

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (6): 1082.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160796
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Weibing1,*( ), LI Jian1, LIU Congmin3, ZHANG Lei4, DAI Hongqi1, LIU Wei2,*(
), LI Jian1, LIU Congmin3, ZHANG Lei4, DAI Hongqi1, LIU Wei2,*( )
)
Received:2016-11-16
Online:2017-06-10
Published:2017-05-23
Contact:
WU Weibing,LIU Wei
E-mail:wbwu@njfu.edu.cn;weiliu_toya@yahoo.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WU Weibing, LI Jian, LIU Congmin, ZHANG Lei, DAI Hongqi, LIU Wei. Water Soluble Polyoxometalate-based Photocatalytic Fuel Cell†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(6): 1082.
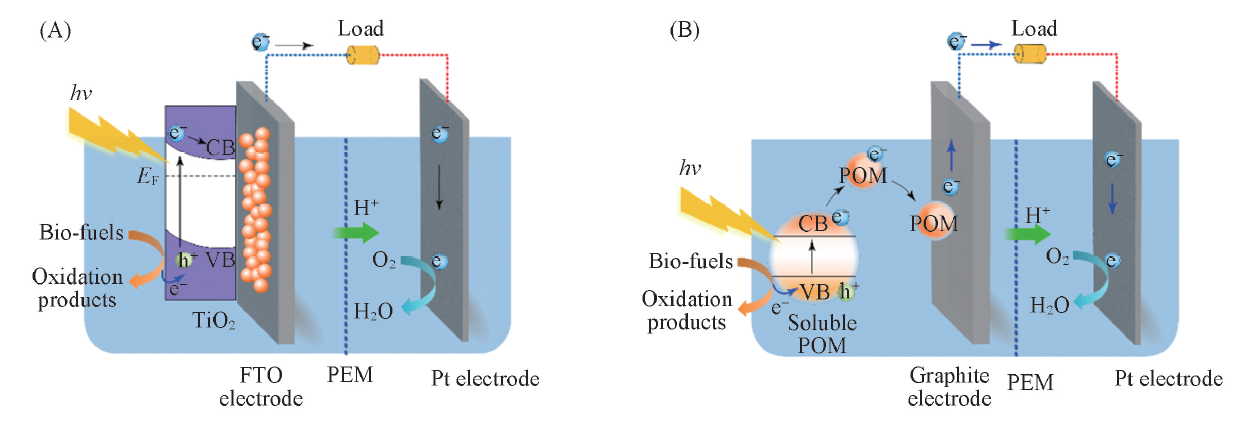
Fig.1 Comparison of traditional photocatalytic fuel cell with TiO2 photo anode(A) and water soluble polyoxometalates based photocatalytic fuel cell(B)
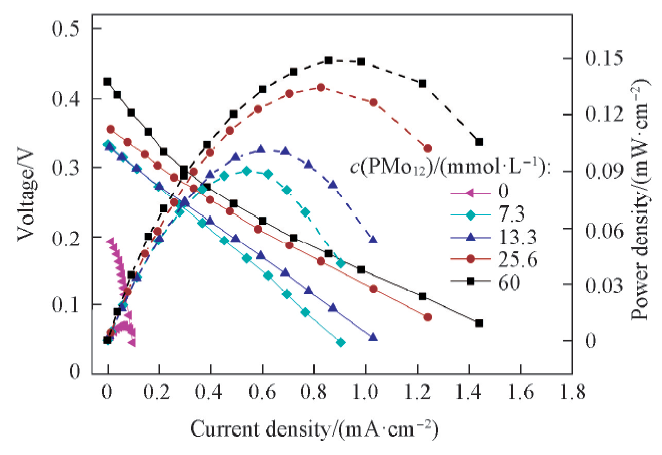
Fig.2 Voltage-current and power-current plots with different concentrations of PMo12c(Glycerol)=1 mol/L. Voltage: solid line;power density: dash line.
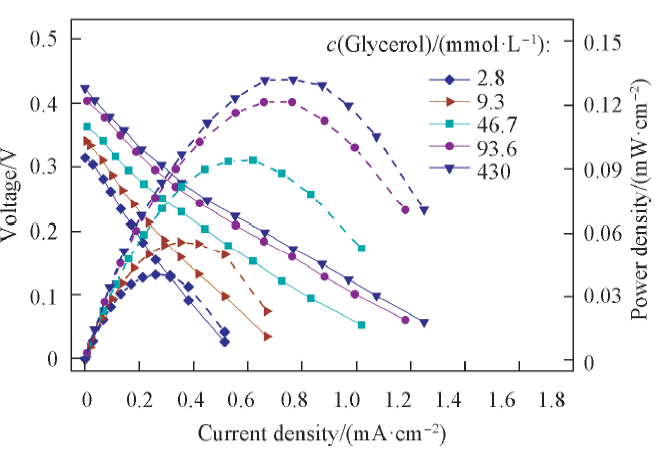
Fig.3 Voltage-current and power-current plots with different concentrations of glycerol c(PMo12)=28.1 mmol/L. Voltage: solid line; power density: dash line.
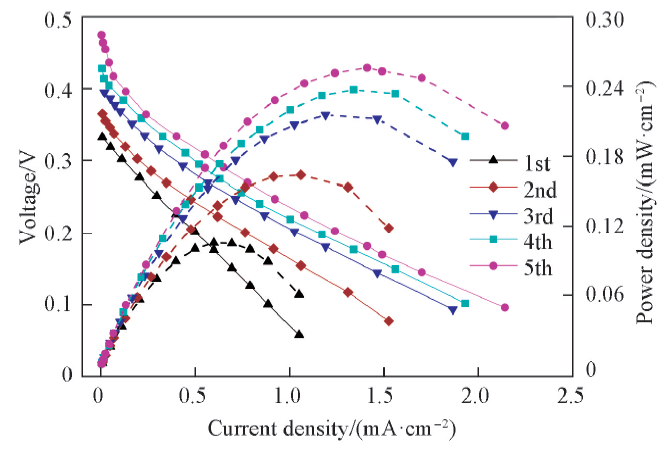
Fig.4 Voltage-current and power-current plots of five repeated irradiation-discharge cycles c(Glycerol)=1 mol/L; c(PMo12)=13.3 mmol/L. Voltage: solid line; power density: dash line.
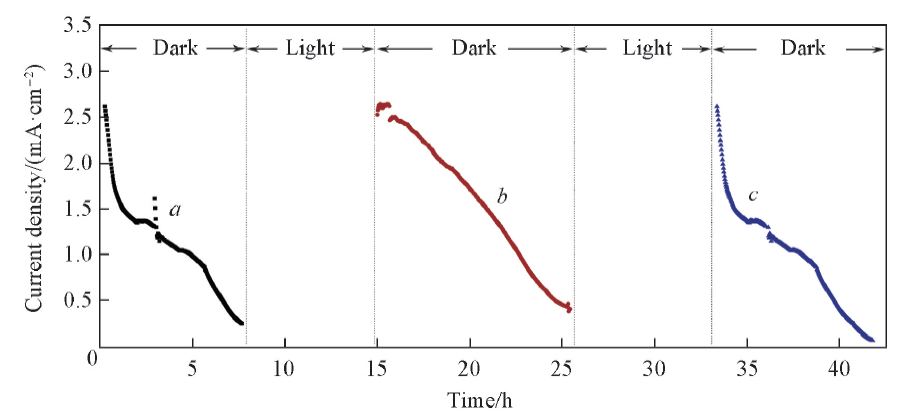
Fig.6 Discharge current density-time plot in the cycles of light-irradiation and discharge The anode electrolyte was pretreated by light-irradiation for 7 h.
| Product | Molar fraction(%) |
|---|---|
| Helium | 29.675 |
| Oxygen | 8.013 |
| Nitrogen | 27.528 |
| Carbon monoxide | 0.004 |
| Carbon dioxide | 0.126 |
Table 1 Analysis of the emission gas*
| Product | Molar fraction(%) |
|---|---|
| Helium | 29.675 |
| Oxygen | 8.013 |
| Nitrogen | 27.528 |
| Carbon monoxide | 0.004 |
| Carbon dioxide | 0.126 |
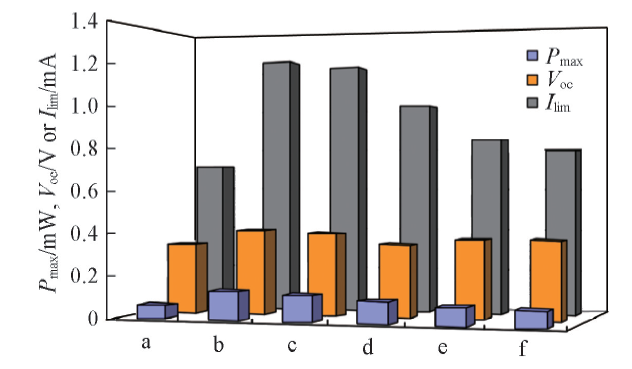
Fig.11 Comparison of cell performance powered with different fuelsFuel: a. EtOH; b. glycol; c. glucose; d. DMF; e. ethylenediamine; f. oxalic acid.The initial feed concentrations for all fuels are: EtOH, glycol and glucose: 1 mol/L, DMF: 4 mol/L, ethylenediamine and oxalic acid: 0.5 mol/L; PMo12 13.3 mmol/L.
| [1] | Tollefson J., Monastersky R., Nature, 2012, 491(7426), 654—655 |
| [2] | Potocnik J., Science, 2007, 315(5813), 810—811 |
| [3] | Liu Y., Li J., Zhou B., Chen H., Wang Z., Cai W., Chem. Commun. , 2011, 47(37), 10314—10316 |
| [4] | Gan Y.X., Gan B. J., Clark E., Su L., Zhang, L., Mater. Res. Bull., 2012, 47(9), 2380—2388 |
| [5] | Ibrahim N., Kamarudin S.K., Minggu L. J., J. Power Sources, 2014, 259(4), 33—42 |
| [6] | Luo J.Y., Chen L. L., Wang Y., Li H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(12), 2468—2474 |
| (骆金苑, 陈琳琳, 王奕, 李红. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(12), 2468—2474) | |
| [7] | Wu J., Liu H., Yuan L., Hou C., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2016, 32(6), 979—984 |
| [8] | Xiang Z., Zhao X., Ge J., Ma S., Zhang Y., Na H., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2016, 32(2), 291—295 |
| [9] | Chen W.M., Sun G. Q., Zhao X. S., Sun P. C., Yang S. H., Xin Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(5), 928—931 |
| (陈维民, 孙公权, 赵新生, 孙丕昌, 杨少华, 辛勤. 高等学校化学学报, 2007, 28(5), 928—931) | |
| [10] | Lamy C., Belgsir E.M., Léger J. M., J. Appl. Electrochem., 2001, 31(7), 799—809 |
| [11] | Barczuk P.J., Lewera A., Miecznikowski K., Kulesza P. J., Augustynski J., Electrochem. Solid-State Lett., 2009, 12, B165—B166 |
| [12] | Brouzgou A., Podias A., Tsiakaras P.J., Appl. Electrochem., 2013, 43(2), 119—136 |
| [13] | Nakagawa N., Kaneda Y., Wagatsuma M., Tsujiguchi T., J. Power Sources, 2012, 199(1), 103—109 |
| [14] | Marchionni A., Bevilacqua M., Bianchini C., Chen Y.X., Filippi J., Chem. Sus. Chem., 2013, 6(3), 518—528 |
| [15] | Antolini E., Gonzalez E.R., J. Power Sources, 2010, 195(11), 3431—3450 |
| [16] | Kamarudin M.Z. F., Kamarudin S. K., Masdar M. S., Daud W. R. W., Int. J. Hydrogen. Energ., 2013, 38(22), 9438—9453 |
| [17] | Kozhevnikov I.V., Chem. Rev., 1998, 98(1), 171—198 |
| [18] | Mizuno N., Misono M., Chem. Rev., 1998, 98(1), 199—218 |
| [19] | Liu W., Cui Y., Du X., Zhang Z., Chao Z., Deng Y., Energ. Environ. Sci., 2016, 9, 467—472 |
| [20] | Liu W., Mu W., Deng Y., Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53(49), 13558 |
| [21] | Liu W., Mu W., Liu M., Zhang X., Cai H., Deng Y., Nat. Commun. , 2014, 5, 3208 |
| [22] | Wu W., Liu W., Mu W., Deng Y., J. Power Sources, 2016, 318, 86—92 |
| [23] | He T., Yao J., Prog. Mater. Sci., 2006, 51(6), 810—879 |
| [24] | Ketchie W.C., Murayama M., Davis R. J., Top. Catal. , 2007, 44(1/2), 307—317 |
| [25] | Maurino V., Bedini A., Minella M., Rubertelli F., Pelizzettiet E., Minero C.J., Adv. Oxid. Technol., 2008, 11(2), 184—192 |
| [26] | Montini T., Gombac V., Sordelli L., Delgado J.J., Chen X., Adami G., Fornasiero P., Chem. Cat. Chem., 2011, 3(3), 574—577 |
| [27] | Molinari A., Maldotti A., Bratovcic A., Magnacca G., Catal. Today, 2013, 206(3), 46—52 |
| [28] | Papaconstantinou E., Chem. Soc. Rev., 1989, 18(1), 1—13 |
| [29] | Mylonas A., Papaconstantinou E., J. Mol. Catal., 1994, 92(3), 261—267 |
| [30] | Antonaraki S., Triantis T.M., Papaconstantinou E., Hiskia A., Catal. Today, 2010, 151(1/2), 119—124 |
| [31] | Papaconstantinou E., J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun., 1982, 1(1), 12—13 |
| [1] | QIN Yongji, LUO Jun. Applications of Single-atom Catalysts in CO2 Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220300. |
| [2] | LIN Zhi, PENG Zhiming, HE Weiqing, SHEN Shaohua. Single-atom and Cluster Photocatalysis: Competition and Cooperation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220312. |
| [3] | TENG Zhenyuan, ZHANG Qitao, SU Chenliang. Charge Separation and Surface Reaction Mechanisms for Polymeric Single-atom Photocatalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220325. |
| [4] | QIU Xinsheng, WU Qin, SHI Daxin, ZHANG Yaoyuan, CHEN Kangcheng, LI Hansheng. Preparation and High Temperature Fuel Cell Performance of Ionic Crosslinked Sulfonated Polyimides for Proton Exchange Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220140. |
| [5] | XIA Wu, REN Yingyi, LIU Jing, WANG Feng. Chitosan Encapsulated CdSe QDs Assemblies for Visible Light-induced CO2 Reduction in an Aqueous Solution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220192. |
| [6] | QIU Liqi, YAO Xiangyang, HE Liangnian. Visible-light-driven Selective Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Catalyzed by Earth-abundant Metalloporphyrin Complexes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220064. |
| [7] | ZHAO Yingzhe, ZHANG Jianling. Applications of Metal-organic Framework-based Material in Carbon Dioxide Photocatalytic Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220223. |
| [8] | WANG Guangqi, BI Yiyang, WANG Jiabo, SHI Hongfei, LIU Qun, ZHANG Yu. Heterostructure Construction of Noble-metal-free Ternary Composite Ni(PO3)2-Ni2P/CdS NPs and Its Visible Light Efficient Catalytic Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220050. |
| [9] | TAO Yu, OU Honghui, LEI Yongpeng, XIONG Yu. Research Progress of Single-atom Catalysts in Photocatalytic Reduction of Carbon Dioxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220143. |
| [10] | CHEN Changli, MI Wanliang, LI Yujing. Research Progress of Single Atom Catalysts in Electrochemical Hydrogen Cycling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220065. |
| [11] | LUO Bian, ZHOU Fen, PAN Mu. Study on Preparation and Accessibility of Hierarchical Porous Carbon Supported Platinum Catalyst [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210853. |
| [12] | FENG Li, SHAO Lanxing, LI Sijun, QUAN Wenxuan, ZHUANG Jinliang. Synthesis of Ultrathin Sm-MOF Nanosheets and Their Visible-light Induced Photodegradation of Mustard Simulant [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210867. |
| [13] | MENG Xiangyu, ZHAN Qi, WU Yanan, MA Xiaoshuang, JIANG Jingyi, SUN Yueming, DAI Yunqian. Photothermal Enhanced Photocatalytic Hydrogenation Performance of Au/RGO/Na2Ti3O7 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210655. |
| [14] | CHEN Wangsong, LUO Lan, LIU Yuguang, ZHOU Hua, KONG Xianggui, LI Zhenhua, DUAN Haohong. Recent Progress in Photoelectrochemical H2 Production Coupled with Biomass-derived Alcohol/aldehyde Oxidation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210683. |
| [15] | GUO Biao, ZHAO Chencan, LIU Xinxin, YU Zhou, ZHOU Lijing, YUAN Hongming, ZHAO Zhen. Effects of Surface Hydrothermal Carbon Layer on the Photocatalytic Activity of Magnetic NiFe2O4 Octahedron [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220472. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||