

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (4): 613.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160803
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Qian, WANG Weina, ZHAO Qiangli, LIU Fengyi, WANG Wenliang*( )
)
Received:2016-11-18
Online:2017-04-10
Published:2017-03-22
Contact:
WANG Wenliang
E-mail:wlwang@snnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
MA Qian, WANG Weina, ZHAO Qiangli, LIU Fengyi, WANG Wenliang. Theoretical Studies on the Reaction Mechanism of Criegee Intermediates RCHOO(R=H, CH3) with NCO Radical†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(4): 613.
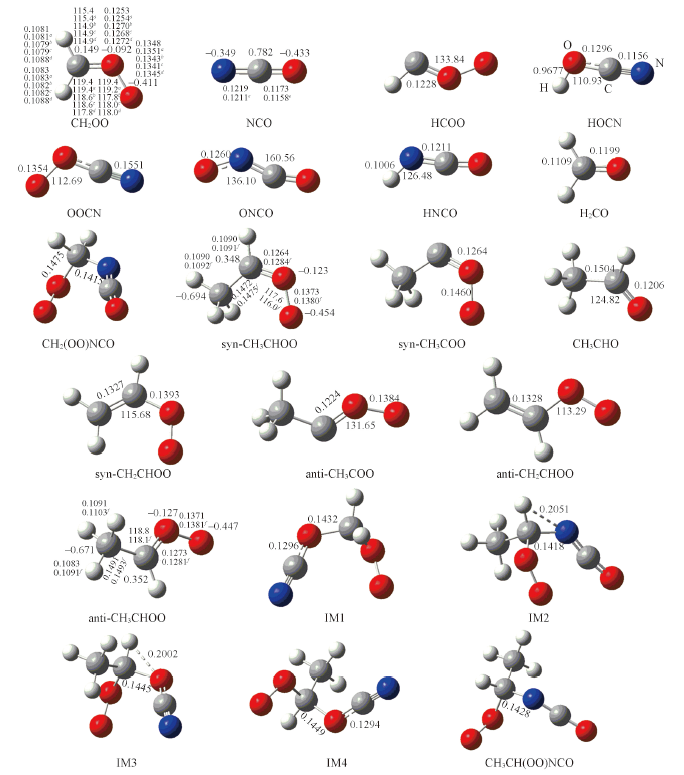
Fig.1 Optimized geometries of reactants and products in the reaction of RCHOO(R=H,CH3)+NCO at the B3LYP/6-311+G(2df,2p) levela. At the B3LYP/AVTZ level[26]; b. at the CCSD(T)-F12/AVTZ level[27]; c. at the CCSD(T)/aug-co-pCV5Z level[28]; d. experimental values from ref.[29]; e. at the BH&HLYP/6-311++G(3df, 3pd) level[30]; f. at the NEVPTZ(1,1)/aug-cc-pVDZ[31]. The charges of the carbon, nitrogen and oxygen atom obtained from NBO analysis, bond lengths are in nm, bond angles are in degrees.
| Species | ΔfH 0—/(kJ·mol-1) | Species | ΔfH 0—/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NCO | 144.18 | CH2(OO)NCO | -57.87 |
| HNCO | -108.06(-110.00)[ | IM1 | 66.08 |
| HCHO | -112.11(-108.70)[ | IM2 | -98.47 |
| CH3CHO | -166.57(-170.70)[ | IM3 | 14.95 |
| CH2OO | 102.26(104.92)[ | IM4 | 10.67 |
| RC1 | 202.33 | CH3CH(OO)NCO | -99.11 |
| RC2 | 129.48 | HOCN | -10.46 |
| RC3 | 169.67 | syn-CH3CHOO | 37.78 |
| RC4 | 152.52 | anti-CH3CHOO | 52.69 |
Table 1 Formation enthalpies ΔfH 0— for some species at the G4 level
| Species | ΔfH 0—/(kJ·mol-1) | Species | ΔfH 0—/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NCO | 144.18 | CH2(OO)NCO | -57.87 |
| HNCO | -108.06(-110.00)[ | IM1 | 66.08 |
| HCHO | -112.11(-108.70)[ | IM2 | -98.47 |
| CH3CHO | -166.57(-170.70)[ | IM3 | 14.95 |
| CH2OO | 102.26(104.92)[ | IM4 | 10.67 |
| RC1 | 202.33 | CH3CH(OO)NCO | -99.11 |
| RC2 | 129.48 | HOCN | -10.46 |
| RC3 | 169.67 | syn-CH3CHOO | 37.78 |
| RC4 | 152.52 | anti-CH3CHOO | 52.69 |
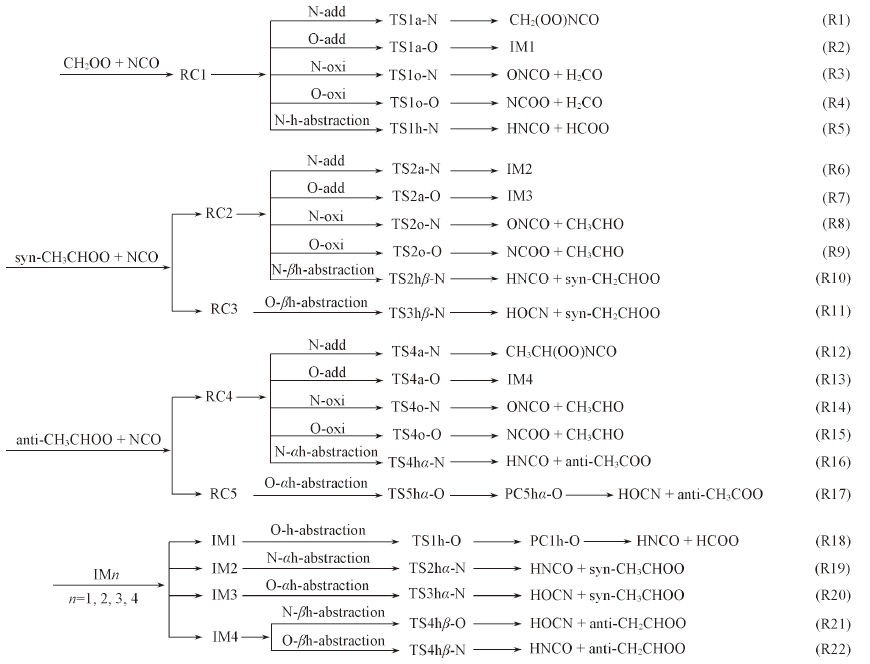
Scheme 2 Possible reaction channels of RCHOO(R=H, CH3) with NCOTSna-N/O, TSno-N/O and TSnh-N/O(n=1—5) stand for transition states of the reaction of addition, oxidation and hydrogen abstraction, respecitively.
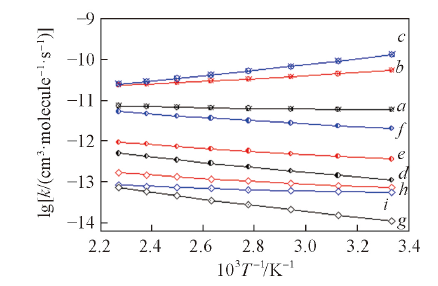
Fig.6 Fitted plots of the rate constants versus the reciprocal of temperature for the favorable channels over the range of 298—500 KO attacking Cl: a. R2; b. R7; c. R13; N attacking O1: d. R3; e. R8; f. R14; N attacking H: g. R5; h. R10; i. R16.
| [1] | Edmond P. F. L., Daniel K. W. M., Dudley E. S., Carl J. P., David L. O., Craig A. T., John M. D., Chem. Eur. J., 2012, 18(39), 12411—12423 |
| [2] | Vereecken L., Harder H., Novelli A., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 14(42), 14682—14695 |
| [3] | Smith M. C., Chang C. H., Chao W., Lin L. C., Takahashi K., Boering K. A., Lin J. J. M., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2015, 6(14), 2708—2713 |
| [4] | Gao Z. F., Wang W. N., Ma Q., Liu F. Y., Wang W. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(3), 513—520 |
| (高志芳, 王渭娜, 马倩, 刘峰毅, 王文亮. 高等学校化学学报, 2016,37(3), 513—520) | |
| [5] | Kuwata K. T., Hermes M. R., Carlson M. J., Zogg C. K., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2010, 114(34), 9192—9204 |
| [6] | Smith M. C., Ting W. L., Chang C. H., Takahashi K., Boering K. A., J. Chem. Phys., 2014, 141(7), 335—362 |
| [7] | Taatjes C. A., Welz O., Eskola A. J., Savee J. D., Scheer A. M., Shallcross D. E., Rotavera B., Lee E. P., Dyke J. M., Mok D. K., Osborn D. L., Percival C. J., Science,2013, 340, 177—180 |
| [8] | Hasson A. S., Kuwata T., Paulson S. E., J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 2001, 106(D24), 34143—34153 |
| [9] | Sheps L., Scully A. M., Au K., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014, 16(48), 26701—26704 |
| [10] | Welz O., Eskola A. J., Sheps L., Rotavera B., Savee J. D., Scheer A. M., Osborn D. L. D., Lowe A., Anwar M., Khan H., Percival C. J., Shallcross D. E., Taatjes C. A., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53(18), 4547—4550 |
| [11] | Miller J. A., Bowman C. T., Prog. Energy Combust. Sci., 1989, 15, 287—338 |
| [12] | Kohse K. H., Cool T. A., Kasper T., Hansen N., Qi F., Westbrook C. K., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2010, 49(21), 3572—3597 |
| [13] | Nelson P. F., Li C. Z., Ledesma E., Energy Fuels., 1996, 10(1), 264—265 |
| [14] | Tian Z., Li Y., Zhang T., Zhu A., Cui Z., Qi F., Combust. Flame, 2007, 151(1/2), 347—365 |
| [15] | Tian Z., Li Y., Zhang T., Zhu A., Qi F., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2008, 112(51), 13549—13555 |
| [16] | Feng W., Hershberger J. F., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2007, 111, 3831—3835 |
| [17] | Li B. T., Zhang J., Wu H. S., Sun G. D., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2007, 111, 7211—7217 |
| [18] | Zhang W. C., Du B. N., Feng C. J., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2007, 442, 1—6 |
| [19] | Bongfen M., Khait Y. G., Hardel C., Hoffmann M. R., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2010, 114, 8831—8836 |
| [20] | Frisch M.J., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Vreven T., Kudin K. N., Burant J. C., Millam J. M., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Barone V., Mennucci B., Cossi M., Scalmani G., Rega N., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Klene M., Li X., Knox J. E., Hratchian H. P., Cross J. B., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J. W., Ayala P. Y., Morokuma K., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Zakrzewski V. G., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Strain M. C., Farkas O., Malick D. K., Rabuck A. D., Raghavachari K., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cui Q., Baboul A.G., Clifford S., Cioslowski J., Stefanov B. B., Liu G., Liashenko A., Piskorz P., Komaromi I., Martin R. L., Fox D. J., Keith T., Al-Laham M. A., Peng C. Y., Nanayakkara A., Challacombe M., Gill P. M. W., Johnson B., Chen W., Wong M. W., Gonzalez C., Pople J. A., Gaussian 09, Revision C.01, Gaussian Inc.,Wallingford CT, 2009 |
| [21] | Curtiss L. A., Raghavachari K., Redfern P. C., Pople J. A., J. Chem. Phys., 1997, 106, 1063—1079 |
| [22] | Curtiss L. A., Redfern P. C., Raghavachari K., Univ I., J. Chem. Phys., 2007, 127(12), 66—70 |
| [23] | Zhang S.W., Truong N. T., VKLab Version 1.0, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, 2001 |
| [24] | Johnston H. S., Heicklen J., J. Phys. Chem., 1962, 66(3), 532—533 |
| [25] | Chen Y., Yan S. H., Xue P., Fu Q., Chen B., Zhao C. D., Journal of Northeast Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 1995, 4, 48—50 |
| (陈玉, 阎淑华, 薛平, 付强, 陈彬, 赵成大. 东北师大学报(自然科学版), 1995, 4, 48—50) | |
| [26] | Nguyen T. N., Putikam R., Lin M. C., J. Chem. Phys., 2015, 142, 124312—124318 |
| [27] | Li J., Carter S., Bowman J. M., Dawes R., Xie D. Q., Guo H., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2014, 5(13), 2364—2369 |
| [28] | McCarthy M. C., Cheng L., Crabtree K. N., Martinez O., Nguyen T. L., Womack C. C., Stanton J. F., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2013, 4(23), 4133—4319 |
| [29] | Nakajima M., Endo Y., J. Chem. Phys., 2013, 139(10), 101103—101107 |
| [30] | Du B., Zhang W., Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 2014, 1044, 55—61 |
| [31] | Lin H. Y., Huang Y. H., Wang X. H., Bowman J. M., Nishimura Y., Witek H. A., Lee Y. P., Nat. Chem., 2015, 10, 1038—1045 |
| [32] | NIST Chemistry Webbook( |
| [33] | Nguyen M. T., Nguyen T. L., Ngan V. T., Nguyen H. M. T., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2007, 448(4—6), 183—188 |
| [34] | Kumar M., Busch D. H., Subramaniam B., Thompson W. H., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2014, 118(10), 1887—1894 |
| [35] | Du B. N., Zhang W. C., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2013, 117, 6883—6892 |
| [36] | Pei L. S., Hu C. J., Liu Y. Z., Zhang Z. Q., Chen Y., Chen C. X., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2003, 381, 199—204 |
| [37] | Stone D., Blitz M., Daubney L., Howes N. U. M., Seakins P., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014, 16, 1139—1149 |
| [1] | ZHOU Zixuan, YANG Haiyan, SUN Yuhan, GAO Peng. Recent Progress in Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide to Methanol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220235. |
| [2] | YANG Dan, LIU Xu, DAI Yihu, ZHU Yan, YANG Yanhui. Research Progress in Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction Reaction over Gold Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220198. |
| [3] | SUN Cuihong, LYU Liqiang, LIU Ying, WANG Yan, YANG Jing, ZHANG Shaowen. Mechanism and Kinetics on the Reaction of Isopropyl Nitrate with Cl, OH and NO3 Radicals [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210591. |
| [4] | JIANG Baozheng, HUANG Wenting, LIU Wenbao, GUO Rongsheng, XU Chengjun, KANG Feiyu. Preparation of Nano-copper Modified Three-dimensional Zinc Mesh Electrode and Its Performance as Anode for Zinc-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220257. |
| [5] | CHENG Yuanyuan, XI Biying. Theoretical Study on the Fragmentation Mechanism of CH3SSCH3 Radical Cation Initiated by OH Radical [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220271. |
| [6] | LUO Qiangqiang, JIN Shaoqing, SUN Hongmin, YANG Weimin. Post-synthesis of Ti-MWW Zeolite via Titanium Incorporation in Liquid Acid Solution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2742. |
| [7] | MENG Fanwei, GAO Qi, YE Qing, LI Chenxi. Potassium Poisoning Mechanism of Cu-SAPO-18 Catalyst for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by Ammonia [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2832. |
| [8] | LI Xinyi, LIU Yongjun. Theoretical Insights into the Cleavage of β-Hydroxy Ketone Catalyzed by Artificial Retro-aldolase RA95.5-8F [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2306. |
| [9] | YANG Yiying, ZHU Rongxiu, ZHANG Dongju, LIU Chengbu. Theoretical Study on Gold-catalyzed Cyclization of Alkynyl Benzodioxin to 8-Hydroxy-isocoumarin [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2299. |
| [10] | WANG Jian, ZHANG Hongxing. Theoretical Study on the Structural-photophysical Relationships of Tetra-Pt Phosphorescent Emitters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2245. |
| [11] | REN Ying, LI Changhua, WANG Tao, XUE Shanshan, ZHANG Tingting, JIA Jianfeng, WU Haishun. Theoretical Studies on Pd-catalyzed Oxidative N─H Carbonylation to Synthesis of 1,3,4-Oxadiazole-2(3H)-one Heterocyclic Compounds [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1793. |
| [12] | LI Yiwei, SHENTU Jiangtao, WANG Jingbo, LI Xiangyuan. Combustion Mechanism Construction Based on Minimized Reaction Network: C1⁃Oxygen Combustion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1871. |
| [13] | TIAN Shengqiao, WEI Meiju. Reaction Mechanism for Rh(Ⅱ)-catalyzed [3+3] Cyclization of Indole Derivatives and Propertis of Product [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1899. |
| [14] | WAN Ren, SONG Fan, PENG Changjun, LIU Honglai. Group Contribution Method for Infinite Dilution Molar Conductivity of Unconventional Ions in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3672. |
| [15] | QI Guodong, YE Xiaodong, XU Jun, DENG Feng. Progress in NMR Studies of Carbohydrates Conversion on Zeolites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 148. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||