

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 512.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190567
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Xiangyuan,YAO Xiaoxia,SHENTU Jiangtao,SUN Xiaohui,LI Juanqin,LIU Mingxia,XU Shimin
Received:2019-11-04
Online:2020-02-26
Published:2020-01-15
Contact:
Xiangyuan LI
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LI Xiangyuan,YAO Xiaoxia,SHENTU Jiangtao,SUN Xiaohui,LI Juanqin,LIU Mingxia,XU Shimin. Combustion Reaction Mechanism Construction by Two-parameter Rate Constant Method †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 512.
| Differential form | Expression for k | Author and publication date[ |
|---|---|---|
| k=ATC | Van’t Hoff, 1898; Bodenstein,1899 | |
| k=ATCe-B/T | Kooij,1893; Trautz, 1909 | |
| k=A | Schwab,1883; van’tHoff,1884; Spohr,1888 | |
| k=ATCeDT | … | |
| k=Ae-B/T | Van’t Hoff,1884; Arrhenius,1889; Kooij, 1893 | |
| k=ATC | Harcurt and Esson,1895; Veley, 1908 |
| Differential form | Expression for k | Author and publication date[ |
|---|---|---|
| k=ATC | Van’t Hoff, 1898; Bodenstein,1899 | |
| k=ATCe-B/T | Kooij,1893; Trautz, 1909 | |
| k=A | Schwab,1883; van’tHoff,1884; Spohr,1888 | |
| k=ATCeDT | … | |
| k=Ae-B/T | Van’t Hoff,1884; Arrhenius,1889; Kooij, 1893 | |
| k=ATC | Harcurt and Esson,1895; Veley, 1908 |
| Reaction | GRI-Mech 3.0[ | UCSD[ | AramcoMech 2.0[ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A/(cm3· mol-1·s-1) | n | E/ (J·mol-1) | A/(cm3· mol-1·s-1) | n | E/ (J·mol-1) | A/(cm3· mol-1·s-1) | n | E/ (J·mol-1) | |
| O+C2H2=H+HCCO | 1.35×107 | 2.00 | 7949 | 4.00×1014 | 0 | 44600 | 2.96×109 | 1.28 | 10342 |
| O+C2H2=CO+CH2 | 6.94×106 | 2.00 | 7949 | 1.60×1014 | 0 | 41400 | 7.40×108 | 1.28 | 10342 |
| C2H3+O2=HCO+CH2O | 4.58×1016 | -1.39 | 4246 | 1.70×1029 | -5.31 | 27209 | 1.16×1016 | -1.13 | 15861 |
| CH2CHO=CH2CO+H | 4.87×1011 | 0.42 | -7342 | 1.05×1037 | -7.19 | 185519 | 1.43×1015 | -0.15 | 190790 |
| CH2CHO=CH3+CO | | | | 1.17×1043 | -9.80 | 183080 | 2.93×1012 | 0.29 | 168454 |
| H+CH3CHO=CH2CHO+H2 | 2.05×109 | 1.16 | 10062 | 1.85×1012 | 0.40 | 22425 | 2.72×103 | 3.10 | 21798 |
| C2H5+O2=HO2+C2H4 | 8.40×1011 | 0 | 16213 | 7.50×1014 | -1.00 | 20082 | 2.09×109 | 0.49 | -1637 |
| CH3O+O2=HO2+CH2O | 4.28×10-13 | 7.60 | -14769 | 4.28×10-13 | 7.60 | -14799 | 4.38×10-19 | 9.50 | -23016 |
| CH3+CH2O=HCO+CH4 | 3.32×103 | 2.81 | 24518 | | | | 3.83×101 | 3.36 | 18024 |
| H+CH4=CH3+H2 | 6.60×108 | 1.62 | 45354 | 1.30×104 | 3.00 | 33629 | 6.14×105 | 2.50 | 40112 |
| OH+CH2O=HCO+H2O | 3.43×109 | 1.18 | -1870 | 3.90×1010 | 0.89 | 1700 | 7.82×107 | 1.63 | -4414 |
| OH+C2H2=H+CH2CO | 2.18×10-4 | 4.50 | -4184 | 1.90×107 | 1.70 | 4179 | 1.58×103 | 2.56 | -3533 |
| OH+C2H6=C2H5+H2O | 3.54×106 | 2.12 | 3640 | 2.20×107 | 1.90 | 4700 | 1.48×107 | 1.90 | 3974 |
| HO2+CH2O=HCO+H2O2 | 5.60×106 | 2.00 | 50207 | 4.11×104 | 2.50 | 42720 | 1.88×104 | 2.70 | 48199 |
| 2CH3(+M)=C2H6(+M) | 6.77×1016 | -1.18 | 2736 | 1.81×1013 | 0 | 0 | 2.28×1015 | -0.69 | 731 |
| CH+H2O=H+CH2O | 5.71×1012 | 0 | -3158 | 1.17×1015 | -0.75 | 0 | 1.77×1016 | -1.22 | 99 |
| CH+CO2=HCO+CO | | | | 4.80×101 | 3.22 | -13500 | 1.70×1012 | 0 | 2863 |
| H+CH3OH=CH2OH+H2 | 1.70×107 | 2.10 | 20376 | 1.35×103 | 3.20 | 14605 | 3.07×105 | 2.55 | 22760 |
| H+CH3OH=CH3O+H2 | 4.20×106 | 2.10 | 20376 | 6.83×101 | 3.40 | 30291 | 1.99×105 | 2.56 | 43095 |
| Reaction | GRI-Mech 3.0[ | UCSD[ | AramcoMech 2.0[ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A/(cm3· mol-1·s-1) | n | E/ (J·mol-1) | A/(cm3· mol-1·s-1) | n | E/ (J·mol-1) | A/(cm3· mol-1·s-1) | n | E/ (J·mol-1) | |
| O+C2H2=H+HCCO | 1.35×107 | 2.00 | 7949 | 4.00×1014 | 0 | 44600 | 2.96×109 | 1.28 | 10342 |
| O+C2H2=CO+CH2 | 6.94×106 | 2.00 | 7949 | 1.60×1014 | 0 | 41400 | 7.40×108 | 1.28 | 10342 |
| C2H3+O2=HCO+CH2O | 4.58×1016 | -1.39 | 4246 | 1.70×1029 | -5.31 | 27209 | 1.16×1016 | -1.13 | 15861 |
| CH2CHO=CH2CO+H | 4.87×1011 | 0.42 | -7342 | 1.05×1037 | -7.19 | 185519 | 1.43×1015 | -0.15 | 190790 |
| CH2CHO=CH3+CO | | | | 1.17×1043 | -9.80 | 183080 | 2.93×1012 | 0.29 | 168454 |
| H+CH3CHO=CH2CHO+H2 | 2.05×109 | 1.16 | 10062 | 1.85×1012 | 0.40 | 22425 | 2.72×103 | 3.10 | 21798 |
| C2H5+O2=HO2+C2H4 | 8.40×1011 | 0 | 16213 | 7.50×1014 | -1.00 | 20082 | 2.09×109 | 0.49 | -1637 |
| CH3O+O2=HO2+CH2O | 4.28×10-13 | 7.60 | -14769 | 4.28×10-13 | 7.60 | -14799 | 4.38×10-19 | 9.50 | -23016 |
| CH3+CH2O=HCO+CH4 | 3.32×103 | 2.81 | 24518 | | | | 3.83×101 | 3.36 | 18024 |
| H+CH4=CH3+H2 | 6.60×108 | 1.62 | 45354 | 1.30×104 | 3.00 | 33629 | 6.14×105 | 2.50 | 40112 |
| OH+CH2O=HCO+H2O | 3.43×109 | 1.18 | -1870 | 3.90×1010 | 0.89 | 1700 | 7.82×107 | 1.63 | -4414 |
| OH+C2H2=H+CH2CO | 2.18×10-4 | 4.50 | -4184 | 1.90×107 | 1.70 | 4179 | 1.58×103 | 2.56 | -3533 |
| OH+C2H6=C2H5+H2O | 3.54×106 | 2.12 | 3640 | 2.20×107 | 1.90 | 4700 | 1.48×107 | 1.90 | 3974 |
| HO2+CH2O=HCO+H2O2 | 5.60×106 | 2.00 | 50207 | 4.11×104 | 2.50 | 42720 | 1.88×104 | 2.70 | 48199 |
| 2CH3(+M)=C2H6(+M) | 6.77×1016 | -1.18 | 2736 | 1.81×1013 | 0 | 0 | 2.28×1015 | -0.69 | 731 |
| CH+H2O=H+CH2O | 5.71×1012 | 0 | -3158 | 1.17×1015 | -0.75 | 0 | 1.77×1016 | -1.22 | 99 |
| CH+CO2=HCO+CO | | | | 4.80×101 | 3.22 | -13500 | 1.70×1012 | 0 | 2863 |
| H+CH3OH=CH2OH+H2 | 1.70×107 | 2.10 | 20376 | 1.35×103 | 3.20 | 14605 | 3.07×105 | 2.55 | 22760 |
| H+CH3OH=CH3O+H2 | 4.20×106 | 2.10 | 20376 | 6.83×101 | 3.40 | 30291 | 1.99×105 | 2.56 | 43095 |
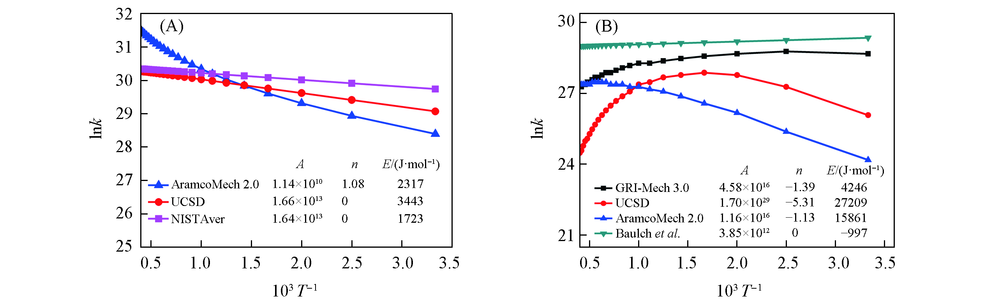
Fig.1 Temperature dependence of reaction rate constants for HO2+H=H2+O2(A) and C2H3+O2=CHO+CH2O(B) by three-parameter fitting and two-parameter fitting
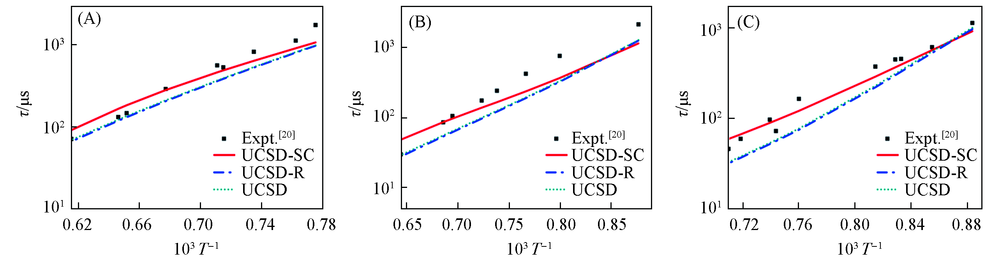
Fig.3 Ignition delay time by UCSD, UCSD-R, UCSD-SC and the experimental data (A) 100% CH4, p=1.09 MPa; (B) 80%/20% CH4/H2, p=2.14 MPa; (C) 60%/40% CH4/H2, p=2.36 MPa.
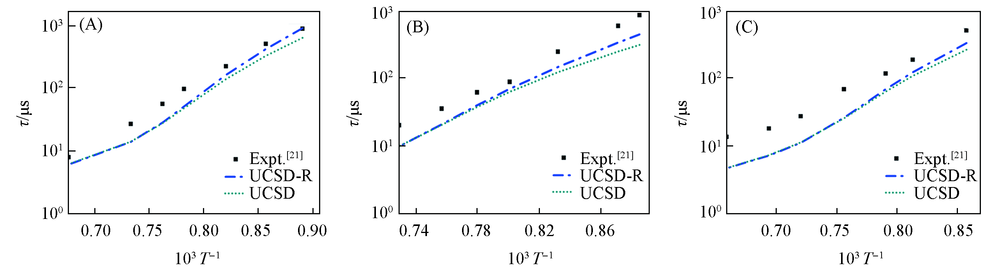
Fig.4 Ignition delay time by UCSD, UCSD-R and the experimental data (A) 6.25%C2H4/18.75%O2/75%N2, p=0.6—0.83 MPa; (B) 6.25%C2H4/18.75%O2/75%N2, p=1.12—1.61 MPa; (C) 11.76%C2H4/17.65%O2/70.59%N2, p=0.64—0.82 MPa.
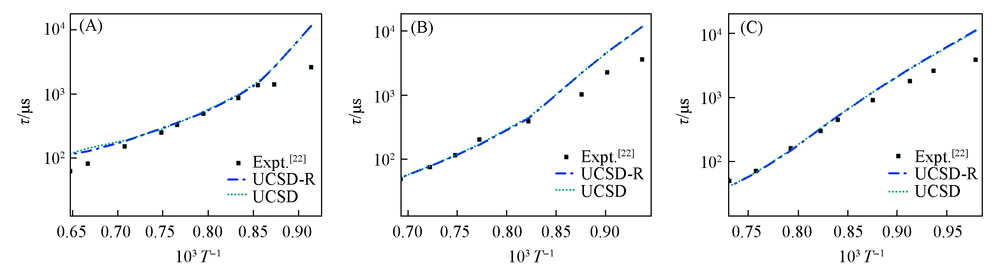
Fig.5 Ignition delay time by UCSD, UCSD-R and the experimental data (A) 30%C2H6/70%H2, p=0.12 MPa; (B) 30%C2H6/70%H2, p=0.41 MPa; (C) 30%C2H6/70%H2, p=1.62 MPa.
| [1] | Laidler K. J ., J. Chem. Educ, 1984, 61( 6), 494— 498 |
| [2] | Tsang W., Hampson R. F ., J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 1986, 15( 3), 1087— 1279 |
| [3] | Wang H., Sheen D. A ., Prog. Energy Combust., 2015, 47, 1— 31 |
| [4] | Smith G. P., Golden D. M., Frenklach M., Moriarty N. W., Eiteneer B., Goldenberg M., Bowman C. T., Hanson R. K., Song S., Gardiner W. C., Lissianski Jr. V. V., Qin Z . 1999. GRI-Mech 3.0. Available at: |
| [5] | Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering(Combustion Research), University of California at San Diego, San Diego Mechanism, Version 2016-12-14. |
| [6] | Li Y., Zhou C. W., Somers K. P., Zhang K. W., Curran H. J ., Proc. Combust. Inst., 2017, 36, 403— 411 |
| [7] | Manion J. A., Huie R. E., Levin R. D., Burgess D. R., Orkin V. L., Tsang W., McGivern W. S., Hudgens J. W., Knyazev V. D., Atkinson D. B., Chai E., Tereza A. M., Lin C. Y., Allison T. C., Mallard W. G., Westley F., Herron J. T., Hampson R. F., Frizzell D. H ., NIST Chemical Kinetics Database, National Institute of Standards and Technology, USA, |
| [8] | Baulch D. L., Bowman C. T., Cobos C. J., Cox R. A., Just T., Kerr J. A., Pilling M. J., Stocker D., Troe J., Tsang W., Walker R. W., Warnatz J ., J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 2005, 34( 3), 757— 1397 |
| [9] | Sutherland J. W., Michael J. V., Pirraglia A. N., Nesbitt F. L., Klemm R. B ., Symposium on Combustion, 1988, 21( 1), 929— 941 |
| [10] | Lindemann F. A., Arrhenius S., Langmuir I., Dhar N. R., Perrin J., McC. Lewis W. C ., Transactions of the Faraday Society, 1922, 17, 598— 606 |
| [11] | Turányi T., Tomlin A. S ., Analysis of Kinetic Reaction Mechanisms, Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, 2014 |
| [12] | Curran H. J ., Proc. Combust. Inst., 2019, 37( 1), 57— 81 |
| [13] | Marcus R. A ., J. Chem. Phys., 1952, 20( 3), 359— 364 |
| [14] | Gilbert R. G., Smith S. C ., Theory of Unimolecular and Recombination Reactions, Blackwell, London, 1990 |
| [15] | Jasper A. W., Miller J. A., Klippenstein S. J ., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2013, 117( 47), 12243— 12255 |
| [16] | Miller J. A., Klippenstein S. J ., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2013, 117( 13), 2718— 2727 |
| [17] | Li X. Y., Shentu J. T., Li Y. W., Li J. Q., Wang J. B ., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190568 |
| ( 李象远, 申屠江涛, 李宜蔚, 李娟琴, 王静波 . 高等学校化学学报, 2020, doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190568) | |
| [18] | Glass I. I., Patterson G. N ., J. Aeronaut. Sci., 1955, 22( 2), 73— 100 |
| [19] | CHEMKIN-PRO 15101, Reaction Design,San Diego, 2010 |
| [20] | Petersen E. L., Hall J. M., Smith S. D., Vries J. D., Amadio A. R., Crofton M. W ., J. Eng. Gas. Turb. Power, 2007, 129( 4), 937— 944 |
| [21] | Penyazkov O. G., Sevrouk K. L., Tangirala V., Joshi N ., Proc. Combust. Inst., 2009, 32( 2), 2421— 2428 |
| [22] | Pan L., Zhang Y. J, Zhang J. X, Tian Z. M, Huang Z. H , Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39( 11), 6024— 6033 |
| [1] | WANG Jian, ZHANG Hongxing. Theoretical Study on the Structural-photophysical Relationships of Tetra-Pt Phosphorescent Emitters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2245. |
| [2] | LI Yiwei, SHENTU Jiangtao, WANG Jingbo, LI Xiangyuan. Combustion Mechanism Construction Based on Minimized Reaction Network: C1⁃Oxygen Combustion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1871. |
| [3] | LI Xiangyuan, SHENTU Jiangtao, LI Yiwei, LI Juanqin, WANG Jingbo. Combustion Mechanism Construction Based on Minimized Reaction Network: Hydrogen-Oxygen Combustion † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 772. |
| [4] | WANG Ning,ZHU Huifang,WANG Lu,ZHANG Tiantian,GU Jiali,SHU Jie. Structural Identification and Asymmetric-exchange Dynamics Study of Esomeprazole Magnesium in Specific Solution as Probed by Using 1H NMR Spectra† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 1919. |
| [5] | LI Yingli, WANG Jingbo, LI Xiangyuan. Kinetic Mechanism Study on Low Temperature for Decalin Combustion† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(6): 1212. |
| [6] | FANG Sheng, LIU Jingjing, DUAN Xuemei, TAO Fuming, LIU Jingyao. Ab initio Calculation and Kinetic Investigation of Monacid-catalyzed Decomposition of Sulfurous Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(8): 1390. |
| [7] | MA Qian, WANG Weina, ZHAO Qiangli, LIU Fengyi, WANG Wenliang. Theoretical Studies on the Reaction Mechanism of Criegee Intermediates RCHOO(R=H, CH3) with NCO Radical† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(4): 613. |
| [8] |
WANG Rui, LI Yili, FENG Xukai, SONG Liang, ZHANG Tianlei, WANG Zhuqing, JIN Lingxia, ZHANG Qiang, XU Qiong, WANG Zhiyin.
Catalytic Effect of n(H2O)(n=1,2) on the Reaction of HO2+NO |
| [9] | GAO Zhifang, WANG Weina, MA Qian, LIU Fengyi, WANG Wenliang. Theoretical Studies on the Reaction Mechanism of Criegee Intermediates CH3CHOO with OH Radicals† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(3): 513. |
| [10] | ZHU Peng, DUAN Xuemei, LIU Jingyao. Mechanism and Kinetics of the Hydrogen-abstraction Reaction of CF2ClC(O)OCH2CH3 with OH Radicals† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(1): 79. |
| [11] | WANG Kuan, CHEN Jiangang, WANG Bozhou, LU Jian, WANG Wenliang, LIU Fengyi, ZHOU Cheng, LIAN Peng, LIU Zhongwen, LIU Zhaotie. Mechanisms and Kinetics of the Synthesis of FOX-12† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(3): 531. |
| [12] | HU Xixi, YANG Junying, XIE Daiqian. State-to-state Quantum Dynamics of Reaction N+NH→N2+H [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(11): 2198. |
| [13] | LI Yue, FANG Decai. Density Functional Theory Studies on the t-Butoxyl Radical Mediated Hydrogen Atom Transfer Reactions† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(10): 1954. |
| [14] | MA Peng, SONG Jinou, SONG Chonglin, LÜ Gang, CHEN Chaoxu, YANG Chuanwang. Effect of H-atom Abstraction Reactions Among C2H3, C2H5OH and CH3HCO on the Combustion of Ethanol-Hydrocarbon Fuels† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(1): 149. |
| [15] | GUO Sha, WANG Weina, JIN Lingxia, WANG Shuai, WANG Wenliang. Mechanistic Studies on CH3CH2O+HCHO Reaction and Rate Constants of Major Channel† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(6): 1300. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||