

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 63.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160658
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Shasha1,2, ZHANG Heng1, WANG Hua2, YUAN Shiling1,*( ), HOU Shifeng2,*(
), HOU Shifeng2,*( )
)
Received:2016-09-21
Online:2017-01-10
Published:2016-12-05
Contact:
YUAN Shiling,HOU Shifeng
E-mail:shilingyuan@sdu.edu.cn;shifenghou@sdu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIU Shasha, ZHANG Heng, WANG Hua, YUAN Shiling, HOU Shifeng. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of EDTA-modified Graphene Oxide for Pb(Ⅱ) and Na(Ⅰ) Removal†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(1): 63.
| Site | σb/nm | εb/(kJ·mol-1) | q/e | Site | σb/nm | ε/(kJ·mol-1) | q/e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C(graphene) | 0.340 | 0.359 | 0.000 | N | 0.298 | 0.879 | -0.210 |
| C(—COO-) | 0.375 | 0.455 | 0.700 | C(—CH3) | 0.340 | 0.115 | 0.034 |
| O(—COO-) | 0.296 | 0.879 | -0.900 | H(—CH3) | 0.250 | 0.052 | 0.071 |
| O(—OH) | 0.307 | 0.649 | -0.513 | Pb2+ | 0.300 | 0.799 | 2.000c |
| H(—OH) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.330 | Na+ | 0.189 | 0.281 | 1.000d |
| Si | 0.339 | 2.450 | 1.310 | Ca2+ | 0.24 | 0.502 | 2.000e |
Table 1 Forced field parameters for GO-EDTA and metal ions used in this worka
| Site | σb/nm | εb/(kJ·mol-1) | q/e | Site | σb/nm | ε/(kJ·mol-1) | q/e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C(graphene) | 0.340 | 0.359 | 0.000 | N | 0.298 | 0.879 | -0.210 |
| C(—COO-) | 0.375 | 0.455 | 0.700 | C(—CH3) | 0.340 | 0.115 | 0.034 |
| O(—COO-) | 0.296 | 0.879 | -0.900 | H(—CH3) | 0.250 | 0.052 | 0.071 |
| O(—OH) | 0.307 | 0.649 | -0.513 | Pb2+ | 0.300 | 0.799 | 2.000c |
| H(—OH) | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.330 | Na+ | 0.189 | 0.281 | 1.000d |
| Si | 0.339 | 2.450 | 1.310 | Ca2+ | 0.24 | 0.502 | 2.000e |
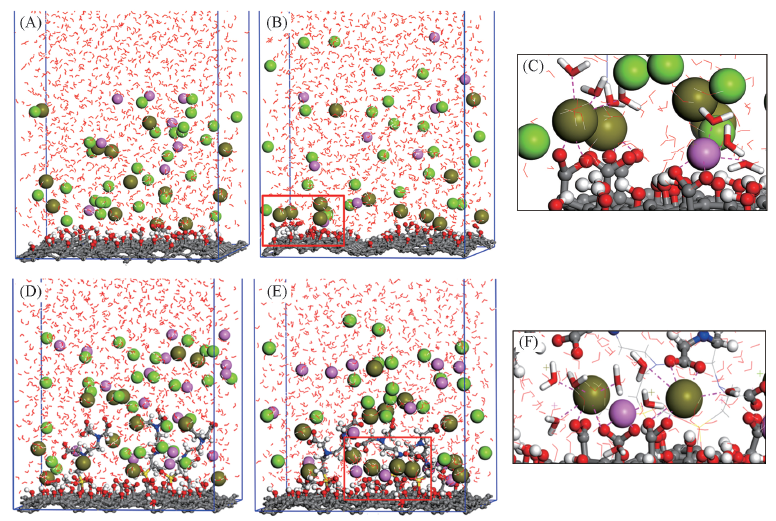
Fig.2 Adsorption of Na+ and Pb2+ on GO(A—C) and CO-EDTA3(D—F)(A) and (D) Initial structures; (B) and (E) final snapshots; (C) and (F) two local amplifications of absorbed layers. The GO and GO-EDTA3 are represented by sticks and balls, respectively. Red and gray balls represent oxygen atoms and carbon atoms, respectively. Sodium ions and lead ions are shown in pink and dark gold balls. Green balls represent chloride ions. Water molecules are represented by red lines.
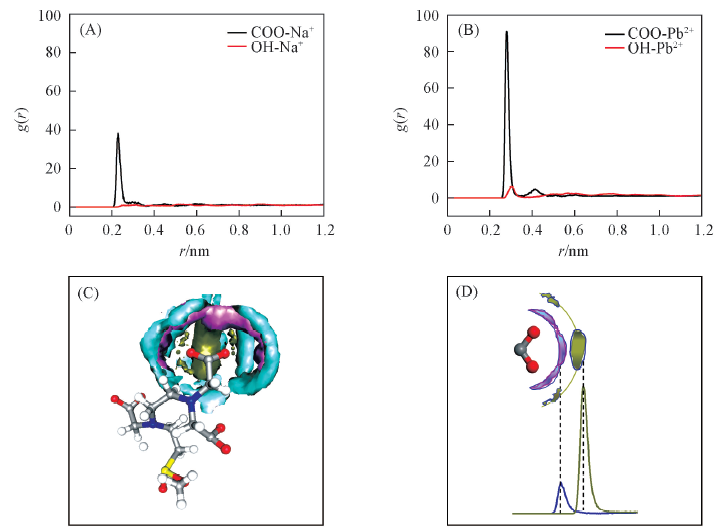
Fig.4 Microstructures of metal ions around carboxyl groups of GO-EDTA3 oxide membrane(A) RDFs of Na+ around carboxyl groups and hydroxyl groups; (B) RDFs of Pb2+ around carboxyl groups and hydroxyl groups; (C) SDFs of Pb2+, Na+ and water molecules around carboxyl groups; (D) schematic diagram of metal ion in absorption layer. Sodium ions are shown in pink ribbon. Lead ions and water molecules are represented in dark gold and blue-green ribbons, respectively.
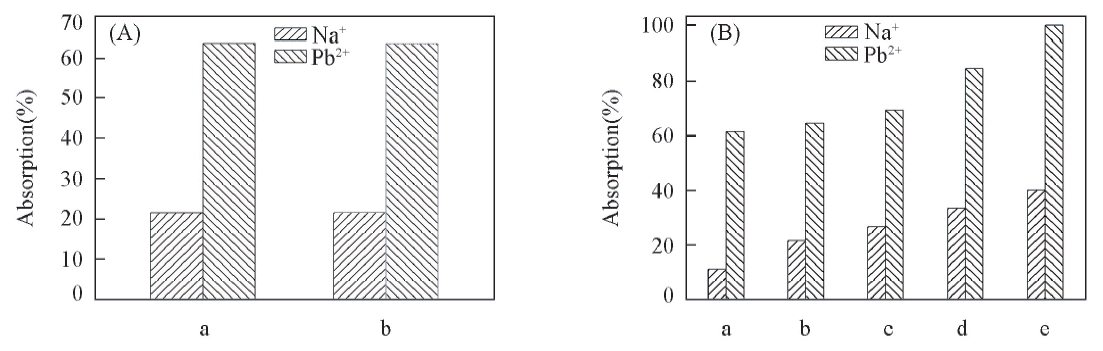
Fig.6 Absorption percentages of Na+ and Pb2+ in considered systems(A) a. GO-EDTA1; b. GO-EDTA1'. (B) a. GO; b. GO-EDTA1; c. GO-EDTA2; d. GO-EDTA3; e. GO-EDTA4.
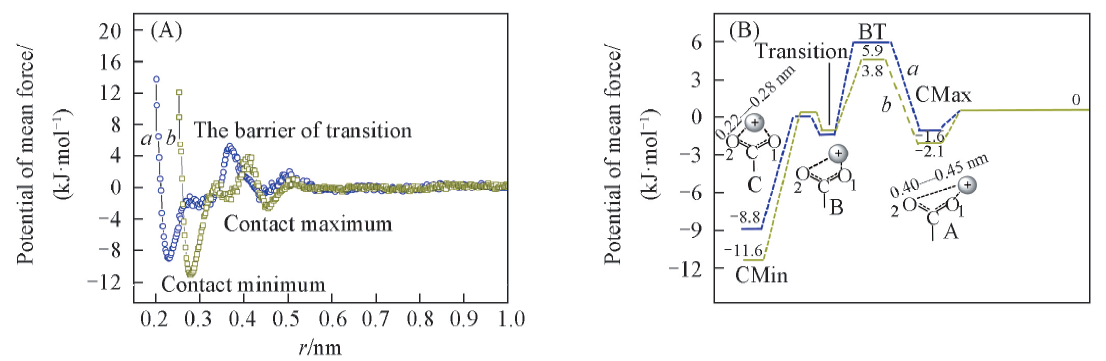
Fig.8 PMF between carboxyl oxygen atoms and metal ions(A) and the binding energy of carboxyl groups and metal ions, and schematic diagram of combining structures at minimum points for clarity(B)a. Na+; b. Pb2+.
| Ion | ΔE+/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔE-/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|
| Na+ | 7.5 | 14.7 |
| Pb2+ | 5.9 | 15.4 |
Table 2 Binding and dissociation energies between ions and carboxyl oxygen atoms
| Ion | ΔE+/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔE-/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|
| Na+ | 7.5 | 14.7 |
| Pb2+ | 5.9 | 15.4 |
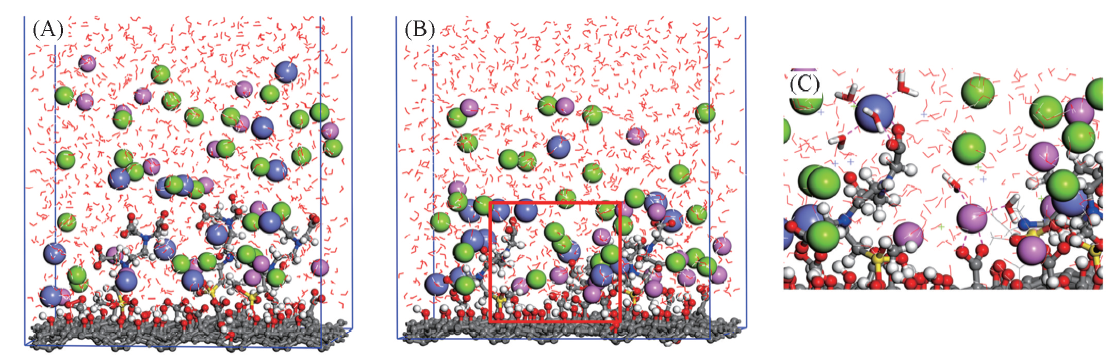
Fig.9 Adsorption of Na+ and Ca2+ on GO-EDTA3(A) Initial structures; (B) final snapshots; (C) local amplifications of absorbed layers. The GO-EDTA3 is represented by sticks and balls. Sodium ions and calcium ions are shown in pink and purple balls. Green balls represent chloride ions.
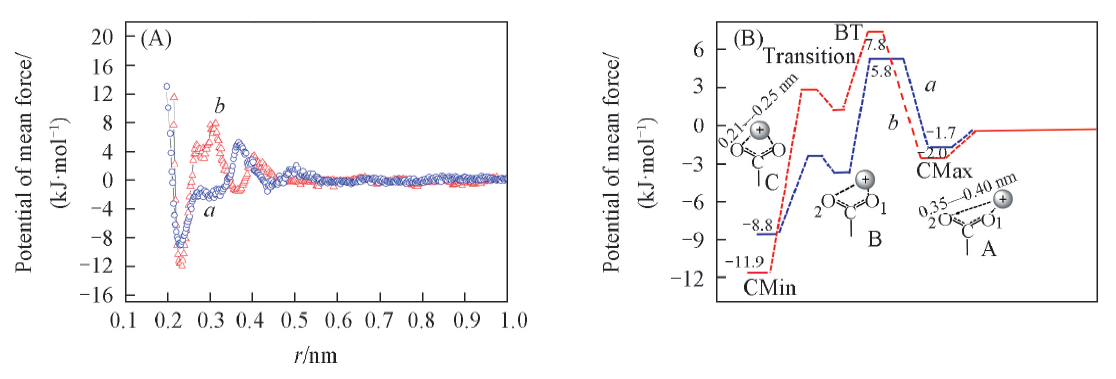
Fig.10 PMF between carboxyl oxygen atoms and metal ions(A) and the binding energy of carboxyl groups and metal ions, and schematic diagram of combining structures at minimum points for clarity(B)a. Na+; b. Ca2+.
| [1] | Agrawal C. M., Ray R. B., Journal of Biomedical Materials Research,2001, 55, 141—150 |
| [2] | Guelcher S. A., Tissue Engineering Part B: Reviews, 2008, 14, 3—17 |
| [3] | Lerf A., He H., Forster M., Klinowski J., The Journal of Physical Chemistry B,1998, 102, 4477—4482 |
| [4] | Dreyer D. R., Park S., Bielawski C. W., Ruoff R. S., Chemical Society Reviews,2010, 39, 228—240 |
| [5] | Mkhoyan K. A., Contryman A. W., Silcox J., Stewart D. A., Eda G., Mattevi C., Miller S., Chhowalla M., Nano Letters,2009, 9, 1058—1063 |
| [6] | Zhao G., Li J., Ren X., Chen C., Wang X., Environmental Science & Technology,2011, 45, 10454—10462 |
| [7] | Lee J. H., Kim B. S., Lee J. C., Park S., Materials Science Forum,2005, 486/487, 510—513 |
| [8] | Repo E., Warchoł J. K., Bhatnagar A., Sillanpää M., Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2011, 358, 261—267 |
| [9] | Madadrang C. J., Kim H. Y., Gao G., Wang N., Zhu J., Feng H., Gorring M., Kasner M. L., Hou S., ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2012, 4, 1186—1193 |
| [10] | Wan S., He F., Wu J., Wan W., Gu Y., Gao B., Journal of Hazardous Materials,2016, 314, 32—40 |
| [11] | Anitha K., Namsani S., Singh J. K., The Journal of Physical Chemistry A,2015, 119, 8349—8358 |
| [12] | Guo K., Zhang H., Yuan S. L., Liu C. B., Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities,2015, 36(11), 2171—2178 |
| (郭凯, 苑世领, 刘成卜. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(11), 2171—2178) | |
| [13] | Ma Y., Zhang H., Yuan S. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2015, 36(2), 386—394 |
| (马莹, 张恒, 苑世领. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(2), 386—394) | |
| [14] | Jorgensen W. L., Maxwell D. S., Tirado-Rives J., Journal of the American Chemical Society,1996, 118, 11225—11236 |
| [15] | Van Der Spoel D., Lindahl E., Hess B., Groenhof G., Mark A. E., Berendsen H. J., Journal of Computational Chemistry,2005, 26, 1701—1718 |
| [16] | Hess B., Kutzner C., David V. D. S., Lindahl E., Journal of Chemical Theory & Computation,2008, 4(3), 435—447 |
| [17] | Accelrys Software Inc., Materials Studio, Release 4.4, Accelrys Software Inc.,San Diego, 2008 |
| [18] | Anitha K., Namsani S., Singh J. K., Journal of Physical Chemistry A,2015, 119, 8349—8358 |
| [19] | Zhang H., Wang H., Lin C. G., Wang L., Yuan S. L., Acta Chimica Sinica,2013, 71(4), 649—656 |
| (张恒, 王华, 蔺存国, 王利, 苑世领. 化学学报, 2013, 71(4), 649—656) | |
| [20] | Andre M. K., Contryman A. W., Silcox J., Stewart D. A., Eda G., Mattevi C., Miller S., Chhowalla M., Nano Letters,2009, 9, 1058—1063 |
| [21] | Allen T. W., Andersen O. S., Roux B., Biophysical Chemistry,2006, 124, 251—267 |
| [22] | Andre M. K., Contryman A. W., Silcox J., Stewart D. A., Eda G., Mattevi C., Miller S., Chhowalla M., Nano Letters,2009, 9, 1058—1063 |
| [23] | Berendsen H., Grigera J., Straatsma T., Journal of Physical Chemistry,1987, 91, 6269—6271 |
| [1] | GAO Zhiwei, LI Junwei, SHI Sai, FU Qiang, JIA Junru, AN Hailong. Analysis of Gating Characteristics of TRPM8 Channel Based on Molecular Dynamics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [2] | ZENG Xianyang, ZHAO Xi, HUANG Xuri. Mechanism of Inhibition of Glucose and Proton Cotransport Protein GlcPSe by Cytochalasin B [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210822. |
| [3] | LI Hua, YANG Ke, HUANG Junfeng, CHEN Fengjuan. Design and Construction of UiO-66-NH2/wood Composite for Efficient Removal of Trace Heavy Metal Ions from Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210701. |
| [4] | CHEN Hanxiang, BIAN Shaoju, HU Bin, LI Wu. Molecular Simulation of the Osmotic Pressures for LiCl-NaCl-KCl-H2O Solution System [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210727. |
| [5] | YANG Junge, GAO Chengqian, LI Boxin, YIN Dezhong. Preparation of High Thermal Conductivity Phase Change Monolithic Materials Based on Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Surface Modified Graphene Oxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210593. |
| [6] | ZHANG Zhibo, SHANG Han, XU Wenxuan, HAN Guangdong, CUI Jinsheng, YANG Haoran, LI Ruixin, ZHANG Shenghui, XU Huan. Self-Assembly of Graphene Oxide at Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Microparticles Toward High-performance Intercalated Nanocomposites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210566. |
| [7] | HU Bo, ZHU Haochen. Dielectric Constant of Confined Water in a Bilayer Graphene Oxide Nanosystem [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [8] | YU Bin, CHEN Xiaoyan, ZHAO Yue, CHEN Weichang, XIAO Xinyan, LIU Haiyang. Graphene Oxide-based Cobalt Porphyrin Composites for Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210549. |
| [9] | WANG Xueli, SONG Xiangwei, XIE Yanning, DU Niyang, WANG Zhenxin. Preparation, Characterization of Partially Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Killing Effect on Human Cervical Cancer Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210595. |
| [10] | ZHANG Mi, TIAN Yafeng, GAO Keli, HOU Hua, WANG Baoshan. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Physicochemical Properties of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Fluoride Dielectrics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220424. |
| [11] | ZHANG Lingyu, ZHANG Jilong, QU Zexing. Dynamics Study of Intramolecular Vibrational Energy Redistribution in RDX Molecule [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220393. |
| [12] | LI Congcong, LIU Minghao, HAN Jiarui, ZHU Jingxuan, HAN Weiwei, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study of the Catalytic Activity of VmoLac Non-specific Substrates Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2518. |
| [13] | LEI Xiaotong, JIN Yiqing, MENG Xuanyu. Prediction of the Binding Site of PIP2 in the TREK-1 Channel Based on Molecular Modeling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2550. |
| [14] | ZHU Deshuai, ZHAO Jianying, YANG Zhenghui, GUO Haiquan, GAO Lianxun. Graphene Oxide/Polyimide Composites with High Energy Storage Density Based on Multilayer Structure [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2694. |
| [15] | LIU Shasha, ZHANG Heng, YUAN Shiling, LIU Chengbu. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Pulsed Electric Field O/W Emulsion Demulsification [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2170. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||