

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (1): 20210613.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20210613
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHI Xiaofan, ZHU Jian, BAI Tianyu, FU Zixuan, ZHANG Jijie( ), BU Xianhe
), BU Xianhe
Received:2021-08-25
Online:2022-01-10
Published:2021-10-08
Contact:
ZHANG Jijie
E-mail:zhangjijie@nankai.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
SHI Xiaofan, ZHU Jian, BAI Tianyu, FU Zixuan, ZHANG Jijie, BU Xianhe. Research Status and Progress of MOFs with Application in Photoelectrochemical Water-splitting[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210613.
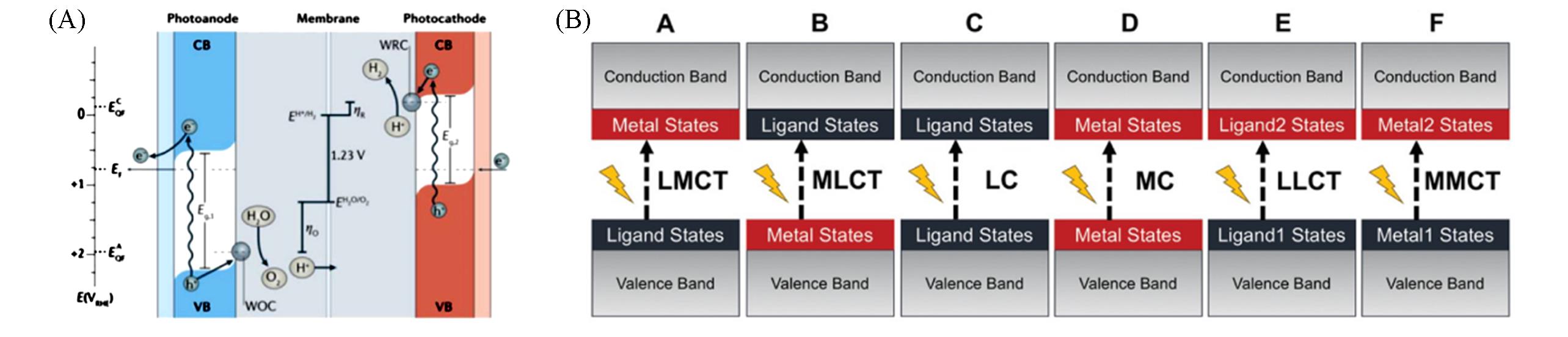
Fig.1 Basic structure of PEC water?splitting system(A)[2], representation of the six types of low?lying excited states found in MOFs as a result of the different characters of the valence band and conduction band edges(B)[54](A) Copyright 2018, Wiley?VCH; (B) Copyright 2020, Wiley?VCH.
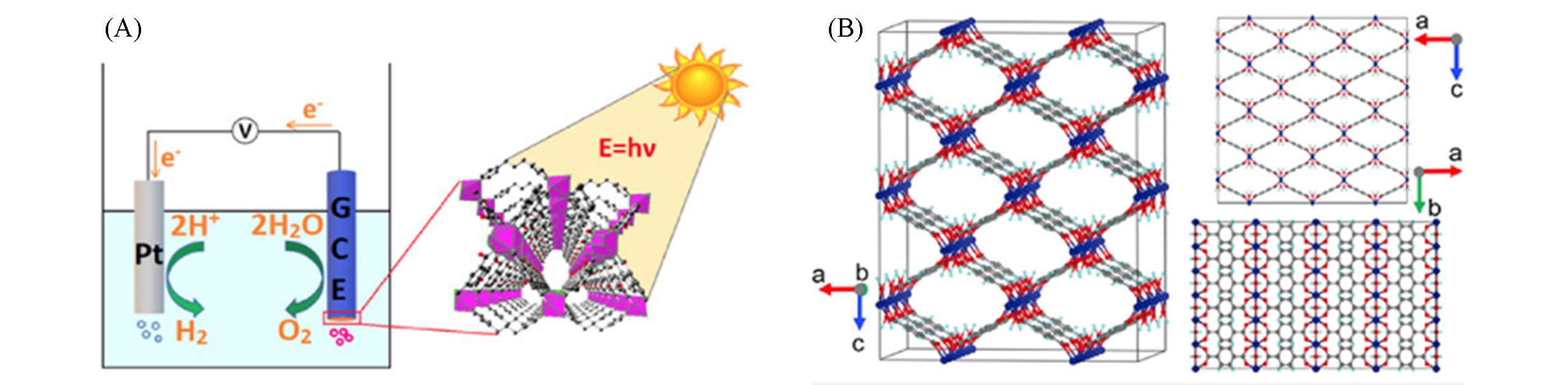
Fig.2 2D Co?MOFs using as the photoanode for photoelectrochemical water?splitting(A)[65], crystal and facet structure of MOF?71(B)[66](A) Copyright 2019, American chemical society; (B) Copyright 2020, Open access.
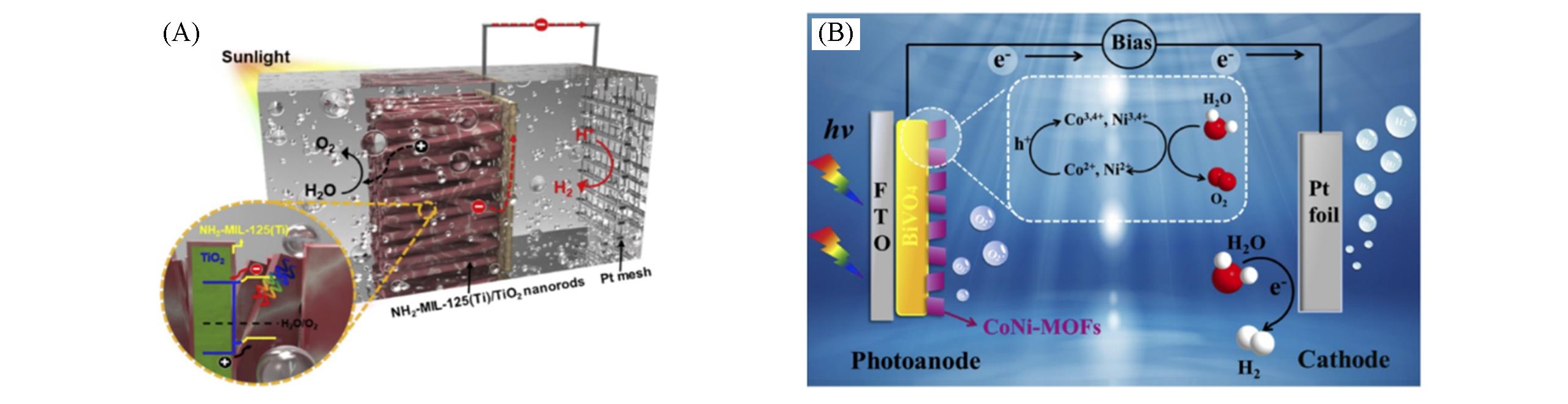
Fig.3 TiO2@MIL?125?NH2 photoanode(A)[72] and BiVO4@CoNi?MOF photoanode for PEC water?splitting(B)[75](A) Copyright 2019, Elsevier; (B) Copyright 2020, Elsevier.
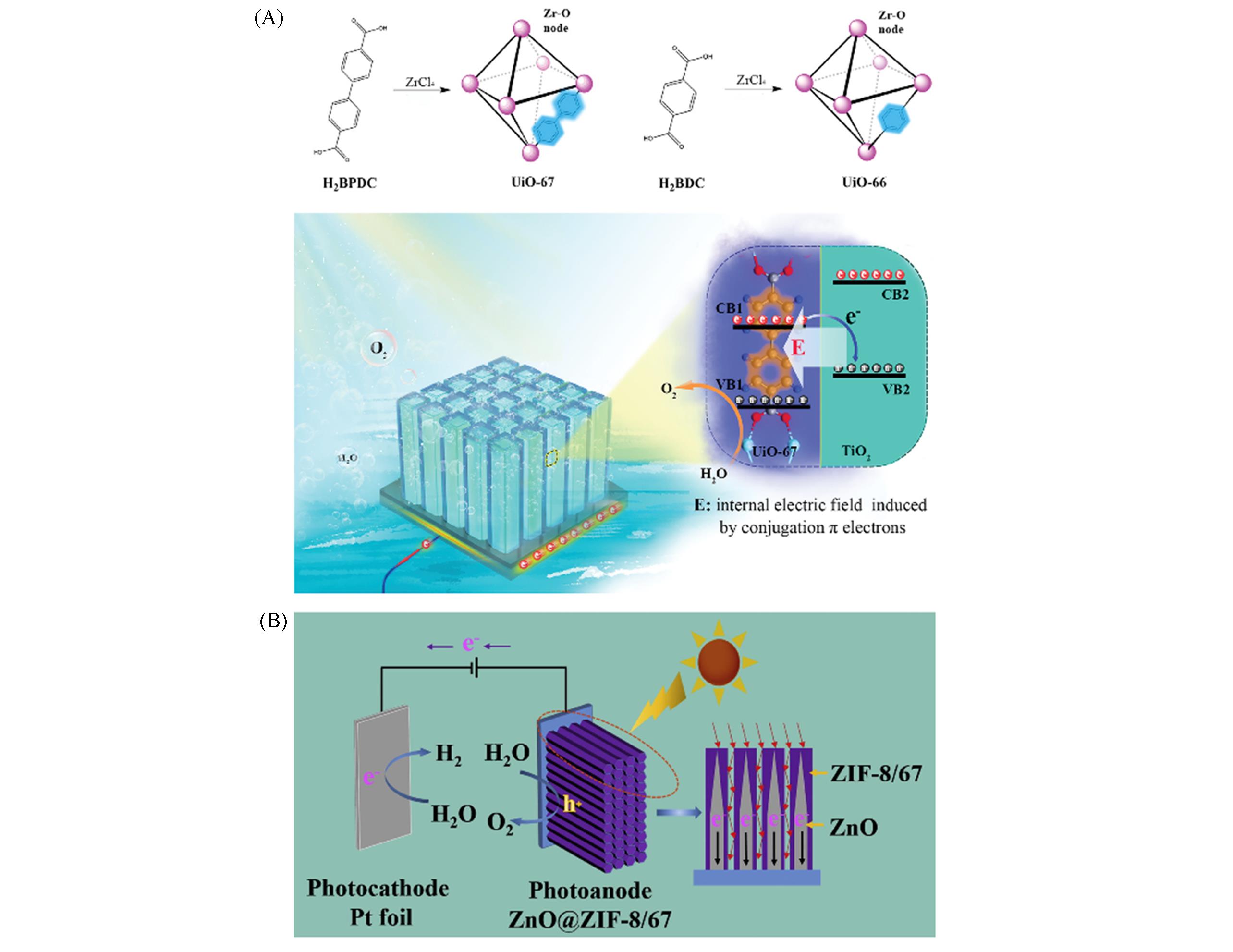
Fig.4 Conjugated π electrons of MOFs driving charge separation for enhanced photoelectrochemical water oxidation(A)[83], mechanisms for explaining the enhanced PEC water splitting efficiency of the ZnO@ZIF?8/ZIF?67 photoelectrode(B)[87](A) Copyright 2021, Wiley?VCH; (B) Copyright 2018, Elsevier.
| Metal center | Photoelectrode | Light source | Electrolyte | Potential/V (vs. RHE) | Photocurrent density/ (mA·cm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | TiO2@NH2?MIL?125[ | Xenon lamp | Artificial seawater | 1.21 | 3.04 |
| TiO2/NH2?MIL?125[ | AM 1.5G | 1 mol/L NaOH | 1.23 | 1.63 | |
| Fe/Co/Ni | BiVO4@Co2(bim)4[ | AM 1.5G | 0.5 mol/L Na2SO4 | 1.23 | 1.20 |
| Fe2O3/NH2?MIL?101(Fe)[ | AM 1.5G | 1 mol/L NaOH | 1.23 | 2.27 | |
| Ti doped Fe2O3@ZIF?67 | AM 1.5G | 1 mol/L KOH | 1.23 | 0.80 | |
| Fe@Ni?MOF/Fe2O3:Ti[ | AM 1.5G | 1 mol/L KOH | 1.23 | 2.30 | |
| BiVO4@CoNi?MOF[ | AM 1.5G | 0.5 mol/L Na2SO4 | 1.23 | 3.20 | |
| FeNi?MOF/TNTA[ | AM 1.5G | 0.1 mol/L Na2SO4 | 1.23 | 1.90 | |
| Fe2O3/MIL?88B@ZIF?67[ | AM 1.5G | 1 mol/L NaOH | 1.23 | 2.52 | |
| Zr | TiO2//UiO?67[ | Xenon lamp(280―800 nm) | 1 mol/L H2SO4 | 1.23 | 2.10 |
| 0.5 mol/L Na2SO4 | 1.91 | ||||
| 1 mol/L KOH | 2.38 | ||||
| ZnO/Zr?MOF?25%[ | AM 1.5G | Acetonitrile solution with 1 mmol/L I2 | 1.20 | 4.12 | |
| Zn | ZnO/ZIF?8@N?CDs[ | AM 1.5G | 0.5 mol/L Na2SO4 | 1.23 | 0.35 |
| ZnO@ZIF?8/ZIF?67[ | AM 1.5G | 0.5 mol/L Na2SO4 | 1.23 | 0.11 | |
| Co3O4@NH2?MOF?5/NF[ | Visible light | 1 mol/L KOH | 1.49 | 32.93 | |
| ZnNi?MOF@ZnO[ | AM 1.5G | 0.5 mol/L Na2SO4 | 1.20 | 1.40 |
Table 1 Performance of reported MOFs-based heterostructure photoelectrodes
| Metal center | Photoelectrode | Light source | Electrolyte | Potential/V (vs. RHE) | Photocurrent density/ (mA·cm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti | TiO2@NH2?MIL?125[ | Xenon lamp | Artificial seawater | 1.21 | 3.04 |
| TiO2/NH2?MIL?125[ | AM 1.5G | 1 mol/L NaOH | 1.23 | 1.63 | |
| Fe/Co/Ni | BiVO4@Co2(bim)4[ | AM 1.5G | 0.5 mol/L Na2SO4 | 1.23 | 1.20 |
| Fe2O3/NH2?MIL?101(Fe)[ | AM 1.5G | 1 mol/L NaOH | 1.23 | 2.27 | |
| Ti doped Fe2O3@ZIF?67 | AM 1.5G | 1 mol/L KOH | 1.23 | 0.80 | |
| Fe@Ni?MOF/Fe2O3:Ti[ | AM 1.5G | 1 mol/L KOH | 1.23 | 2.30 | |
| BiVO4@CoNi?MOF[ | AM 1.5G | 0.5 mol/L Na2SO4 | 1.23 | 3.20 | |
| FeNi?MOF/TNTA[ | AM 1.5G | 0.1 mol/L Na2SO4 | 1.23 | 1.90 | |
| Fe2O3/MIL?88B@ZIF?67[ | AM 1.5G | 1 mol/L NaOH | 1.23 | 2.52 | |
| Zr | TiO2//UiO?67[ | Xenon lamp(280―800 nm) | 1 mol/L H2SO4 | 1.23 | 2.10 |
| 0.5 mol/L Na2SO4 | 1.91 | ||||
| 1 mol/L KOH | 2.38 | ||||
| ZnO/Zr?MOF?25%[ | AM 1.5G | Acetonitrile solution with 1 mmol/L I2 | 1.20 | 4.12 | |
| Zn | ZnO/ZIF?8@N?CDs[ | AM 1.5G | 0.5 mol/L Na2SO4 | 1.23 | 0.35 |
| ZnO@ZIF?8/ZIF?67[ | AM 1.5G | 0.5 mol/L Na2SO4 | 1.23 | 0.11 | |
| Co3O4@NH2?MOF?5/NF[ | Visible light | 1 mol/L KOH | 1.49 | 32.93 | |
| ZnNi?MOF@ZnO[ | AM 1.5G | 0.5 mol/L Na2SO4 | 1.20 | 1.40 |
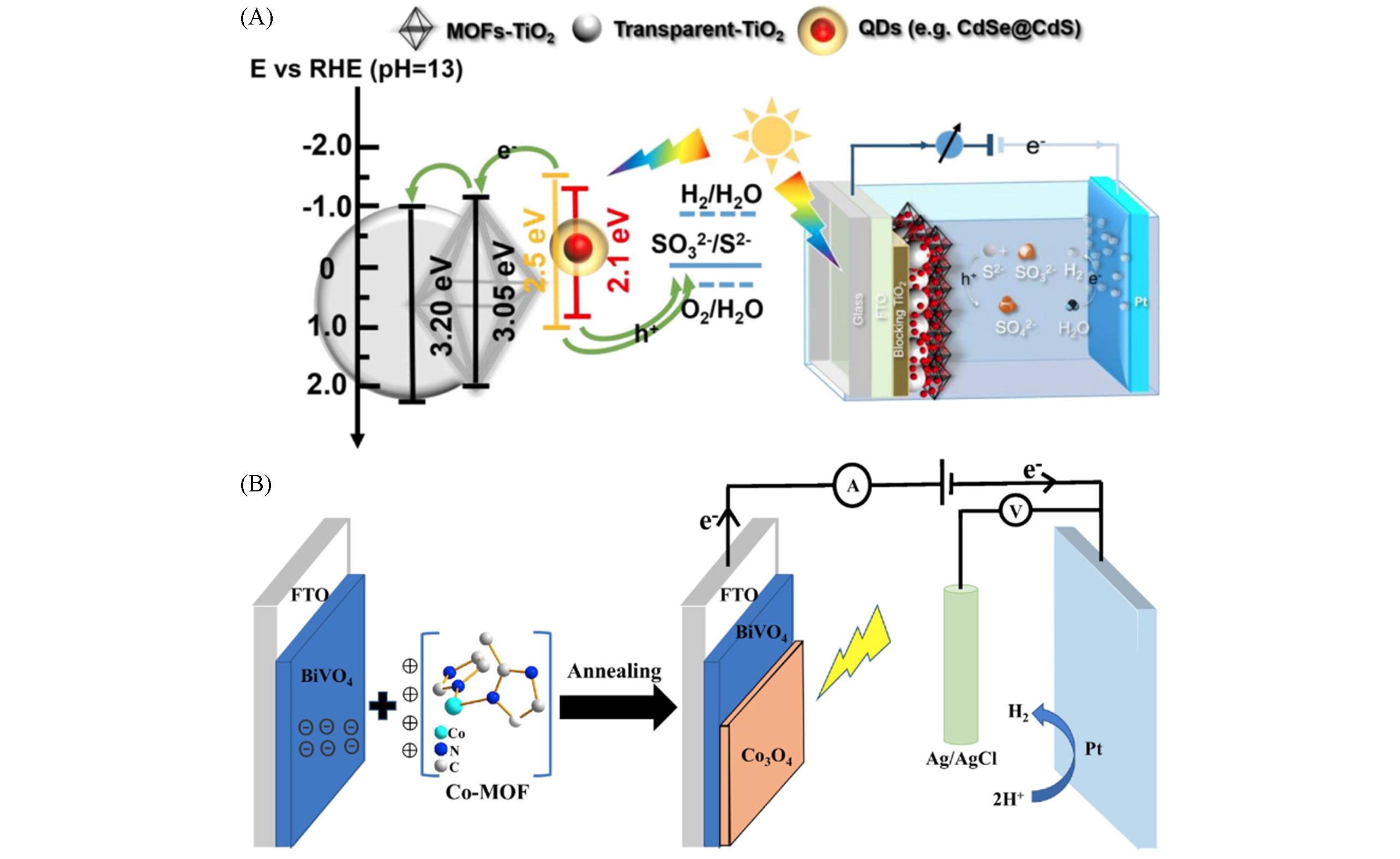
Fig.5 Ti?MOF derived heterophase TiO2 photoanode(A)[94] and Co?MOF derived BiVO4@Co3O4 photoanode(B)[95](A) Copyright 2020, Elsevier; (B) Copyright 2019, Elsevier.
MOFs precursor | MOFs?based photoelectrode | Light source | Electrolyte | Potential/V (vs. RHE) | Photocurrent density/ (mA·cm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH2?MIL?125 | MoS2 coupled dual?phase TiO2[ | AM 1.5G | 0.35 mol/L Na2S and 0.25 mol/L Na2SO3 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| TixFe1-xOy@Fe2O3[ | AM 1.5G | 1 mol/L NaOH | 1.23 | 0.724 | |
| M?TiO2/CdSe[ | AM 1.5G | 0.25 mol/L Na2S and 0.35 mol/L Na2SO3 | 0.9 | 7.55 | |
| ZIF?67 | Co3O4/BiVO4[ | Xenon lamp | 0.5 mol/L K2H2PO4 with Na2SO3 | 1.23 | 2.35 |
| Co3O4/TiO2[ | Xenon lamp | 1 mol/L NaOH | 1.23 | 1.04 | |
| Co3C/TiO2[ | ― | 1 mol/L NaOH | 1.23 | 2.6 | |
| ZIF?8/ZIF?67 | Zn0.4Co0.6O4/BiVO4[ | AM 1.5G | 0.5 mol/L K2H2PO4 | 1.23 | 3.55 |
| MIL?88B | Fe2O3@C photoanode[ | AM 1.5G | Neutral aqueous | 1.65 | 2.5 |
| FeP@C photocathode[ | AM 1.5G | -0.07 | 10 | ||
| HKUST?1 | FeOOH/Cu2O/Ce?Fe2O3[ | AM 1.5G | 1 mol/L KOH | 1.23 | 4.2 |
Table 2 Performance of reported MOFs-derived photoelectrodes
MOFs precursor | MOFs?based photoelectrode | Light source | Electrolyte | Potential/V (vs. RHE) | Photocurrent density/ (mA·cm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH2?MIL?125 | MoS2 coupled dual?phase TiO2[ | AM 1.5G | 0.35 mol/L Na2S and 0.25 mol/L Na2SO3 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| TixFe1-xOy@Fe2O3[ | AM 1.5G | 1 mol/L NaOH | 1.23 | 0.724 | |
| M?TiO2/CdSe[ | AM 1.5G | 0.25 mol/L Na2S and 0.35 mol/L Na2SO3 | 0.9 | 7.55 | |
| ZIF?67 | Co3O4/BiVO4[ | Xenon lamp | 0.5 mol/L K2H2PO4 with Na2SO3 | 1.23 | 2.35 |
| Co3O4/TiO2[ | Xenon lamp | 1 mol/L NaOH | 1.23 | 1.04 | |
| Co3C/TiO2[ | ― | 1 mol/L NaOH | 1.23 | 2.6 | |
| ZIF?8/ZIF?67 | Zn0.4Co0.6O4/BiVO4[ | AM 1.5G | 0.5 mol/L K2H2PO4 | 1.23 | 3.55 |
| MIL?88B | Fe2O3@C photoanode[ | AM 1.5G | Neutral aqueous | 1.65 | 2.5 |
| FeP@C photocathode[ | AM 1.5G | -0.07 | 10 | ||
| HKUST?1 | FeOOH/Cu2O/Ce?Fe2O3[ | AM 1.5G | 1 mol/L KOH | 1.23 | 4.2 |
| 1 | Chaubey R., Sahu S., James O. O., Maity S., Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev., 2013, 23, 443—462 |
| 2 | Tilley S. D., Adv. Energy. Mater., 2019, 9, 1802877 |
| 3 | He Y. M., Hamann T., Wang D. W., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48, 2182—2215 |
| 4 | Sheng X., Xu T., Feng X. J., Adv. Mater., 2019, 31, 1805132 |
| 5 | Wang Z., Li C., Domen K., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48, 2109—2125 |
| 6 | Yang W., Moon J., ChemSusChem, 2019, 12, 1889—1899 |
| 7 | Fujishima A., Honda K., Nature, 1972, 238, 37—38 |
| 8 | Li R., Zhang F., Wang D., Yang J., Li M., Zhu J., Zhou X., Han H., Li C., Nat. Commun., 2013, 4, 1432 |
| 9 | Lv R., Wang T., Su F., Zhang P., Li C., Gong J., Nano Energy, 2014, 7, 143—150 |
| 10 | Wang M., Wang Z., Zhang B., Jiang W., Bao X., Cheng H., Zheng Z., Wang P., Liu Y., Whangbo M. H., Li Y., Dai Y., Huang B., ACS Catal., 2020, 10, 13031—13039 |
| 11 | Li Y., Wang K., Huang D., Li L., Tao J., Ghany N. A. A., Jiang F., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2021, 286, 119872 |
| 12 | Tan J., Yang W., Lee H., Park J., Kim K., Hutter O. S., Phillips L. J., Shim S., Yun J., Park Y., Lee J., Major J. D., Moon J., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2021, 286, 119890 |
| 13 | Zhang M., Li F., Benetti D., Nechache R., Wei Q., Qi X., Rosei F., Nano Energy, 2021, 81, 105626 |
| 14 | Zhang Z., Wang P., Energ. Environ. Sci., 2012, 5, 9948 |
| 15 | Zhang L., Gao Y., Ding X., Yu Z., Sun L., ChemSusChem, 2014, 7, 2801—2804 |
| 16 | Sanchez⁃Tovar R., Fernandez⁃Domene R. M., Garcia⁃Garcia D. M., Garcia⁃Anton J., J. Power Sources, 2015, 286, 224—231 |
| 17 | Herault N., Kaliginedi V., Broekmann P., Fromm K. M., Acta Crystallogr. A, 2016, 72, S78—S79 |
| 18 | Zhang L., Cui P., Yang H., Chen J., Xiao F., Guo Y., Liu Y., Zhang W., Huo F., Liu B., Adv. Sci., 2016, 3, 1500243 |
| 19 | Zhang X., Yang H., Zhang B., Shen Y., Wang M., Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 3, 1500273 |
| 20 | Dong Z., Ding D., Li T., Ning C., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018, 443, 321—328 |
| 21 | Kwon J., Cho H., Lee H., Yeo J., Hong S., Han S., Ko S. H., ECS. J. Solid. State. Sc., 2018, 7, Q131—Q135 |
| 22 | Zheng X. L., Dinh C. T., de Arquer F. P. G., Zhang B., Liu M., Voznyy O., Li Y. Y., Knight G., Hoogland S., Lu Z. H., Du X. W., Sargent E. H., Small, 2020, 16, 2004354 |
| 23 | Zhang C., Ai L., Jiang J., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3, 3074—3081 |
| 24 | Huerta⁃Flores A. M., Chavez⁃Angulo G., Carrasco⁃Jaim O. A., Torres⁃Martinez L. M., Garza⁃Navarro M. A., J. Photoch. Photobio. A, 2021, 410, 113077 |
| 25 | Kyesmen P. I., Nombona N., Diale M., J. Alloy. Compd., 2021, 863, 158724 |
| 26 | Li Y., Wu Q., Bu Q., Zhang K., Lin Y., Wang D., Zou X., Xie T., Chinese J. Catal., 2021, 42, 762—771 |
| 27 | Li Y., Wu Q., Chen Y., Zhang R., Li C., Zhang K., Li M., Lin Y., Wang D., Zou X., Xie T., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2021, 290, 120058 |
| 28 | Ma H., Hwang J. B., Chae W. S., Chung H. S., Choi S. H., Mahadik M. A., Lee H. H., Jang J. S., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2021, 549, 149233 |
| 29 | Moss B., Babacan O., Kafizas A., Hankin A., Adv. Energy Mater., 2021, 11, 2003286 |
| 30 | Tokubuchi T., Arbi R. I., Pan Z., Katayama K., Turak A., Sohn W. Y., J. Photoch. Photobio. A, 2021, 410, 113179 |
| 31 | Zhang L., Xue X., Guo T., Bi L., Hu T., Tan L., Zhang X., Jiang J., Hong K., Zhang Q., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46, 12897—12905 |
| 32 | Ye K. H., Wang J. Y., Li N., Liu Z. Q., Guo S. H., Guo Y. P., Su Y. Z., Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2014, 45, 116—119 |
| 33 | Patel P. P., Hanumantha P. J., Velikokhatnyi O. I., Datta M. K., Hong D., Gattu B., Poston J. A., Manivannan A., Kumta P. N., J. Power Sources, 2015, 299, 11—24 |
| 34 | Iqbal M. Z., Siddique S., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43, 21502—21523 |
| 35 | Zhang F. Q., Hu Y., Sun R. N., Fu H., Peng K. Q., Front. Chem., 2019, 7, 206 |
| 36 | Reddy C. V., Reddy K. R., Shetti N. P., Shim J., Aminabhavi T. M., Dionysiou D. D., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45, 18331—18347 |
| 37 | Samuel E., Joshi B., Kim M. W., Swihart M. T., Yoon S. S., Nano Energy, 2020, 72, 104648 |
| 38 | Wannapop S., Somdee A., Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2020, 115, 107857 |
| 39 | Khan I., Jalilov A., Fujii K., Qurashi A., Solar Rrl, 2021, 5, 2000741 |
| 40 | Yang Q., Du J., Nie X., Yang D., Bian L., Yang L., Dong F., He H., Zhou Y., Yang H., ACS Catal., 2021, 11, 1242—1247 |
| 41 | Ge J., Ding X., Jiang D., Zhang L., Du P., Catal. Lett., 2021, 151, 1231—1238 |
| 42 | Li J., Griep M., Choi Y., Chu D., Chem. Commun., 2018, 54, 3331—3334 |
| 43 | Abdi F. F., Savenije T. J., May M. M., Dam B., van de Krol R., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2013, 4, 2752—2757 |
| 44 | Yang W., Xiong Y., Zou L., Zou Z., Li D., Mi Q., Wang Y., Yang H., Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2016, 11, 283 |
| 45 | Chen Z., Cummins D., Reinecke B. N., Clark E., Sunkara M. K., Jaramillo T. F., Nano Lett., 2011, 11, 4168—4175 |
| 46 | Digdaya I. A., Adhyaksa G. W. P., Trześniewski B. J., Garnett E. C., Smith W. A., Nat. Commun., 2017, 8, 15968 |
| 47 | Yuan S., Feng L., Wang K. C., Pang J. D., Bosch M., Lollar C., Sun Y. J., Qin J. S., Yang X. Y., Zhang P., Wang Q., Zou L. F., Zhang Y. M., Zhang L. L., Fang Y., Li J. L., Zhou H. C., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1704303 |
| 48 | Li A. L., Gao Q., Xu J., Bu X. H., Coord. Chem. Rev., 2017, 344, 54—82 |
| 49 | Yu M. H., Space B., Franz D., Zhou W., He C., Li L., Krishna R., Chang Z., Li W., Hu T. L., Bu X. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 17703—17712 |
| 50 | Kong L., Zhu J., Shuang W., Bu X. H., Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8, 1801515 |
| 51 | Chang Z., Yang D. H., Xu J., Hu T. L., Bu X. H., Adv. Mater., 2015, 27, 5432—5441 |
| 52 | Liu X. T., Wang K., Chang Z., Zhang Y. H., Xu J., Zhao Y. S., Bu X. H., Angew. Chem., 2019, 131, 14028—14034 |
| 53 | Han S. Y., Pan D. L., Chen H., Bu X. B., Gao Y. X., Gao H., Tian Y., Li G. S., Wang G., Cao S. L., Wan C. Q., Guo G. C., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 9864—9869 |
| 54 | Fumanal M., Ortega⁃Guerrero A., Jablonka K. M., Smit B., Tavernelli I., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30, 2003792 |
| 55 | Alvaro M., Carbonell E., Ferrer B., Xamena F., Garcia H., Chem. Eur. J., 2007, 13, 5106—5112 |
| 56 | Zhang M., Zhang A. M., Chen Y., Xie J., Xin Z. F., Chen Y. J., Kan Y. H., Li S. L., Lan Y. Q., Zhang Q., Energy Storage Materials, 2020, 29, 172—181 |
| 57 | Gao J., Huang Q., Wu Y., Lan Y. Q., Chen B., Adv. Energy Sustain. Res., 2021, 2, 2100033 |
| 58 | Kong L. J., Zhong M., Shuang W., Xu Y. H., Bu X. H., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 2378—2407 |
| 59 | Bakuru V. R., Dmello M. E., Kalidindi S. B., ChemPhysChem, 2019, 20, 1177—1215 |
| 60 | Kataoka Y., Sato K., Miyazaki Y., Masuda K., Tanaka H., Naito S., Mori W., Energ. Environ. Sci., 2009, 2, 397—400 |
| 61 | Zhan W. W., Kuang Q., Zhou J. Z., Kong X. J., Xie Z. X., Zheng L. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 1926—1933 |
| 62 | Lou X. W. D., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 59, 4634—4650 |
| 63 | Jia M., Xiong W., Yang Z., Cao J., Zhang Y., Xiang Y., Xu H., Song P., Xu Z., Coord. Chem. Rev., 2021, 434, 213780 |
| 64 | Gong Y. N., Liu J. W., Shao B. Z., Zhong D. C., Lu T. B., Flatchem, 2021, 27, 100240 |
| 65 | Natarajan K., Gupta A. K., Ansari S. N., Saraf M., Mobin S. M., ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2019, 11, 13295—13303 |
| 66 | Liu C., Shen X., Johnson G., Zhang Y., Zhang C., Chen J., Li L., Sheehan C., Peng Z., Zhang S., Front. Chem., 2020, 8, 604239 |
| 67 | Liao T., Kou L., Du A., Gu Y., Sun Z., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 9159—9166 |
| 68 | Cadiau A., Kolobov N., Srinivasan S., Goesten M. G., Haspel H., Bavykina A. V., Tchalala M. R., Maity P., Goryachev A., Poryvaev A. S., Eddaoudi M., Fedin M. V., Mohammed O. F., Gascon J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 13468—13472 |
| 69 | Cheng X. M., Dao X. Y., Wang S. Q., Zhao J., Sun W. Y., ACS Catal., 2020, 11, 650—658 |
| 70 | Guo F., Guo J. H., Wang P., Kang Y. S., Liu Y., Zhao J., Sun W. Y., Chem. Sci., 2019, 10, 4834—4838 |
| 71 | Song H., Sun Z., Xu Y., Han Y., Xu J., Wu J., Sun T., Meng H., Zhang X., Sep. Purif. Technol., 2019, 228, 115764 |
| 72 | Yoon J. W., Kim D. H., Kim J. H., Jang H. W., Lee J. H., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2019, 244, 511—518 |
| 73 | Nasalevich M. A., Becker R., Ramos Fernandez E. V., Castellanos S., Veber S. L., Fedin M. V., Kapteijn F., Reek J. N. H., van der Vlugt J. I., Gascon J., Energ. Environ. Sci., 2015, 8, 364—375 |
| 74 | Ding M., Jiang H. L., CCS Chem., 2020, 2, 2740—2748 |
| 75 | Zhou S., Chen K., Huang J., Wang L., Zhang M., Bai B., Liu H., Wang Q., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2020, 266, 118513 |
| 76 | Zhang W., Li R., Zhao X., Chen Z., Law A. W. K., Zhou K., ChemSusChem, 2018, 11, 2710—2716 |
| 77 | Lionet Z., Kamata Y., Nishijima S., Toyao T., Kim T. H., Horiuchi Y., Lee S. W., Matsuoka M., Res. Chem. Intermed., 2018, 44, 4755—4764 |
| 78 | Wu F., Xie J., You Y., Zhao Z., Wang L., Chen X., Yang P., Huang Y., ACS Appl. Energ. Mater., 2020, 3, 4867—4876 |
| 79 | Wang K., Liu Y., Kawashima K., Yang X., Yin X., Zhan F., Liu M., Qiu X., Li W., Mullins C. B., Li J., Adv. Sci., 2020, 7, 2002563 |
| 80 | You S. M., El Rouby W. M. A., Thamilselvan A., Tsai C. K., Darmanto W., Doong R. A., Millet P., Nanomaterials, 2020, 10, 1688 |
| 81 | Hong D. H., Reddy D. A., Reddy K. A. J., Gopannagari M., Kumar D. P., Kim T. K., J. Catal., 2020, 391, 471—479 |
| 82 | Zhao S., Wang Y., Dong J., He C. T., Yin H., An P., Zhao K., Zhang X., Gao C., Zhang L., Lv J., Wang J., Zhang J., Khattak A. M., Khan N. A., Wei Z., Zhang J., Liu S., Zhao H., Tang Z., Nat. Energy, 2016, 1, 16184 |
| 83 | Wang X., Sun W., Tian Y., Dang K., Zhang Q., Shen Z., Zhan S., Small, 2021, 17, 2100367 |
| 84 | He T., Chen S., Ni B., Gong Y., Wu Z., Song L., Gu L., Hu W., Wang X., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 3493—3498 |
| 85 | da Trindade L. G., Borba K. M. N., Trench A. B., Zanchet L., Teodoro V., Pontes F. M. L., Longo E., Mazzo T. M., J. Solid State Chem., 2021, 293, 121794 |
| 86 | Han H., Karlicky F., Pitchaimuthu S., Shin S. H. R., Chen A. P., Small, 2019, 15, 1902771 |
| 87 | Jia G., Liu L., Zhang L., Zhang D., Wang Y., Cui X., Zheng W., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018, 448, 254—260 |
| 88 | Fiaz M., Hussain D., Athar M., Ionics, 2021, 27, 759—770 |
| 89 | Peng Z., Abbas S. C., Lv J., Yang R., Wu M., Wang Y., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44, 2446—2453 |
| 90 | Ming Y., Purewal J., Yang J., Xu C. C., Soltis R., Warner J., Veenstra M., Gaab M., Muller U., Siegel D. J., Langmuir, 2015, 31, 4988—4995 |
| 91 | Taheri M., Tsuzuki T., ACS Mater. Lett., 2021, 3, 255—260 |
| 92 | Tang R., Yin R., Zhou S., Ge T., Yuan Z., Zhang L., Yin L., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5, 4962—4971 |
| 93 | Li C. H., Huang C. L., Chuah X. F., Raja D. S., Hsieh C. T., Lu S. Y., Chem. Eng. J., 2019, 361, 660—670 |
| 94 | Shi L., Benetti D., Li F., Wei Q., Rosei F., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2020, 263, 118317 |
| 95 | Xu D., Xia T., Fan W., Bai H., Ding J., Mao B., Shi W., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2019, 491, 497—504 |
| 96 | Ding Q., Gou L., Wei D., Xu D., Fan W., Shi W., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46, 24965—24976 |
| 97 | Xu D., Ding Q., Zheng Y., Li Q., Tan F., Ding J., Shi W., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2021, 561, 150057 |
| 98 | Tang R., Zhou S., Zhang L., Yin L., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1706154 |
| 99 | Shit S. C., Mondal I., Pendem S., Bai L. Y., Park J. Y., Mondal J., ChemElectroChem, 2018, 5, 2842—2849 |
| 100 | Li S. M., Tan J., Jiang Z. J., Wang J., Li Z. Q., Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 384, 123354 |
| 101 | Wu J., Huang P., Fan H., Wang G., Liu W., ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2020, 12, 30304—30312 |
| 102 | Chen J., Chen X., Zhang X., Yuan Y., Bi R., You F., Wang Z., Yu R., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2020, 36(1), 120—126 |
| 103 | Wang J., Xue C., Yao W., Liu J., Gao X., Zong R., Yang Z., Jin W., Tao D., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2019, 250, 369—381 |
| 104 | Yuan X., Mu Q., Xue S., Su Y., Zhu Y., Sun H., Deng Z., Peng Y., J. Energy Chem., 2021, 60, 202—208 |
| 105 | Zhu Y. P., Yin J., Abou Hamad E., Liu X., Chen W., Yao T., Mohammed O. F., Alshareef H. N., Adv. Mater., 2020, 32, 1906368 |
| 106 | Xiao J. D., Shang Q. C., Xiong Y. J., Zhang Q., Luo Y., Yu S. H., Jiang H. L., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 9389—9393 |
| 107 | Zhang J., Bai T., Huang H., Yu M. H., Fan X., Chang Z., Bu X. H., Adv. Mater., 2020, 32, 2004747 |
| 108 | Jiang Z., Xu X., Ma Y., Cho H. S., Ding D., Wang C., Wu J., Oleynikov P., Jia M., Cheng J., Zhou Y., Terasaki O., Peng T., Zan L., Deng H., Nature, 2020, 586, 549—554 |
| 109 | Ifraemov R., Shimoni R., He W. H., Peng G. M., Hod I., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 3046—3053 |
| 110 | Ren X., Wei S., Wang Q., Shi L., Wang X. S., Wei Y., Yang G., Philo D., Ichihara F., Ye J., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2021, 286, 119924 |
| [1] | ZHANG Hongwei, CHEN Wen, ZHAO Meiqi, MA Chao, HAN Yunhu. Research Progress of Single Atom Catalysts in Electrochemistry [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220129. |
| [2] | LIU Jiaqi, LI Tianbao. Preparation and Photoelectrochemical Performance of BiVO4/CuBi2O4 Thin Film Photoanodes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20220017. |
| [3] | CHEN Wangsong, LUO Lan, LIU Yuguang, ZHOU Hua, KONG Xianggui, LI Zhenhua, DUAN Haohong. Recent Progress in Photoelectrochemical H2 Production Coupled with Biomass-derived Alcohol/aldehyde Oxidation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210683. |
| [4] | LI Shurong, WANG Lin, CHEN Yuzhen, JIANG Hailong. Research Progress of Metal⁃organic Frameworks on Liquid Phase Catalytic Chemical Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210575. |
| [5] | XUE Jinbo, GAO Guoxiang, SHEN Qianqian, LIU Tianwu, LIU Xuguang, JIA Husheng. Construction of a Novel S-scheme CdS-BiVO4 Heterojunction Photoelectrodes and Research on Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2493. |
| [6] | TANG Ding, ZHONG Shuiping. Preparation and Photoelectrochemical Performance of Bi1-xFexVO4 Thin Film Photoanodes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2509. |
| [7] | SHI Jiangwei, MENG Nannan, GUO Yamei, YU Yifu, ZHANG Bin. Recent Advances of Two-dimensional Materials for Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 492. |
| [8] | QI Yi, LI Qiaowei. Synthesis of Pillared-layer Metal-organic Frameworks from Anthracene Luminescent Linkers and Their Piezochromic Properties † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 417. |
| [9] | JIANG Yuanyuan, LI Boyu, LU Yizhong, WU Tongshun, HAN Dongxue. Oxygen Evolution Reaction Electrocatalytic Performance Analysis of Electroless Plated Ni-Bx [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2774. |
| [10] | LIU Fen, ZHOU Min, WANG Suxia, WANG Rong, YANG Ning, MA Yongjun. Study on Photoelectrocatalytic Decolorization Mechanism of Methylene Blue Under the Visible-light Irradiation by Measuring Chemical Oxygen Demand Index† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1988. |
| [11] | HE Pengchen,ZHOU Jian,ZHOU Awu,DOU Yibo,LI Jianrong. MOFs-Based Materials for Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 855. |
| [12] | ZOU Jiayun, LIU Yipu, CHEN Hui, LI Guodong. Enhanced Hydrogen Evolution Catalytic Activity of Cobalt-embedded Carbon Nanotubes by Thermal Vacuum Activation† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(6): 1249. |
| [13] | HAN Zhiying, LI Youji, LIN Xiao, WANG Ziyu, LI Ziqin, WANG Hao. Preparation and Photoelectrocatalytic Performance of Fe2O3/ZnO Composite Electrode Loading on Conductive Glass† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(4): 771. |
| [14] | FENG Xiaolei, QU Zongkai, CHEN Jun, WANG Dengdeng, CHEN Xu, YANG Wensheng. NiFe2O4/NiO Nanocomposites as Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Evolution Reaction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 1999. |
| [15] | WU Juan, ZHAO Bowen, HUANG Chao, CHEN Dongmei, ZHU Bixue. Supramolecular Design of Coordination Complexes of Zn(Ⅱ) and Vapor Adsorption for MeOH† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(6): 1069. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||