

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (7): 1163.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160777
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
PAN Shuai, LI Zhanhong, CHEN Yang, ZHAO Xueling, CHEN Cheng, ZHU Zhigang*( )
)
Received:2016-11-09
Online:2017-07-10
Published:2017-06-20
Contact:
ZHU Zhigang
E-mail:zgzhu@sspu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
PAN Shuai, LI Zhanhong, CHEN Yang, ZHAO Xueling, CHEN Cheng, ZHU Zhigang. Glucose Biosensor Based on Rebuilding the Surface of the Spiral-type Pt-Ir Electrode†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1163.
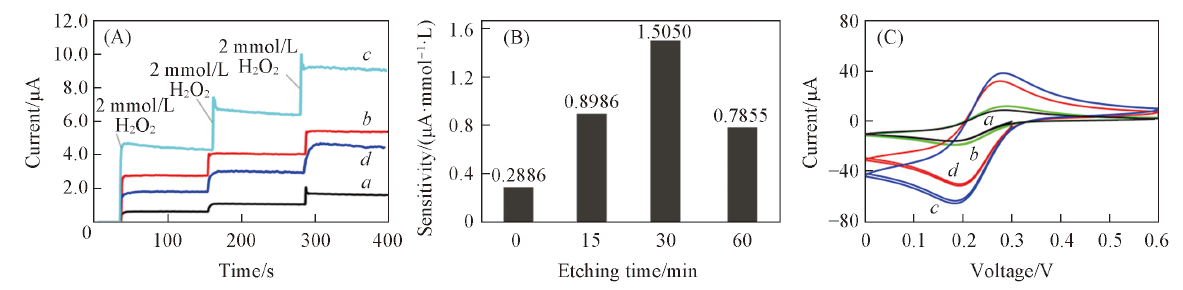
Fig.2 Chronoamperometry responses of the spiral-type Pt-Ir electrode with different etching time to hydrogen peroxide(at 0.5 V vs. Ag/AgCl reference)(A), hydrogen peroxide sensitivity for the spiral-type Pt-Ir electrode with different etching time(B) and cyclic voltammograms of the spiral-type Pt-Ir electrode in 0.4 mmol/L K3(FeCN6)/0.1 mol/L KCl aqueous solution at 50 mV/s scanning rate with different etching time(C)Etching time/min: a. 0; b. 15; c. 30; d. 60.
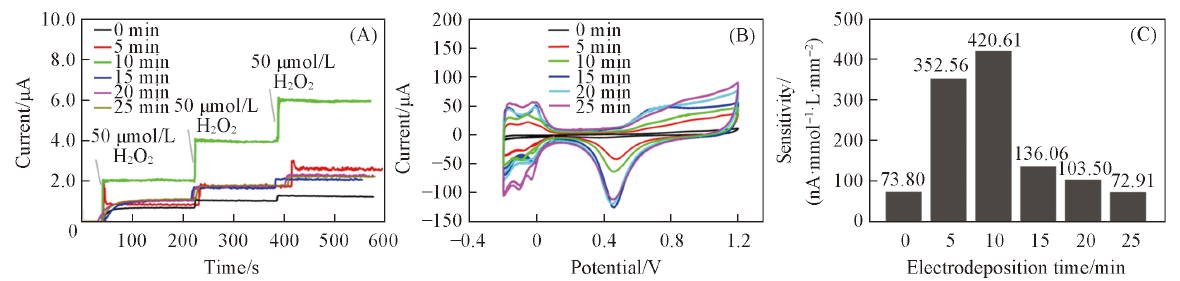
Fig.4 Chronoamperometry responses of etched spiral-type Pt-Ir electrode with different electrodeposition time to hydrogen peroxide(at 0.5 V vs. Ag/AgCl)(A) and cyclic voltammograms of etched electrode in 0.1 mol/L H2SO4 aqueous solution at 50 mV/s scanning rate with different electrodeposition time(B) and hydrogen peroxide sensitivity for etched electrode with different electrodeposition time(C)
| Etching time/min | Electro-deposition time/min | Deposition amount of platinum nanoparticles/mg | Active surface area/cm2 | Activity surface area/ Deposition amount of Pt/(cm2·mg-1) | Increased time of active surface area* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.039 | 0 | 0 |
| 30 | 5 | 0.28 | 0.489 | 1.75 | 12.54 |
| 30 | 10 | 0.41 | 0.786 | 1.92 | 19.15 |
| 30 | 15 | 0.79 | 1.026 | 1.30 | 25.30 |
| 30 | 20 | 1.11 | 1.070 | 0.96 | 26.44 |
| 30 | 25 | 1.50 | 1.435 | 0.95 | 36.80 |
Table 1 Mass specific activity and active surface area of the spiral-type Pt-Ir electrode with different electrodeposition time
| Etching time/min | Electro-deposition time/min | Deposition amount of platinum nanoparticles/mg | Active surface area/cm2 | Activity surface area/ Deposition amount of Pt/(cm2·mg-1) | Increased time of active surface area* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.039 | 0 | 0 |
| 30 | 5 | 0.28 | 0.489 | 1.75 | 12.54 |
| 30 | 10 | 0.41 | 0.786 | 1.92 | 19.15 |
| 30 | 15 | 0.79 | 1.026 | 1.30 | 25.30 |
| 30 | 20 | 1.11 | 1.070 | 0.96 | 26.44 |
| 30 | 25 | 1.50 | 1.435 | 0.95 | 36.80 |
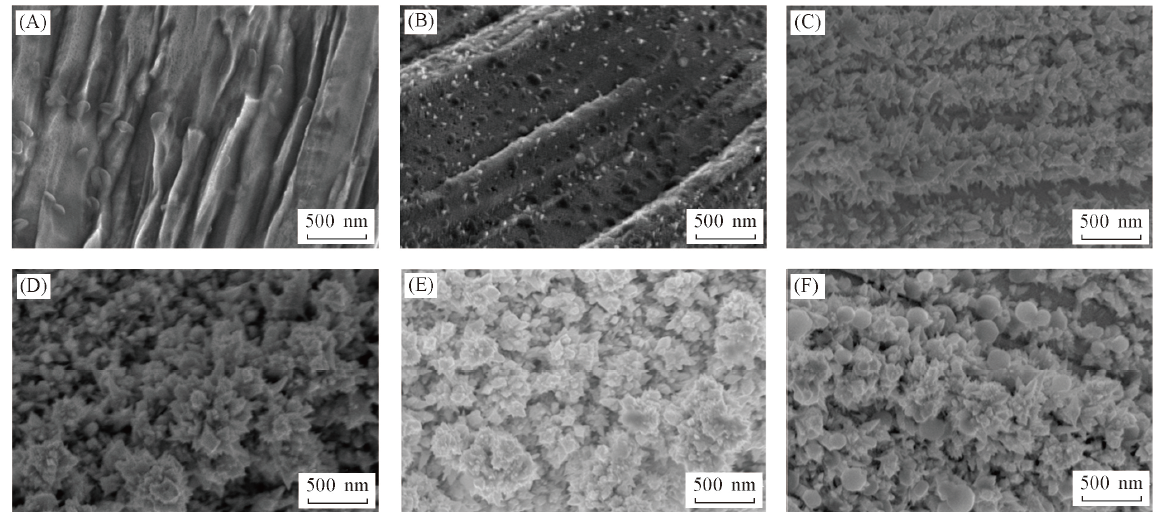
Fig.5 SEM images of the etched spiral-type Pt-Ir electrode with various electrochemical deposition time Deposition time/min: (A) 0; (B) 5; (C) 10; (D) 15; (E) 20; (F) 25.
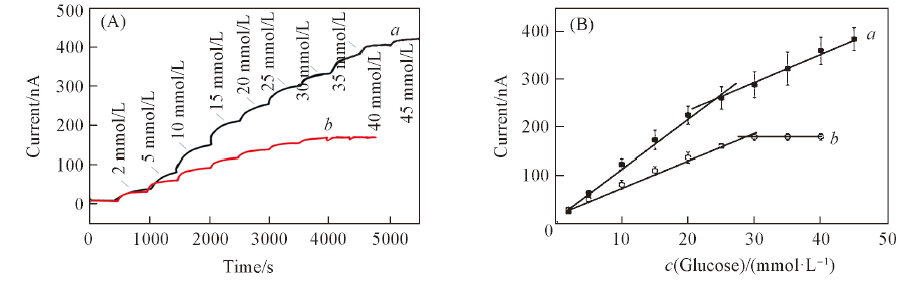
Fig.6 Amperometric response of etched PtNPs/GOD/Epoxy-PU electrode(a) and GOD/Epoxy-PU electrode(b) in different concentrations of glucose solution(A) and linear response curves of etched PtNPs/GOD/Epoxy-PU electrode(a) and GOD/Epoxy-PU electrode(b)(B)
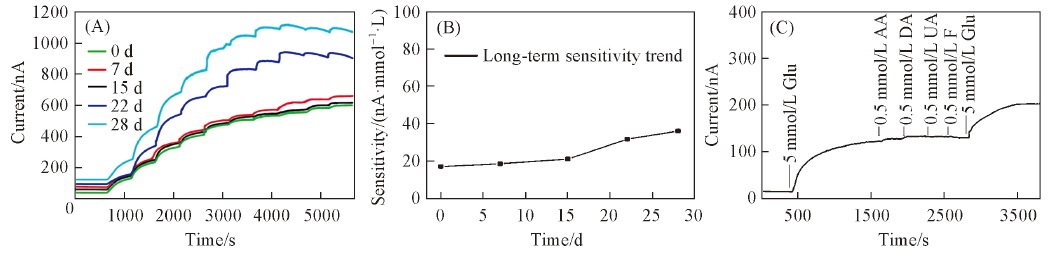
Fig.7 Amperometric response(A) and sensitivity changes(B) of etched PtNPs/GOD/Epoxy-PU electrode within four weeks and sensor response to sequential additions of 5 mmol/L glucose, 0.5 mmol/L AA, 0.5 mmol/L DA, 0.5 mmol/L UA, 0.5 mmol/L F and 5 mmol/L glucose(C)
| [1] | Shabi A. Z., Jae H. S., Talanta,2016, 149, 30—42 |
| [2] | Wilson G. S., Gifford R., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2005, 20, 2388—2403 |
| [3] | Zhu. Z. G., Garcia-Gancedo L., Chen C., Zhu X. R., Xie H. Q., Flewitt A. J., Milne W. L., Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 2013, 178, 586—592 |
| [4] | Wild S., Roglic G., Green A., Sicree R., King H., Diabetes Care,2004, 27, 1047—1053 |
| [5] | Wei C., Li X., Xu F., Methods,2004, 6, 1550—1557 |
| [6] | Zhu Z. G., Garcia-Gancedo L., Flewitt A. J., Milne W. L., Moussy F., J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 2012, 87, 256—262 |
| [7] | Clark L. C., Lyons C., Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci., 1962, 102, 29—45 |
| [8] | Abraham A. A., Fei R. C., Cote G. L., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces., 2013, 12(5), 832—838 |
| [9] | Dolgin E., Nature, 2012, 485, s6—s8 |
| [10] | Liu S., Yue R. F., Transducer and Microsystem Technology,2015, 34(1), 97—100 |
| (刘尚,岳瑞峰.传感器与微系统, 2015, 24(1), 97—100) | |
| [11] | Koh A., Lu Y., Schoenfisch M. H., Anal. Chem., 2013, 85(21), 10488—10494 |
| [12] | Croce Jr. R. A., Vaddiraju S. S., Kondo J., Biomed. Microdevices,2013, 15(1), 151—160 |
| [13] | Yu B., Wang C., Ju Y. M., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2008, 23, 1278—1284 |
| [14] | Yu B., Moussy Y., Moussy F., Front. Biosci., 2005, 10, 512—520 |
| [15] | Santhisagar V., Allen L., J. Diabetes Sci. Technol., 2013, 7(2), 441—451 |
| [16] | Sudip C., Raj C. R., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2009, 24, 3264—3268 |
| [17] | Xu L., Lin Y. Q., Chen X., Lu Y. L., Yang W. S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2016, 37(3), 442—447 |
| (徐亮,林有芹,陈旭,路艳罗,杨文胜.高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(3), 442—447) | |
| [18] | Guo S. J., Wen D., Zhai Y. M., Dong S. J., Wan E. K., ACS Nano,2010, 4(7), 3959—3968 |
| [19] | Yu J. Y., Zhu Z. G., Chen C., Li Z. H., Chen Y. X., Chin. J. Sens.Actuators,2016, 29(1), 10—14 |
| (余江渊, 朱志刚, 陈诚, 李崭虹, 陈云霞.传感技术学报, 2016, 29(1), 10—14) | |
| [20] | Robert A., Croce J., Biomed.Microdevices,2013, 15, 151—160 |
| [21] | Wang J., Chem. Rev., 2008, 108, 814—825 |
| [22] | Vaddiraju S., Legassey A., Qiang L. L., Wang Y., Burgess D. J., Papadimitrakopoulos F., J. Diabetes Sci. Technol., 2010, 4(6), 1540—1562 |
| [23] | Nichols S. P., Koh A., Storm W. L., Shin J. H., Schoenfisch M. H., Chem. Rev., 2013, 113, 2528—2549 |
| [24] | Ge C. J., Lu W. B., Sun X. P., Tian J., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2016, 32(3), 433—436 |
| [25] | Zhu Z. G., Garcia-Gancedo L., Flewitt A. J., Xie H. Q., Moussy F., Milne W. L., Sensors,2012, 12, 5996—6022 |
| [26] | Shi H. Y., Wu Y., Wang W., Song W. B., Liu T. M., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2013, 29(5), 861—867 |
| [1] | YAO Qing, YU Zhiyong, HUANG Xiaoqing. Progress in Synthesis and Energy-related Electrocatalysis of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220323. |
| [2] | HUANG Qiuhong, LI Wenjun, LI Xin. Organocatalytic Enantioselective Mannich-type Addition of 5H-Oxazol-4-ones to Isatin Derived Ketimines [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220131. |
| [3] | LIU Suyu, DING Fei, LI Qian, FAN Chunhai, FENG Jing. Azobenzene-integrated DNA Nanomachine [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220122. |
| [4] | GAO Jian, FENG Yiyu, FANG Wenyu, WANG Hui, GE Jing, FENG Wei. Alkane Grafted Phase Change Azobenzene Materials Based on Low Temperature Heat Release [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220146. |
| [5] | HE Beibei, YANG Kuihua, LYU Rui. Construction of Mn-Cu Bimetal Containing Phyllosilicate Nanozyme and Evaluation of the Enzyme-like Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220150. |
| [6] | ZHANG Zhicai, WANG Yuge, GU Qianqian, LYU Yongpeng, XIAO Jianshu, YIN Yuan, SUN Hongguo, ZHENG Yafang, SUN Zhaoyan. Flocculation of Fillers in Isoprene Rubber and Its Effects on Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220155. |
| [7] | GE Yicong, NIE Wanli, SUN Guofeng, CHEN Jiaxuan, TIAN Chong. Silver-catalyzed [5+1] Cyclization of 2-Vinylanilines with Benzisoxazoles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220142. |
| [8] | WANG Ruina, SUN Ruifen, ZHONG Tianhua, CHI Yuwu. Fabrication of a Dispersible Large-sized Graphene Quantum Dot Assemblies from Graphene Oxide and Its Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence Behaviors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220161. |
| [9] | YAO Yiting, LYU Jiamin, YU Shen, LIU Zhan, LI Yu, LI Xiaoyun, SU Baolian, CHEN Lihua. Preparation of Hierarchical Microporous-mesoporous Fe2O3/ZSM-5 Hollow Molecular Sieve Catalytic Materials and Their Catalytic Properties for Benzylation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220090. |
| [10] | GUO Zhiqiang, YANG Boru, XI Chanjuan. Recent Advances in Reductive Functionalization of Carbon Dioxide with Borohydride Reagents [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220199. |
| [11] | SONG Yingying, HUANG Lin, LI Qingsen, CHEN Limiao. Preparation of CuO/BiVO4 Photocatalyst and Research on Carbon Dioxide Reduction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220126. |
| [12] | LI Zhiguang, QI Guodong, XU Jun, DENG Feng. Role of Catalyst Acidity in Glucose Conversion over Sn-Al-β Zeolite as Studied by Solid-state NMR [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220138. |
| [13] | SHI Naike, ZHANG Ya, SANSON Andrea, WANG Lei, CHEN Jun. Uniaxial Negative Thermal Expansion and Mechanism in Zn(NCN) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220124. |
| [14] | HUANG Mingxin, ZHOU Lei, WANG Xuezhong. Measurement of Particle Size Distribution of Battery Slurries Using Ultrasonic Attenuation Spectroscopy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220040. |
| [15] | LIU Qingqing, WANG Pu, WANG Yongshuai, ZHAO Man, DONG Huanli. Synthesis and Topochemical Polymerization Study of Naphthalene/perylene Imides Substituted Diacetylene Derivatives [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220091. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||