

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (12): 2246.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160428
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIN Xiao, LI Youji*( ), LI Ming, TANG Ningmei, LI Ziqin, HAN Zhiying
), LI Ming, TANG Ningmei, LI Ziqin, HAN Zhiying
Received:2016-06-13
Online:2016-12-10
Published:2016-11-18
Contact:
LI Youji
E-mail:bcclyj@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIN Xiao, LI Youji, LI Ming, TANG Ningmei, LI Ziqin, HAN Zhiying. Preparation and Photoelectrocatalytic Performance of CuO/V2O5/FTO Composite Nanofibers Electrode†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(12): 2246.
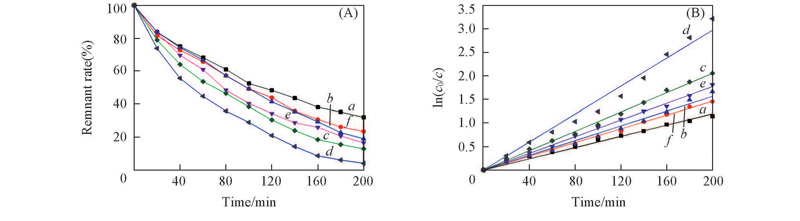
Fig.8 Effects of degradation time on MB degradation remnant rate and ln(c0/c) of different catalysta. V2O5. n(V)/n(Cu): b. 4∶1; c. 2∶1; d. 1∶1; e. 1∶2; f. 1∶4. (B) a. y=0.0149x, R2=0.992; b. y=0.0088x, R2=0.999; c. y=0.0073x, R2=0.998; d. y=0.0060x, R2=0.997; e. y=0.0078x, R2=0.996; f. y=0.0103x, R2=0.999.
| [1] | Dai G. P., Liu S. Q., Liang Y., Luo T., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 264, 157—161 |
| [2] | Xin Y. J., Gao M. C., Wang Y. C., Ma D., Chem. Eng. J., 2014, 242, 162—169 |
| [3] | Li M., Li Y. J., Xu P., Lin X., Han W. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(8), 1596—1605 |
| (李铭, 李佑稷, 徐鹏, 林晓, 韩文轩. 高等学校化学学报,2015, 36(8), 1596—1605) | |
| [4] | Dimitrijevic N. M., Tepavcevic S., Liu Y., Rajh T., Silver S. C., Tiede D. M., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117(30), 15540—15544 |
| [5] | Sui Y. j., Su C. Y., Yang X. D., Hu J. L., Lin X. J., J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2015, 410(2), 226—234 |
| [6] | Guo H. F., Marianna K., Mikko H., Markku L., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2010, 95(3), 358—364 |
| [7] | Li S. P., Liao J. J., Lin S. W., Cao Y., Li J. B., J. Chin. Ceram. Soc., 2011, 39(6), 1034—1044 |
| (李士普, 廖建军, 林仕伟, 曹阳, 李建保. 硅酸盐学报,2011, 39(6), 1034—1044) | |
| [8] | Brezesinski K., Ostermann R., Hartmann P., Perlich J., Brezesinski T., Chem. Mater., 2010, 22, 3079—3084 |
| [9] | Lu B. G., Li X. D., Wang T. H., Xie E. Q., J. Mater. A: Chem., 2013, 1(12), 3900—3906 |
| [10] | Liu B. X., Wang J. S., Li H. Y., Wu J. S., Li Z. F., Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2012, 28(3), 465—470 |
| (刘柏雄, 王金淑, 李洪义, 吴俊书, 李志飞. 无机化学学报,2012, 28(3), 465—470) | |
| [11] | Dai Y. M., Lee W. W., Lin W., Chen. C., J. Chin. Chem. Soc., 2013, 60(12), 1415—1424 |
| [12] | Li X. M., Lü N., Liang S. L., Li X. H., Chin. J. Lumin., 2014, 35(6), 695—700 |
| (李晓梅, 吕娜, 梁士利, 李兴华. 发光学报,2014, 35(6), 695—700) | |
| [13] | Yousef A., Barakat A. M., Kim H. Y., Appl. Catal. A, 2013, 467, 98—106 |
| [14] | Li X., Li J. H., Li S. J., Fang X., Fang F., Chu X. Y., Wang X. H., Hu J. X., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities., 2013, 29(6), 1032—1035 |
| [15] | Shi H. M., Zhou M., Song D. F., Pan X. J., Fu J. C., Zhou J. Y., Ma S. Y., Wang T., Ceram. Int., 2014, 40(7), 10383—10393 |
| [16] | Chuai H. Y., Zhou D. F., Zhu X. F., Yang G. C., Li Z. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(5), 941—948 |
| (揣宏媛, 周德凤, 朱晓飞, 杨国程, 李朝辉. 高等学校化学学报,2014, 35(5), 941—948) | |
| [17] | Wang H. Z., Liu N., Lu J., Yao S. W., Jiang S. S., Zhang W. G., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities., 2015, 31(5), 846—850 |
| [18] | Luo F., Zhou D. F., Yang G. C., Liu J. W., Li Z. H., Meng J., Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2013, 29(3), 500—506 |
| (罗飞, 周德凤, 杨国程, 刘建伟, 李朝辉, 孟健. 无机化学学报,2013, 29(3), 500—506) | |
| [19] | Suresh R., Giribabu K., Manigandan R., Munusamy S., Kumar S. P., Muthamizh S., Stephen A., Narayanan V., J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 598, 151—160 |
| [20] | Wang Y., Zhang J. W., Liu L. X., Zhu C. Q., Liu X. Q., Su Q., Mater. Lett., 2012, 75, 95—98 |
| [21] | Guo Y., Li J. H., Gao Z. Q., Zhu X., Liu Y., Wei Z. B., Zhao W., Sun C., Appl. Catal. B-Environ., 2016, 192(5), 57—71 |
| [22] | Marwa A., Joseph P. T., Zhang L., Kam T. L., Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2016, 152, 87—93 |
| [23] | Liu W. M., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2013, 29(2), 314—318 |
| [24] | Cornelia B., Corina O., Corina M., Carmen L., Paula S., Sorin O., Chin. J. Chem. Eng., 2014, 22(1), 38—42 |
| [25] | Liu H., Wu Y., Zhang J., ACS Appl. Mat. Interfaces, 2011, 3(5), 1757—1764 |
| [26] | Wang D. J., Guo L., Li D. S., Fu F., Wang W. L., Yan H. T., Spectrosc. Spect. Anal., 2008, 28(4), 788—792 |
| (王丹军, 郭莉, 李东升, 付峰, 王文亮, 闫宏涛. 光谱学与光谱分析,2008, 28(4), 788—792) | |
| [27] | Chin S., Park E., Kim M., Bae G., Jurng J., Mater. Lett., 2012, 75, 57—60 |
| [28] | Su C. Y., Shao C. L., Liu Y. C., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2011, 59, 220—227 |
| [29] | Patil C. E., Jadhav P. R., Tarwal N. L., Deshmukh H. P., Karanjkar M. M., Patil P. S., Mater. Chem. Phys., 2011, 126, 711—716 |
| [1] | WU Yu, LI Xuan, YANG Hengpan, HE Chuanxin. Construction of Cobalt Single Atoms via Double-confinement Strategy for High-performance Electrocatalytic Reduction of Carbon Dioxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220343. |
| [2] | YANG Ruiqi, YU Xin, LIU Hong. Scientific Study of Photocatalytic Material Based on Sn3O4 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1340. |
| [3] | WANG Xia, LIU Yanji, JIA Yongfeng, JI Lei, HU Quanli, DUAN Limei, LIU Jinghai. Preparative Chemistry of N-containing Porous Carbon Nanofibers for Capacity Improvement in Lithium-sulfur Battery † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 829. |
| [4] | QIN Chunping, WANG Xianliu, TANG Han, YI Bingcheng, LIU Chang, ZHANG Yanzhong. Osteogenesis-promoting Effects of the Electrospun Nanofibers Containing Decellularized Bone Matrix † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 780. |
| [5] | LIU Fen, ZHOU Min, WANG Suxia, WANG Rong, YANG Ning, MA Yongjun. Study on Photoelectrocatalytic Decolorization Mechanism of Methylene Blue Under the Visible-light Irradiation by Measuring Chemical Oxygen Demand Index† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1988. |
| [6] | WANG Yongpeng,XU Zibo,LIU Mengzhu,ZHANG Haibo,JIANG Zhenhua. Non-enzymatic Glucose Sensor Based on the Electrospun Porous Foamy Copper Oxides Micro-nanofibers† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1310. |
| [7] | CAI Jiao,YU Qiongwei,HE Xiaomei,XU Jing,DING Qiong,FENG Yuqi. Preparation of SiW11 Incorporated SiO2 Nanofibers(SiW11/SiO2) and Its Application in the Analysis of Polyamines in Arabidopsis† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 901. |
| [8] | ZHAO Yuxuan,CHEN Yanjun,PAN Guxin,WANG Chang,PENG Zhenbo,SUN Zongxu,LIANG Yongri,SHI Qisong. Preparation and Performance of Novel Tb-PEG+Eu-PEG/PANI/PAN Luminescent-electrical-phase Change Composite Fibers by Electrospinning† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 824. |
| [9] | GAO Ningxiao,XU Yulong,LIU Yong. Preparation of Carbon Dots from Soy Milk Powder and Fluorescent Nanofibers Containing Carbon Dots† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(3): 555. |
| [10] | ZHANG Xinmu,CUI Xiangxu,YAOMA Kangyue,LI Tingting,ZHANG Zhiming. Electrospinning Preparation and Photocatalytic Activity of H4SiW12O40/Ethylene Vinyl Alcohol Copolymer Nanofibrous Membrane† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 372. |
| [11] | XU Dan,DING Yadan,WANG Xue,CONG Tie,LIU Junping,HONG Xia,PAN Ying. Microdroplet Detection of Protein Based on Superhydrophobic Polystyrene Film† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 1913. |
| [12] | NIE Guangdi, ZHU Yun, TIAN Di, WANG Ce. Research Progress in the Electrospun Nanofiber-based Supercapacitor Electrode Materials† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1349. |
| [13] | ZHOU Ying, WANG Xianliu, YI Bingcheng, YU Zhepao, YANG Shangying, SHEN Yanbing, ZHANG Yanzhong. Engineering Shape Memory Enabled Composite Nanofibers for Bone Tissue Engineering† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1554. |
| [14] | HAN Zhiying, LI Youji, LIN Xiao, WANG Ziyu, LI Ziqin, WANG Hao. Preparation and Photoelectrocatalytic Performance of Fe2O3/ZnO Composite Electrode Loading on Conductive Glass† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(4): 771. |
| [15] | REN Jing, WANG Shugang, LI Yanchun, YANG Qingbiao, SONG Yan, LI Yaoxian. Preparation of AOPAN@PAN Coaxial Nanofiber Membrane and It’s Adsorption Property† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(4): 825. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||