

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 429.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160775
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Rui1, LI Yili1, FENG Xukai1, SONG Liang1, ZHANG Tianlei1,*( ), WANG Zhuqing2, JIN Lingxia1, ZHANG Qiang1, XU Qiong1, WANG Zhiyin1
), WANG Zhuqing2, JIN Lingxia1, ZHANG Qiang1, XU Qiong1, WANG Zhiyin1
Received:2016-11-08
Online:2017-03-10
Published:2017-02-23
Contact:
ZHANG Tianlei
E-mail:ztianlei88@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Rui, LI Yili, FENG Xukai, SONG Liang, ZHANG Tianlei, WANG Zhuqing, JIN Lingxia, ZHANG Qiang, XU Qiong, WANG Zhiyin. Catalytic Effect of n(H2O)(n=1,2) on the Reaction of HO2+NOHNO3 †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(3): 429.
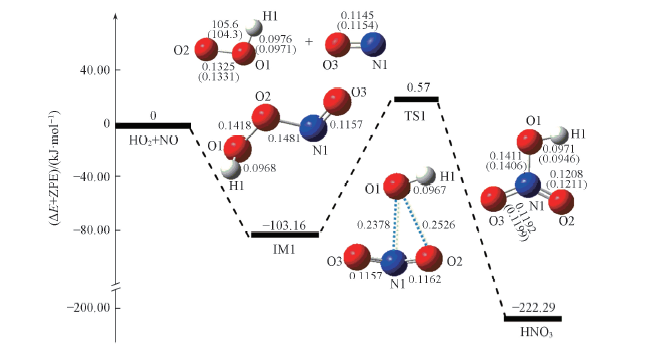
Fig.1 Schematic energy diagrams for the HO2+NO HNO3 reaction Bond lengths are in nm: bond anyels are in deyree. The values in parenthese are the experimental values and taken from Ref. [33].
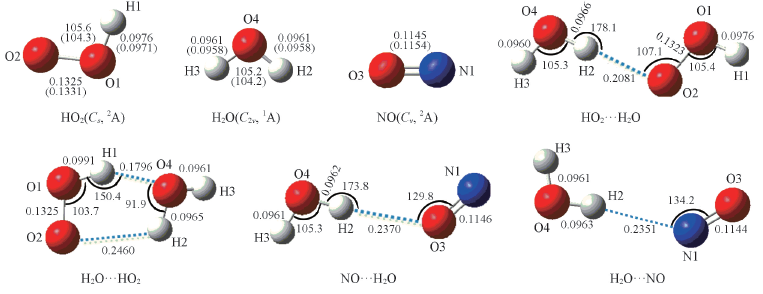
Fig.2 Geometrical parameters for HO2, NO, H2O, H2O…HO2, HO2…H2O, NO…H2O and ON…H2O complexes optimized at the B3LYP/6-311+G(2df,2p) level of theory Bond lengths are in nm, bond angles are in degree. The values in paranthese are the experimental values and taken from Ref.[32].
| System | ZPE/ (kJ·mol-1) | S/ (J·mol-1·K-1) | ΔE/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔH/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔG/ (kJ·mol-1) | (ΔE+ZPE)/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O+NO+H2O | 0 | 148.76 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| H2O…HOO+NO | 10.65 | 121.69 | -39.61 | -32.02 | 1.75 | -28.96 |
| IMW1 | 19.36 | 88.12 | -139.85 | -125.57 | -49.93 | -120.49 |
| TSW1 | 10.94 | 94.59 | -22.68 | -6.89 | 60.68 | -3.62 |
| IMWF1 | 28.94 | 79.91 | -286.55 | -266.43 | -180.55 | -257.62 |
| HOO…H2O+NO | 6.60 | 129.24 | -14.62 | -8.34 | 16.01 | -8.02 |
| IMW2 | 16.05 | 94.65 | -118.16 | -105.26 | -37.75 | -102.11 |
| TSW2 | 12.34 | 87.11 | -0.17 | 5.22 | 82.12 | 12.16 |
| IMWF2 | 24.87 | 91.60 | -254.28 | -235.17 | -163.86 | -229.42 |
| NO…H2O+HOO | 2.49 | 137.10 | -4.69 | -0.85 | 13.69 | -2.21 |
| IMW3 | 15.74 | 95.45 | -114.71 | -101.86 | -35.35 | -98.97 |
| TSW3 | 13.73 | 85.27 | -4.35 | 1.72 | 80.92 | 9.38 |
| IMWF3 | 25.16 | 79.93 | -254.90 | -235.69 | -164.31 | -229.74 |
| H2O…NO+HOO | 2.92 | 129.99 | -6.35 | -4.87 | 18.54 | -3.43 |
| IMW4 | 16.04 | 90.76 | -123.22 | -111.02 | -38.67 | -107.18 |
| TSW4 | 11.90 | 87.65 | -2.10 | 3.82 | 80.05 | 9.79 |
| HNO3+H2O | 20.20 | 108.67 | -242.49 | -229.21 | -179.20 | -222.29 |
Table 1 Zero-point energy(ZPE), entropies(S), relative energies(ΔE, ΔE+ZPE), free energies[ΔG(298 K)] and enthalpies[ΔH(298 K)] for the HO2+NO reaction with a water molecule at the CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//B3LYP/6-311+G(2df,2p) level of theory*
| System | ZPE/ (kJ·mol-1) | S/ (J·mol-1·K-1) | ΔE/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔH/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔG/ (kJ·mol-1) | (ΔE+ZPE)/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O+NO+H2O | 0 | 148.76 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| H2O…HOO+NO | 10.65 | 121.69 | -39.61 | -32.02 | 1.75 | -28.96 |
| IMW1 | 19.36 | 88.12 | -139.85 | -125.57 | -49.93 | -120.49 |
| TSW1 | 10.94 | 94.59 | -22.68 | -6.89 | 60.68 | -3.62 |
| IMWF1 | 28.94 | 79.91 | -286.55 | -266.43 | -180.55 | -257.62 |
| HOO…H2O+NO | 6.60 | 129.24 | -14.62 | -8.34 | 16.01 | -8.02 |
| IMW2 | 16.05 | 94.65 | -118.16 | -105.26 | -37.75 | -102.11 |
| TSW2 | 12.34 | 87.11 | -0.17 | 5.22 | 82.12 | 12.16 |
| IMWF2 | 24.87 | 91.60 | -254.28 | -235.17 | -163.86 | -229.42 |
| NO…H2O+HOO | 2.49 | 137.10 | -4.69 | -0.85 | 13.69 | -2.21 |
| IMW3 | 15.74 | 95.45 | -114.71 | -101.86 | -35.35 | -98.97 |
| TSW3 | 13.73 | 85.27 | -4.35 | 1.72 | 80.92 | 9.38 |
| IMWF3 | 25.16 | 79.93 | -254.90 | -235.69 | -164.31 | -229.74 |
| H2O…NO+HOO | 2.92 | 129.99 | -6.35 | -4.87 | 18.54 | -3.43 |
| IMW4 | 16.04 | 90.76 | -123.22 | -111.02 | -38.67 | -107.18 |
| TSW4 | 11.90 | 87.65 | -2.10 | 3.82 | 80.05 | 9.79 |
| HNO3+H2O | 20.20 | 108.67 | -242.49 | -229.21 | -179.20 | -222.29 |
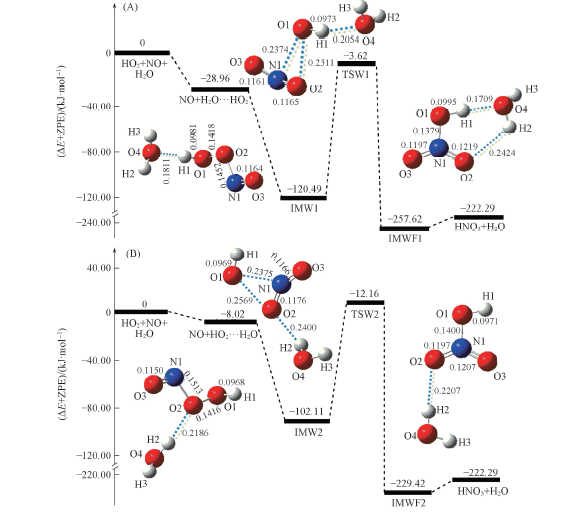
Fig.3 Schematic energy diagrams for H2O…HO2+NO(channel RW1, A) and HO2…H2O+NO(channel RW2, B) reactions at the CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//B3LYP/6-311+G(2df,2p)+ZPE level
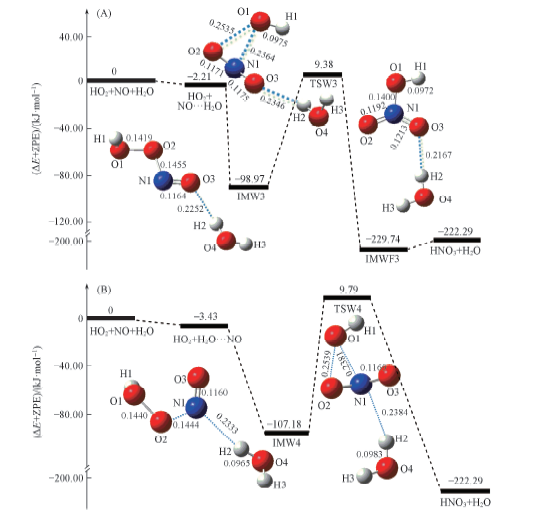
Fig.4 Schematic energy diagrams in the reaction of NO…H2O+HO2(channel RW3, A) and ON…H2O+HO2 (channel RW4, B) at the CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//B3LYP/6-311+G(2df,2p)+ZPE level
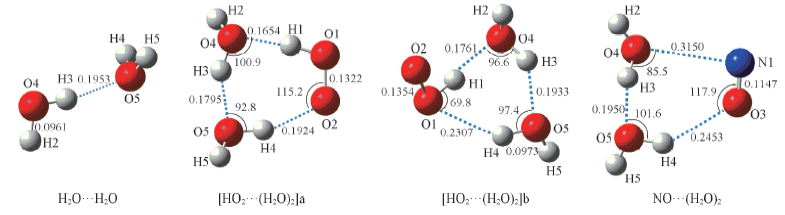
Fig.5 Geometrical parameters for (H2O)2, HO2…(H2O)2 and NO…(H2O)2 complexes optimized at the B3LYP/6-311+G(2df,2p) level of theory Bond lengths are in nm, bond angles are in degree.
| System | ZPE/ (kJ·mol-1) | S/ (J·mol-1·K-1) | ΔE/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔH/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔG/ (kJ·mol-1) | (ΔE+ZPE)/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HO2+NO+(H2O)2 | 0 | 173.153 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| [HO2…(H2O)2]a+NO | 14.53 | 132.57 | -66.62 | -57.71 | -7.08 | -52.09 |
| IMWW1 | 22.08 | 99.25 | -160.58 | -145.38 | -53.19 | -138.51 |
| TSWW1 | 14.81 | 88.92 | 22.32 | 23.75 | 128.82 | 37.12 |
| IMWWF1 | 30.29 | 94.70 | -308.12 | -287.57 | -189.70 | -277.83 |
| [HO2…(H2O)2]b+NO | 11.96 | 132.40 | -28.38 | -22.37 | 28.47 | -12.74 |
| IMWW2 | 21.88 | 100.62 | -164.80 | -149.80 | -59.31 | -142.91 |
| TSWW2 | 14.86 | 105.12 | -38.97 | -30.15 | 54.71 | -24.11 |
| IMWWF2 | 28.15 | 101.28 | -296.89 | -276.46 | -186.79 | -268.74 |
| NO…(H2O)2+HO2 | 3.58 | 152.58 | -9.35 | -4.72 | 20.95 | -5.77 |
| IMWW3 | 20.87 | 90.25 | -67.97 | -58.68 | 44.75 | -41.70 |
| TSWW3 | 12.39 | 101.892 | -29.09 | -22.47 | 66.42 | -16.70 |
| HNO3+(H2O)2 | 20.20 | 133.06 | -242.49 | -229.21 | -179.20 | -222.29 |
Table 2 Zero-point energy(ZPE), entropies(S), relative energies[ΔE, Δ(E+ZPE)], free energies[ΔG(298 K)] and enthalpies[ΔH(298 K)] for water dimer-catalyzed the HO2+NO reaction at the CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//B3LYP/6-311+G(2df,2p) level of theory
| System | ZPE/ (kJ·mol-1) | S/ (J·mol-1·K-1) | ΔE/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔH/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔG/ (kJ·mol-1) | (ΔE+ZPE)/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HO2+NO+(H2O)2 | 0 | 173.153 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| [HO2…(H2O)2]a+NO | 14.53 | 132.57 | -66.62 | -57.71 | -7.08 | -52.09 |
| IMWW1 | 22.08 | 99.25 | -160.58 | -145.38 | -53.19 | -138.51 |
| TSWW1 | 14.81 | 88.92 | 22.32 | 23.75 | 128.82 | 37.12 |
| IMWWF1 | 30.29 | 94.70 | -308.12 | -287.57 | -189.70 | -277.83 |
| [HO2…(H2O)2]b+NO | 11.96 | 132.40 | -28.38 | -22.37 | 28.47 | -12.74 |
| IMWW2 | 21.88 | 100.62 | -164.80 | -149.80 | -59.31 | -142.91 |
| TSWW2 | 14.86 | 105.12 | -38.97 | -30.15 | 54.71 | -24.11 |
| IMWWF2 | 28.15 | 101.28 | -296.89 | -276.46 | -186.79 | -268.74 |
| NO…(H2O)2+HO2 | 3.58 | 152.58 | -9.35 | -4.72 | 20.95 | -5.77 |
| IMWW3 | 20.87 | 90.25 | -67.97 | -58.68 | 44.75 | -41.70 |
| TSWW3 | 12.39 | 101.892 | -29.09 | -22.47 | 66.42 | -16.70 |
| HNO3+(H2O)2 | 20.20 | 133.06 | -242.49 | -229.21 | -179.20 | -222.29 |
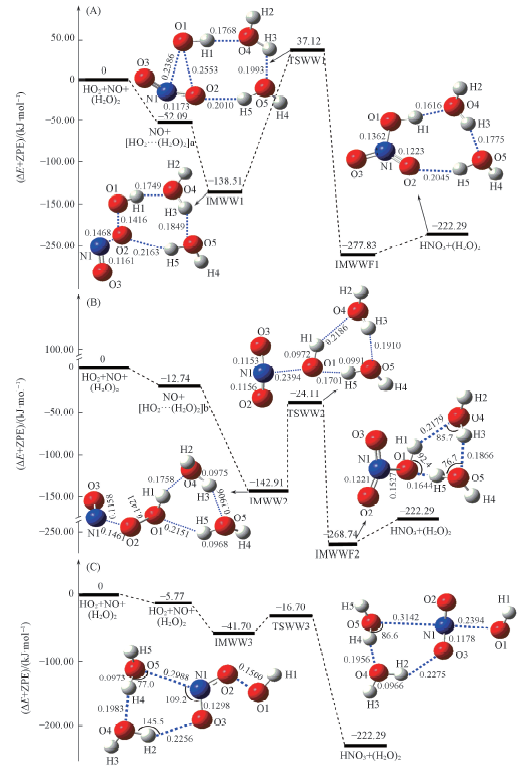
Fig.6 Schematic energy diagrams in the reaction of HO2…(H2O)2+NO(A, B) and NO…(H2O)2+HO2 (channel RWW3, C) at the CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//B3LYP/6-311+G(2df,2p)+ZPE level (A) Channel RWW1; (B) channel RWW2.
| h/km | T/K | 1014kR1 | 1013kRW1 | 1015k'RW1 | 1011kRWW2 | 1025k'RWW2 | 1015kRWW3 | 1028k'RWW3 | 1013ktotal | k'RW1/ktotal(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 298.2 | 5.69 | 1.80 | 381 | 1.23 | 566 | 50.5 | 0.178 | 4.38 | 67.93 |
| 0 | 288.2 | 5.76 | 1.68 | 240 | 1.33 | 975 | 38.6 | 1.74 | 2.98 | 58.83 |
| 2 | 275.2 | 5.91 | 1.53 | 243 | 1.50 | 390 | 23.8 | 6.47 | 3.02 | 61.32 |
| 4 | 262.2 | 6.14 | 1.40 | 200 | 1.74 | 220 | 15.6 | 35.3 | 2.61 | 58.73 |
| 6 | 249.3 | 6.48 | 1.29 | 78.1 | 2.06 | 27.0 | 10.8 | 410 | 1.43 | 37.70 |
| 8 | 236.3 | 6.97 | 1.19 | 46.7 | 2.55 | 7.49 | 7.71 | 1010 | 1.16 | 28.15 |
| 10 | 223.3 | 7.72 | 1.12 | 27.2 | 3.29 | 1.85 | 5.72 | 2890 | 1.04 | 19.57 |
| 12 | 216.7 | 8.24 | 1.09 | 9.92 | 3.84 | 0.205 | 4.64 | 947 | 0.923 | 8.36 |
Table 3 Rate constants(cm3·molecule-1·s-1) for the process of HNO3 formation occurring through the reactions of HO2+NO, H2O…HO2+NO, [HO2…(H2O)2]b+NO and NO…(H2O)2+HO2 within the temperature range of 216.7—298.2 K*
| h/km | T/K | 1014kR1 | 1013kRW1 | 1015k'RW1 | 1011kRWW2 | 1025k'RWW2 | 1015kRWW3 | 1028k'RWW3 | 1013ktotal | k'RW1/ktotal(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 298.2 | 5.69 | 1.80 | 381 | 1.23 | 566 | 50.5 | 0.178 | 4.38 | 67.93 |
| 0 | 288.2 | 5.76 | 1.68 | 240 | 1.33 | 975 | 38.6 | 1.74 | 2.98 | 58.83 |
| 2 | 275.2 | 5.91 | 1.53 | 243 | 1.50 | 390 | 23.8 | 6.47 | 3.02 | 61.32 |
| 4 | 262.2 | 6.14 | 1.40 | 200 | 1.74 | 220 | 15.6 | 35.3 | 2.61 | 58.73 |
| 6 | 249.3 | 6.48 | 1.29 | 78.1 | 2.06 | 27.0 | 10.8 | 410 | 1.43 | 37.70 |
| 8 | 236.3 | 6.97 | 1.19 | 46.7 | 2.55 | 7.49 | 7.71 | 1010 | 1.16 | 28.15 |
| 10 | 223.3 | 7.72 | 1.12 | 27.2 | 3.29 | 1.85 | 5.72 | 2890 | 1.04 | 19.57 |
| 12 | 216.7 | 8.24 | 1.09 | 9.92 | 3.84 | 0.205 | 4.64 | 947 | 0.923 | 8.36 |
| [1] | Zhu R. S., Lin M. C., Phys. Chem. Comm., 2001, 4(25), 127—132 |
| [2] | Wallington T. J., Dagaut P., Kurylo M. J., Chem. Rev., 1992, 92(4), 667—710 |
| [3] | Leu M., J. Chem. Phys., 1979, 70(4), 1662—1666 |
| [4] | Xu W. B., Earth Environ., 1999, 27(3),86—91 |
| (徐文彬. 地球与环境, 1999, 27(3), 86—91) | |
| [5] | Atkinson R., Baulch D. L., Co R. A., Crowley J. N., Atmos. Chem. Phys., 2004, 3(6), 1461—1738 |
| [6] | Bardwell M. W., Bacak A., Raventos M. T., Percival C. J., Sanchez-Reyna G., Shallcross D. E., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2003, 5(11), 2381—2385 |
| [7] | Zhang J., Donahue N. M., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2006, 110(21), 6898—6911 |
| [8] | Lightfoot P. D., Cox R. A., Crowley J. N., Destriau M., Hayman G. D., Jenkin M. E., Atmos. Environ., 1992, 26(10), 1805—1961 |
| [9] | Howard C. J., J. Chem. Phys., 1979, 71(6), 2352—2359 |
| [10] | Butkovskaya N., Le Bras G., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2007, 111(37), 9047—9053 |
| [11] | Atkinson R., Baulch D. L., Cox R. A., Hampson R. F., Kerr J. A., Rossi M. J., Troe J., J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data,1997, 26(6), 1329—1499 |
| [12] | Chakraborty D., Park J., Lin M. C., Chem. Phys., 1998, 231(1), 39—49 |
| [13] | Jemialade A. A., Thrush B. A., J. Chem. Soc., 1990, 86(20), 3355—3363 |
| [14] | Margitan J. J., J. Phys.Chem., 1984, 88(15), 129—130 |
| [15] | Dyke J. M., Jonathan N., Lewis A. E., Mol. Phys., 1983, 50(1), 77—89 |
| [16] | Thrush B. A., Wilkinson J. P. T., Chem. Phys. Lett., 1981, 81(1), 1—3 |
| [17] | Butkovskaya N. I., Kukui A., Pouvesl N., Le Bras G. J., Phys. Chem. A, 2005, 109(29), 6509—6520 |
| [18] | Butkovskaya N., Rayez M. T., Rayez J. C., Kukui A., Le B. G., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2009, 113(42), 11327—11342 |
| [19] | Buszek R. J., Francisco J. S., Anglada J. M., Int. Rev. Phys. Chem., 2011, 30(3), 335—369 |
| [20] | Pfeilsticker K., Lotter A., Peters C., Bosch H., Science,2003, 300(5628), 2078—2080 |
| [21] | Dunn M. E., Pokon E. K., Shields G. C., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126(8), 2647—2653 |
| [22] | Vaida V., J. Chem. Phys., 2011, 135(2), 020901 |
| [23] | Gonzalez C., Schlegel H. B., J. Chem. Phys., 1989, 90(4), 2154—2161 |
| [24] | Zhang T. L., Yang C., Feng X. K., Kang J., Song L., Lu Y., Wan Z. Y., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016, 18(26), 17414—17427 |
| [25] | Zhang T. L., Wang R., Wang W. L., Min S. T., Xu Q., Wang Z. Y., Comput. Theor. Chem., 2014, 1045, 135—144 |
| [26] | Viegas L. P., Varandas A. J., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2016, 120(8), 1560—1568 |
| [27] | Zhu R. S., Lin M. C., Phys. Chem. Comm., 2003, 6(13), 51—54 |
| [28] | Gonzalez C., Schlegel H. B., J. Chem. Phys., 1989, 90(4), 2154—2161 |
| [29] | Frisch M.J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Montgomery J. A. Jr., Vreven T., Kudin K. N., Burant J. C., Millam J. M., Iyengar S., Tomasi S. J., Barone V., Mennucci B., Cossi M., Scalmani G., Rega N., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Klene M., Li X., Knox J. E., Hratchian H. P., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J. W., Ayala P. Y., Morokuma K., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Zakrzewski V. G., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Strain M. C., Farkas O., Malick D. K., Rabuck A. D., Raghavachari K., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cui Q., Baboul A. G., Clifford S., Cioslowski J., Stefanov B. B., Liu G., Liashenko A., Piskorz P., Komaromi I., Martin R. L., Fox D. J., Keith T., Al-Laham M. A., Peng C. Nanayakkara Y., Challacombe M., Gill P. M. W., Johnson B., Chen W., Wong M. W., Gonzalez C., Pople J. A., Gaussian 03, Revision D.02, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, 2004 |
| [30] | Zhang S.W., Truong N. T., VKLab Version1.0, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, 2001 |
| [31] | Si W. J., Zhuo S. P., Ju G. Z., Acta Phys. Chim. Sinica, 2003, 19(10), 974—977 |
| (司维江, 禚淑萍, 居冠之. 物理化学学报, 2003, 19(10), 974—977) | |
| [32] | Chen J.F., Cheng W., Dou Y. L.,J. Mol. Sci., 2016, (6), 515—522 |
| (陈静飞, 成伟, 窦玉龙. 分子科学学报, 2016, (6), 515—522) | |
| [33] | From the NIST Chemistry Webbook, . |
| [34] | Long B., Tan X. F., Long Z. W., Wang Y. B., Ren D. S., Zhang W. J., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2011, 115(24), 6559—6567 |
| [35] | Yung Y. L., DeMore W. B., J. Atmos. Chem., 2001, 39(2), 215—216 |
| [36] | Zhu R. S., Lin M. C., J. Chem. Phys., 2003, 119(20), 10667—10677 |
| (Ed.:Y, Z, S) |
| [1] | CHEN Jialu, HUANG Shuo. Application of Nanopore Sequencing Technology in the Detection of Nucleic Acid Modifications [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(Album-4): 20220333. |
| [2] | Jinhan Sheng, Qizhen Zheng, Ming Wang. Non-viral delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(Album-4): 20220344. |
| [3] | FAN Jianling, TANG Hao, QIN Fengjuan, XU Wenjing, GU Hongfei, PEI Jiajing, CEHN Wenxing. Nitrogen Doped Ultra-thin Carbon Nanosheet Composited Platinum-ruthenium Single Atom Alloy Catalyst for Promoting Electrochemical Hydrogen Evolution Process [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220366. |
| [4] | CHENG Qian, YANG Bolong, WU Wenyi, XIANG Zhonghua. S-doped Fe-N-C as Catalysts for Highly Reactive Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220341. |
| [5] | WU Yu, LI Xuan, YANG Hengpan, HE Chuanxin. Construction of Cobalt Single Atoms via Double-confinement Strategy for High-performance Electrocatalytic Reduction of Carbon Dioxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220343. |
| [6] | WANG Xintian, LI Pan, CAO Yue, HONG Wenhao, GENG Zhongxuan, AN Zhiyang, WANG Haoyu, WANG Hua, SUN Bin, ZHU Wenlei, ZHOU Yang. Techno-economic Analysis and Industrial Application Prospects of Single-atom Materials in CO2 Catalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220347. |
| [7] | YANG Jingyi, LI Qinghe, QIAO Botao. Synergistic Catalysis Between Ir Single Atoms and Nanoparticles for N2O Decomposition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220388. |
| [8] | HUANG Qiuhong, LI Wenjun, LI Xin. Organocatalytic Enantioselective Mannich-type Addition of 5H-Oxazol-4-ones to Isatin Derived Ketimines [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220131. |
| [9] | LIU Suyu, DING Fei, LI Qian, FAN Chunhai, FENG Jing. Azobenzene-integrated DNA Nanomachine [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220122. |
| [10] | HE Beibei, YANG Kuihua, LYU Rui. Construction of Mn-Cu Bimetal Containing Phyllosilicate Nanozyme and Evaluation of the Enzyme-like Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220150. |
| [11] | WENG Meiqi, SHANG Guiming, WANG Jiatai, LI Shenghua, FAN Zhi, LIN Song, GUO Minjie. Template Simulation of Organophosphorus Nerve Agent Molecularly Imprinted Polymers [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220136. |
| [12] | LI Lin, QI Fenglian, QIU Lili, MENG Zihui. Dynamic Amorphous Photonic Structure Patterns Assembled by Hexagonal Magnetic Nanosheets [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220123. |
| [13] | GE Yicong, NIE Wanli, SUN Guofeng, CHEN Jiaxuan, TIAN Chong. Silver-catalyzed [5+1] Cyclization of 2-Vinylanilines with Benzisoxazoles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220142. |
| [14] | JIA Yanggang, SHAO Xia, CHENG Jie, WANG Pengpeng, MAO Aiqin. Preparation and Lithium Storage Performance of Pseudocapacitance-controlled Perovskite High-entropy Oxide La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3 Anode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220157. |
| [15] | LIU Shuwei, JIN Hao, YIN Wanzhong, ZHANG Hao. Gemcitabine/polypyrrole Composite Nanoparticles for Chemo-photothermal Combination Ovarian Cancer Therapy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220345. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||