

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 1212.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180160
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Yingli, WANG Jingbo*( ), LI Xiangyuan
), LI Xiangyuan
Received:2018-03-01
Online:2018-06-10
Published:2018-05-22
Contact:
WANG Jingbo
E-mail:wangjingbo@scu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LI Yingli, WANG Jingbo, LI Xiangyuan. Kinetic Mechanism Study on Low Temperature for Decalin Combustion†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(6): 1212.
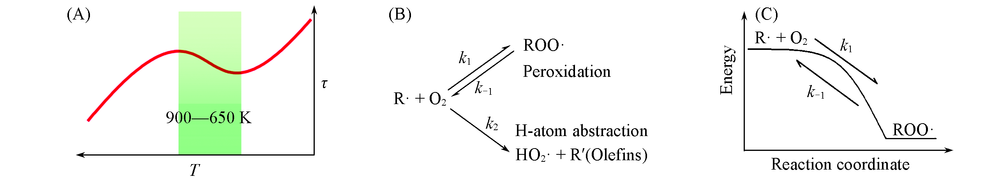
Fig.1 Negative temperature coefficient effect of low temperature ignition delay(A), the disproportionation reaction of radical oxidation(B) and the barrierless reaction for O2 addition(C)
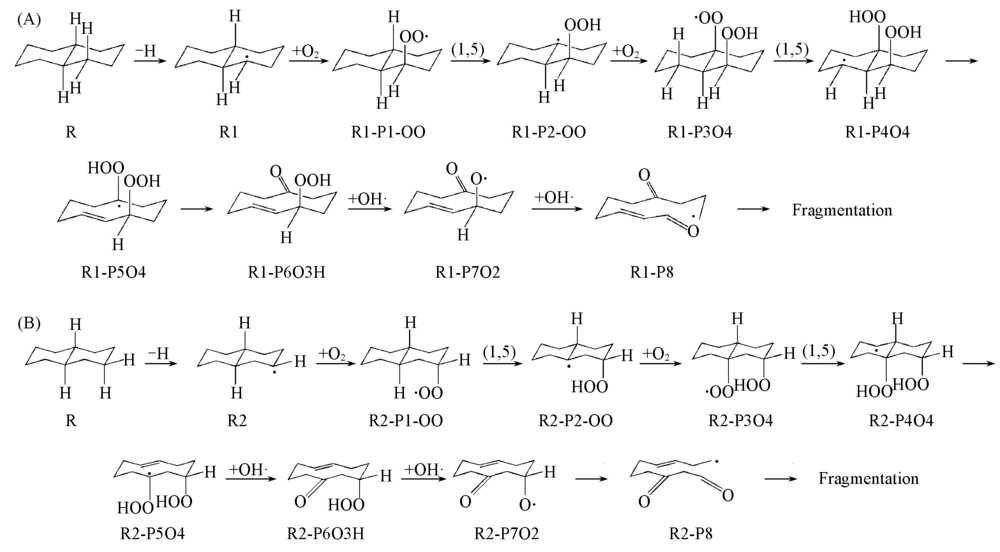
Fig.3 Low temperature oxidation reactions of decalin starting from C—H bond breaking at the α position(A) and β position(B)Species designation is also given.
| Number of reaction | Reaction | lgA* | Ea/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| r1 | R=R1+H | 14.91 | 300.33 |
| r2 | R1+O2=R1-P1-OO | -0.62 | 63.79 |
| r3 | R1-P1-OO→R1-P2-OO | 10.23 | 186.90 |
| r4 | R1-P2-OO+O2=R1-P3O4 | -8.17 | -114.99 |
| r5 | R1-P3O4→R1-P4O4 | 5.82 | 181.46 |
| r6 | R1-P4O4→R1-P5O4 | 10.51 | 72.12 |
| r7 | R1-P5O4→R1-P6O3H+OH | 12.39 | 65.93 |
| r8 | R1-P6O3H→R1-P7O2+OH | 11.22 | 40.56 |
| r9 | R1-P7O2→R1-P8 | 13.28 | 221.98 |
| r10 | R=R2+H | 12.39 | 376.02 |
| r11 | R2+O2=R2-P1-OO | -15.59 | -4.77 |
| r12 | R2-P1-OO→R2-P2-OO | 13.04 | 214.23 |
| r13 | R2-P2-OO+O2=R2-P3O4 | -13.58 | -126.50 |
| r14 | R2-P3O4→R2-P4O4 | 8.25 | 177.35 |
| r15 | R2-P4O4→R2-P5O4 | 8.48 | 63.67 |
| r16 | R2-P5O4→R2-P6O3H+OH | 13.84 | 46.17 |
| r17 | R2-P6O3H→R2-P7O2+OH | 22.58 | 28.05 |
| r18 | R2-P7O2→R2-P8 | 11.26 | 214.78 |
Table 1 High-pressure limit rate parameters for low temperature oxidation reactions of decalin in the temperature range of 500—1500 K*
| Number of reaction | Reaction | lgA* | Ea/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| r1 | R=R1+H | 14.91 | 300.33 |
| r2 | R1+O2=R1-P1-OO | -0.62 | 63.79 |
| r3 | R1-P1-OO→R1-P2-OO | 10.23 | 186.90 |
| r4 | R1-P2-OO+O2=R1-P3O4 | -8.17 | -114.99 |
| r5 | R1-P3O4→R1-P4O4 | 5.82 | 181.46 |
| r6 | R1-P4O4→R1-P5O4 | 10.51 | 72.12 |
| r7 | R1-P5O4→R1-P6O3H+OH | 12.39 | 65.93 |
| r8 | R1-P6O3H→R1-P7O2+OH | 11.22 | 40.56 |
| r9 | R1-P7O2→R1-P8 | 13.28 | 221.98 |
| r10 | R=R2+H | 12.39 | 376.02 |
| r11 | R2+O2=R2-P1-OO | -15.59 | -4.77 |
| r12 | R2-P1-OO→R2-P2-OO | 13.04 | 214.23 |
| r13 | R2-P2-OO+O2=R2-P3O4 | -13.58 | -126.50 |
| r14 | R2-P3O4→R2-P4O4 | 8.25 | 177.35 |
| r15 | R2-P4O4→R2-P5O4 | 8.48 | 63.67 |
| r16 | R2-P5O4→R2-P6O3H+OH | 13.84 | 46.17 |
| r17 | R2-P6O3H→R2-P7O2+OH | 22.58 | 28.05 |
| r18 | R2-P7O2→R2-P8 | 11.26 | 214.78 |
| Name of reaction | Specified reaction | lg[A/(mol-1·cm3·s-1)] | Ea/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| JetSurF 2.0[ |  | 12.06 | -6.36 |
| r1[ |  | 10.52 | -1.09 |
| r2[ |  | 10.36 | -11.09 |
| r3[ |  | 12.28 | -4.35 |
| r4[ |  | 11.28 | -17.62 |
Table 2 Results of one-step O2 addition to ethylcyclohexane radicals in the literature
| Name of reaction | Specified reaction | lg[A/(mol-1·cm3·s-1)] | Ea/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| JetSurF 2.0[ |  | 12.06 | -6.36 |
| r1[ |  | 10.52 | -1.09 |
| r2[ |  | 10.36 | -11.09 |
| r3[ |  | 12.28 | -4.35 |
| r4[ |  | 11.28 | -17.62 |
| Name of reaction | Specified reaction | lg(A/s-1) | Ea/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| r1[ |  | 11.51 | 100.75 |
| r2[ |  | 11.77 | 97.28 |
| r[ |  | 11.42 | 85.10 |
| r3[ |  | 11.78 | 85.35 |
Table 3 Kinetic parameters of 1,5 H-shift reactions from the literature
| Name of reaction | Specified reaction | lg(A/s-1) | Ea/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| r1[ |  | 11.51 | 100.75 |
| r2[ |  | 11.77 | 97.28 |
| r[ |  | 11.42 | 85.10 |
| r3[ |  | 11.78 | 85.35 |
| [1] | Hilpert M., Mora B. A., Ni J., Rule A. M., Nachman K. E., Curr. Environ. Health Rep., 2015, 2(4), 412—422 |
| [2] | Ogawa H., Ibuki T., Takayuki M. A., Miyamoto N., Energy Fuels, 2007, 21(3), 1517—1521 |
| [3] | Ranzi E., Energy & Fuels, 2006, 20(3), 1024—1032 |
| [4] | He J. N., Li Y. L., Zhang C. H., Li P., Li X. Y., Acta Phys. Chim. Sinica, 2015, 31(5), 836—842 |
| (何九宁, 李有亮, 张昌华, 李萍, 李象远. 物理化学学报, 2015, 31(5), 836—842) | |
| [5] | Battin-Leclerc F., Prog. Energ. Combust.Sci., 2008, 34(4), 440—498 |
| [6] | Kyungchan C., Violi A., J. Org. Chem., 2007, 72(9), 3179—85 |
| [7] | Dagaut P., Ristori A., Frassoldati A., Faravelli T., Dayma G., Ranzi E., Proc. Combust. Inst., 2013, 34(1), 289—296 |
| [8] | Zámostný P., Bělohlav Z., Starkbaumová L., Patera J., J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol., 2010, 87(2), 207—216 |
| [9] | Ondruschka B., Zimmermann G., Remmler M., Sedlackova M., Pola J., J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol., 1990, 18(1), 19—32 |
| [10] | Yang Y., Boehman A. L., Combust. Flame, 2010, 157(3), 495—505 |
| [11] | Zeng M., Li Y., Yuan W., Zhou Z., Wang Y., Zhang L., Qi F., Combust. Flame, 2016, 167(5), 228—237 |
| [12] | Zhu Y., Davidson D. F., Hanson R. K., Zhu Y., Davidson D. F., Hanson R. K., Combust. Flame, 2014, 161(2), 371—383 |
| [13] | Zhang W. F., Xian L. Y., Yong K. L., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2016, 32(9), 2216—2222 |
| (张巍峰, 鲜雷勇, 雍康乐. 物理化学学报, 2016, 32(9), 2216—2222) | |
| [14] | Ranzi E., Frassoldati A., Grana R., Prog. Energ. Combust.Sci., 2012, 38(4), 468—501 |
| [15] | Tan N. X., Wang F., Liu A. K., Guo J. J., Xu J. Q., Li S. H., Li X. Y., The 29th Annual Meeting of the Chinese Chemical Societ., Beijing, 2014 |
| (谈宁馨, 王繁, 刘爱科, 郭俊江, 徐佳琪, 李树豪, 李象远. 中国化学会第29届学术年会摘要集, 北京, 2014) | |
| [16] | Zhang K., Banyon C., Bugler J., Curran H. J., Rodriguez A., Herbinet O., Battin-Leclerc F., B’Chirc C., Heuferc K. A., Combust. Flame, 2016, 172(10), 116—135 |
| [17] | Rashidi M. J. A., Mehl M., Pitz W. J., Mohamed S., Sarathy S. M., Combust. Flame, 2017, 183, 358—371 |
| [18] | Frisch M. J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Scalmani G., Barone V., Mennucci B., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Caricato M., Li X., Hratchian H. P., Izmaylov A. F., Bloino J., Zheng G., Sonnenberg J. L., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Vreven T., Montgomery J. A., Peralta J. E., Ogliaro F., Bearpark M., Heyd J. J., Brothers E., Kudin K. N., Staroverov V. N., Kobayashi R., Normand J., Raghavachari K., Rendell A., Burant J. C., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Cossi M., Rega N., Millam J. M., Klene M., Knox J. E., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J. W., Martin R. L., Morokuma K., Zakrzewski V. G., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Farkas O., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cioslowski J., Fox D. J., Gaussian 09, Revision A.01, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, 2009 |
| [19] | Becke A. D., J. Chem. Phys., 1998, 98(7), 5648—5652 |
| [20] | Lee C., Yang W., Parr R. G., Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter., 1988, 37(2), 785—789 |
| [21] | Gonzalez C., Schlegel H. B., J. Chem. Phys., 1989, 90(4), 2154—2161 |
| [22] | Montgomery J. A., Frisch M. J., Ochterski J. W., Petersson G. A., J. Chem. Phys., 1999, 110(6), 2822—2827 |
| [23] | Altarawneh M. K., Dlugogorski B. Z., Kennedy E. M., Mackie J. C., Combust. Flame, 2013, 160(1), 9—16 |
| [24] | NIST Computational Chemistry Comparison and Benchmark Database, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 101, Release 19, April 2018, Editor, Russell D. Johnson III, |
| [25] | Mokrushin V. T. W., Zachariah M., Knyazev V., Chem.Rate, Version 1.5.., National Institute of Standards and Technolog., Gaithersburg, MD, 2009 |
| [26] | Zádor J., Taatjes C. A., Fernandes R. X., Prog. Energ. Combust. Sci., 2011, 37(4), 371—421 |
| [27] | Li S. J., Tan N. X., Yao Q., Li Z. R., Li X. Y., Acta Phys. Chim. Sinica, 2015, 31(5), 859—865 |
| (李尚俊, 谈宁馨, 姚倩, 李泽荣, 李象远. 物理化学学报, 2015, 31(5), 859—865) | |
| [28] | Ning H. B., Gong C. M., Tan N. X., Li Z. R., Li X. Y., Combust. Flame, 2015, 162(11), 4167—4182 |
| [29] | Wang H., Dames E., Sirjean B., Sheen D.A., Tangko R., Violi A., Lai J. Y. W., Egolfopoulos F. N., Davidson D. F., Hanson R. K., Bowman C. T., Law C. K., Tsang W., Cernansky N. P., Miller D. L., Lindstedt R. P.,A High-temperature Chemical Kinetic Model of n-alkane(up to n-dodecane), Cyclohexane, and Methyl-, Ethyl-, n-Propyl and n-Butyl-cyclohexane Oxidation at High Temperatures, JetSurF Version 2.0, September 19, 2010() |
| [30] | Xing L., Zhang L., Zhang F., Jiang J., Combust. Flame, 2017, 182(8), 216—224 |
| [31] | Miyoshi A., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2011, 115(15), 3301—3325 |
| [1] | REN Nana, XUE Jie, WANG Zhifan, YAO Xiaoxia, WANG Fan. Effects of Thermodynamic Data on Combustion Characters of 1,3-Butadiene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220151. |
| [2] | WANG Jian, ZHANG Hongxing. Theoretical Study on the Structural-photophysical Relationships of Tetra-Pt Phosphorescent Emitters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2245. |
| [3] | LI Yiwei, SHENTU Jiangtao, WANG Jingbo, LI Xiangyuan. Combustion Mechanism Construction Based on Minimized Reaction Network: C1⁃Oxygen Combustion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1871. |
| [4] | LI Xiangyuan, SHENTU Jiangtao, LI Yiwei, LI Juanqin, WANG Jingbo. Combustion Mechanism Construction Based on Minimized Reaction Network: Hydrogen-Oxygen Combustion † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 772. |
| [5] | LI Xiangyuan,YAO Xiaoxia,SHENTU Jiangtao,SUN Xiaohui,LI Juanqin,LIU Mingxia,XU Shimin. Combustion Reaction Mechanism Construction by Two-parameter Rate Constant Method † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 512. |
| [6] | WANG Ning,ZHU Huifang,WANG Lu,ZHANG Tiantian,GU Jiali,SHU Jie. Structural Identification and Asymmetric-exchange Dynamics Study of Esomeprazole Magnesium in Specific Solution as Probed by Using 1H NMR Spectra† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 1919. |
| [7] | FANG Sheng, LIU Jingjing, DUAN Xuemei, TAO Fuming, LIU Jingyao. Ab initio Calculation and Kinetic Investigation of Monacid-catalyzed Decomposition of Sulfurous Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(8): 1390. |
| [8] | MA Qian, WANG Weina, ZHAO Qiangli, LIU Fengyi, WANG Wenliang. Theoretical Studies on the Reaction Mechanism of Criegee Intermediates RCHOO(R=H, CH3) with NCO Radical† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(4): 613. |
| [9] |
WANG Rui, LI Yili, FENG Xukai, SONG Liang, ZHANG Tianlei, WANG Zhuqing, JIN Lingxia, ZHANG Qiang, XU Qiong, WANG Zhiyin.
Catalytic Effect of n(H2O)(n=1,2) on the Reaction of HO2+NO |
| [10] | GAO Zhifang, WANG Weina, MA Qian, LIU Fengyi, WANG Wenliang. Theoretical Studies on the Reaction Mechanism of Criegee Intermediates CH3CHOO with OH Radicals† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(3): 513. |
| [11] | ZHU Peng, DUAN Xuemei, LIU Jingyao. Mechanism and Kinetics of the Hydrogen-abstraction Reaction of CF2ClC(O)OCH2CH3 with OH Radicals† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(1): 79. |
| [12] | WANG Kuan, CHEN Jiangang, WANG Bozhou, LU Jian, WANG Wenliang, LIU Fengyi, ZHOU Cheng, LIAN Peng, LIU Zhongwen, LIU Zhaotie. Mechanisms and Kinetics of the Synthesis of FOX-12† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(3): 531. |
| [13] | HU Xixi, YANG Junying, XIE Daiqian. State-to-state Quantum Dynamics of Reaction N+NH→N2+H [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(11): 2198. |
| [14] | LI Yue, FANG Decai. Density Functional Theory Studies on the t-Butoxyl Radical Mediated Hydrogen Atom Transfer Reactions† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(10): 1954. |
| [15] | MA Peng, SONG Jinou, SONG Chonglin, LÜ Gang, CHEN Chaoxu, YANG Chuanwang. Effect of H-atom Abstraction Reactions Among C2H3, C2H5OH and CH3HCO on the Combustion of Ethanol-Hydrocarbon Fuels† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(1): 149. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||