

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (8): 1750.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170844
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Yingyu, ZHAO Huaiyuan, HOU Zhaoyin*( )
)
Received:2017-12-25
Online:2018-08-10
Published:2018-06-25
Contact:
HOU Zhaoyin
E-mail:zyhou@zju.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Yingyu, ZHAO Huaiyuan, HOU Zhaoyin. Synthesis of Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO Catalyst and Its Application in Selective Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1750.
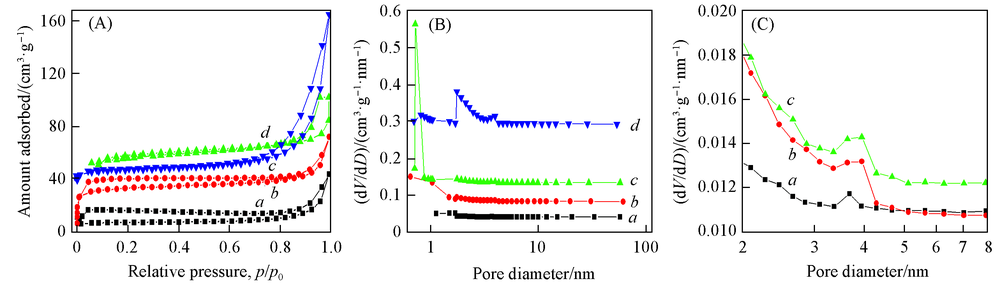
Fig.1 N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms(A) and pores size distributions(B, C) of Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-500(a), Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-600(b), Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-700(c) and Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-900(d)Profile (C) is the enlarged part of profile (B).
| Sample | Pore volume/(cm3·g-1) | Pore size/nm | SBET/(m2·g-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micropore | Mesopore | Micropore | Mesopore | ||
| Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-500 | — | 0.171 | — | 3.66 | 179.9 |
| Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-600 | — | 0.171 | — | 3.93 | 199.1 |
| Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-700 | 0.119 | 0.177 | 0.71 | 3.92 | 324.3 |
| Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-900 | 0.089 | 0.081 | 0.80,1.74 | 3.93 | 174.4 |
Table 1 Structures of Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO catalysts
| Sample | Pore volume/(cm3·g-1) | Pore size/nm | SBET/(m2·g-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micropore | Mesopore | Micropore | Mesopore | ||
| Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-500 | — | 0.171 | — | 3.66 | 179.9 |
| Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-600 | — | 0.171 | — | 3.93 | 199.1 |
| Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-700 | 0.119 | 0.177 | 0.71 | 3.92 | 324.3 |
| Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-900 | 0.089 | 0.081 | 0.80,1.74 | 3.93 | 174.4 |
| No. | Sample | Raman analysis | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID/IG | I2D/IG | ||
| 1 | GO | 0.92 | 0.26 |
| 2 | Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-500 | 1.02 | 0.13 |
| 3 | Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-600 | 0.95 | 0.19 |
| 4 | Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-700 | 0.95 | 0.21 |
| 5 | Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-900 | 0.94 | 0.16 |
Table 2 Raman analysis results of different catalysts
| No. | Sample | Raman analysis | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ID/IG | I2D/IG | ||
| 1 | GO | 0.92 | 0.26 |
| 2 | Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-500 | 1.02 | 0.13 |
| 3 | Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-600 | 0.95 | 0.19 |
| 4 | Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-700 | 0.95 | 0.21 |
| 5 | Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-900 | 0.94 | 0.16 |
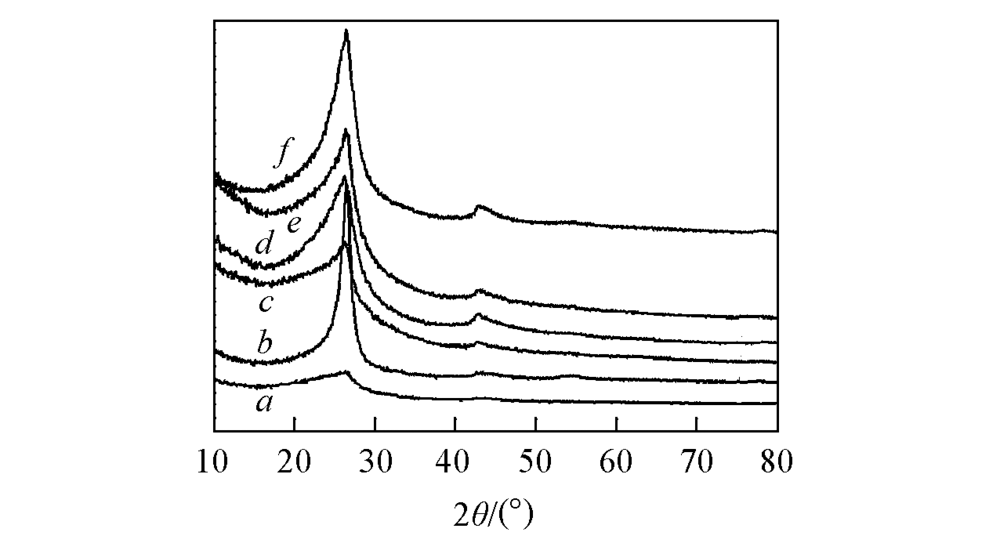
Fig.3 XRD patterns of N-free catalyst(a), Fe-free catalyst(b), Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-500(c), Fe2O3/ rGO/N-rGO-600(d), Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-700(e) and Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-900(f)
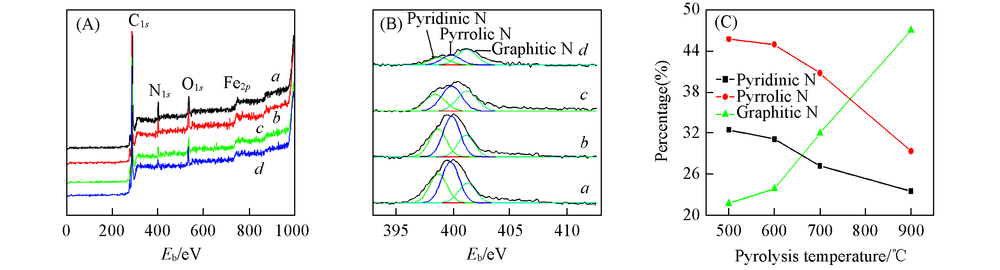
Fig.7 XPS spectra of elemental analysis in survey(A) and N1s(B) and percentage of nitrogen species(C) of Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-500(a), Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-600(b), Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-700(c) and Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-900(d)
| Sample | Relative molar percentage(%) | Relative elemental percentage(%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | N | Fe | Pyridinic N | Pyrrolic N | Graphitic N | |
| Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-500 | 84.55 | 7.61 | 7.83 | 0.01 | 32.5 | 45.8 | 21.7 |
| Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-600 | 84.75 | 7.34 | 7.81 | 0.10 | 31.1 | 45.0 | 23.9 |
| Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-700 | 85.53 | 7.00 | 7.30 | 0.17 | 27.2 | 40.8 | 32.0 |
| Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-900 | 90.18 | 6.18 | 3.52 | 0.12 | 23.5 | 29.4 | 47.1 |
Table 3 Surface composition of Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO catalysts*
| Sample | Relative molar percentage(%) | Relative elemental percentage(%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | N | Fe | Pyridinic N | Pyrrolic N | Graphitic N | |
| Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-500 | 84.55 | 7.61 | 7.83 | 0.01 | 32.5 | 45.8 | 21.7 |
| Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-600 | 84.75 | 7.34 | 7.81 | 0.10 | 31.1 | 45.0 | 23.9 |
| Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-700 | 85.53 | 7.00 | 7.30 | 0.17 | 27.2 | 40.8 | 32.0 |
| Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-900 | 90.18 | 6.18 | 3.52 | 0.12 | 23.5 | 29.4 | 47.1 |
| No. | Sample | Conversion(%) | Selectivity(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AN | Othersb | |||
| 1 | Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-500 | 71.4 | 82.3 | 17.7 |
| 2 | Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-600 | 76.7 | 86.4 | 13.6 |
| 3 | Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-700 | 86.5 | 90.2 | 9.8 |
| 4 | Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-900 | 72.4 | 82.8 | 17.2 |
| 5 | Fe3O4@MgO | 29.8 | 75.7 | 24.3 |
| 6 | Fe3O4@SiO2 | 33.9 | 81.5 | 18.5 |
| 7 | Fe3O4@Al2O3 | 41.5 | 85.0 | 15.0 |
| 8 | Fe3O4@AC | 44.0 | 91.1 | 9.9 |
| 9 | N-free catalyst | 42.6 | 88.8 | 11.2 |
| 10 | Fe-free catalyst | 27.8 | 86.4 | 13.6 |
| 11 | GO | 16.4 | 76.8 | 23.2 |
Table 4 Hydrogenation of nitrobenzene over different catalystsa
| No. | Sample | Conversion(%) | Selectivity(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AN | Othersb | |||
| 1 | Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-500 | 71.4 | 82.3 | 17.7 |
| 2 | Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-600 | 76.7 | 86.4 | 13.6 |
| 3 | Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-700 | 86.5 | 90.2 | 9.8 |
| 4 | Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-900 | 72.4 | 82.8 | 17.2 |
| 5 | Fe3O4@MgO | 29.8 | 75.7 | 24.3 |
| 6 | Fe3O4@SiO2 | 33.9 | 81.5 | 18.5 |
| 7 | Fe3O4@Al2O3 | 41.5 | 85.0 | 15.0 |
| 8 | Fe3O4@AC | 44.0 | 91.1 | 9.9 |
| 9 | N-free catalyst | 42.6 | 88.8 | 11.2 |
| 10 | Fe-free catalyst | 27.8 | 86.4 | 13.6 |
| 11 | GO | 16.4 | 76.8 | 23.2 |
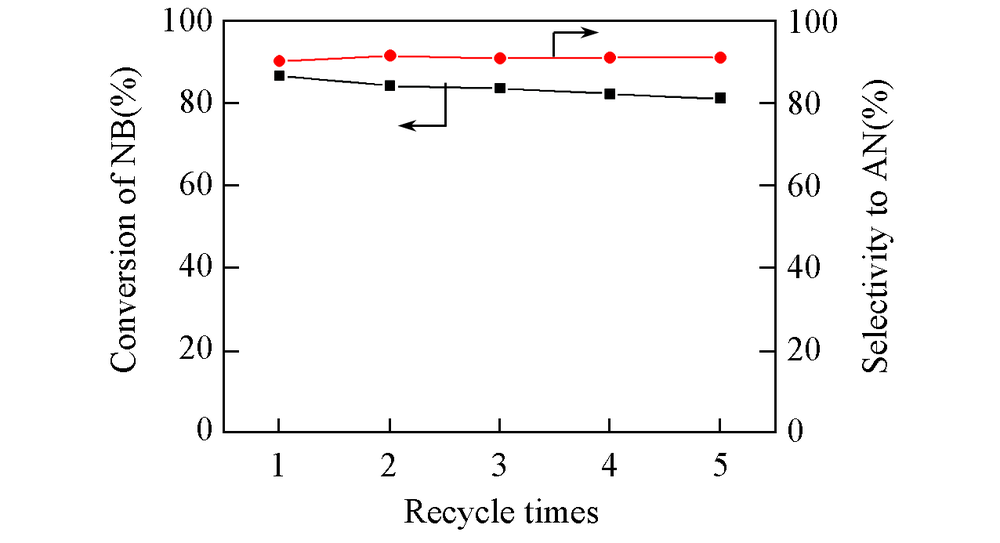
Fig.8 Recycle experiment over Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-700 catalystReaction conditions: 0.25 mmol nitrobenzene in 8.0 mL ethanol, initial n(Fe)=10 μmol, 120 ℃, p(H2)=2.0 MPa, 4.0 h.
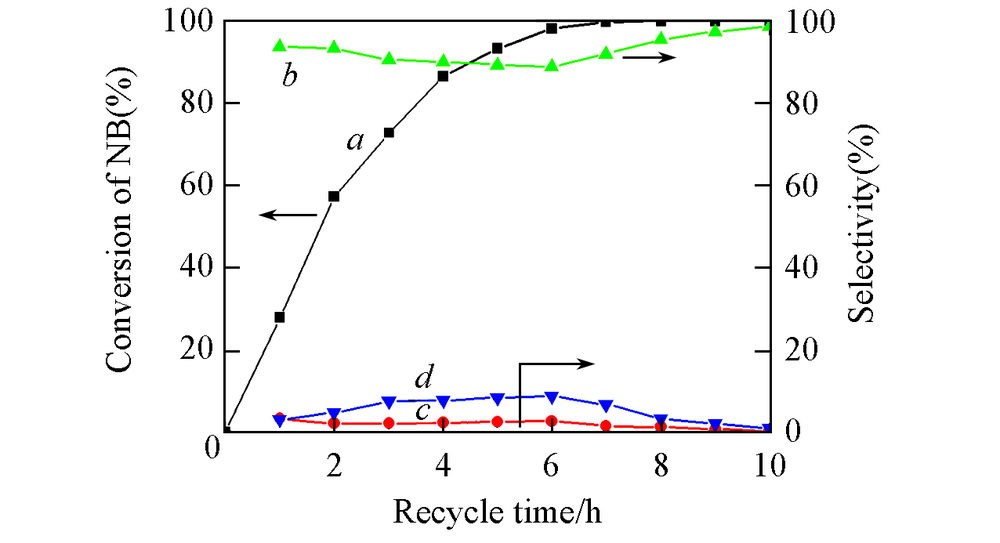
Fig.9 Time-on-stream of NB hydrogenation over Fe2O3/rGO/N-rGO-700 catalysta. Conversion of NB; b. selectivity to AN; c. selectivity to NSB; d. selectivity to PHA. Reaction conditions: 0.25 mmol nitrobenzene in 8.0 mL ethanol, initial n(Fe)=10 μmol, 120 ℃, p(H2)=2.0 MPa.
| [1] | Blaser H.U., Science, 2006, 313(5785), 312—313 |
| [2] | Meng X.C., Cheng H. Y., Akiyama Y., Hao Y. F., Qiao W. B., Yu Y. C., Zhao F. Y., Fujita S. I., Arai M., J. Catal., 2009, 264(1), 1—10 |
| [3] | Li C.H., Yu Z. X., Yao K. F., Ji S. F., Liang J., J. Mol. Catal. A, 2005, 226(1), 101—105 |
| [4] | Nie R.F., Wang J. H., Wang L. N., Qin Y., Chen P., Hou Z. Y., Carbon, 2012, 50(2), 586—596 |
| [5] | Gelder E.A., Jackson S. D., Lok C. M, Catal. Lett., 2002, 84(3/4), 205—208 |
| [6] | Chary K.V. R., Srikanth C. S., Catal. Lett., 2008, 128(1/2), 164—170 |
| [7] | Corma A., Concepcion P., Serna P., Angew. Chem. Int.Ed., 2007, 46(38), 7266—7269 |
| [8] | Burge H.D., Collins D. J., Davis B. H, Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev., 1980, 19(3), 389—391 |
| [9] | Li H.X., Zhao Q. F., Wan Y., Dai W. L., Qiao M. H., J. Catal., 2006, 244(2), 251—254 |
| [10] | Wang J.H., Yuan Z. L., Nie R. F., Hou Z. Y., Zheng X. M, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2010, 49(10), 4664—4669 |
| [11] | Jagadeesh R.V., Wienhoefer G., Westerhaus F. A., Surkus A. E., Pohl M. M., Junge H., Junge K., Beller M, Chem. Commun., 2011, 47(39), 10972—10974 |
| [12] | Schlogl R., Angew. Chem. Int.Ed., 2003, 42(18), 2004—2008 |
| [13] | Kandemir T., Schuster M.E., Senyshyn A., Behrens M., Schloegl R, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(48), 12723—12726 |
| [14] | Vojvodic A., Medford A.J., Studt F., Abild-Pedersen F., Khan T. S., Bligaard T., Norskov J. K, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2014, 598, 108—112 |
| [15] | Galvis H.M. T., Bitter J. H., Khare C. B., Ruitenbeek M., Dugulan A. I., de Jong K. P., Science, 2012, 335(6070), 835—838 |
| [16] | Koeken A.C. J., Galvis H. M. T., Davidian T., Ruitenbeek M., de Jong K. P, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012, 51(29), 7190—7193 |
| [17] | Schulz H., Catal. Today, 2013, 214, 140—151 |
| [18] | Jacobs G., Ma W.P., Gao P., Todic B., Bhatelia T., Bukur D. B., Davis B. H., Catal. Today, 2013, 214, 100—139 |
| [19] | Qi G.S., Yang R. T., Appl. Catal. B, 2003, 44(3), 217—225 |
| [20] | Guo X.G., Fang G. Z., Li G., Ma H., Fan H. J., Yu L., Ma C., Wu X., Deng D. H., Wei M. M., Tan D. L., Si R., Zhang S., Li J. Q., Sun L. T., Tang Z. C., Pan X. L., Bao X. H., Science, 2014, 344(6184), 616—619 |
| [21] | Lefevre M., Proietti E., Jaouen F., Dodelet J.P., Science, 2009, 324(5923), 71—74 |
| [22] | Jagadeesh R.V., Surkus A. E., Junge H., Pohl M. M., Radnik J., Rabeah J., Huan H., Schunemann V., Bruckner A., Beller M., Science, 2013, 342(6162), 1073—1076 |
| [23] | Shi J.J., Wang Y. Y., Du W. C., Hou Z. Y., Carbon, 2016, 99, 330—337 |
| [24] | Du W.C., Xia S. X., Nie R. F., Hou Z. Y, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2014, 53(12), 4589—4594 |
| [25] | Nie R.F., Shi J. J., Du W. C., Ning W. S., Hou Z. Y., Xiao F. S., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(32), 9037—9045 |
| [26] | Zeng X.Y., You C. H., Leng L. M., Dang D., Qiao X. C., Li X. H., Li Y. W., Liao S. J., Adzic R. R., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(21), 11224—11231 |
| [27] | Chen J.L., Yan X. P., J. Mater. Chem., 2010, 20(21), 4328—4332 |
| [28] | Shi J.J., Zhao M. S., Wang Y. Y., Fu J., Lu X. Y., Hou Z. Y., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4(16), 5842—5848 |
| [29] | Stankovich S., Dikin D.A., Piner R. D., Kohlhaas K. A., Kleinhammes A., Jia Y. Y., Wu Y., Nguyen S. T., Ruoff R. S., Carbon, 2007, 45(7), 1558—1565 |
| [30] | Liu S., Wang J.Q., Zeng J., Ou J. F., Li Z. P., Liu X. H., Yang S. R., J. Power Sources, 2010, 195(15), 4628—4633 |
| [31] | Liang Y.Y., Li Y. G., Wang H. L., Zhou J. G., Wang J., Regier T., Dai H. J., Nat. Mater., 2011, 10(10), 780—786 |
| [32] | Gao Y.J., Hu G., Zhong J., Shi Z. J., Zhu Y. S., Su D. S., Wang J. G., Bao X. H., Ma D, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(7), 2109—2113 |
| [33] | Wu Z.S., Winter A., Chen L., Sun Y., Turchanin A., Feng X. L., Müllen K, Adv. Mater., 2012, 24(37), 5130—5135 |
| [34] | Chen P., Xiao T.Y., Qian Y. H., Li S. S., Yu S. H, Adv. Mater., 2013, 25(23), 3192—3196 |
| [35] | Xiao M.L., Zhu J. B., Feng L. G., Liu C. P., Xing W, Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(15), 2521—2527 |
| [36] | Hu Y., Jensen J.O., Zhang W., Martin S., Chenitz R., Pan C., Xing W., Bjerrum N. J., Li Q. F., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(4), 1752—1760 |
| [37] | Guo D.H., Shibuya R., Akiba C., Saji S., Kondo T., Nakamura J., Science, 2016, 351(6271), 361—365 |
| [38] | Zhao Y., Watanabe K., Hashimoto K., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(4), 1450—1456 |
| [39] | Nie R., Miao M., Du W.C., Shi J. J., Liu Y. C., Hou Z. Y., Appl. Catal. B, 2016, 180, 607—613 |
| [40] | Groves M.N., Chan A. S. W., Malardier-Jugroot C., Jugroot M, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2009, 481(4—6), 214—219 |
| [41] | Kim H., Robertson A.W., Kim S. O., Kim J. M., Warner J. H., ACS Nano, 2015, 9(6), 5947—5957 |
| [1] | WANG Ruina, SUN Ruifen, ZHONG Tianhua, CHI Yuwu. Fabrication of a Dispersible Large-sized Graphene Quantum Dot Assemblies from Graphene Oxide and Its Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence Behaviors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220161. |
| [2] | ZHANG Xinxin, XU Di, WANG Yanqiu, HONG Xinlin, LIU Guoliang, YANG Hengquan. Effect of Mn Promoter on CuFe-based Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Higher Alcohols [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220187. |
| [3] | ZHOU Zixuan, YANG Haiyan, SUN Yuhan, GAO Peng. Recent Progress in Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide to Methanol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220235. |
| [4] | DING Yang, WANG Wanhui, BAO Ming. Recent Progress in Porous Framework-immobilized Molecular Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Formic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220309. |
| [5] | HUANG Xiaoshun, MA Haiying, LIU Shujuan, WANG Bin, WANG Hongli, QIAN Bo, CUI Xinjiang, SHI Feng. Recent Advances on Indirect Conversion of Carbon Dioxide to Chemicals [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220222. |
| [6] | ZHOU Leilei, CHENG Haiyang, ZHAO Fengyu. Research Progress of CO2 Hydrogenation over Pd-based Heterogeneous Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220279. |
| [7] | SONG Youwei, AN Jiangwei, WANG Zheng, WANG Xuhui, QUAN Yanhong, REN Jun, ZHAO Jinxian. Effects of Ag,Zn,Pd-doping on Catalytic Performance of Copper Catalyst for Selective Hydrogenation of Dimethyl Oxalate [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20210842. |
| [8] | YAN Jiasen, HAN Xianying, DANG Zhaohan, LI Jiangang, HE Xiangming. Preparation and Performance of Paraffin/Expanded Graphite/Graphene Composite Phase Change Heat Storage Material [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220054. |
| [9] | CAO Lei, CHEN Meijun, YUAN Gang, CHANG Gang, ZHANG Xiuhua, WANG Shengfu, HE Hanping. Solution-gated Graphene Field Effect Transistor Sensor Based on Crown Ether Functionalization for the Detection of Mercury Ion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210688. |
| [10] | HU Huimin, CUI Jing, LIU Dandan, SONG Jiaxin, ZHANG Ning, FAN Xiaoqiang, ZHAO Zhen, KONG Lian, XIAO Xia, XIE Zean. Influence of Different Transition Metal Decoration on the Propane Dehydrogenation Performance over Pt/M-DMSN Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210815. |
| [11] | ZHENG Xuelian, YANG Cuicui, TIAN Weiquan. The Second Order Nonlinear Optical Properties of Azulene-defect Graphene Nanosheets with Full Armchair Edge [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210806. |
| [12] | MENG Xiangyu, ZHAN Qi, WU Yanan, MA Xiaoshuang, JIANG Jingyi, SUN Yueming, DAI Yunqian. Photothermal Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogenation Performance of Au/RGO/Na2Ti3O7 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210655. |
| [13] | YU Bin, CHEN Xiaoyan, ZHAO Yue, CHEN Weichang, XIAO Xinyan, LIU Haiyang. Graphene Oxide-based Cobalt Porphyrin Composites for Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210549. |
| [14] | WANG Xueli, SONG Xiangwei, XIE Yanning, DU Niyang, WANG Zhenxin. Preparation, Characterization of Partially Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Killing Effect on Human Cervical Cancer Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210595. |
| [15] | HU Bo, ZHU Haochen. Dielectric Constant of Confined Water in a Bilayer Graphene Oxide Nanosystem [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||