

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (3): 448.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180521
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Ying*( ), KANG Junjun, ZHAO Xueru, XU Wenkai, QI Qi
), KANG Junjun, ZHAO Xueru, XU Wenkai, QI Qi
Received:2019-07-24
Online:2019-03-10
Published:2019-08-21
Contact:
LI Ying
E-mail:liying_791190@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LI Ying, KANG Junjun, ZHAO Xueru, XU Wenkai, QI Qi. Preparation of Gold-modified Magnetic Graphene-based Molecularly Imprinted Composites and Electrochemical Sensing Detection of Dinbutyl Phthalate in Water†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(3): 448.
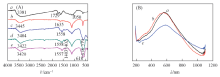
Fig.3 FTIR spectra(A) of GO(a), Au@RGO(b), Fe3O4@RGO(c), Au@Fe3O4@RGO(d) and Au@Fe3O4@RGO-MIP(e) and ultraviolet(UV) spectra(B) of Au@RGO(a), Au@Fe3O4@RGO(b) and Au@Fe3O4@RGO-MIP(c)
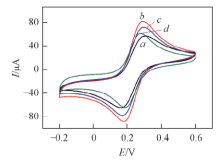
Fig.4 CV curves of Au@RGO(a), Au@Fe3O4@RGO(b), Au@Fe3O4@RGO-MIP(c), Au@Fe3O4@RGO-MIP(d) after binding templateCV curves were recorded between -0.5 V to 0.5 V in 5 mmol/L K3[Fe(CN)6] solution containing 0.1 mol/L KCl at a scan rate of 50 mV/s.
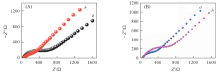
Fig.5 Electrochemical impedance spectra of Au@RGO(a), Au@Fe3O4@RGO(b)(A), Au@Fe3O4@RGO-MIP(a) and Au@Fe3O4@RGO-MIP(b)(B) after binding templateEIS of various electrodes were recorded between -0.5 V to 0.5 V in 5 mmol/L K3[Fe(CN)6] solution containing 0.1 mol/L KCl at a scan rate of 50 mV/s.
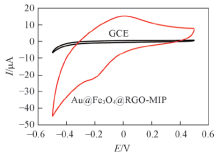
Fig.6 CV curves of DBP detectionCV curves of various electrodes were recorded between -0.5 V to 0.5 V in 0.1 mol/L PBS solution at a scan rate of 50 mV/s.
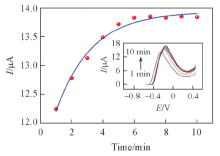
Fig.7 Adsorption kinetic curve on the response to DBP for Au@Fe3O4@RGO-MIPs electrode in PBS solution containing 10 μmol/L DBPThe insert is the DBP for Au@Fe3O4@RGO-MIP at different times. DPV of various electrodes were recorded between -0.5 V to 0.5 V in 0.1 mol/L PBS solution at a scan rate of 50 mV/s, the amplitude of 50 mV, the pulse width of 50 ms, pulse cycle of 200 ms.
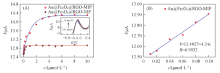
Fig.8 Different concentration curves of DBP on Au@Fe3O4@RGO-MIP and Au@Fe3O4@RGO-NIP(A) and linear relationship curve of Au@Fe3O4@RGO-MIP detects DBP(B)Inset is the DPV curves of Au@Fe3O4@RGO-MIP for different concentrations of DBP. DPV of various electrodes were recorded between -0.5 V to 0.5 V in 0.1 mol/L PBS solution at a scan rate of 50 mV/s, the amplitude of 50 mV, the pulse width of 50 ms, pulse cycle of 200 ms.
| Sensor | LOD/(nmol·L-1) | Linear range/(μmol·L-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| MWCNTs@GONRs/GCE | 25.15 | 1.44—229.93 | [ |
| DBP-MMIP-CL | 2.09 | 20.8—38400 | [ |
| MGO@Au NPs-MIPs | 0.80 | 2.5—5 | [ |
| Nano-Ni(OH)2 QCM | 17.96 | 0.018—0.072 | [ |
| Au@Fe3O4@RGO-MIP | 0.305 | 0.01—0.1 | This work |
Table 1 Comparison with the other electrochemical sensors for determination of DBP
| Sensor | LOD/(nmol·L-1) | Linear range/(μmol·L-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| MWCNTs@GONRs/GCE | 25.15 | 1.44—229.93 | [ |
| DBP-MMIP-CL | 2.09 | 20.8—38400 | [ |
| MGO@Au NPs-MIPs | 0.80 | 2.5—5 | [ |
| Nano-Ni(OH)2 QCM | 17.96 | 0.018—0.072 | [ |
| Au@Fe3O4@RGO-MIP | 0.305 | 0.01—0.1 | This work |
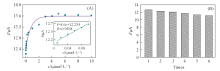
Fig.10 Response curve of Au@Fe3O4@RGO-MIP modified electrode to DBP concentration in lake water(A) and reproducibility of Au@Fe3O4@RGO-MIP for the detection of DBP(B)Inset of (A) is the calibration curve.
| [1] | Li J., Su Q., Li K. Y., Sun C. F., Zhang W. B., Food Chem., 2013, 141(4), 3714—3720 |
| [2] | Wang T., Wang J., Zhang C. L., Yang Z., Dal X. P., Cheng M. S., Hou X. H., Analyst, 2015, 140(15), 5308—5316 |
| [3] | Barp L., Purcaro G., Franchina F. A., Zoccali M., Sciarrone D., Tranchida P. Q., Mondello L., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2015, 887, 237—244 |
| [4] | Du L. P., Ma L. J., Qiao Y., Lu Y., Xiao D. G., Food Chem., 2016, 197, 1200—1206 |
| [5] | Liu M., Peng Q. Q., Cheng Y. F., Tang Q., Feng Q., Food Chem., 2015, 176, 12—16 |
| [6] | Liu Q., Yang H. J., Shi Y. X., Shu L., Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2012, 20(8), 968—975 |
| (刘庆, 杨红军, 史衍玺, 舒龙. 中国生态农业学报, 2012, 20(8), 968—975) | |
| [7] | US Environmental Protection Agency, Phthalates Action Plan, 2012-03-12 |
| [8] | Zhang S. H., Yang Q., Li Z., Wang W. J., Zang X. H., Zang X. H., Wang C., Wang Z., Food Chem., 2019, 263, 258—264 |
| [9] | Xu W. Z., Zhang X. M., Huang W. H., Nie Y. J., Yang W. M., Chinese J. Anal. Chem., 2017, 45(4), 521—528 |
| (徐婉珍, 张枭明, 黄卫红, 聂仪晶, 杨文明. 分析化学, 2017, 45(4), 521—528) | |
| [10] | Javier G. S., Miguel Ángel G. C., Bárbara S. R., Javier H. B., Miguel Ángel R. D., Chemosphere, 2019, 201, 254—261 |
| [11] | Dai X. Y., Wu P., Environmental Science Guide, 2017, 36(1), 80—82 |
| (戴轩宇, 吴鹏. 环境科学导刊, 2017, 36(1), 80—82) | |
| [12] | Liang Y. R., Zhang Z. M., Liu Z. J., Wang K., Wu X. Y., Zeng K., Meng H., Zhang Z., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2017, 91, 199—202 |
| [13] | Yang X., Zhang Z. H., Cheng X., Zhang M. L., Luo L. J., Peng M. J., Nie L. H., Chinese J. Anal. Chem., 2012, 40(6), 870—876 |
| (杨潇, 张朝晖, 陈星, 张明磊, 罗丽娟, 彭密军, 聂丽华. 分析化学, 2012, 40(6), 870—876) | |
| [14] | Zeng H.H.., Li X. Q., Hao W. L., Zhang L. Z., Wei T., Zhao X. F., Liu Y. Y., Li J. H.,J. Hazard. Mater., 2017, 324, 250—257 |
| [15] | Zhao L. J., Gao L., Yi L. X., Jiang C., Zhao K., Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2017, 37(1), 109—113 |
| (赵丽君, 高磊, 衣玲学, 姜晨, 赵昆. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2017, 37(1), 109—113) | |
| [16] | He F., Tian Y. X., Xu Z. L., Luo L., Yang J. Y., Wang H., Sun Y. M., Du Q. F., Shen Y. D., J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A, 2019, 81(4), 80—88 |
| [17] | Feng N. X., Yu J., Mo C. H., Zhao H. M., Li Y. W., Wu B. X., Cai Q. Y., Li H., Zhou D. M., Wong M. H., Sci. Total Environ., 2019, 616, 117—127 |
| [18] | Guo J. B., Chen W., Jiang L. J., Ma F., Zheng G. C., Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2014, 20(6), 1104—1110 |
| (郭静波, 陈微, 姜丽杰, 马放, 郑国臣. 应用与环境生物学报, 2014, 20(6), 1104—1110) | |
| [19] | Yáñez-Sedeño P., Campuzano S., Pingarrón J. M., Analytica Chimica Acta, 2017, 960, 1—17 |
| [20] | Zamora-Gálvez A., Ait-Lahcen A., Mercante L. A., Analytical Chemistry, 2016, 88(7), 3573—3584 |
| [21] | Han Q., Shen X., Zhu W. Y., Zhu C. H., Zhou X. M., Jiang H. J., Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2016, 79, 180—186 |
| [22] | Yola M. L., Eren T., Atar N., Sens. Actuators, B, 2015, 210, 149—157 |
| [23] | Hummers Jr.W. S.., Offeman R. E.,J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1958, 80(6), 1339 |
| [24] | Kovtyukhova N. I., Ollivier P. J., Martin B. R., Mallouk T. E., Chizhik C. A., Buzaneva E. V., Gorchinskiy A. D., Chem. Mater., 1999, 11(3), 771—778 |
| [25] | Li S. H., Liu C. H., Yin G. H., Zhang Q., Luo J. H., Wu N. C., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2017, 91, 687—691 |
| [26] | Tanhaei M., Mahjoub A. R., Safarifard V., Mater. Lett., 2019, 41, 189—195 |
| [27] | Li D., Liu Y. R., Lin B. P., Sun Y., Yang H., Chemical Progress, 2015, 27(4), 404—415 |
| (李丹, 刘玉荣, 林保平, 孙莹, 杨洪. 化学进展, 2015, 27(4), 404—415) | |
| [28] | Lu X. J., Preparation, Characterization and Supercapacitance Characteristics of Graphene—Based Conductive Polymer Composites, Nanjing Aerospace University, Naijing, 2011 |
| (卢向军. 石墨烯基导电聚合物复合材料的制备、 表征及其超电容特性研究, 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2011) | |
| [29] | Wang Y., Zhai F., Hasebe Y., Jia H. M., Zhang Z. Q., Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg., 2019, 122, 174—182 |
| [30] | Hao J. X., Wu K. B., Wan C. D., Tang Y., Talanta, 2019, 185, 550—556 |
| [31] | Mathew G., Dey P., Das R., Chowdhury S. D., Das M. P., Veluswamy P., Neppolian B., Das J., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2019, 115, 53—60 |
| [32] | Tung V. C., Allen M. J., Yang Y., Kaner R. B., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2009, 4(1), 25—29 |
| [33] | Zhang J., Ma J., Fan X., Peng W., Zhang G., Catal. Commun., 2017, 89, 148—151 |
| [34] | Dabiri M., Lehi N. F., Movahed S. K., Catal. Lett., 2016, 146(9), 1674—1686 |
| [35] | Wang D. M., Duan H. C., Lü J. H., Lü C. L., Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(10), 5088—5097 |
| [36] | Yan G. W., Zhang Y., Di W. H., Qin W. P., Dyes Pigm., 2019, 159, 28—34 |
| [37] | Qiu H.M.., Fan L. L., Li X. J., Li L. L., Sun M., Luo C. N.,J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. Anal., 2013, 75, 123—129 |
| [38] | Li X. J., Wang X. X., Li L. L., Duan H. M., Luo C. N., Talanta, 2015, 131, 354—360 |
| [39] | Hu R. H., Zhang K. H., Fan G. K., Luo Z. Y., Li G., Meas. Sci. Technol., 2015, 26, 055102 |
| [1] | WANG Ruina, SUN Ruifen, ZHONG Tianhua, CHI Yuwu. Fabrication of a Dispersible Large-sized Graphene Quantum Dot Assemblies from Graphene Oxide and Its Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence Behaviors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220161. |
| [2] | LI Yulong, XIE Fating, GUAN Yan, LIU Jiali, ZHANG Guiqun, YAO Chao, YANG Tong, YANG Yunhui, HU Rong. A Ratiometric Electrochemical Sensor Based on Silver Ion Interaction with DNA for the Detection of Silver Ion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220202. |
| [3] | YAN Jiasen, HAN Xianying, DANG Zhaohan, LI Jiangang, HE Xiangming. Preparation and Performance of Paraffin/Expanded Graphite/Graphene Composite Phase Change Heat Storage Material [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220054. |
| [4] | WANG Junyang, LIU Zheng, ZHANG Qian, SUN Chunyan, LI Hongxia. Application of DNA Silver Nanoclusters in the Fluorescence Biosensors based on Functional Nucleic Acids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220010. |
| [5] | CAO Lei, CHEN Meijun, YUAN Gang, CHANG Gang, ZHANG Xiuhua, WANG Shengfu, HE Hanping. Solution-gated Graphene Field Effect Transistor Sensor Based on Crown Ether Functionalization for the Detection of Mercury Ion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210688. |
| [6] | ZHENG Xuelian, YANG Cuicui, TIAN Weiquan. The Second Order Nonlinear Optical Properties of Azulene-defect Graphene Nanosheets with Full Armchair Edge [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210806. |
| [7] | YANG Junge, GAO Chengqian, LI Boxin, YIN Dezhong. Preparation of High Thermal Conductivity Phase Change Monolithic Materials Based on Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Surface Modified Graphene Oxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210593. |
| [8] | ZHANG Zhibo, SHANG Han, XU Wenxuan, HAN Guangdong, CUI Jinsheng, YANG Haoran, LI Ruixin, ZHANG Shenghui, XU Huan. Self-Assembly of Graphene Oxide at Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Microparticles Toward High-performance Intercalated Nanocomposites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210566. |
| [9] | HU Bo, ZHU Haochen. Dielectric Constant of Confined Water in a Bilayer Graphene Oxide Nanosystem [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [10] | YU Bin, CHEN Xiaoyan, ZHAO Yue, CHEN Weichang, XIAO Xinyan, LIU Haiyang. Graphene Oxide-based Cobalt Porphyrin Composites for Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210549. |
| [11] | WANG Xueli, SONG Xiangwei, XIE Yanning, DU Niyang, WANG Zhenxin. Preparation, Characterization of Partially Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Killing Effect on Human Cervical Cancer Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210595. |
| [12] | WEI Chuangyu, CHEN Yanli, JIANG Jianzhuang. Fabrication of Electrochemical Sensor for Dopamine and Uric Acid Based on a Novel Dimeric Phthalocyanine-involved Quintuple-decker Modified Indium Tin Oxide Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210582. |
| [13] | MA Lijuan, GAO Shengqi, RONG Yifei, JIA Jianfeng, WU Haishun. Theoretical Investigation of Hydrogen Storage Properties of Sc, Ti, V-decorated and B/N-doped Monovacancy Graphene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2842. |
| [14] | ZHAO Lingyun, HUANG Hanxiong, LUO Duyu, SU Fengchun. Effect of Flexibility of Composites on Performances of Sensors with Micro-structured Inverted Pyramid Arrays [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2953. |
| [15] | PAN Xiaojun, BAO Rongrong, PAN Caofeng. Research Progress of Flexible Tactile Sensors Applied to Wearable Electronics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2359. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||