

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 465.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190488
• Articles:Inorganix Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Fengren1,2,LIU Yongjia1,LU Xuemin2,ZHU Bangshang1,2,*
Received:2019-09-16
Online:2020-02-17
Published:2020-01-06
Contact:
Bangshang ZHU
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WU Fengren,LIU Yongjia,LU Xuemin,ZHU Bangshang. Controllable Preparation of Polydopamine Modified Gold Nanoflowers and Its Application in Photothermal Therapy †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 465.
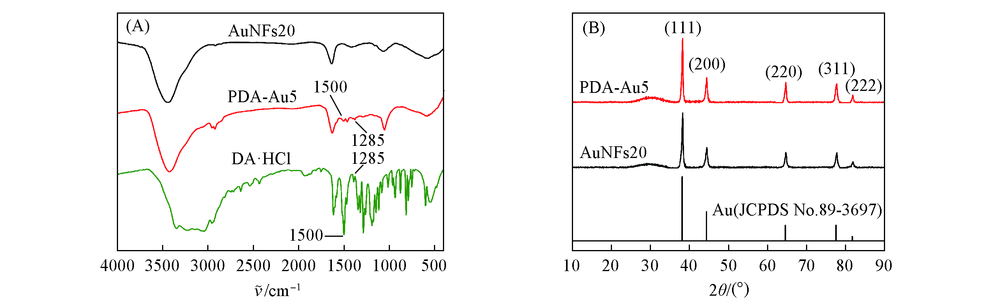
Fig.4 FTIR spectra of AuNFs prepared with 20 μL AA(AuNFs20), AuNFs modified with 5 mg/mL DA·HCl(PDA-Au5) and DA·HCl(A) and XRD patterns of standard Au(JCPDS No. 89-3697), AuNFs20 and PDA-Au5(B)
| [1] | Jia W. F., Li J. R., Lin G. H., Jiang L ., Cryst. Growth. Des., 2011, 11( 9), 3822— 3827 |
| [2] | Li S. N., Zhang L. Y., Wang T. T., Li L., Su Z. M ., Chem. Commun., 2015, 51( 76), 14338— 14341 |
| [3] | Wang C. R., Yan X. Z., Yu Y. F ., Mater. Res. Innov., 2014, 18( Sup2), 585— 590 |
| [4] | Ong X. Y., Chen S., Nabavi E., Regoutz A., Payne D. J., Elson D. S., Dexter D. T., Dunlnop I. E., Porter A. E ., ACS. Appl. Mater. Inter., 2017, 9( 45), 39259— 39270 |
| [5] | Zhong L., Zhai X. D., Zhu X F., Yao P. P., Liu M. H ., Langmuir, 2010, 26( 8), 5876— 5881 |
| [6] | Feng J. J., Chen S. S., Chen X. L., Zhang X. F., Wang A. J. J ., Colloid Interf. Sci., 2017, 509, 73— 81 |
| [7] | Wang A. J., Qin S. F., Zhou D. L., Cai L. Y., Chen J. R., Feng J. J ., Rsc. Adv., 2013, 3( 34), 14766— 14773 |
| [8] | Jian Y. Y., Deng Z. J., Yang D., Deng X., Li Q., Sha Y. L., Li C. H., Xu D. S ., Nano Res., 2015, 8( 7), 2152— 2161 |
| [9] | Barbosa S., Agrawal A., Rodríguez-Lorenzo L., Alvarez-Puebla R. A., Komowski A., Weller H., Liz-Marzan L. M ., Langmuir, 2010, 26( 18), 14943— 14950 |
| [10] | Han J., Li J. R., Jia W. F., Yao L. M., Li X. Q., Jiang L., Tian Y ., Int. J. Nanomed., 2014, 9, 517— 526 |
| [11] | Kumari S., Singh R. P ., Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2012, 50( 3), 878— 883 |
| [12] | Zhao L., Sun X., Ji X., Li J., Yang W., Peng X ., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 16645— 16651 |
| [13] | Mao K., Chen Y., Wu Z., Zhou X., Shen A., Hu J ., J. Agric. Food Chem., 2014, 62, 10638— 10645 |
| [14] | Zhao X. M., Qi T. Y., Kong H. F., Hao M., Wang Y. Q., Li J., Liu B. C., Gao Y. Y., Jiang J. L ., Int. J. Nanomed., 2018, 13, 6413— 6428 |
| [15] | Liu Z. G., Qu S. X., Wen J ., Prog. Chem., 2015, 27( 2/3), 212— 219 |
| ( 刘宗光, 屈树新, 翁杰 . 化学进展, 2015, 27( 2/3), 212— 219) | |
| [16] | Liu Y. W., Guo Z ., Chem. J., Chinese Universities, 2015, 36( 7), 1389— 1394 |
| ( 刘宇炜, 郭卓 . 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36( 7), 1389— 1394) | |
| [17] | Khlebtsov B. N., Burov A. M., Khlebtsov N. G ., Appl. Mater. Today, 2019, 15, 67— 76 |
| [18] | Jiang Y. Y., Wu X. J., Li Q., Li J. J., Xu D. S ., Nanotechnology, 2011, 22( 38), 385601 |
| [19] | Luo Y. S., Ji X. H., Zhuang J. Q., Yang W. S ., Colloid Surface A, 2014, 463, 28— 36 |
| [20] | de Vries W. C., Niehues M., Wissing M., Wurthwein T., Masing F., Fallnich C., Studer A., Ravoo J. J ., Nanoscale, 2019, 11( 19), 9384— 9391 |
| [21] | Garrido C., Wsiss-Lopez B. E., Vallette M. M. C ., Spectrosc. Lett., 2016, 49( 1), 11— 18 |
| [22] | Chen W. F., Qin M., Chen X. Y., Wang Q., Zhang Z. R., Sun X ., Theranostics, 2018, 8( 8), 2229— 2241 |
| [23] | Poinard B., Neo S. Z. Y., Yeo E. L. L., Heng H. P. S., Neoh K. G., Kah J. C. Y ., ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2018, 10( 25), 21125— 21136 |
| [24] | Fu J. W., Chen Z. H., Wang M. H., Liu S. J., Zhang J. H., Zhang J. N., Han R. P., Xu Q ., Chem. Eng. J., 2015, 259, 53— 61 |
| [1] | LIU Shuwei, JIN Hao, YIN Wanzhong, ZHANG Hao. Gemcitabine/polypyrrole Composite Nanoparticles for Chemo-photothermal Combination Ovarian Cancer Therapy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220345. |
| [2] | YU Pengdong, GUAN Xinghua, WANG Dongdong, XIN Zhirong, SHI Qiang, YIN Jinghua. Preparation and Properties of Novel Optical and Thermal Dual Response Shape Memory Polymers [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220085. |
| [3] | FAN Xiaohui, WANG Yang, YANG Yuanyuan, ZHANG Yuhong. Preparation and Properties of Gold Nanocages/Hyaluronic Acid Core-shell Nanocarriers with pH/Enzyme/ Photothermal Multiple Responses [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210855. |
| [4] | WANG Xueli, SONG Xiangwei, XIE Yanning, DU Niyang, WANG Zhenxin. Preparation, Characterization of Partially Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Killing Effect on Human Cervical Cancer Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210595. |
| [5] | ZHANG Zhibo, SHANG Han, XU Wenxuan, HAN Guangdong, CUI Jinsheng, YANG Haoran, LI Ruixin, ZHANG Shenghui, XU Huan. Self-Assembly of Graphene Oxide at Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Microparticles Toward High-performance Intercalated Nanocomposites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210566. |
| [6] | XU Huan, KE Lyu, TANG Mengke, SHANG Han, XU Wenxuan, ZHANG Zilin, FU Yanan, HAN Guangdong, CUI Jinsheng, YANG Haoran, GAO Jiefeng, ZHANG Shenghui, HE Xinjian. In⁃situ Liquid Exfoliation of Montmorillonite Nanosheets in Poly(lactic acid) to Resist Oxygen Permeation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220316. |
| [7] | WANG Ye, ZHANG Xiaosi, SUN Lijing, LI Bing, LIU Lin, YANG Miao, TIAN Peng, LIU Zhongyi, LIU Zhongmin. Morphology Control of SAPO Molecular Sieves under the Assistance of Organosilane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 683. |
| [8] | LU Feng, GONG Yi, ZHAO Ting, ZHAO Ning, JU Wenwen, FAN Quli, HUANG Wei. Seedless Synthesis of Gold Nanorods with Narrow Absorption Using Binary Surfactant Mixture [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 700. |
| [9] | SUN Qirui, ZHAO Nan, LIU Shuwei, XIN Hua, ZHANG Hao, ZHANG Lening. Polydopamine-coated Fe3O4/methylprednisolone/cyclophosphamide Superparticles for the Magnetic Targeting Treatment of Pulmonary Fibrosis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3225. |
| [10] | LU Man,SONG Chunmei,WAN Bo. Thixotropic Behavior of Hydrophobically Modified Ethoxylated Urethane-thickened Waterborne Latex † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1108. |
| [11] | SHI Xiaoyu, WANG Songmeng, LIU Lingyan, CHANG Weixing, LI Jing. Controllable Synthesis of Amphiphilic Block Copolymer PMnEOS-b-PAA and co-Assembly Morphologies of PMDEOS-b-PAA/PS-b-PAA [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2545. |
| [12] | SHAO Wei, LEE Jiyoung, LI Fangyuan, LING Daishun. Organic Small Molecule Nanoparticles for Phototheranostics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2356. |
| [13] | WANG Yue, GUO Xiaohong, ZHOU Guangdong, CHENG Tiexin. Effect of Alkyl Benzene Sulfonate Surfactant on Morphology and Structure of Calcium Silicate Hydrate † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1795. |
| [14] | LIU Yun, LI Ting, WANG Yang, DONG Weifu. Preparation of Multi-scale Superhydrophobic Cotton/Polydopamine/Silica Composite for Selective Oil Absorption [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1775. |
| [15] | REN Wei, TIAN Ye, XING Lingli, YANG Yuexi, DING Tong, LI Xingang. K Promoted Nanosheets-like Hydrotalcite-derived CoAlO Metal Oxides for Catalytic Soot Combustion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1670. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||