

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 20220749.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220749
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
XU Jianing, BAI Wenjing, LOU Yuhan, YU Haipeng( ), DOU Shuo(
), DOU Shuo( )
)
Received:2022-12-06
Online:2023-05-10
Published:2023-01-09
Contact:
YU Haipeng, DOU Shuo
E-mail:yuhaipeng20000@nefu.edu.cn;doushuo@nefu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
XU Jianing, BAI Wenjing, LOU Yuhan, YU Haipeng, DOU Shuo. Electrocatalytic Oxidative Cleavage of Lignin: Facile and Efficient Biomass Valorization Strategy[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(5): 20220749.
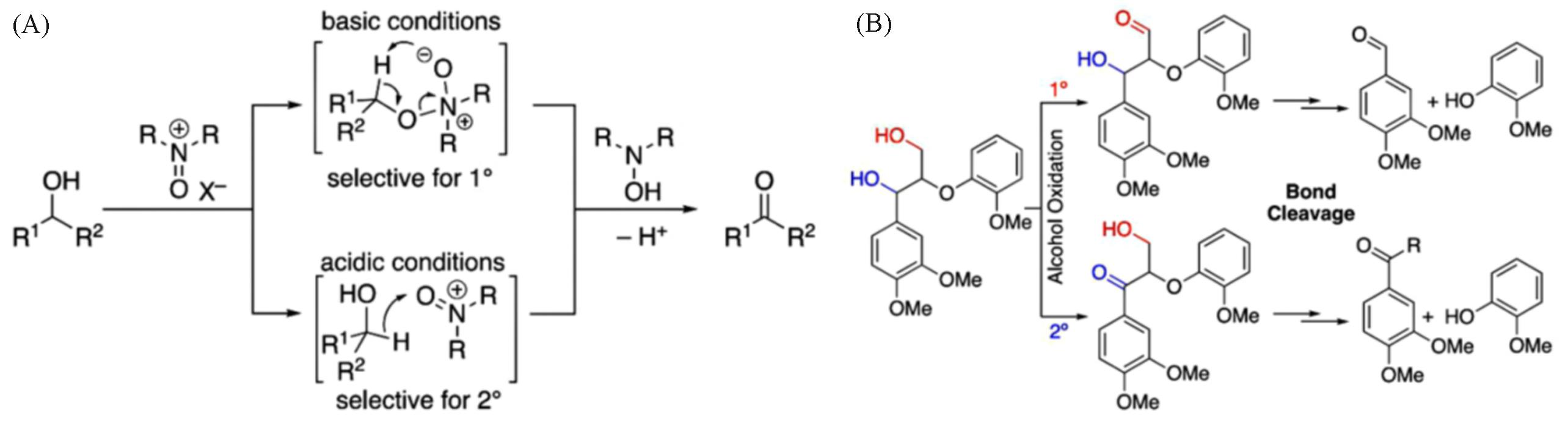
Fig.2 Mechanism of alcohol oxidation by oxoammonium under basic and acidic conditions(A) and chemoselective alcohol oxidation strategies for cleavage of β⁃O⁃4 lignin model(B)[48]
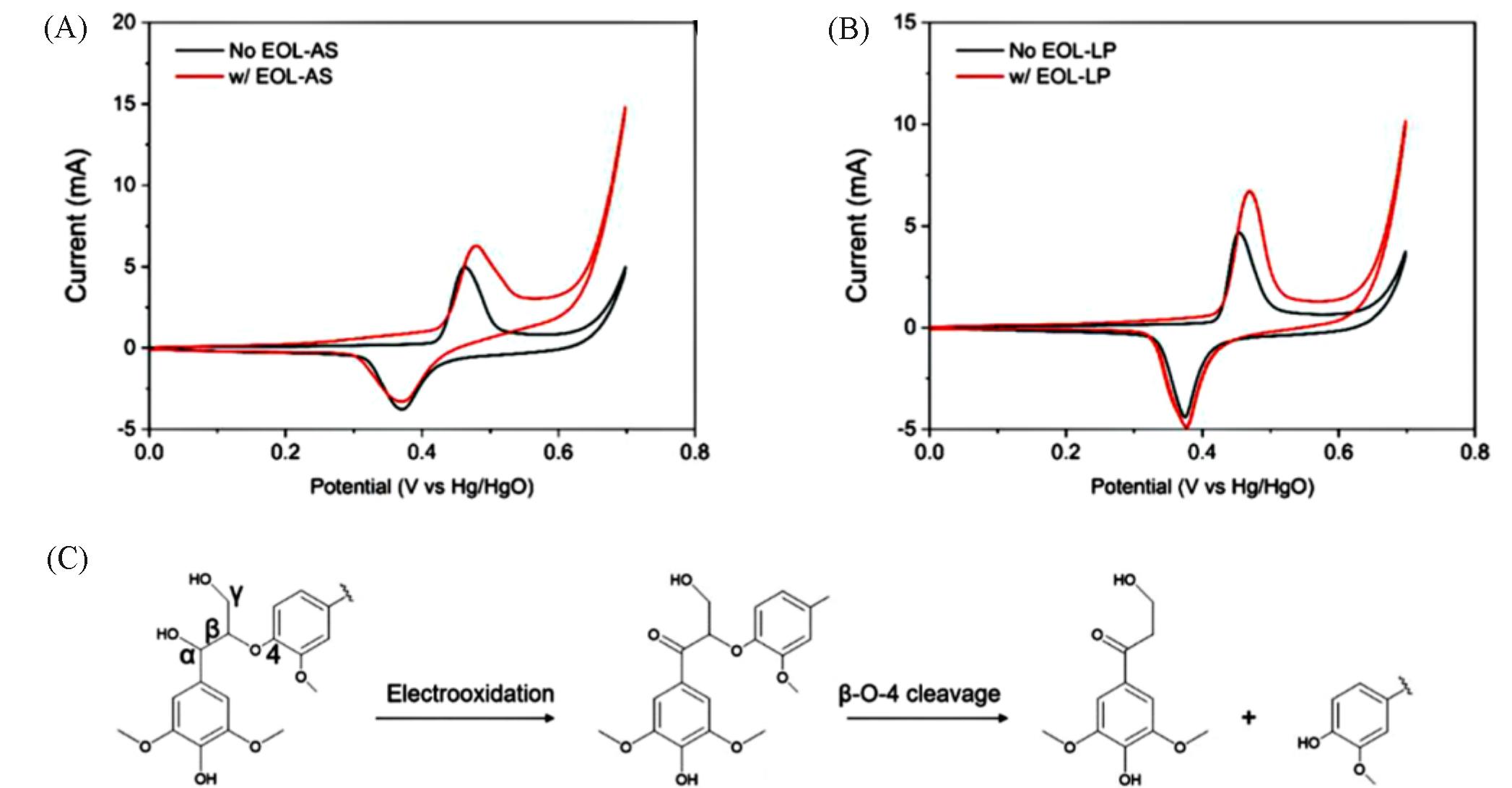
Fig.4 Cyclic voltammograms of nickel foam in 1.0 mol/L KOH before and after the addition of 20 mg of EOL⁃AS(A) and EOL⁃LP(B) lignin and schematic representation of the oxidation and cleavage of the lignin β⁃O⁃4 unit(C)[59]
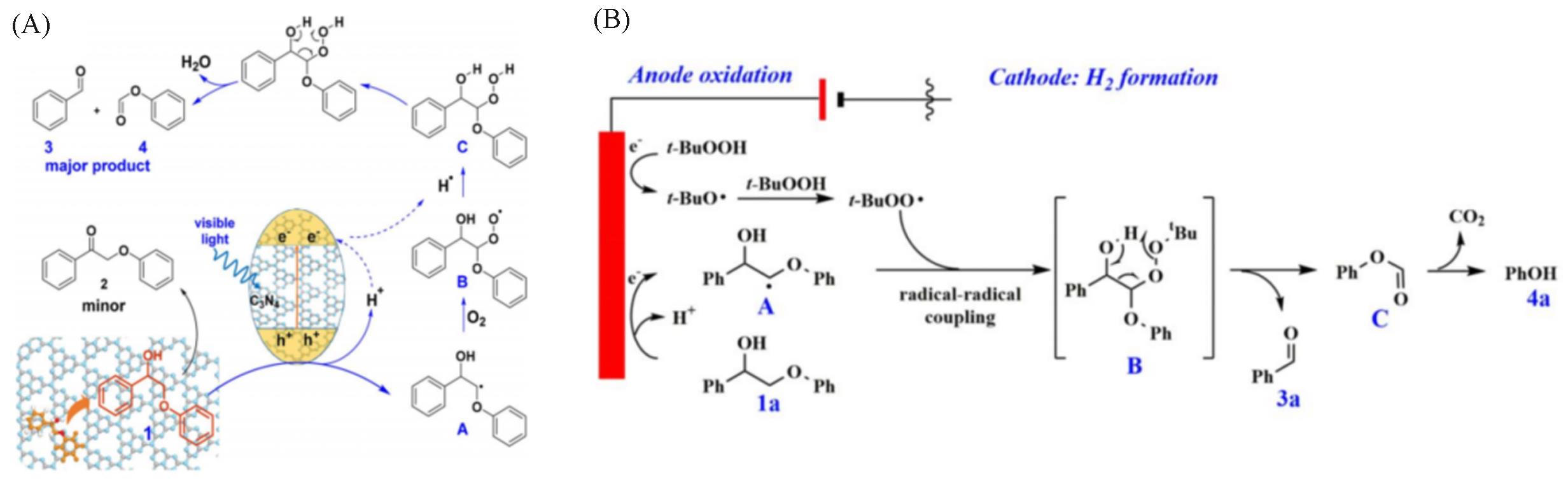
Fig.5 Mechanism of mesoporous graphitic carbon nitrides on catalyzing the transformation of lignin model molecule(A)[82] and mechanism for the electrocatalytic C α —C β bond cleavage of the lignin model compound(B)[83](A) Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society; (B) Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society
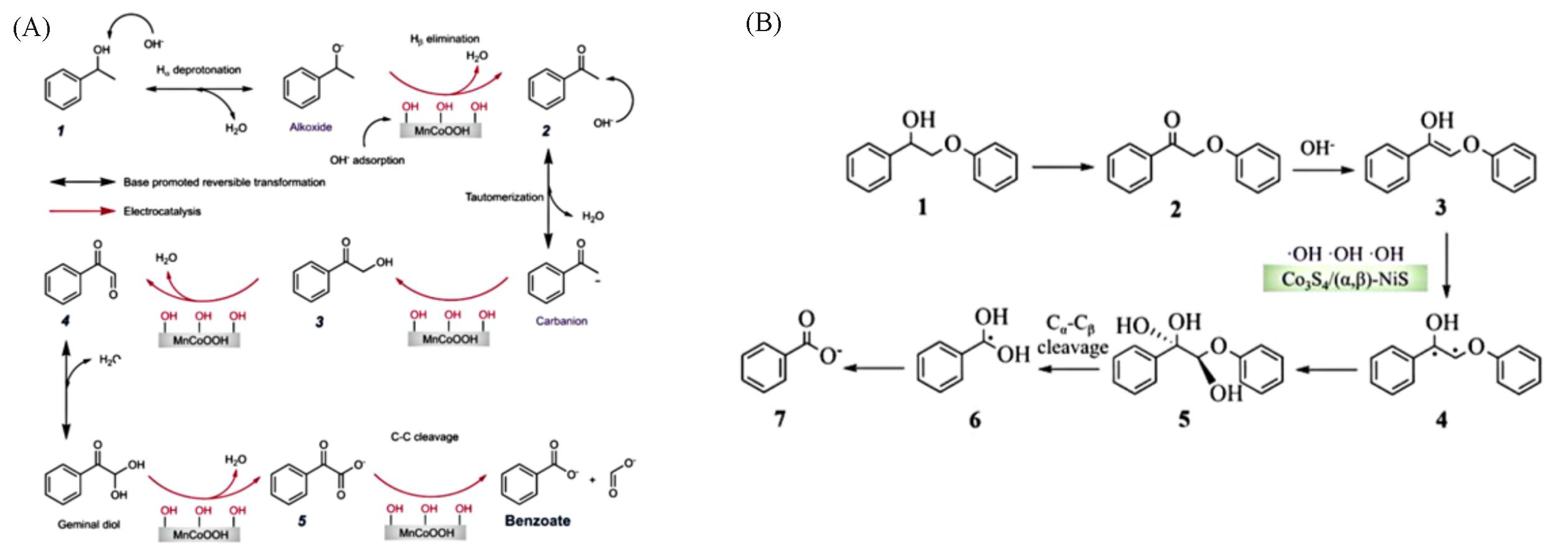
Fig.6 A plausible tandem nucleophilic oxidation reaction(NOR) mechanism for electrochemical oxidation (A)[87] and proposed oxidation pathways of PPE(B)[88]1. PPE; 2. 2⁃Phenoxy⁃1⁃phe⁃nylethanone; 3. (Z)⁃2⁃phenoxy⁃1⁃phenylethen⁃1⁃ol; 4. the intermediates of free radical
| 1 | Yang C., Maldonado S., Stephenson C. R. J., ACS Catal., 2021, 11(16), 10104—10114 |
| 2 | Zhang L. J., Rao T. U., Wang J. Y., Ren D. Z., Sirisommboonchai S., Choi C., Machida H., Huo Z. B., Norinaga K., Fuel Process. Technol., 2022, 226, 107097 |
| 3 | Li C. Z., Zhao X. C., Wang A. Q., Huber G. W., Zhang T., Chem. Rev., 2015, 115(21), 11559—11624 |
| 4 | Park J. H., Jin M. H., Lee D. W., Lee Y. J., Song G. S., Park S. J., Namkung H., Song K. H., Choi Y. C., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2019, 53(23), 14041—14053 |
| 5 | Lei L. J., Wang Y. H., Zhang Z. X., An J. H., Wang F., ACS Catal., 2020, 10(15), 8788—8814 |
| 6 | Jing Y. X., Guo Y., Xia Q. N., Liu X. H., Wang Y. Q., Chem., 2019, 5(10), 2520—2546 |
| 7 | Rinaldi R., Jastrzebski R., Clough M. T., Ralph J., Kennema M., Bruijnincx P. C. A., Weckhuysen B. M., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55(29), 8164—8215 |
| 8 | Luo N. C., Wang M., Li H. J., Zhang J., Liu H. F., Wang F., ACS Catal., 2016, 6(11), 7716—7721 |
| 9 | Hendry A., Åhlén M., Fernandes T., Cheung O., Sanna A., Bioresource Technol., 2020, 317, 124008 |
| 10 | Shen X. J., Zhang C. F., Han B. X., Wang, F., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2022, 51(5), 1608—1628 |
| 11 | Sudarsanam P., Zhong R. Y., van den Bosch S., Coman S. M., Parvulescu V. I., Sels B. F., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018, 47(22), 8349—8402 |
| 12 | da Cruz M. G. A., Gueret R., Chen J. H., Piątek J., Beele B., Sipponen M. H., Frauscher M., Budnyk S., Rodrigues B. V. M., Slabon A., ChemSusChem, 2022, 15(15), e20220718 |
| 13 | Chatterjee S., Saito T., ChemSusChem, 2015, 8(23), 3941—3958 |
| 14 | Zhou S. J., Wang H. M., Xiong S. J., Sun J. M., Wang Y. Y., Yu S. X., Sun Z. H., Wen J. L., Yuan T. Q., ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2021, 9(36), 12017—12042 |
| 15 | Ashokkumar V., Venkatkarthick R., Jayashree S., Chuetor S., Dharmaraj S., Kumar G., Chen W. H., Ngamcharussrivichai C., Bioresource Technol., 2022, 344, 126195 |
| 16 | Zhang C. F., Wang F., Acc. Chem. Res., 2020, 53(2), 470—484 |
| 17 | Zhang Z. R., Song J. L., Han B. X., Chem. Rev., 2017, 117(10), 6834—6880 |
| 18 | Lee K., Jing Y. X., Wang Y. Q., Yan N., Nature Rev. Chem., 2022, 6(9), 635—652 |
| 19 | Garedew M., Lin F., Song B., DeWinter T. M., Jackson J. E., Saffron C. M., Lam C. H., Anastas P. T., ChemSusChem, 2020, 13(17), 4214—4237 |
| 20 | Kumar A., Biswas B., Saini K., Kumar A., Kumar J., Krishna B. B., Bhaskar T., Renew. Energ., 2021, 172, 121—129 |
| 21 | Yang C. X., Chen H. N., Peng T., Liang B. Y., Zhang Y., Zhao W., Chinese J. Catal., 2021, 42(11), 1831—1842 |
| 22 | Weng J. K., Chapple C., New Phytol., 2010, 187(2), 273—285 |
| 23 | Xia Q. Q., Chen C. J., Yao Y. G., He S. M., Wang X. Z., Li, J. G., Gao J. L., Gan W. T., Jiang B., Cui M. J., Hu L. B., Adv. Mater., 2021, 33(8), 2001588 |
| 24 | Bajwa D. S., Pourhashem G., Ullah A. H., Bajwa S. G., Ind. Crop. Prod., 2019, 139, 111526 |
| 25 | Gao M., Jiang Z. C., Ding W., Shi B., Green Chem., 2022, 24(1), 375—383 |
| 26 | Kubo S., Kadla J. F., J. Polym. Environ., 2005, 13(2), 97—105 |
| 27 | Galkin M. V., Samec J. S. M., ChemSusChem, 2016, 9(13), 1544—1558 |
| 28 | Peng T., Zhuang T. T., Yan Y., Qian J., Dick G. R., de Bueren J. B., Hung S. F., Zhang Y., Wang Z. Y., Wicks J., de Arquer F. P. G., Abed J., Wang N., Rasouli A. S., Lee G., Wang M., He D. P., Wang Z., Liang Z. X., Song L., Wang X., Chen B., Ozden A., Lum Y. W., Leow W. R., Luo M. C., Meira D. M., Ip A. H., Luterbacher J. S., Zhao W., Sargent E. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143(41), 17226—17235 |
| 29 | Tian H. F., Guo G. P., Fu X. W., Yao Y. Y., Yuan L., Xiang A. M., Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2018, 120, 475—490 |
| 30 | Fan Y. Y., Liu C., Kong X. C., Han Y., Lei M., Xiao R., Green Energy Environ., 2022, 7(6), 1318—1326 |
| 31 | Wu X. J., Luo N. C., Xie S. J., Zhang H. K., Zhang Q. H., Wang F., Wang Y., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49(17), 6198—6223 |
| 32 | Zaheer M., Kempe R., ACS Catal., 2015, 5(3), 1675—1684 |
| 33 | Ha J. M., Hwang K. R., Kim Y. M., Jae J., Kim K. H., Lee H. W., Kim J. Y., Park Y. K., Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev., 2019, 111, 422—441 |
| 34 | Beckham G. T., Johnson C. W., Karp E. M., Salvachúa D., Vardon D. R., Curr. Opin. Biotech., 2016, 42, 40—53 |
| 35 | Perez J. M., Sener C., Misra S., Umana G. E., Coplien J., Haak D., Li Y. D., Maravelias C. T., Karlen S. D., Ralph J., Donohue T. J., Noguera D. R., Green Chem., 2022, 24(7), 2795—2811 |
| 36 | Zirbes M., Waldvogel S. R., Curr. Opin. Green Sust., 2018, 14, 19—25 |
| 37 | Garedew M., Lam C. H., Petitjean L., Huang S. Q., Song B., Lin F., Jackson J. E., Saffron C. M., Anastas P. T., Green Chem., 2021, 23(8), 2868—2899 |
| 38 | Deuss P. J., Barta K., Coordin. Chem. Rev., 2016, 306, 510—532 |
| 39 | Ma R. S., Guo M., Zhang X., Catal. Today, 2018, 302, 50—60 |
| 40 | Luo J. Z., Melissa P., Zhao W. G., Wang Z., Zhu Y. H., ChemistrySelect, 2016, 1(15), 4596—4601 |
| 41 | Guadix⁃Montero S., Sankar M., Top. Catal., 2018, 61(3/4), 183—198 |
| 42 | Kärkäs M. D., Matsuura B. S., Monos T. M., Magallanes G., Stephenson C. R. J., Org. Biomol. Chem., 2016, 14(6), 1853—1914 |
| 43 | Fang Z., Flynn M. G., Jackson J. E., Hegg E. L., Green Chem., 2021, 23(1), 412—421 |
| 44 | Limosin D., Pierre G., Cauquis G., Holzforschung, 1986, 40(1), 31—36 |
| 45 | Vanholme R., Demedts B., Morreel K., Ralph J., Boerjan W., Plant Physiol., 2010, 153(3), 895—905 |
| 46 | Liu Y. Q., Wang X. C., Wu Q. M., Pei W. H., Teo M. J., Chen Z. S., Huang C. X., Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2022, 222, 994—1006 |
| 47 | Kishioka S, Yamada A., J. Electroanal. Chem., 2005, 578(1), 71—77 |
| 48 | Rafiee M., Alherech M., Karlen S. D., Stahl S. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(38), 15266—15276 |
| 49 | Bosque I., Magallanes G., Rigoulet M., Kärkäs M. D., Stephenson C. R. J., ACS Central. Science, 2017, 3(6), 621—628 |
| 50 | Gao W. J., Lam C. M., Sun B. G., Little R. D., Zeng C. C., Tetrahedron, 2017, 73(17), 2447—2454 |
| 51 | Pan K., Tian M., Jiang Z. H., Kjartanson B., Chen A. C., Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 60, 147—153 |
| 52 | Wang Y. S., Yang F., Liu Z. H., Yuan L., Li G., Catal. Commun., 2015, 67, 49—53 |
| 53 | Beliaeva K., Grimaldos⁃Osorio N., Ruiz⁃Lopez E., Burel L., Vernoux P., Caravaca A., Int. J. Hydrogen Energ., 2021, 46(72), 35752—35764 |
| 54 | Naderi Nasrabadi M., Bateni F., Chen Z. W., Harrington P. B., Staser J. A., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2019, 166(10), E317—E322. |
| 55 | Zhao H., Li C. F., Liu L. Y., Palma B., Hu Z. Y., Renneckar S., Larter S., Li Y., Kibria M. G., Hu J. G., Su B. L., J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2021, 585, 694—704 |
| 56 | Schmitt D., Regenbrecht C., Hartmer M., Stecker F., Waldvogel S. R., Beilstein J. Org. Chem., 2015, 11, 473—480 |
| 57 | Smith C. Z., Utley J. H. P., Hammond J. K., J. Appl. Electrochem., 2011, 41(4), 363—375 |
| 58 | Zirbes M., Schmitt D., Beiser N., Pitton D., Hoffmann T., Waldvogel S. R., ChemElectroChem, 2019, 6(1), 155—161 |
| 59 | Yan K. L., Zhang Y., Tu M. B., Sun Y. J., Energ. Fuel., 2020, 34(10), 12703—12709 |
| 60 | Ma X., Ma J., Li M., Gu Y., Wang T., Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 2022, 204, 110091 |
| 61 | Ghahremani R., Staser J. A., Holzforschung, 2018, 72(11), 951—960 |
| 62 | Honorato A. M. B., Khalid M., Curvelo A. A. D., Varela H., Shahgaldi S., Polymers⁃Basel, 2022, 14(18), 3781 |
| 63 | Deng Z., Fan H. X., Lan C. X., Zhang S. M., Li G., J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2022, 108, 130—138 |
| 64 | Fraile J. M., García J. I., Hormigón Z., Mayoral J. A., Saavedra C. J., Salvatella L., ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2018, 6(2), 1837—1847 |
| 65 | Zeng J. J., Mills M. J. L., Simmons B. A., Kent M. S., Sale K. L., Green Chem., 2017, 19(9), 2145—2154 |
| 66 | Sturgeon M. R., Kim S., Lawrence K., Paton R. S., Chmely S. C., Nimlos M., Foust T. D., Beckham G. T., ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2014, 2(3), 472—485 |
| 67 | Jiang X. Y., Qiang L., Dong X. C., Bin H., Dong,C. Q., J. Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2016, 44(3), 335—341 |
| 68 | Zhou Y., Remón J., Jiang Z., Matharu A. S., Hu C., Green Energy Environ., 2023, doi: org/10.1016/j.gee.2022.03.001 |
| 69 | Kim S., Chmely S. C., Nimlos M. R., Bomble Y. J., Foust T. D., Paton R. S., Beckham G. T., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2011, 2(22), 2846—2852 |
| 70 | Beste A., Buchanan A. C., J. Org. Chem., 2011, 76(7), 2195—2203 |
| 71 | Dong L., Lin L. F., Han X., Si X. Q., Liu X. H., Guo Y., Lu F., Rudić S., Parker S. F., Yang S. H., Wang Y. Q., Chem, 2019, 5(6), 1521—1536 |
| 72 | Huang J. B., Wu S. B., Cheng H., Ming L., Liang J. J., Hong T., J. Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2015, 43(4), 429—436 |
| 73 | Pandey M. P., Kim C. S., Chem. Eng. Technol., 2011, 34(1), 29—41 |
| 74 | Du X., Tricker A. W., Yang W. S., Katahira R., Liu W., Kwok T. T., Gogoi P., Deng Y. L., ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2021, 9(23), 7719—7727 |
| 75 | Du X., Zhang H. C., Sullivan K. P., Gogoi P., Deng Y. L., Chemsuschem, 2020, 13(17), 4318—4343 |
| 76 | Wu K., Cao M., Zeng Q., Li X., Green Energy Environ., 2022, 8(2), 383—405 |
| 77 | Zhang C. F., Wang F., Chinese J. Catal., 2017, 38(7), 1102—1107 |
| 张超锋, 王峰. 催化学报, 2017, 38(7), 1102—1107 | |
| 78 | Han G. Q., Yan T., Zhang W., Zhang Y. C., Lee D. Y., Cao Z., Sun Y. J., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(12), 11341—11349 |
| 79 | Cui T. T., Ma L. N., Wang S. B., Ye C. L., Liang X., Zhang Z. D., Meng G., Zheng L. R., Hu H. S., Zhang J. W., Duan H. H., Wang D. S., Li Y. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143(25), 9429—9439 |
| 80 | Sedai B., Diaz⁃Urrutia C., Baker R. T., Wu R. L., Silks L. P., Hanson S. K., ACS Catal., 2013, 3(12), 3111—3122 |
| 81 | Wang X. T., Chu S., Shao J. J., Liu C., Luo Z. C., Xiao R., Zhang H. Y., ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2022, 10(35), 11555—11566 |
| 82 | Liu H. F., Li H. J., Lu J. M., Zeng S., Wang M., Luo N. C., Xu S. T., Wang F., ACS Catal., 2018, 8(6), 4761—4771 |
| 83 | Ma L. N., Zhou H., Kong X. G., Li Z. H., Duan H. H., ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2021, 9(4), 1932—1940 |
| 84 | Amadio E., Di Lorenzo R., Zonta C., Licini G., Coordin. Chem. Rev., 2015, 301, 147—162 |
| 85 | Rahimi A., Azarpira A., Kim H., Ralph J., Stahl S. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(17), 6415—6418 |
| 86 | Zhou H., Li Z. H., Ma L. N., Duan H. H., Chem. Commun., 2022, 58(7), 897—907 |
| 87 | Zhou H., Li Z. H., Xu S. M., Lu L. L., Xu M., Ji K. Y., Ge R. X., Yan Y. F., Ma L. N., Kong X. G., Zheng L. R., Duan H. H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 133(16), 9058—9064 |
| 88 | Wang N., Xue R.,Yang N., Sun H., Zhang B. Y., Ma Z. M., Ma Y. Q., Zang L. H., J. Alloy. Compd., 2022, 929, 167324 |
| 89 | Gao H., Wang J., Liu M., Wang S., Li W., An Q., Li K., Wei L., Han C., Zhai S., Bioresource Technol., 2022, 127333 |
| 90 | Kang Y., Lu X. M., Zhang G. J., Yao X. Q., Xin J. Y., Yang S. Q., Yang Y. Q., Xu J. L., Feng M., Zhang S. J., ChemSusChem, 2019, 12(17), 4005—4013 |
| [1] | CHI Liping, NIU Zhuangzhuang, LIAO Jie, TANG Kaibin, GAO Minrui. Recent Progress in Intercalation Chemistry of Transition Metal Oxides for Electrocatalytic Applications [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(5): 20220740. |
| [2] | LI Xuan, QI Shuai, ZHOU Weiliang, LI Xiaojie, JING Lingyan, FENG Chao, JIANG Xingxing, YANG Hengpan, HU Qi, HE Chuanxin. Advances in Nanofiber-based Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(5): 316. |
| [3] | ZHANG Xiaoran, ZHENG Jianyun, LYU Yanhong, WANG Shuangyin. Recent Advances in Green C-N Coupling for Urea Synthesis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(5): 20220717. |
| [4] | DU Lei, LIU Zhaoqing. Non-precious Metal Catalysts for Electro-oxidation Upgrading of 5-Hydroxymethy Furfural [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(5): 20220710. |
| [5] | GAO Fengyu, CHEN Du, LUO Ning, YAO Xiaolong, DUAN Erhong, YI Honghong, ZHAO Shunzheng, TANG Xiaolong. Catalytic Performance and Reaction Mechanism of Chlorobenzene Oxidation over MnO x -CeO2 Catalyst [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(4): 20220690. |
| [6] | XIA Wenwen, YU Hongjing, WANG Shiye, YAO Li, LI Xiangyuan. Combustion Mechanism Construction Based on Minimized Reaction Network: Combustion of Aromatic Hydrocarbon [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(4): 20220616. |
| [7] | YANG Qingfeng, LYU Liang, LAI Xiaoyong. Progress on Preparation and Electrocatalytic Application of Hollow MOFs [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(1): 20220666. |
| [8] | QIN Yongji, LUO Jun. Applications of Single-atom Catalysts in CO2 Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220300. |
| [9] | YAO Qing, YU Zhiyong, HUANG Xiaoqing. Progress in Synthesis and Energy-related Electrocatalysis of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220323. |
| [10] | LIN Gaoxin, WANG Jiacheng. Progress and Perspective on Molybdenum Disulfide with Single-atom Doping Toward Hydrogen Evolution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220321. |
| [11] | WANG Sicong, PANG Beibei, LIU Xiaokang, DING Tao, YAO Tao. Application of XAFS Technique in Single-atom Electrocatalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220487. |
| [12] | HAN Fuchao, LI Fujin, CHEN Liang, HE Leiyi, JIANG Yunan, XU Shoudong, ZHANG Ding, QI Lu. Enhance of CoSe2/C Composites Modified Separator on Electrochemical Performance of Li-S Batteries at High Sulfur Loading [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220163. |
| [13] | ZHOU Zixuan, YANG Haiyan, SUN Yuhan, GAO Peng. Recent Progress in Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide to Methanol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220235. |
| [14] | YANG Dan, LIU Xu, DAI Yihu, ZHU Yan, YANG Yanhui. Research Progress in Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction Reaction over Gold Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220198. |
| [15] | WANG Lijun, LI Xin, HONG Song, ZHAN Xinyu, WANG Di, HAO Leiduan, SUN Zhenyu. Efficient Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction to CO by Tuning CdO-Carbon Black Interface [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220317. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||