

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (6): 1076.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160866
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2016-12-02
Online:2017-06-10
Published:2017-05-08
Contact:
WANG Haishui
E-mail:wanghsh@scut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHOU Xinhui, WANG Haishui. Co-effect of L-Cysteine Self-assembled Monolayers and Mixed Solvents on Chiral Separation of DL-glutamic Acid†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(6): 1076.
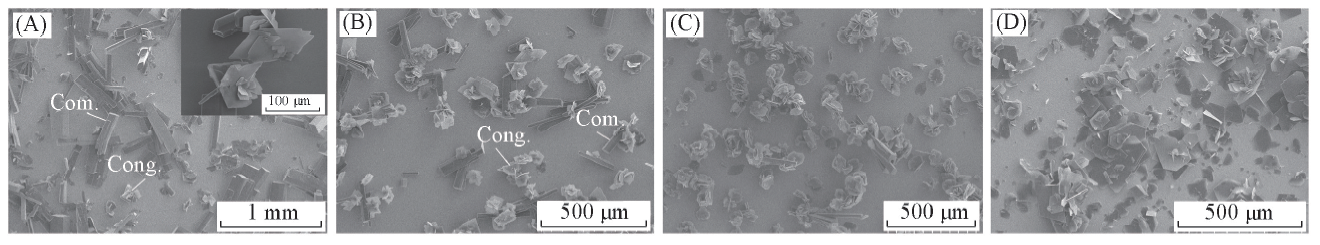
Fig.2 SEM images of glutamic acid crystals obtained on the L-Cys SAMs from the mixed solution of water and ethanol with different volume fractions of ethanolVolume fraction of ethanol: (A) 30%; (B) 40%; (C) 50%; (D) 60%.
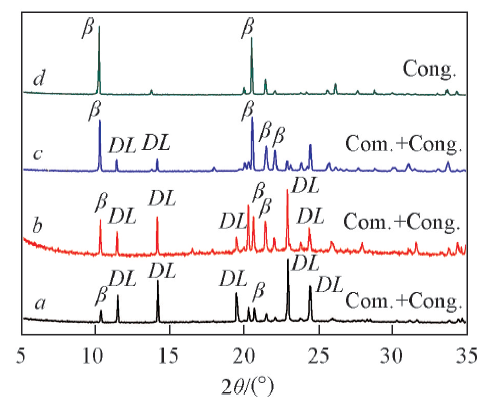
Fig.4 XRD patterns of glutamic acid crystals obtained on L-Cys SAMs from the mixed solution of water and ethanolVolume fraction of ethanol in mixed solution: a. 30%; b. 40%; c. 50%; d. 60%.
| No. | Solvent | Content of D-Glu(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solution | Crystals | ||
| 1 | 60% ethanol | 50 | 58.25 |
| 2 | 60% ethanol | 58.25 | 66.25 |
| 3 | 60% ethanol | 66.25 | 75.2 |
| 4 | 60% ethanol | 75.2 | 82.2 |
| 5 | Water | 82.2 | 100 |
Table 1 Chiral separation of racemic glutamic acid
| No. | Solvent | Content of D-Glu(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solution | Crystals | ||
| 1 | 60% ethanol | 50 | 58.25 |
| 2 | 60% ethanol | 58.25 | 66.25 |
| 3 | 60% ethanol | 66.25 | 75.2 |
| 4 | 60% ethanol | 75.2 | 82.2 |
| 5 | Water | 82.2 | 100 |
| [1] | Millership J.S., Fitzpatrick A., Chirality, 1993, 5, 573—576 |
| [2] | Caldwell J., J. Clin. Pharmacol., 1992, 32(10), 925—929 |
| [3] | Hutt A.J., Tan S. C., Drugs, 1996, 52(Suppl 5), 1—12 |
| [4] | Caner H., Groner E., Levy L., Agranat I., Drug Discovery Today, 2004, 9(3), 105—110 |
| [5] | Ulman A., Chem. Rev., 1996, 96(4), 1533—1554 |
| [6] | Singh A., Lee I.S., Kim K., Myerson A. S., CrystEngComm., 2011, 13, 24—32 |
| [7] | Harding J.H., Freeman C. L., Duffy D. M., CrystEngComm., 2014, 16, 1430—1438 |
| [8] | Aizenberg J., Black A.J., Whitesides G. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1999, 121(18), 4500—4509 |
| [9] | Liu Q., Wang H.S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(12), 2681—2685 |
| (柳青, 王海水. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(12), 2681—2685) | |
| [10] | Lee A.Y., Ulman A., Myerson A. S., Langmuir, 2002, 18(15), 5886—5898 |
| [11] | Kang J.F., Zaccaro J., Ulman A., Myerson A., Langmuir, 2000, 16(8), 3791—3796 |
| [12] | Moshe H., Levi G., Mastai Y., Cryst EngComm., 2013, 15, 9203—9209 |
| [13] | Pan X.F., Wang H. S., Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2014, 30(6), 1312—1316 |
| (潘晓芳, 王海水. 无机化学学报, 2014, 30(6), 1312—1316) | |
| [14] | Zhang S., Wang H.S., Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2013, 29(1), 31—35 |
| (张素, 王海水. 无机化学学报, 2013, 29(1), 31—35) | |
| [15] | Hiremath R., Basile J.A., Varney S. W., Swift J. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127(51), 18321—18327 |
| [16] | Banno N., Nakanishi T., Matsunaga M., Asahi T., Osaka T., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126(2), 428—429 |
| [17] | Nakanishi T., Banno N., Matsunaga M., Asahi T., Osaka T., Colloids Surf., A, 2006, 284, 270—275 |
| [18] | Chen J., Myerson A.S., Cryst. Eng. Comm., 2012, 14, 8326—8329 |
| [19] | Singh A., Myerson A.S., J. Pharm. Sci., 2010, 99(9), 3931—3940 |
| [20] | Kühnle A., Linderoth T.R., Hammer B., Besenbacher F., Nature, 2002, 415, 891—893 |
| [21] | Dakkouri A.S., Kolb D. M., Edelstein-Shima R., Mandler D., Langmuir, 1996, 12(11), 2849—2852 |
| [22] | Dodero G., Michieli L.D., Cavalleri O., Rolandi R., Oliveri L., Daccà A., Parodi R., Colloids Surf. A, 2000, 175, 121—128 |
| [23] | Kühnle A., Linderoth T.R., Schunack M., Besenbacher F., Langmuir, 2006, 22(5), 2156—2160 |
| [24] | Fajín J.L. C., Gomes J. R. B., Cordeiro M. N. D. S., Langmuir, 2013, 29, 8856—8864 |
| [25] | Hong C., Wang H., Acta Chim. Sinica, 2014, 72(6), 739—742 |
| (洪传敏, 王海水. 化学学报, 2014, 72(6), 739—742) | |
| [26] | Lü R.Z., Nucleation of Aspartic Acid on Self-assembled Monolayers, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, 2012 |
| (吕荣禛. 自组装膜诱导天冬氨酸晶体生长的相关研究, 广州: 华南理工大学, 2012) | |
| [27] | Kera Y., Aoyama H., Matsumura H., Hasegawa A., Nagasaki H., Yamada R., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1995, 1243, 282—286 |
| [28] | Benešová T Honzátko A., Pilin A., Votruba J., Flieger M., J. Sep. Sci., 2004, 27, 330—334 |
| [29] | Viedma C., Origins Life Evol. Biospheres, 2001, 31, 501—509 |
| [30] | Ejgenberg M., Mastai Y., Chem. Commun., 2011, 47, 12161—12163 |
| [31] | Schöll J., Bonalumi D., Vicum L., Mazzotti M., Cryst. Growth Des., 2006, 6(4), 881—891 |
| [32] | Alatalo H., Hatakka H., Kohonen J., Reinikainen S., Louhi-Kultanen M.,AIChE J., 2010, 56(8), 2063—2076 |
| [33] | Latha M.P., Rao V. M., Rao T. S., Rao G. N., Acta Chim. Slov., 2007, 54, 160—165 |
| [34] | Dogan A., Köseoglu F., Kiliç E., Anal. Biochem., 2002, 309, 75—78 |
| [35] | Jabbari M., Gharib F., Acta Chim.Slov., 2010, 57, 325—331 |
| [36] | Filimon A., Jacob P., Hergenröder R., Jürgensen A., Langmuir, 2012, 28, 8692—8699 |
| [37] | Elsner M.P., Ziomek G., Seidel-Morgenstern A., AIChE J., 2009, 55(3), 640—649 |
| [1] | WANG Bodong, PAN Meichen, ZHUO Ying. Construction of Electrochemiluminescence Sensing Interface Based on Silver Nanoclusters-Silica Nanoparticles and Biomolecular Recognition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3519. |
| [2] | FU Kefei, LIAN Huiting, WEI Xiaofeng, SUN Xiangying, LIU Bin. Construction of Cyclodextrin-based Impedance Sensor for Recognition of L-Cysteine † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 706. |
| [3] | GUO Zhaopei,LIN Lin,CHEN Jie,TIAN Huayu,CHEN Xuesi. Polyglutamic Acid Grafted Polyethylene Glycol@Calcium Carbonate Based Shielding System for Improving Polyethyleneimine Gene Transfection Efficiency † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 235. |
| [4] | PENG Yuyu,WANG Yu,YU Xinyao,ZENG Julan,XIAO Zhongliang,CAO Zhong. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of L-Cysteine Based on Mono(6-mercapto-6-deoxy)-β-cyclodextrin Modified Gold Electrode † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 268. |
| [5] | WEN Jing, XU Zhimin, QI Desheng, WANG Jiayu, YU Shuangjiang, HE Chaoliang, HAN Bing. PLG-g-TA/RGD Enzyme-catalyzed Crosslinked Hydrogel for Adhesion and Three-dimensional Culture of Hyaline Chondrocytes † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 2020. |
| [6] | YAN Shifeng,WANG Weidong,REN Jie,TENG Changchang,YIN Jingbo. Biomimetic Mineralization of Hydroxyapatite Mediated by Poly(L-glutamic acid) Hydrogels in Simulated Body Fluid† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 815. |
| [7] | JIAN Yuhang, YAN Shifeng, LI Xing, HUANG Yanan, YIN Jingbo. Synthesis and Characterization of Injectable Hydrogels Based on Star β-CD-g-poly(L-glutamic acid) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(8): 1489. |
| [8] | LI Xing, YAN Shifeng, JIAN Yuhang, YIN Jingbo. Synthesis and Characterization of Injectable Poly(L-glutamic acid) Hydrogels [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5): 872. |
| [9] | LI Yingtu, LI Libo, ZHOU Jian. Molecular Dynamics Simulations on the Adhesion of DOPA to Self-assembled Monolayers† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5): 798. |
| [10] | ZHANG Luge, XUE Zexu, ZHANG Chong, YAN Hui. Molecular Dynamics Studies on the Selective Deposition of 3(5)-(9-Anthryl) Pyrazole onto Self-assembled Monolayers† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(3): 505. |
| [11] | LI Guifei, WU Jie, WANG Bo, ZHANG Weijun, YAN Shifeng, YIN Jingbo. Fabrication and Characterization of PLGA-based Supermolecular Hydrogel† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(12): 2582. |
| [12] | HE Ning, SUN Hechun, XU Huanxi, SHAO Zhangzhang. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Comblike Non-virus Gene Delivery Vector with the Poly(L-glutamic acid) as Backbone† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(9): 2019. |
| [13] | NIE Guizhen, LI Laisheng, CHENG Biaoping, ZHOU Rendan, ZHANG Hongfu. Enantioseparations of Dihydropyridine Drugs by Sulfobutyl Ether-β-Cyclodextrin Modified Capillary Electrochromatography† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(7): 1414. |
| [14] | ZHOU Rendan, LI Laisheng, CHENG Biaoping, NIE Guizhen, ZHANG Hongfu. Preparation and Evaluation of a Novel 6-mono-Nitrophenylamino-β-cyclodextrin Bonded SBA-15 Chiral Stationary Phase for HPLC† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(6): 1152. |
| [15] | WEI Zhaojun, CHEN Ye, WANG Dongmei, FANG Wenxiang, CHEN Tao, ZHANG Suning. Synthesis and Solution Properties of CS-g-PLGA Graft Polyampholytes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(6): 1348. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
