

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2021, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 492.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20200686
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHI Jiangwei1, MENG Nannan2, GUO Yamei1( ), YU Yifu2, ZHANG Bin1(
), YU Yifu2, ZHANG Bin1( )
)
Received:2020-09-14
Online:2021-02-10
Published:2021-02-05
Contact:
ZHANG Bin
E-mail:ymguo@tju.edu.cn;bzhang@tju.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
SHI Jiangwei, MENG Nannan, GUO Yamei, YU Yifu, ZHANG Bin. Recent Advances of Two-dimensional Materials for Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 492.
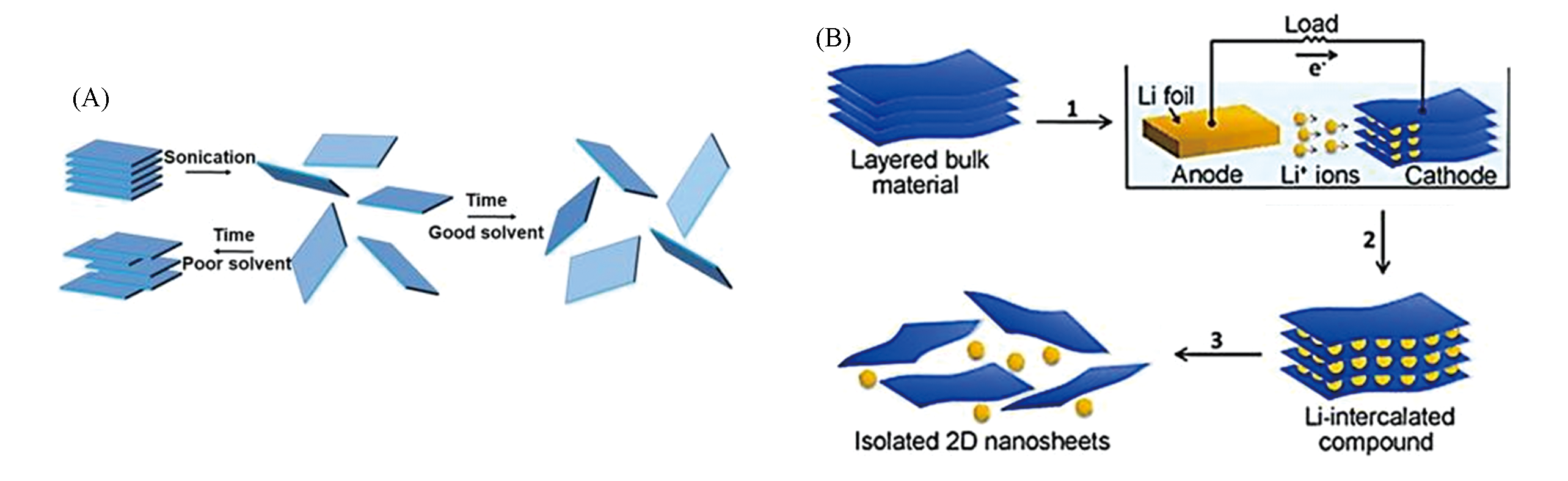
Fig.2 Scheme for the liquid exfoliation of bulk materials into 2D nanosheets by ultrasonic treatment(A)[42] and electrochemical lithium ions intercalation process for the fabrication of 2D nanosheets from the layered bulk materials(B)[46]note:(A) Copyright 2013, American Association for the Advancement of Science; (B) Copyright 2011, Wiley-VCH.
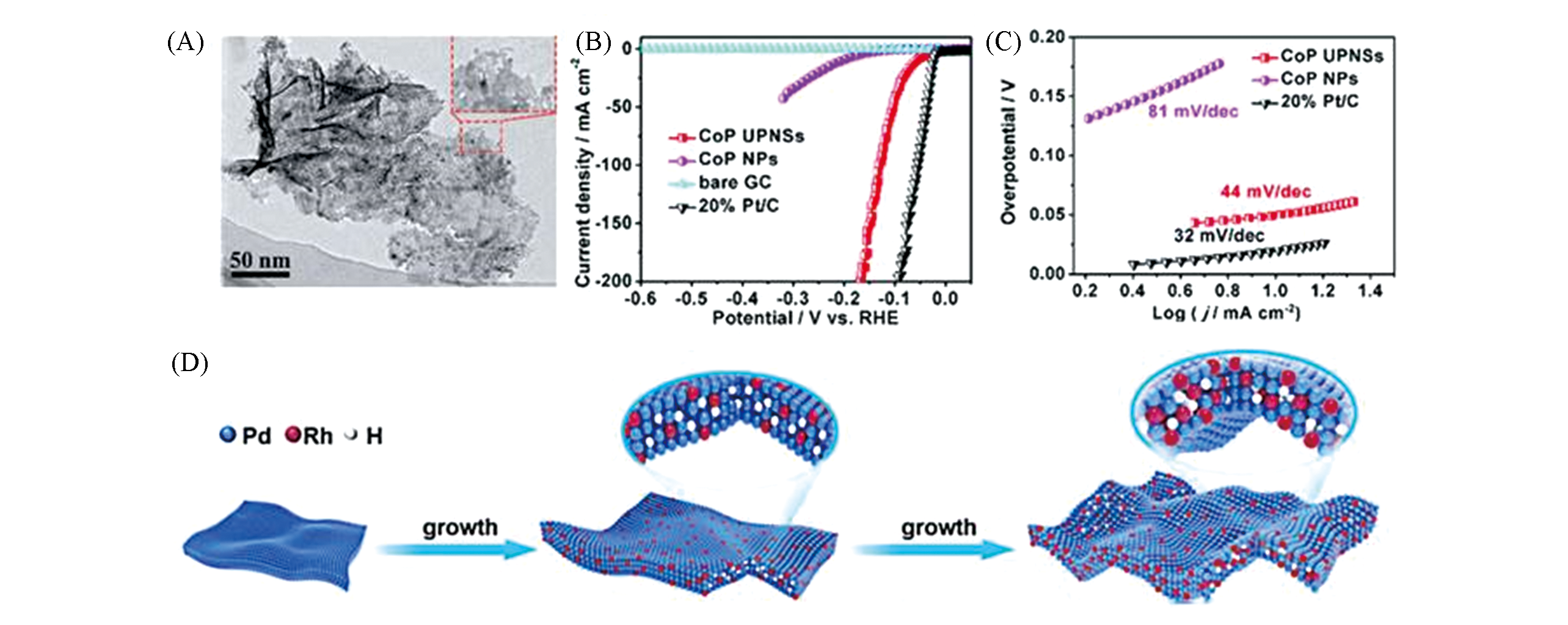
Fig.3 TEM image of CoP nanosheeets(A), the corresponding Tafel plots of CoP ultrathin porous nanosheets(UPNSs), CoP nanoparticles(NPs) and 20% Pt/C in 0.5 mol/L H2SO4 at a scan rate of 2 mV/s(B), mass activity as a function of the overpotential for CoP UPNSs and NPs(C)[54] and scheme for the growth process of RhPd?H(D)[58]note:(A—C) Copyright 2017, Royal Society of Chemistry; (D) Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society.
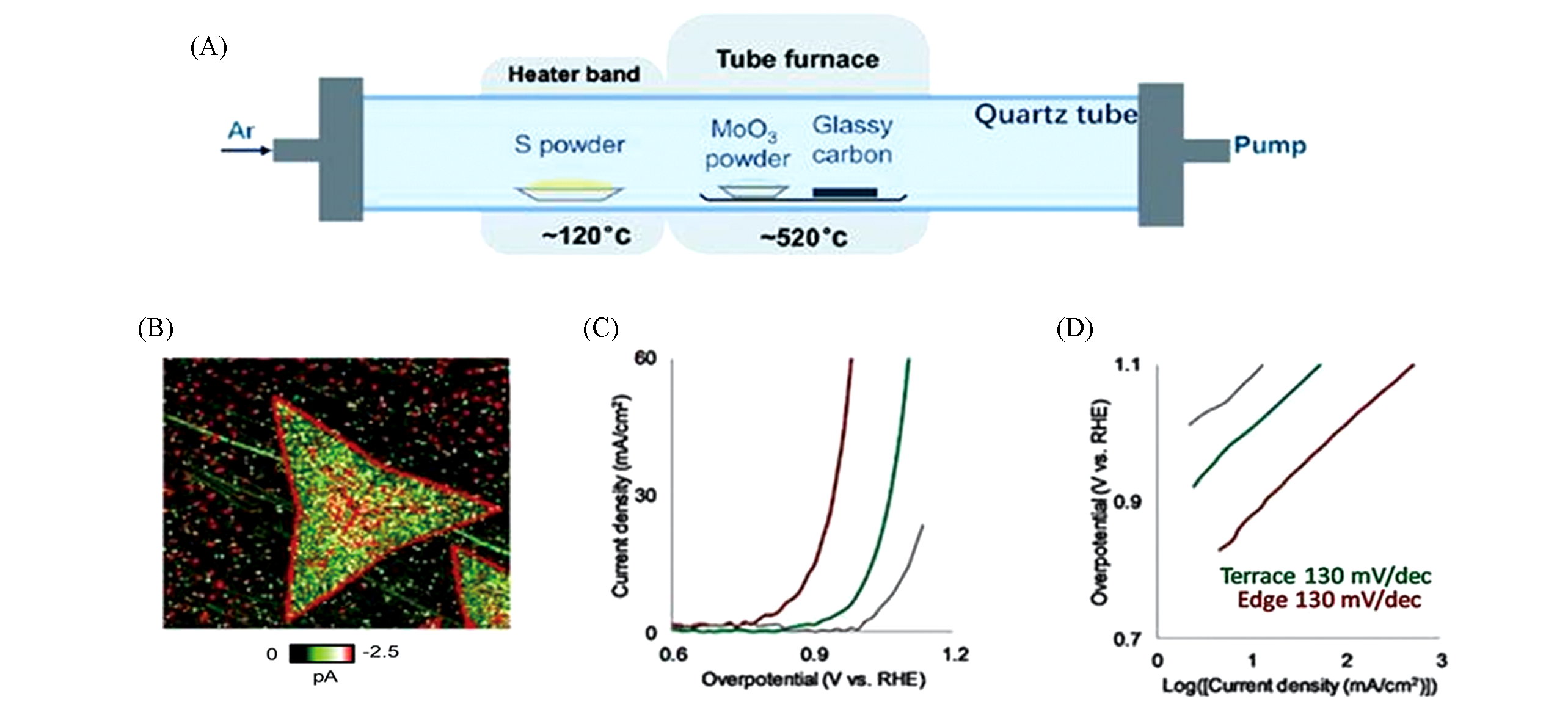
Fig.4 Schematic diagram for dual temperature zone CVD synthesis of vertical MoS2 nanosheets on glassy carbon(A)[62], the current image of MoS2 nanosheets on highly oriented pyrolytic graphite(HOPG) substrate with 15 μm× 15 μm of scan sizes and 130 V/s of scan rate at -1.3 V vs. RHE sweep voltage(B), overpotential(C) and Tafel slope(D) on the MoS2 edge(red), terrace(green), and HOPG edge(grey) regions[63]note:(A) Copyright 2018, Royal Society of Chemistry; (B—D) Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH.
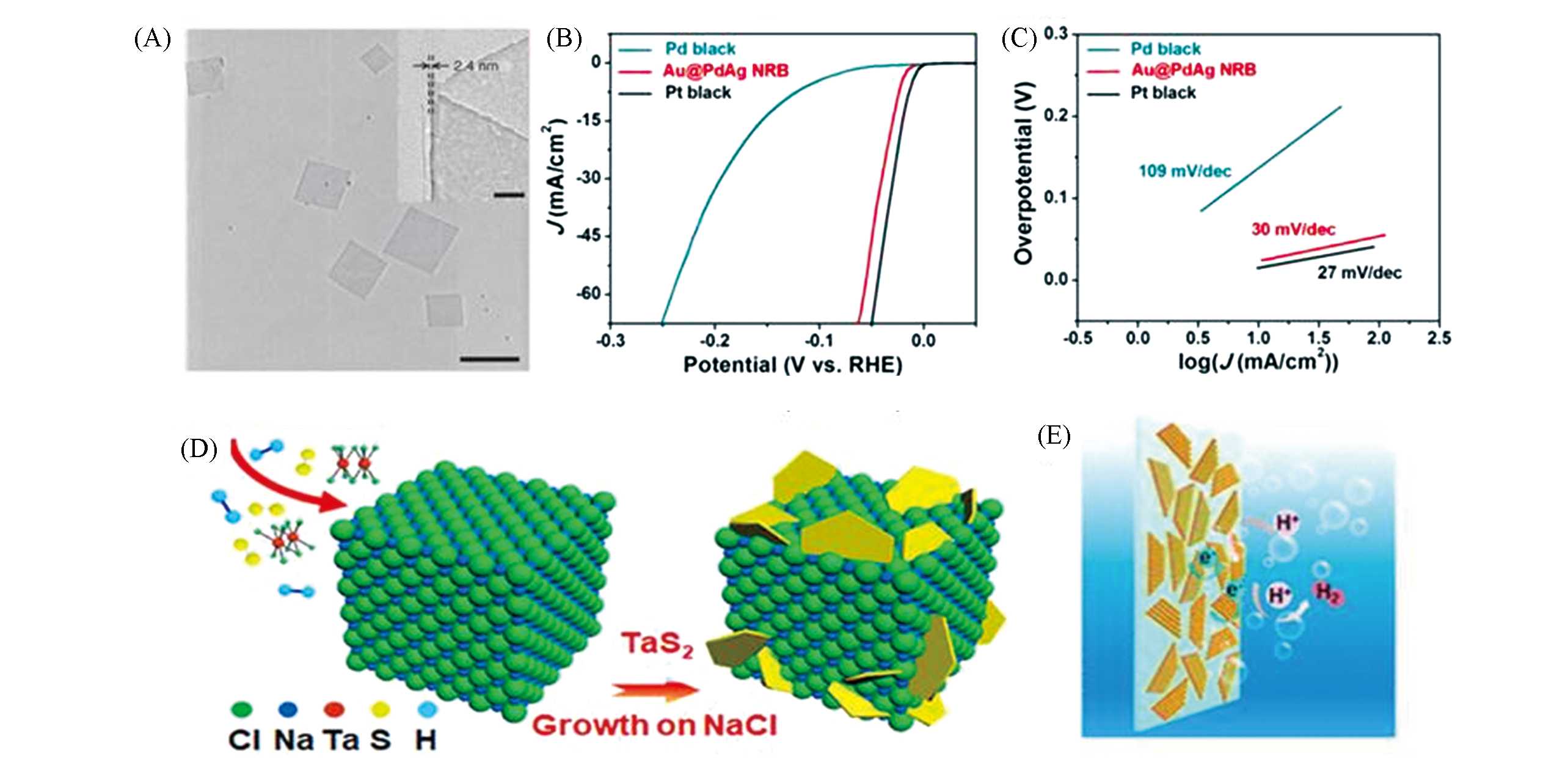
Fig.5 Typical TEM image of Au nanosheets on graphene oxide(GO) with a scale bar of 500 nm(A)[65], onset potentials and overpotentials(at the current density of 10.0 mA/cm2) of 4H/fcc Au@PdAg NRBs, Pd black, and Pt black(B) and the corresponding Tafel plots(C)[66], schematic illustration for the growth of 2D TaS2 nanosheets on micron?sized NaCl crystals(D) and schematic illustration of TaS2 for the HER process(E)[67]note:(A) Copyright 2011, Springer Nature; (B, C) Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society;(D, E) Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society.
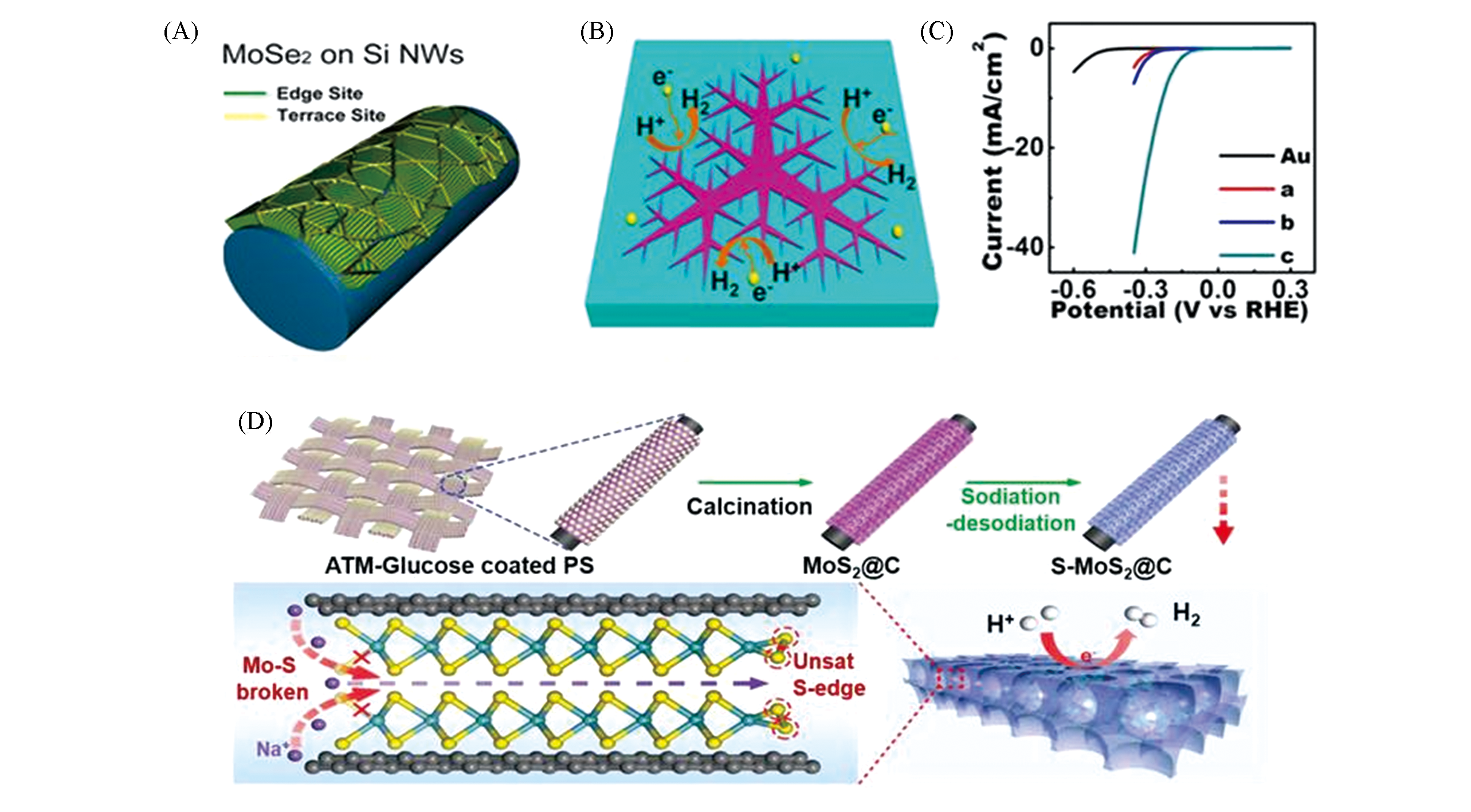
Fig.6 Scheme of MoSe2 nanofilm with molecular layers perpendicular to a curved surface(A)[72], schematic view illustrating the edges of fractal monolayer MoS2 flakes as active catalytic sites for HER(B), polarization curves of bare Au foil and MoS2/Au foils(a, b and c represent the coverage of 12%, 40%, and 60% for MoS2, respectively)(C)[73] and schematic illustration of the preparation process and microstructure of unsaturated sulfur edge MoS2 nanosheet?carbon macroporous(D)[74]note:(A) Copyright 2013, American Chemical Society;(B,C) Copyright 2014, American Chemical Society;(D) Copyright 2016, Wiley-VCH.
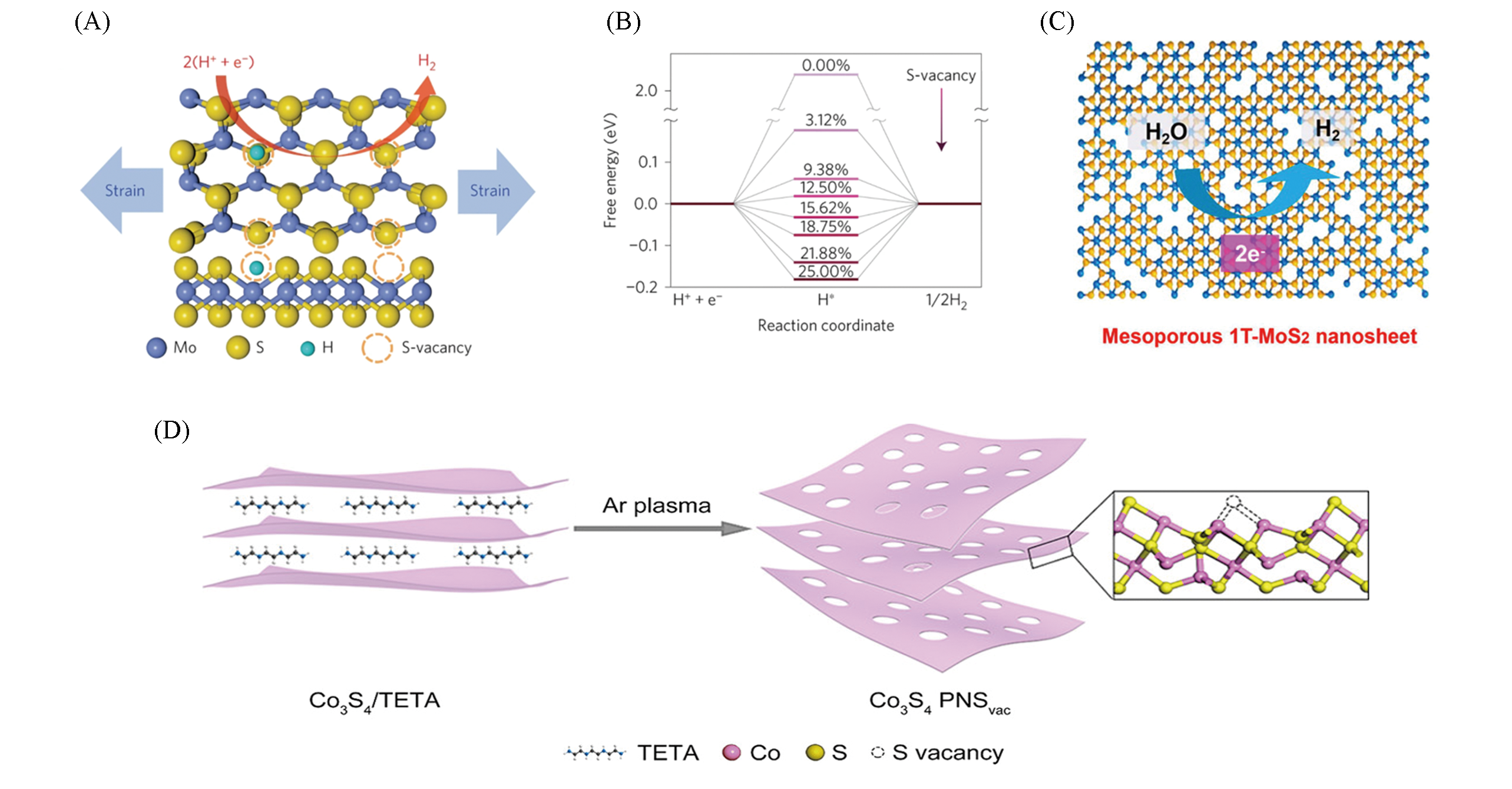
Fig.7 Scheme for the top(upper panel) and side(lower panel) views of MoS2 with strained S?vacancies on the basal plane(A) and free energy vs. the reaction coordinate of HER for the S?vacancy range of 0—25%(B)[75], scheme for mesoporous 1T?MoS2 nanosheets for catalyzing HER(C)[76] and scheme for the preparation of Co3S4 PNSvac(D)[77]note:(A, B) Copyright 2016, Springer Nature; (C) Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society;(D) Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society.
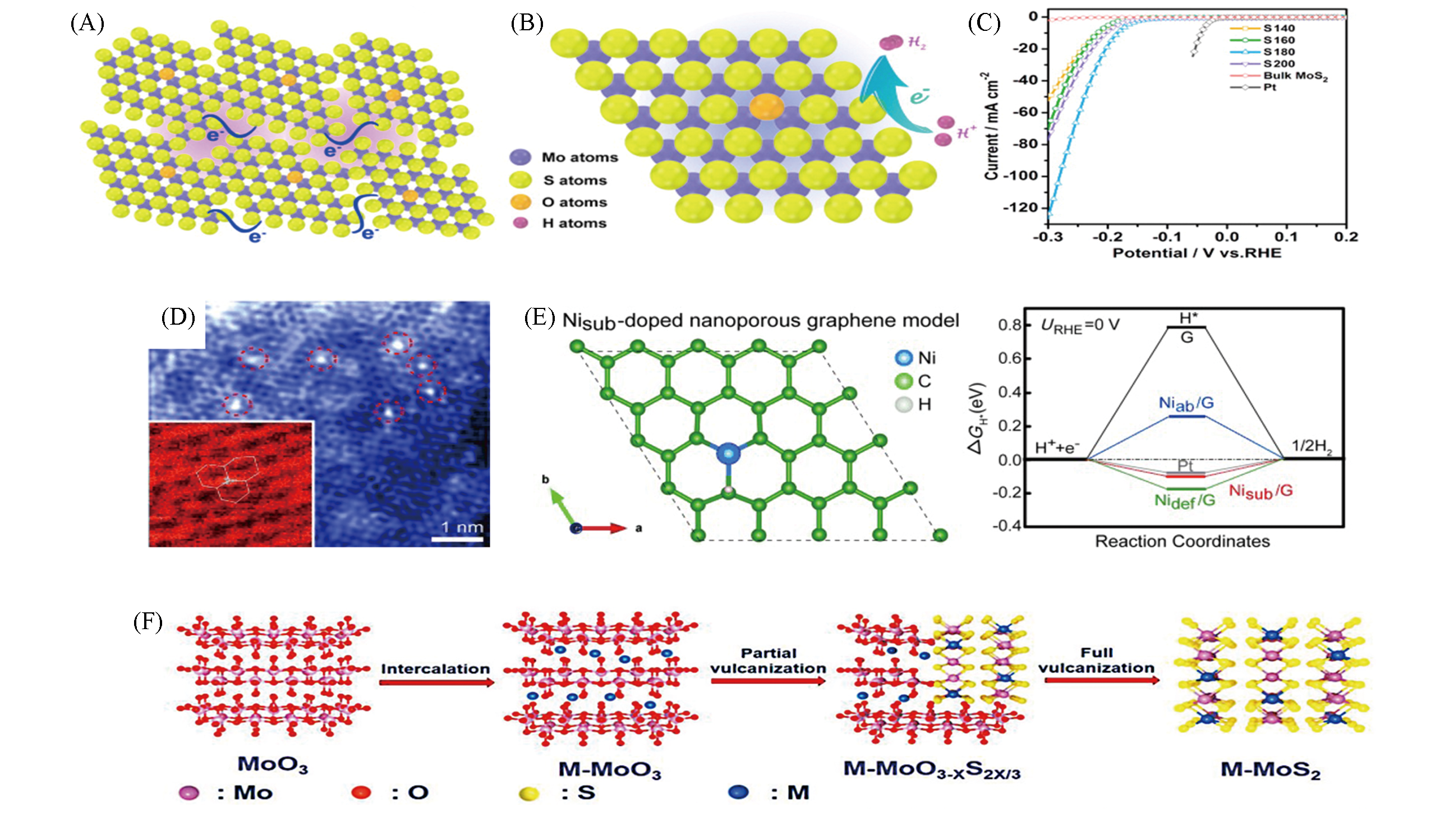
Fig.8 Schematic representation of the disordered structure in oxygen?incorporated MoS2 ultrathin nanosheets(A), constructed model of an individual oxygen?incorporated MoS2 nanodomain and the illustration of the HER process at the active sites(B), polarization curves of the oxygen?incorporated MoS2 ultrathin nanosheets(C)[81], TEM image of Ni?doped nanoporous graphene(G)(D), hydrogen adsorption sites and configuration of the interstitial atoms in the hollow centers of the benzene rings (Nisub))/G model with ΔGH*=-0.10 eV(left) and calculated Gibbs free energy diagram(right) of the HER at equilibrium potential for a Pt catalyst and Ni?doped graphene(substitutional dopants occupying C sites in the graphene lattice(Niab)/G, Nisub/G, and anchoring atoms on defect sites(Nidef)/G) samples(E)[82] and schematic illustration for the synthesis of multi?heteroatoms?doped MoS2(M?MoS2)(F)[83]note:(A, C) Copyright 2013, American Chemical Society; (D, E) Copyright 2015, Wiley-VCH; (F) Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH.
| 1 | Chu S., Majumdar A., Nature, 2012, 488(7411), 294—303 |
| 2 | Ren S., Joulié D., Salvatore D., Torbensen K., Wang M., Robert M., Berlinguette C. P., Science, 2019, 365(6451), 367—369 |
| 3 | Seh Z. W., Kibsgaard J., Dickens C. F., Chorkendorff I., Nørskov J. K., Jaramillo T. F., Science, 2017, 355(6321), eaad4998 |
| 4 | Zhang B., Xu W., Lu Z., Sun J., Transactions of Tianjin University, 2020, 26(3), 188—196 |
| 5 | Cao X., Tan C., Sindoro M., Zhang H., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46(10), 2660—2677 |
| 6 | Cao X., Tan C., Zhang X., Zhao W., Zhang H., Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(29), 6167—6196 |
| 7 | Ma A., Chen Y., Liu Y., Gui J., Yu Y., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2020, 36(4), 699—702 |
| 8 | Wang Y., Yu Y., Jia R., Zhang C., Zhang B., National Science Review, 2019, 6(4), 730—738 |
| 9 | Yu Y., Shi Y., Zhang B., Accounts of Chemical Research, 2018, 51(7), 1711—1721 |
| 10 | Jiao Y., Zheng Y., Jaroniec M. T., Qiao S. Z., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44(8), 2060—2086 |
| 11 | Lu Q., Yu Y., Ma Q., Chen B., Zhang H., Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(10), 1917—1933 |
| 12 | Chen Y., Yang K., Jiang B., Li J., Zeng M., Fu L., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(18), 8187—8208 |
| 13 | Shi W., Liu X., Deng T., Huang S., Ding M., Miao X., Zhu C., Zhu Y., Liu W., Wu F., Gao C., Yang S. W., Yang H. Y., Shen J., Cao X., Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(33), 1907404 |
| 14 | Han S., Yun Q., Tu S., Zhu L., Cao W., Lu Q., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7(43), 24691—24714 |
| 15 | Liu W., Yu L., Yin R., Xu X., Feng J., Jiang X., Zheng D., Gao X., Gao X., Que W., Ruan P., Wu F., Shi W., Cao X., Small, 2020, 16(10), 1906775 |
| 16 | Lu Q., Wang A. L., Cheng H., Gong Y., Yun Q., Yang N., Li B., Chen B., Zhang Q., Zong Y., Gu L., Zhang H., Small, 2018, 14(30), 1801090 |
| 17 | Faber M. S., Jin S., Energy Environmental Science, 2014, 7(11), 3519—3542 |
| 18 | Li X., Hao X., Abudula A., Guan G., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4(31), 11973—12000 |
| 19 | Liang J., Ma F., Hwang S., Wang X., Sokolowski J., Li Q., Wu G., Su D., Joule, 2019, 3(4), 956—991 |
| 20 | Xie J., Zhang H., Li S., Wang R., Sun X., Zhou M., Zhou J., Lou X. W., Xie Y., Adv. Mater., 2013, 25(40), 5807—5813 |
| 21 | Thoi V. S., Sun Y., Long J. R., Chang C. J., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42(6), 2388—2400 |
| 22 | Yan Y., He T., Zhao B., Qi K., Liu H., Xia B. Y., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6(33), 15905—15926 |
| 23 | Sun R. B., Guo W. X., Han X., Hong X., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2020, 36(4), 597—610 |
| 24 | Sun Y. F., Gao S., Lei F. C., Xie Y., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44(3), 623—636 |
| 25 | Wang H., Yuan H., Sae Hong S., Li Y., Cui Y., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44(9), 2664—2680 |
| 26 | Xu M., Liang T., Shi M., Chen H., Chem. Rev., 2013, 113(5), 3766—3798 |
| 27 | Zhang H., ACS Nano, 2015, 9(10), 9451—9469 |
| 28 | Li Z., Zhang X., Cheng H., Liu J., Shao M., Wei M., Evans D. G., Zhang H., Duan X., Adv. Energy Mater., 2020, 10(11), 1900486 |
| 29 | Tao H., Gao Y., Talreja N., Guo F., Texter J., Yan C., Sun Z., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(16), 7257—7284 |
| 30 | Liu W., Yin R., Xu X., Zhang L., Shi W., Cao X., Adv. Sci., 2019, 6(12), 1802373 |
| 31 | Wu Y., Wang D., Li Y., Science China Materials, 2016, 59, 938—996 |
| 32 | Tan C., Cao X., Wu X. J., He Q., Yang J., Zhang X., Chen J., Zhao W., Han S., Nam G. H., Sindoro M., Zhang H., Chem. Rev., 2017, 117(9), 6225—6331 |
| 33 | Pottathara Y. B., Grohens Y., Kokol V., Kalarikkal N., Thomas S., Nanomaterials Synthesis, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2019 |
| 34 | Novoselov K. S., Geim A. K., Morozov S. V., Jiang D., Zhang Y., Dubonos S. V., Grigorieva I. V., Firsov A. A., Science, 2004, 306(5696), 666—669 |
| 35 | Liu F., You L., Seyler K. L., Li X., Yu P., Lin J., Wang X., Zhou J., Wang H., He H., Pantelides S. T., Zhou W., Sharma P., Xu X., Ajayan P. M., Wang J., Liu Z., Nature Commun., 2016, 7(1), 12357 |
| 36 | Buscema M., Groenendijk D. J., Blanter S. I., Steele G. A., van der Zant H. S. J., Castellanos⁃Gomez A., Nano Lett., 2014, 14(6), 3347—3352 |
| 37 | Dean C. R., Young A. F., Meric I., Lee C., Wang L., Sorgenfrei S., Watanabe K., Taniguchi T., Kim P., Shepard K. L., Hone J., Nature Nanotech., 2010, 5(10), 722—726 |
| 38 | Yi M., Shen Z., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(22), 11700—11715 |
| 39 | Pan X., Hong X., Xu L., Li Y., Yan M., Mai L., Nano Today, 2019, 28, 100764 |
| 40 | Wang J., Yan M., Zhao K., Liao X., Wang P., Pan X., Yang W., Mai L., Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(7), 1604464 |
| 41 | Yan M., Zhou X., Pan X., Wang J., Xia L., Yu K., Liao X., Xu X., He L., Mai L., Nano Research, 2018, 11(6), 3205—3212 |
| 42 | Nicolosi V., Chhowalla M., Kanatzidis M. G., Strano M. S., Coleman J. N., Science, 2013, 340(6139), 1226419 |
| 43 | Hernandez Y., Nicolosi V., Lotya M., Blighe F. M., Sun Z., De S., McGovern I. T., Holland B., Byrne M., Gun Ko Y. K., Boland J. J., Niraj P., Duesberg G., Krishnamurthy S., Goodhue R., Hutchison J., Scardaci V., Ferrari A. C., Coleman J. N., Nature Nanotech., 2008, 3(9), 563—568 |
| 44 | Nguyen T. P., Choi S., Jeon J. M., Kwon K. C., Jang H. W., Kim S. Y., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016, 120(7), 3929—3935 |
| 45 | Wang H., Song T., Su X., Li Z., Wang J., ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2020, 8(2), 1262—1267 |
| 46 | Zeng Z., Yin Z., Huang X., Li H., He Q., Lu G., Boey F., Zhang H., Angew. Chem. Inter. Ed., 2011, 50(47), 11093—11097 |
| 47 | Zeng Z., Tan C., Huang X., Bao S., Zhang H., Energy & Environmental Science, 2014, 7(2), 797—803 |
| 48 | Shi W., Song S., Zhang H., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42(13), 5714—5743 |
| 49 | Sun Y., Gao S., Lei F., Liu J., Liang L., Xie Y., Chem. Sci., 2014, 5(10), 3976—3982 |
| 50 | Sun Y., Liu Q., Gao S., Cheng H., Lei F., Sun Z., Jiang Y., Su H., Wei S., Xie Y., Nature Commun., 2013, 4(1), 2899 |
| 51 | Sun Y., Sun Z., Gao S., Cheng H., Liu Q., Piao J., Yao T., Wu C., Hu S., Wei S., Xie Y., Nature Commun., 2012, 3(1), 1057 |
| 52 | Zhang X., Zhang J., Zhao J., Pan B., Kong M., Chen J., Xie Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(29), 11908—11911 |
| 53 | Wu F., Gao X., Xu X., Jiang Y., Gao X., Yin R., Shi W., Liu W., Lu G., Cao X., Chemsuschem, 2020, 13(6), 1537—1545 |
| 54 | Zhang C., Huang Y., Yu Y., Zhang J., Zhuo S., Zhang B., Chem. Sci., 2017, 8(4), 2769—2775 |
| 55 | Zhang Q., Kuang Y., Li Y., Jiang M., Cai Z., Pang Y., Chang Z., Sun X., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7(16), 9517—9522 |
| 56 | Yin Y., Zhang Y., Gao T., Yao T., Zhang X., Han J., Wang X., Zhang Z., Xu P., Zhang P., Cao X., Song B., Jin S., Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(28), 1700311 |
| 57 | Lu X., Lin Y., Dong H., Dai W., Chen X., Qu X., Zhang X., Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1), 42309 |
| 58 | Fan J., Wu J., Cui X., Gu L., Zhang Q., Meng F., Lei B. H., Singh D. J., Zheng W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142(7), 3645—3651 |
| 59 | Wong S. L., Liu H., Chi D., Progr. Crystal Growth Character. Mater., 2016, 62(3), 9—28 |
| 60 | Pollard A. J., Nair R. R., Sabki S. N., Staddon C. R., Perdigao L. M. A., Hsu C. H., Garfitt J. M., Gangopadhyay S., Gleeson H. F., Geim A. K., Beton P. H., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113(38), 16565—16567 |
| 61 | Jiang S., Zhang Z., Zhang N., Huan Y., Gong Y., Sun M., Shi J., Xie C., Yang P., Fang Q., Li H., Tong L., Xie D., Gu L., Liu P., Zhang Y., Nano Research, 2018, 11(4), 1787—1797 |
| 62 | He M., Kong F., Yin G., Lv Z., Sun X., Shi H., Gao B., RSC Adv., 2018, 8(26), 14369—14376 |
| 63 | Takahashi Y., Kobayashi Y., Wang Z., Ito Y., Ota M., Ida H., Kumatani A., Miyazawa K., Fujita T., Shiku H., Korchev Y. E., Miyata Y., Fukuma T., Chen M., Matsue T., Angew. Chem. Inter. Ed., 2020, 59(9), 3601—3608 |
| 64 | Tan C., Zhang H., Nature Commun., 2015, 6(1), 7873 |
| 65 | Huang X., Li S., Huang Y., Wu S., Zhou X., Li S., Gan C. L., Boey F., Mirkin C. A., Zhang H., Nature Commun., 2011, 2(1), 292 |
| 66 | Fan Z., Luo Z., Huang X., Li B., Chen Y., Wang J., Hu Y., Zhang H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(4), 1414—1419 |
| 67 | Huan Y., Shi J., Zou X., Gong Y., Xie C., Yang Z., Zhang Z., Gao Y., Shi Y., Li M., Yang P., Jiang S., Hong M., Gu L., Zhang Q., Yan X., Zhang Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(47), 18694—18703 |
| 68 | Yang S., Niu W., Wang A. L., Fan Z., Chen B., Tan C., Lu Q., Zhang H., Angew. Chem. Inter. Ed., 2017, 56(15), 4252—4255 |
| 69 | Huang C., Huang Y., Liu C., Yu Y., Zhang B., Angew. Chem. Inter. Ed., 2019, 58(35), 12014—12017 |
| 70 | Wang Z., Xu L., Huang F., Qu L., Li J., Owusu K. A., Liu Z., Lin Z., Xiang B., Liu X., Zhao K., Liao X., Yang W., Cheng Y. B., Mai L., Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9(21), 1900390 |
| 71 | Kong D., Wang H., Cha J. J., Pasta M., Koski K. J., Yao J., Cui Y. J. N. l., Nano Lett., 2013, 13(3), 1341—1347 |
| 72 | Wang H., Kong D., Johanes P., Cha J. J., Zheng G., Yan K., Liu N., Cui Y., Nano Lett., 2013, 13(7), 3426—3433 |
| 73 | Zhang Y., Ji Q., Han G., Ju J., Shi J., Ma D., Sun J., Zhang Y., Li M., Lang X. Y., Zhang Y., Liu Z., ACS Nano,2014, 8(8), 8617—8624 |
| 74 | Xu Q., Liu Y., Jiang H., Hu Y., Liu H., Li C., Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9(2), 1802553 |
| 75 | Li H., Tsai C., Koh A. L., Cai L., Contryman A. W., Fragapane A. H., Zhao J., Han H. S., Manoharan H. C., Abild⁃Pedersen F., Nørskov J. K., Zheng X., Nature Mater., 2016, 15(1), 48—53 |
| 76 | Yin Y., Han J., Zhang Y., Zhang X., Xu P., Yuan Q., Samad L., Wang X., Wang Y., Zhang Z., Zhang P., Cao X., Song B., Jin S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(25), 7965—7972 |
| 77 | Zhang C., Shi Y., Yu Y., Du Y., Zhang B., ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(9), 8077—8083 |
| 78 | Zhao Y., Tang M. T., Wu S., Geng J., Han Z., Chan K., Gao P., Li H., J. Catalysis, 2020, 382, 320—328 |
| 79 | Zheng Y., Jiao Y., Li L. H., Xing T., Chen Y., Jaroniec M., Qiao S. Z., ACS Nano, 2014, 8(5), 5290—5296 |
| 80 | Jiang H., Zhu Y., Su Y., Yao Y., Liu Y., Yang X., Li C., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(24), 12642—12645 |
| 81 | Xie J., Zhang J., Li S., Grote F., Zhang X., Zhang H., Wang R., Lei Y., Pan B., Xie Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(47), 17881—17888 |
| 82 | Qiu H. J., Ito Y., Cong W., Tan Y., Liu P., Hirata A., Fujita T., Tang Z., Chen M., Angew. Chem. Intern. Ed., 2015, 54(47), 14031—14035 |
| 83 | Yang W., Zhang S., Chen Q., Zhang C., Wei Y., Jiang H., Lin Y., Zhao M., He Q., Wang X., Du Y., Song L., Yang S., Nie A., Zou X., Gong Y., Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(30), 2001167 |
| [1] | QIN Yongji, LUO Jun. Applications of Single-atom Catalysts in CO2 Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220300. |
| [2] | YAO Qing, YU Zhiyong, HUANG Xiaoqing. Progress in Synthesis and Energy-related Electrocatalysis of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220323. |
| [3] | FAN Jianling, TANG Hao, QIN Fengjuan, XU Wenjing, GU Hongfei, PEI Jiajing, CEHN Wenxing. Nitrogen Doped Ultra-thin Carbon Nanosheet Composited Platinum-ruthenium Single Atom Alloy Catalyst for Promoting Electrochemical Hydrogen Evolution Process [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220366. |
| [4] | LIN Gaoxin, WANG Jiacheng. Progress and Perspective on Molybdenum Disulfide with Single-atom Doping Toward Hydrogen Evolution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220321. |
| [5] | WANG Sicong, PANG Beibei, LIU Xiaokang, DING Tao, YAO Tao. Application of XAFS Technique in Single-atom Electrocatalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220487. |
| [6] | HAN Fuchao, LI Fujin, CHEN Liang, HE Leiyi, JIANG Yunan, XU Shoudong, ZHANG Ding, QI Lu. Enhance of CoSe2/C Composites Modified Separator on Electrochemical Performance of Li-S Batteries at High Sulfur Loading [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220163. |
| [7] | WANG Ruhan, JIA Shunhan, WU Limin, SUN Xiaofu, HAN Buxing. CO2-involved Electrochemical C—N Coupling into Value-added Chemicals [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220395. |
| [8] | WANG Lijun, LI Xin, HONG Song, ZHAN Xinyu, WANG Di, HAO Leiduan, SUN Zhenyu. Efficient Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction to CO by Tuning CdO-Carbon Black Interface [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220317. |
| [9] | YANG Lijun, YU Yang, ZHANG Lei. Construction of Dual-functional 2D/3D Hydrid Co2P-CeO x Heterostructure Integrated Electrode for Electrocatalytic Urea Oxidation Assisted Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220082. |
| [10] | WANG Guangqi, BI Yiyang, WANG Jiabo, SHI Hongfei, LIU Qun, ZHANG Yu. Heterostructure Construction of Noble-metal-free Ternary Composite Ni(PO3)2-Ni2P/CdS NPs and Its Visible Light Efficient Catalytic Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220050. |
| [11] | XIA Tian, WAN Jiawei, YU Ranbo. Progress of the Structure-property Correlation of Heteroatomic Coordination Structured Carbon-based Single-atom Electrocatalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220162. |
| [12] | ZHANG Hongwei, CHEN Wen, ZHAO Meiqi, MA Chao, HAN Yunhu. Research Progress of Single Atom Catalysts in Electrochemistry [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220129. |
| [13] | WU Jun, HE Guanchao, FEI Huilong. Self-supported Film Electrodes Decorated with Single Atoms for Energy Electrocatalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220051. |
| [14] | CHEN Changli, MI Wanliang, LI Yujing. Research Progress of Single Atom Catalysts in Electrochemical Hydrogen Cycling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220065. |
| [15] | CHEN Zhaoyang, XUE Yurui, LI Yuliang. Synthesis and Applications of Graphdiyne Based Zerovalent Atomic Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220063. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||