

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 20210683.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20210683
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Wangsong1, LUO Lan1, LIU Yuguang1, ZHOU Hua2, KONG Xianggui1, LI Zhenhua1( ), DUAN Haohong2(
), DUAN Haohong2( )
)
Received:2021-09-23
Online:2022-02-10
Published:2021-10-22
Contact:
LI Zhenhua
E-mail:LZH0307@mail.buct.edu.cn;hhduan@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
CHEN Wangsong, LUO Lan, LIU Yuguang, ZHOU Hua, KONG Xianggui, LI Zhenhua, DUAN Haohong. Recent Progress in Photoelectrochemical H2 Production Coupled with Biomass-derived Alcohol/aldehyde Oxidation[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210683.
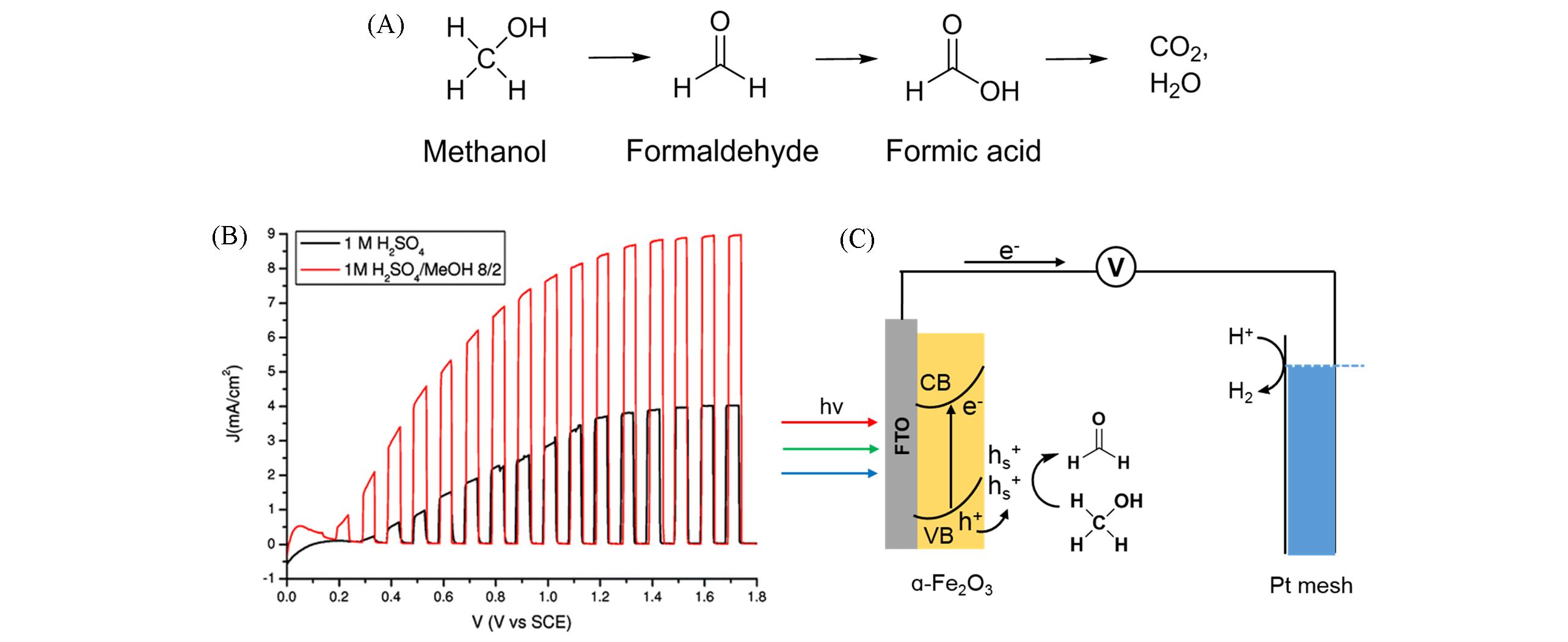
Fig.1 Methanol oxidation reaction path(A), shuttered LSV curves of WO3 photoanode in 1 mol/L H2SO4(black) and 1 mol/L n(H2SO4)/n(CH3OH)=8∶2(red)(B)[31], mechanism of methanol PEC oxidation on α?Fe2O3 photoanode(C)[32](B) The incident irradiance is 0.120 W/cm2. Copyright 2011, American Chemical Society.
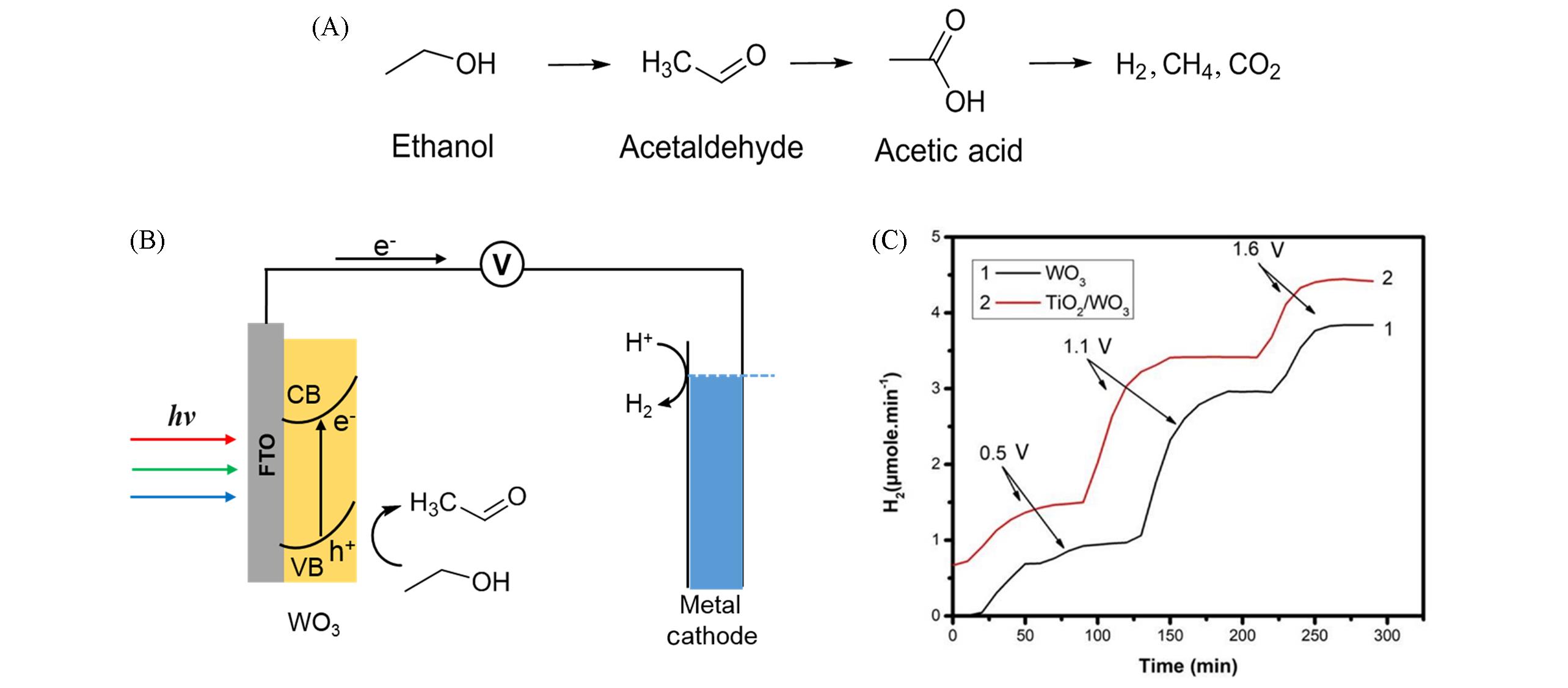
Fig.2 Ethanol oxidation reaction path(A), mechanism of ethanol PEC oxidation on WO3 photoanode(B)[43] and variation of the photoelectrocatalytic hydrogen production rate by applying various electric biases(C)[46](C) Biases are marked on the graph, and they are expressed in volts vs. Ag/AgCl electrode. The two curves correspond to the two photoanodes. Copyright 2019, Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute.
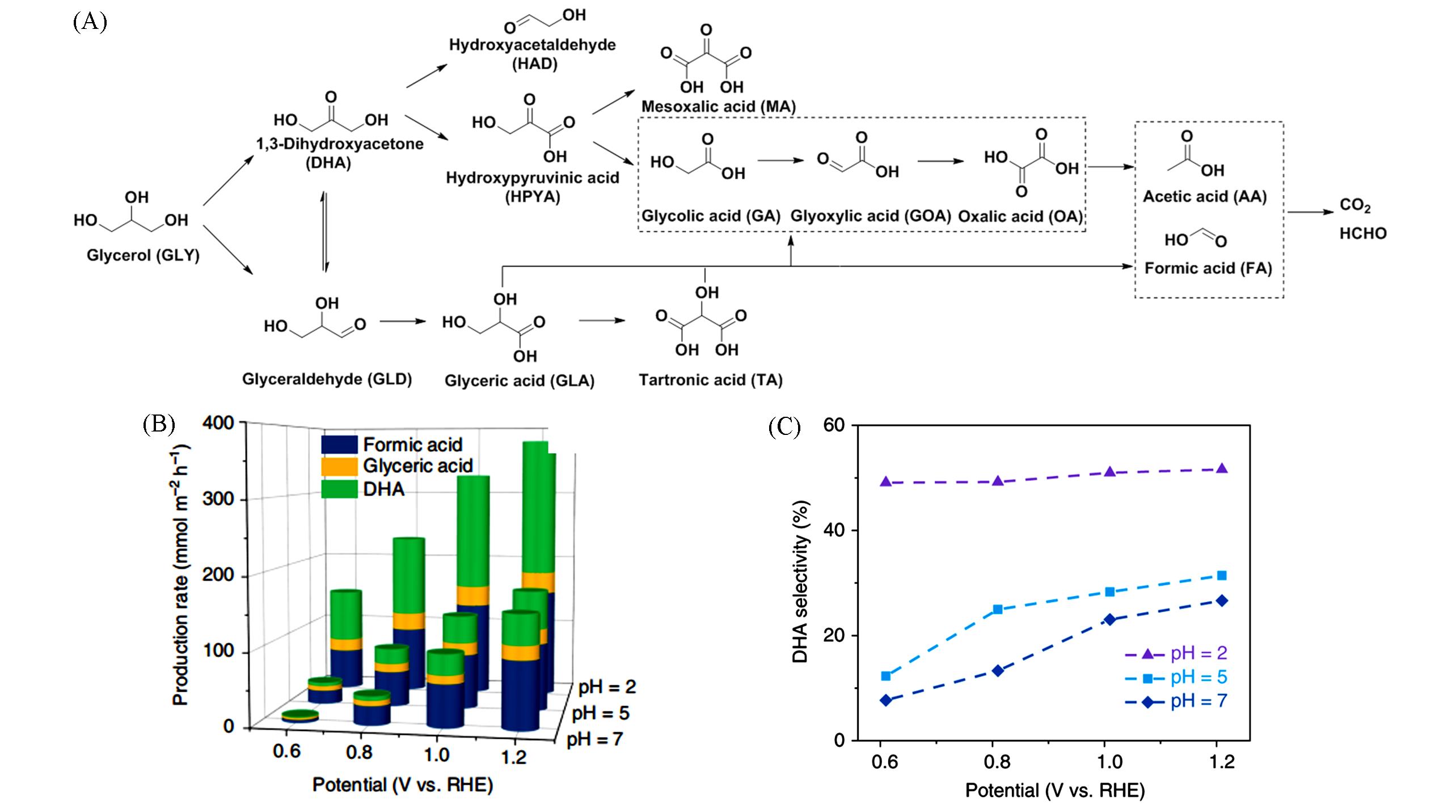
Fig.3 Glycerin oxidation reaction path(A), production rate of glycerol oxidation products on BiVO4 photoanode at pH of 2, 5, and 7(B) and selectivity of DHA produced in an H?type cell at pH = 2, 5, and 7(C)[55](B, C) Copyright 2019, Springer Nature.
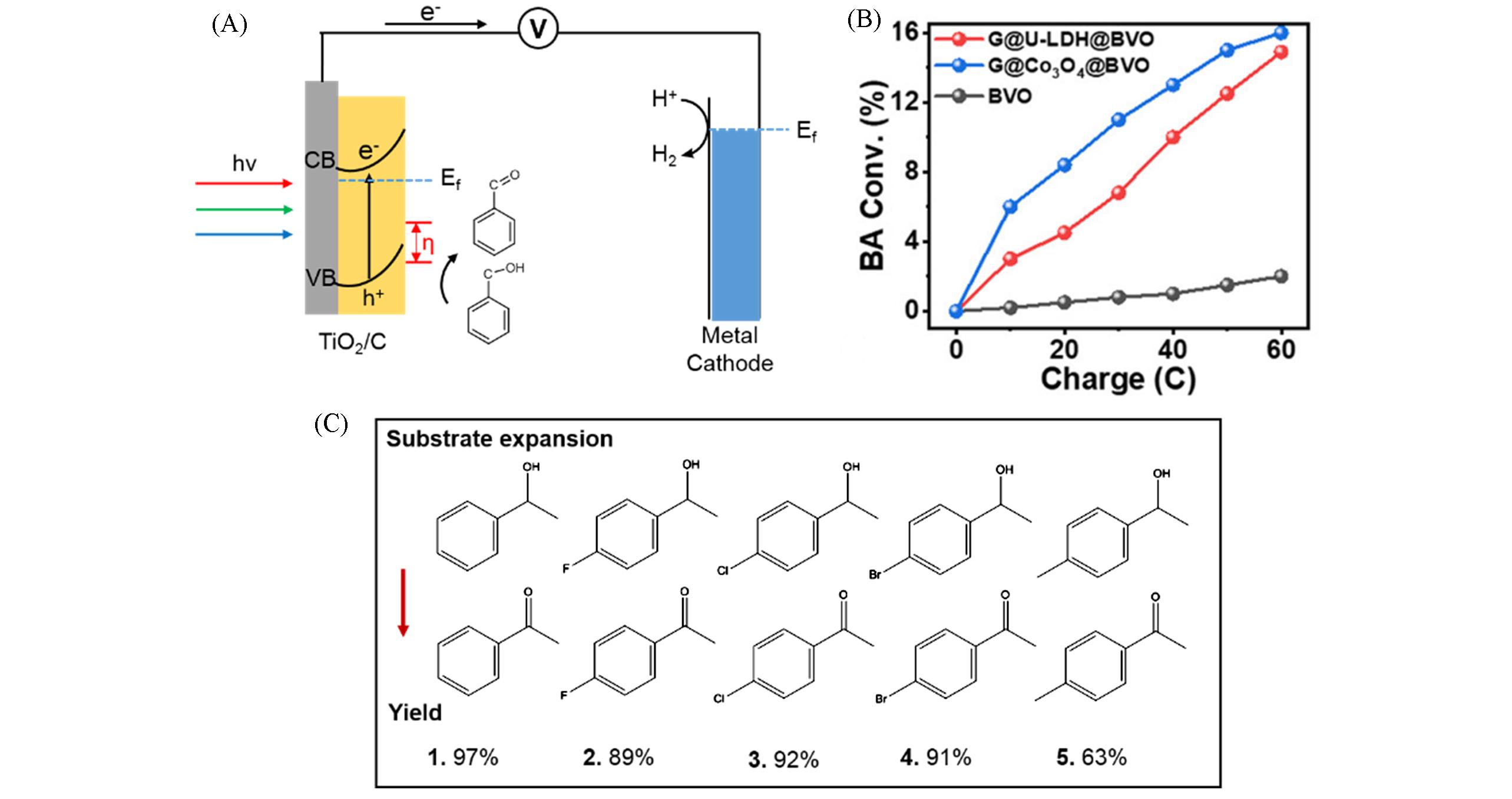
Fig.5 Schematic illustration for the PEC benzyl alcohol oxidation process(A)[76], benzyl alcohol(BA) conversion as a function of charge passed during the PEC oxidation of BA on BiVO4(BVO), G@Co3O4@BVO, and G@U?LDH@BVO photoanodes under illumination(AM 1.5G, 100 mW/cm2) at 1.2 V(vs. RHE) for 4 h(B)[77] and PEC oxidation of other aromatic alcohol on BiVO4 /WO3(C)[79](B) Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society.
| 1 | Fulcheri L., Schwob Y., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 1995, 20(3), 197—202 |
| 2 | Yang W., Prabhakar R. R., Tan J., Tilley S. D., Moon J., Chem. Soc. Rev.,2019, 48(19), 4979—5015 |
| 3 | Fujishima A., Honda K., Nature, 1972, 238, 3 |
| 4 | Jiang C., Moniz S. J. A., Wang A., Zhang T., Tang J., Chem. Soc. Rev.,2017, 46(15), 4645—4660 |
| 5 | Landman A., Dotan H., Shter G. E., Wullenkord M., Houaijia A., Maljusch A., Grader G. S., Rothschild A., Nat. Mater.,2017, 16(6), 646—651 |
| 6 | Zhang H., Yu Y., Zhang L., Dong S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2018, 57(6), 1547—1551 |
| 7 | Ma L. N., Zhou H., Xu M., Hao P. P., Kong X. G., Duan H. H., Chem. Sci.,2020, 12(3), 938—945 |
| 8 | Feng Y., Long S., Tang X., Sun Y., Luque R., Zeng X., Lin L., Chem. Soc. Rev.,2021, 50(10), 6042—6093 |
| 9 | Duan H. H., Dong J. C., Gu X. R., Peng Y. K., Chen W. X., Issariyakul T., Myers W. K., Li M. J., Yi N., Kilpatrick A. F. R., Wang Y., Zheng X. S., Ji S. F., Wang Q., Feng J. T., Chen D. L., Li Y. D., Buffet J. C., Liu H., Tsang S. C. E., O’Hare D., Nat. Commun.,2017, 8, 591 |
| 10 | Wu X., Fan X., Xie S., Lin J., Cheng J., Zhang Q., Chen L., Wang Y., Nat. Catal., 2018, 1(10), 772—780 |
| 11 | Wu X., Luo N., Xie S., Zhang H., Zhang Q., Wang F., Wang Y., Chem. Soc. Rev.,2020, 49(17), 6198—6223 |
| 12 | Duan H. H., Liu J. C., Xu M., Zhao Y. F., Ma X. L., Dong J. C., Zheng X. S., Zheng J. W., Allen C. S., Danaie M., Peng Y. K., Issariyakul T., Chen D. L., Kirkland A. I., Buffet J. C., Li J., Tsang S. C. E., O’Hare D., Nat. Catal.,2019, 2(12), 1078—1087 |
| 13 | Antoniadou M., Bouras P., Strataki N., Lianos P., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2008, 33(19), 5045—5051 |
| 14 | Antoniadou M., Kondarides D. Ι., Labou D., Neophytides S., Lianos P., Sol. Energy Mater Sol. Cells, 2010, 94(3), 592—597 |
| 15 | Melero J. A., Iglesias J., Garcia A., Energy Environ. Sci.,2012, 5(6), 7393—7420 |
| 16 | Seger B., Lu G. Q., Wang L., J. Mater. Chem.,2012, 22(21), 10709—10715 |
| 17 | Wang G., Ling Y., Lu X., Wang H., Qian F., Tong Y., Li Y., Energy Environ. Sci.,2012, 5(8), 8215—8219 |
| 18 | Xie S., Zhai T., Li W., Yu M., Liang C., Gan J., Lu X., Tong Y., Green Chem.,2013, 15(9), 2434—2440 |
| 19 | Zhang Z., Yuan Y., Fang Y., Liang L., Ding H., Shi G., Jin L., J. Electroanal. Chem.,2007, 610(2), 179—185 |
| 20 | Wang Y. Y., Liu H. Z., Han B. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11), 2393—2403(王艳燕, 刘会贞, 韩布兴. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(11), 2393—2403) |
| 21 | Wang X., Xi S., Lee W. S. V., Huang P., Cui P., Zhao L., Hao W., Zhao X., Wang Z., Wu H., Wang H., Diao C., Borgna A., Du Y., Yu Z. G., Pennycook S., Xue J., Nat. Commun.,2020, 11, 4647 |
| 22 | Xiong L., Sun Z., Zhang X., Zhao L., Huang P., Chen X., Jin H., Sun H., Lian Y., Deng Z., Rummerli M. H., Yin W., Zhang D., Wang S., Peng Y., Nat. Commun.,2019, 10, 3782 |
| 23 | Zhang Z., Liu J., Wang J., Wang Q., Wang Y., Wang K., Wang Z., Gu M., Tang Z., Lim J., Zhao T., Ciucci F., Nat. Commun.,2021, 12, 5235 |
| 24 | Zhao D., Zhuang Z., Cao X., Zhang C., Peng Q., Chen C., Li Y., Chem. Soc. Rev.,2020, 49(7), 2215—2264 |
| 25 | Wang M., Liu M., Lu J., Wang F., Nat. Commun.,2020, 11, 1083 |
| 26 | Chen X. B., Shen S. H., Guo L.J., Samuel S. M., Chem. Rev., 2010, 110(11), 6503—6570 |
| 27 | Mohapatra S. K., Raja K. S., Mahajan V. K., Misra M., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112(29), 11007—11012 |
| 28 | Ahmed A. Y., Kandiel T. A., Oekermann T., Günnemann C., Bahnemann D., ACS Appl. Energy Mater.,2019, 2(7), 5308—5318 |
| 29 | Lu X., Zheng D., Zhang P., Liang C., Liu P., Tong Y., Chem. Commun.,2010, 46(41), 7721—7723 |
| 30 | Gan J., Lu X., Zhai T., Zhao Y., Xie S., Mao Y., Zhang Y., Yang Y., Tong Y., J. Mater. Chem.,2011, 21(38), 14685—14692 |
| 31 | Cristino V., Caramori S., Argazzi R., Meda L., Marra G. L., Bignozzi C. A., Langmuir,2011, 27(11), 7276—7284 |
| 32 | Mesa C. A., Kafizas A., Francas L., Pendlebury S. R., Pastor E., Ma Y., Le Formal F., Mayer M. T., Gratzel M., Durrant J. R., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2017, 139(33), 11537—11543 |
| 33 | Jia C. C., Yin H. M., Ma H. Y., Wang R. Y., Ge X. B., Zhou A. Q., Xu X. H., Ding Y., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113(36), 16138—16143 |
| 34 | Zheng B. F., Tang O. Y., Wang Z., Long J., Chen Y., Liu Z. Q., Chem. Commun.,2018, 54(69), 9583—9586 |
| 35 | Mohajernia S., Hejazi S., Andryskova P., Zoppellaro G., Tomanec O., Zboril R., Schmuki P., ChemElectroChem,2019, 6(4), 1244—1249 |
| 36 | Wu J. F., Lastick S. M., Updegraff D. M., Nature, 1986, 321, 887—888 |
| 37 | Chen X., Kuhn E., Jennings E. W., Nelson R., Tao L., Zhang M., Tucker M. P., Energy Environ. Sci.,2016, 9(4), 1237—1245 |
| 38 | Choi J. A., Hwang J. H., Dempsey B. A., Abou⁃Shanab R. A. I., Min B., Song H., Lee D. S., Kim J. R., Cho Y., Hong S., Jeon B. H., Energy Environ. Sci.,2011, 4(9), 3513—3520 |
| 39 | Enquist N. M., Faust A. M., Bravo D. D., Santos C. N., Raisner R. M., Hanel A., Sarvabhowman P., Le C., Regitsky D. D., Cooper S. R., Peereboom L., Clark A., Martinez Y., Goldsmith J., Cho M. Y., Donohoue P. D., Luo L., Lamberson B., Tamrakar P., Kim E. J., Villari J. L., Gill A., Tripathi S. A., Karamchedu P., Paredes C. J., Rajgarhia V., Kotlar H. K., Bailey R. B., Miller D. J., Ohler N. L., Swimmer C., Yoshikuni Y., Nature, 2014, 505(7482), 239—243 |
| 40 | Tao L., Foust T. D., Joule, 2021, 5(3), 524—526 |
| 41 | Du R., Wang J., Wang Y., Hubner R., Fan X., Senkovska I., Hu Y., Kaskel S., Eychmuller A., Nat. Commun.,2020, 11, 1590 |
| 42 | Eagan N. M., Kumbhalkar M. D., Buchanan J. S., Dumesic J. A., Huber G. W., Nat. Rev. Mater.,2019, 3(4), 223—249 |
| 43 | Barczuk P. J., Lewera A., Miecznikowski K., Kulesza P., Augustynski J., Electrochem. Solid⁃State Lett., 2009, 12, B165—B166 |
| 44 | Zhou B., Schulz M., Lin H. Y., Shah S. I., Qu J., Huang C. P., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2009, 92(1/2), 41—49 |
| 45 | Doukas E., Balta P., Raptis D., Avgouropoulos G., Lianos P., Materials,2018, 11(8), 1269 |
| 46 | Adamopoulos P. M., Papagiannis I., Raptis D., Lianos P., Catalysts,2019, 9(12), 976 |
| 47 | Lari G. M., Pastore G., Haus M., Ding Y., Papadokonstantakis S., Mondelli C., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., Energy Environ. Sci.,2018, 11(5), 1012—1029 |
| 48 | Sun D., Yamada Y., Sato S., Ueda W., Green Chem.,2017, 19(14), 3186—3213 |
| 49 | Wang Y., Furukawa S., Song S., He Q., Asakura H., Yan N., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2020, 59(6), 2289—2293 |
| 50 | Zhang X., Cui G., Feng H., Chen L., Wang H., Wang B., Zhang X., Zheng L., Hong S., Wei M., Nat. Commun.,2019, 10, 5812 |
| 51 | Wang H. Y., Liu T., He Z. F., Wang X. W., Chen J. H., Wang J. Y., Jiang Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(3), 650—655(王奂祎, 刘涛, 贺站锋, 王晓伟, 陈君和, 王娟芸, 蒋毅. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(3), 650—655) |
| 52 | Mohapatra S. K., Raja K. S., Mahajan V. K., Misra M., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112, 11007—11012 |
| 53 | Palmas S., Pozzo A. D., Mascia M., Vacca A., Ricci P. C., Matarrese R., J. Solid State Electrochem.,2012, 16(7), 2493—2502 |
| 54 | Wu Y. H., Kuznetsov D. A., Pflug N. C., Fedorov A., Müller C. R., J. Mater. Chem. A,2021, 9(10), 6252—6260 |
| 55 | Liu D., Liu J. C., Cai W., Ma J., Yang H. B., Xiao H., Li J., Xiong Y., Huang Y., Liu B., Nat. Commun.,2019, 10, 1779 |
| 56 | Vo T. G., Kao C. C., Kuo J. L., Chiu C. C., Chiang C. Y., Appl. Catal. B: Environ.,2020, 278, 119303 |
| 57 | Zhou H., Li Z. H., Kong X. G., Duan H. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7), 1449—1460(周华, 栗振华, 孔祥贵, 段昊泓. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(7), 1449—1460) |
| 58 | Han G., Jin Y. H., Burgess R. A., Dickenson N. E., Cao X. M., Sun Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2017, 139(44), 15584—15587 |
| 59 | Kong L. Z., Miao G., Luo H., Sun Y. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1), 11—18(孔令照, 苗改, 罗虎, 孙予罕. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(1), 11—18) |
| 60 | Motagamwala A. H., Won W. Y., Sener C., Alonso D. M., Maravelias C. T., Dumesic A. J., Sci. Adv., 2018, 4(1), 9722 |
| 61 | Payne K. A. P., Marshall S. A., Fisher K., Cliff M. J., Cannas D. M., Yan C., Heyes D. J., Parker D. A., Larrosa I., Leys D., ACS Catal.,2019, 9(4), 2854—2865 |
| 62 | Zhang Z., Huber G. W., Chem. Soc. Rev.,2018, 47(4), 1351—1390 |
| 63 | Bonincontro D., Lolli A., Villa A., Prati L., Dimitratos N., Veith G. M., Chinchilla L. E., Botton G. A., Cavani F., Albonetti S., Green Chem.,2019, 21(15), 4090—4099 |
| 64 | Chadderdon D. J., Xin L., Qi J., Qiu Y., Krishna P., More K. L., Li W., Green Chem.,2014, 16(8), 3778—3786 |
| 65 | Kim M., Su Y., Aoshima T., Fukuoka A., Hensen E. J. M., Nakajima K., ACS Catal.,2019, 9(5), 4277—4285 |
| 66 | Cha H. G., Choi K. S., Nat. Chem.,2015, 7(4), 328—333 |
| 67 | Chadderdon D. J., Wu L. P., McGraw Z. A., Panthani M., Li W., ChemElectroChem,2019, 6(13), 3387—3392 |
| 68 | Chen Y. Z., Wang Z. U., Wang H., Lu J., Yu S. H., Jiang H. L., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2017, 139(5), 2035—2044 |
| 69 | Feng D., Dong Y., Zhang L., Ge X., Zhang W., Dai S., Qiao Z. A., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59(44), 19503—19509 |
| 70 | Zhou H., Li Z. H., Xu S. M., Lu L. L., Xu M., Ji K. Y., Ge R. X., Yan Y. F., Ma L. N., Kong X. G., Zheng L. R., Duan H. H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2021, 60(16), 8976—8982 |
| 71 | Lin R., Wan J., Xiong Y., Wu K., Cheong W. C., Zhou G., Wang D., Peng Q., Chen C., Li Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2018, 140(29), 9078—9082 |
| 72 | Qian W. H., Huang W., Cong Y. F., Li F. S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6), 1178—1183(钱文浩, 黄玮, 丛玉凤, 李富盛. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(6), 1178—1183) |
| 73 | Huang H., Yu C., Han X., Huang H., Wei Q., Guo W., Wang Z., Qiu J., Energy Environ. Sci.,2020, 13(12), 4990—4999 |
| 74 | Shang C., Liu Z. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2011, 133(25), 9938—9947 |
| 75 | Wu Z., Wang J., Zhou Z., Zhao G., J. Mater. Chem. A,2017, 5(24), 12407—12415 |
| 76 | Zhang R. K., Shao M. F., Li Z., Ning F. Y., Wei M., Evans D. G., Duan X., Chem. Eur. J.,2017, 23(34), 8142—8147 |
| 77 | Luo L., Wang Z.J., Xiang X., Yan D. P., Ye J. H., ACS Catal.,2020, 10(9), 4906—4913 |
| 78 | Arcas R., Peris E., Mas⁃Marzá E., Fabregat⁃Santiago F., Sustainable Energy Fuels,2021, 5(4), 956—962 |
| 79 | Tateno H., Miseki Y., Sayama K., ChemElectroChem, 2017, 4(12), 3283—3287 |
| [1] | GONG Yanxi, WANG Jianbing, CHAI Buyu, HAN Yuanchun, MA Yunfei, JIA Chaomin. Preparation of Potassium Doped g-C3N4 Thin Film Photoanode and Its Application in Photoelectrocatalytic Oxidation of Diclofenac Sodium in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220005. |
| [2] | WANG Mingzhi, ZHENG Yanping, WENG Weizheng. Catalytic Methane Combustion over CeO2 Supported PdO and Ce1‒x Pd x O2‒δ Species [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210816. |
| [3] | LIU Jiaqi, LI Tianbao. Preparation and Photoelectrochemical Performance of BiVO4/CuBi2O4 Thin Film Photoanodes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20220017. |
| [4] | HE Yujing, LI Jiale, WANG Dongyang, WANG Fuling, XIAO Zuoxu, CHEN Yanli. Zinc-based Activated Fe/Co/N Doped Biomass Carbon Electrocatalysts with High Oxygen Reduction Activity [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220475. |
| [5] | JIANG Shan, SHEN Qianqian, LI Qi, JIA Husheng, XUE Jinbo. Pd-loaded Defective TiO2 Nanotube Arrays for Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220206. |
| [6] | LI Shurong, WANG Lin, CHEN Yuzhen, JIANG Hailong. Research Progress of Metal⁃organic Frameworks on Liquid Phase Catalytic Chemical Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210575. |
| [7] | XUE Jinbo, GAO Guoxiang, SHEN Qianqian, LIU Tianwu, LIU Xuguang, JIA Husheng. Construction of a Novel S-scheme CdS-BiVO4 Heterojunction Photoelectrodes and Research on Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2493. |
| [8] | TANG Ding, ZHONG Shuiping. Preparation and Photoelectrochemical Performance of Bi1-xFexVO4 Thin Film Photoanodes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2509. |
| [9] | WU Qiliang, MEI Jinghao, LI Zheng, FAN Haidong, ZHANG Yanwei. Photo-thermal Coupling Water Splitting over Fe-doped TiO2 with Various Nanostructures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1837. |
| [10] | XU Anqi, LI Bin, DU Fanglin. Synthesis of Ordered Mesoporous TiO2 and Their Application for Hydrogen Production from Photocatalytic Water-splitting [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 978. |
| [11] | WANG Yishu, LI Xue, YAN Li, XU Hongyun, ZHU Yuxin, SONG Yanhua, CUI Yanjuan. Photocatalytic Reduction Performance of Z-scheme Two-dimensional BCN/Sn3O4 Composite Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3722. |
| [12] | QI Guodong, YE Xiaodong, XU Jun, DENG Feng. Progress in NMR Studies of Carbohydrates Conversion on Zeolites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 148. |
| [13] | JIN Shaoqing, SUN Hongmin, YANG Weimin. Applications of Zeolite Catalysts in Chemical Industry [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 217. |
| [14] | LI Xiao,XING Lisha,ZHAO Wanjun,WANG Yongzhao,ZHAO Yongxiang. Preparation and Characterization of Pd-Cu/hydroxyapatite Catalyst and Its Catalytic Performance for Room-temperature CO Oxidation in Humid Circumstances† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1600. |
| [15] | ZHOU Hua, LI Zhenhua, KONG Xianggui, DUAN Haohong. Recent Progress in Electrochemical Catalytic Conversion of Biomass Platform Molecules into High-value Added Fuels and Chemicals† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1449. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||