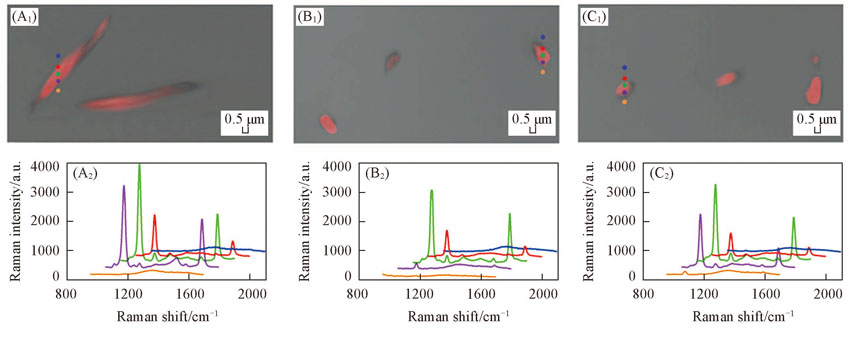
Fig.6 SERS(A1—C1) and the original Raman spectra(A2—C2) of five different points(A1)—(C1) Merged pictures of photographic images and Raman mappings of different bacterial strains. The maps are constructed on the band area at 1075 cm-1; (A2)—(C2) the Raman spectra in colors are collected from the points highlighted with same color by Raman confocal microscopy. (A1, A2) B. Subtilis; (B1, B2) E. Faecium(Van A); (C1, C2) E. Faecalis(Van B).
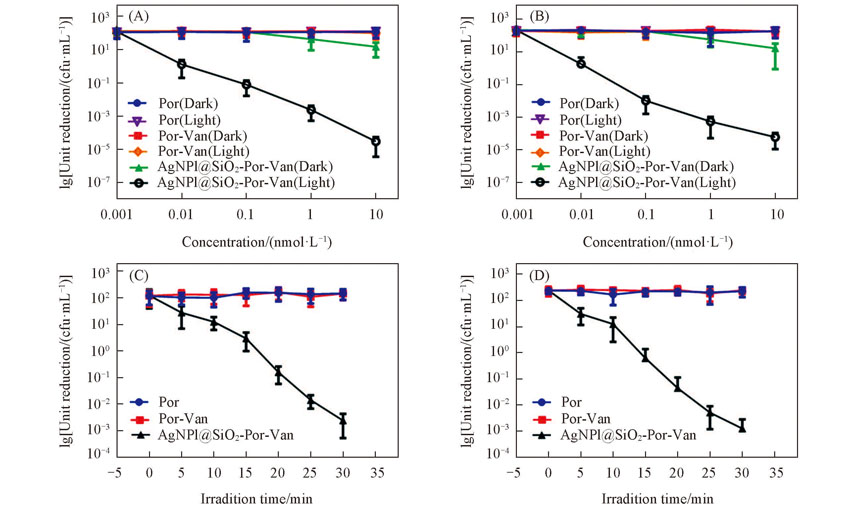
Fig.7 Dose(A, B) and light(C, D) dependent photodynamic inactivation effect of Por, Por-Van and AgNPl@SiO2-Por-Van towards E. faecium(VanA)(A, C) and E. faecalis(VanB)(B, D) (A, B) The irradiation time is 30 min; (B, D) the concentration is 10 nmol/L.
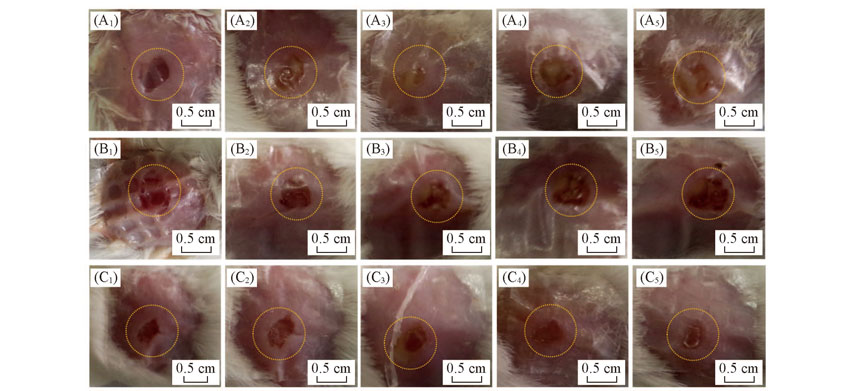
Fig.9 Color photographs of infection sites(wounds created at the mice back) of animals from different experimental groups(A1)—(A5) Non-treated; (B1—B5) AgNPl@SiO2-Por-Van treated without illumination; (C1)—(C5) AgNPl@SiO2-Por-Van treated with illumination. Time/d: (A1—C1) 0; (A2—C2) 1; (A3—C3) 2; (A4—C4) 3; (A5—C5) 4.
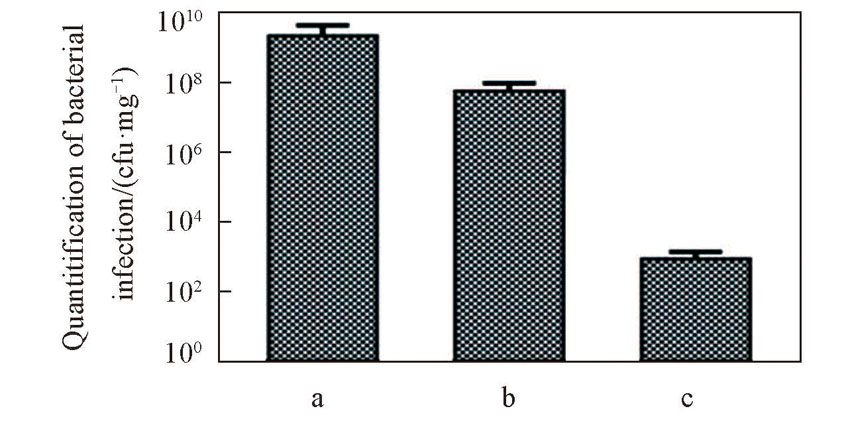
Fig.10 Quantitification of bacterial infection after the in vivo aPDT treatment at the fourth daya. Non-treated; b. AgNPl@SiO2-Por-Van treated without illumination; c. AgNPl@SiO2-Por-Van treated with illumination.
| [1] | Xing B., Jiang T., Bi W., Yang Y., Li L., Ma M., Chang C. K., Xu B., Yeow E. K., Chem. Commun., 2011, 47(5), 1601—1603 |
| [2] | Patel R., Gallagher J. C., Ann. Pharmacother., 2015, 49(1), 69—85 |
| [3] | Putty S., Vemula H., Bobba S., Gutheil W. G., Anal. Biochem., 2013, 442(2), 166—171 |
| [4] | Li L., Xu B., Curr. Pharm. Des., 2005, 11(24), 3111—3124 |
| [5] | Gao Y., Qiao G., Zhuo L., Li N., Liu Y., Tang B., Chem. Commun., 2011, 47(18), 5316—5318 |
| [6] | Jiang C., Cheng H., Yuan A., Tang X., Wu J., Hu Y., Acta Biomater., 2015, 14(1), 61—69 |
| [7] | Yuan A., Yang B., Wu J., Hu Y., Ming X., Acta Biomater., 2015, 21(1), 63—73 |
| [8] | Shi J., Chen Z., Wang L., Wang B., Xu L., Hou L., Zhang Z., Acta Biomater., 2016, 29(1), 282—297 |
| [9] | Vatansever F., de Melo W. C., Avci P., Vecchio D., Sadasivam M., Gupta A., Chandran R., Karimi M., Parizotto N. A., Yin R., Tegos G. P., Hamblin M. R., FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 2013, 37(6), 955—989 |
| [10] | Al-Ahmad A., Tennert C., Karygianni L., Wrbas K. T., Hellwig E., Altenburger M. J., J. Med. Chem., 2013, 62(3), 467—473 |
| [11] | Niu X., Chen H., Wang Y., Wang W., Sun X., Chen L., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6(7), 5152—5160 |
| [12] | Fang H., Zhang C. X., Liu L., Zhao Y. M., Xu H. J., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2015, 64(2), 434—441 |
| [13] | Tan Y. B., Zou J. M., Gu N., Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2015, 10(1), 417—424 |
| [14] | Zhao L., Kim T. H., Kim H. W., Ahn J. C., Kim S. Y., Acta Biomater., 2015, 20(1), 155—164 |
| [15] | Wang Y., Yan B., Chen L., Chem. Rev., 2013, 113(3), 1391—1428 |
| [16] | Lin D., Qin T., Wang Y., Sun X., Chen L., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6(2), 1320—1329 |
| [17] | Zhang W., Wang Y., Sun X., Wang W., Chen L., Nanoscale, 2014, 6(23), 14514—14522 |
| [18] | Wang Y., Chen L., Liu P., Chemistry, 2012, 18(19), 5935—5943 |
| [19] | Zhang J. L., Ma X., Xu M. X., Zong Y., Ren B., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(7), 1257—1261 |
| (张金亮, 马鑫, 徐梦溪, 宗铖, 任斌.高等学校化学学报, 2016,37(7), 1257—1261) | |
| [20] | Zou X., Dong S., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110(43), 21545—21550 |
| [21] | Gao C., Lu Z., Liu Y., Zhang Q., Chi M. I., Cheng Q., Yin Y., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 2012, 51(23), 5629—5633 |
| [22] | Xia Y., Ye J., Tan K., Wang J., Yang G., Anal. Chem., 2013, 85(13), 6241—6247 |
| [23] | Ung T., Liz-Marzan L. M., Mulvaney P., Langmuir, 1998, 14(14), 3740—3748 |
| [24] | Liz-Marzan L. M., Giersig M., Mulvaney P., Langmuir, 1996, 12(18), 4329—4335 |
| [25] | Murphy C.J., Gole A. M., Hunyadi S. E., Stone J. W., Sisco P. N., Alkilany A., Kinard B. E., Hankins P.,Chem. Commun., 2008, (5), 544—557 |
| [26] | Prevo B. G., Esakoff S. A., Mikhailovsky A., Zasadzinski J. A., Small, 2008, 4(8), 1183—1195 |
| [27] | Xia L., Kim N. H., Kim K., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2007, 306(1), 50—55 |
| [28] | González B., Colilla M., Vallet-Regí M., Chem. Mater., 2008, 20(15), 4826—4834 |
| [1] | YANG Jingyi, SHI Siqi, PENG Huaitao, YANG Qihao, CHEN Liang. Integration of Atomically Dispersed Ga Sites with C3N4 Nanosheets for Efficient Photo-driven CO2 Cycloaddition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220349. |
| [2] | XIA Wu, REN Yingyi, LIU Jing, WANG Feng. Chitosan Encapsulated CdSe QDs Assemblies for Visible Light-induced CO2 Reduction in an Aqueous Solution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220192. |
| [3] | SONG Yingying, HUANG Lin, LI Qingsen, CHEN Limiao. Preparation of CuO/BiVO4 Photocatalyst and Research on Carbon Dioxide Reduction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220126. |
| [4] | TAO Yu, OU Honghui, LEI Yongpeng, XIONG Yu. Research Progress of Single-atom Catalysts in Photocatalytic Reduction of Carbon Dioxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220143. |
| [5] | XI Jing, CHEN Na, YANG Yanbing, YUAN Quan. Recent Progress in Controlled Synthesis of Persistent Luminescence Nanomaterials for Diagnosis Applications [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3247. |
| [6] | SUN Yaguang, ZHANG Hanyan, MING Tao, XU Baotong, GAO Yu, DING Fu, XU Zhenhe. Synthesis of ZnIn2S4/g-C3N4 Nanocomposites with Efficient Photocatalytic H2 Generation Activity by a Simple Hydrothermal Method [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3160. |
| [7] | LI Chenchen, NA Yong. g-C3N4/CdS/Ni Composite as a Bifunctional Photocatalyst for H2 Generation and 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural Oxidation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2896. |
| [8] | WU Qiliang, MEI Jinghao, LI Zheng, FAN Haidong, ZHANG Yanwei. Photo-thermal Coupling Water Splitting over Fe-doped TiO2 with Various Nanostructures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1837. |
| [9] | ZHU Qichen, XIONG Ming, TAO Siyu, TANG Siwei, REN Qizhi. Effect of Light Source on the Photocatalytic Performance of Dihydroxynaphthalene by Water-soluble Sulfonated Porphyrins [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1933. |
| [10] | YANG Sixian, ZHONG Wenyu, LI Chaoxian, SU Qiuyao, XU Bingjia, HE Guping, SUN Fengqiang. Photochemical Fabrication and Performance of Polyaniline Nanowire/SnO2 Composite Photocatalyst [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1942. |
| [11] | WEI Hong, YANG Xiaoyu, LI Kebin, HAO Miao, FU Ran. Enhancement Effect of Low-power Ultrasound on Iopamidol Chlorination and the Degradation Pathway [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1863. |
| [12] | LI Dongping, LI Bin, LI Changheng, YU Xuegang, SHAN Yan, CHEN Kezheng. Synthesis and Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Ni5P4/g-C3N4 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1292. |
| [13] | GUI Chen, WANG Haolin, SHAO Baixuan, YANG Yujing, XU Guangqing. Molten-salt-assistance Synthesis and Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Performances of g-C3N4 Nanostructures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 827. |
| [14] | MA Zihui, WANG Mengyan, CAO Hongyu, TANG Qian, WANG Lihao, ZHENG Xuefang. Transient Absorption and Decay Kinetic Properties of Photo-excited Metal Coordinated Tetraphenylporphyrin [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 767. |
| [15] | ZHAO Yuhui, LI Mingle, LONG Saran, FAN Jiangli, PENG Xiaojun. Spectroscopic Characterization of Solvation Effect for a Polarity-Sensitive BDP [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2018. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||