

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (6): 1216.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150939
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Boyuan, GUO Zhaoxia*( ), YU Jian*(
), YU Jian*( )
)
Received:2015-12-09
Online:2016-06-10
Published:2016-05-10
Contact:
GUO Zhaoxia,YU Jian
E-mail:guozx@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn;yujian03@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHANG Boyuan, GUO Zhaoxia, YU Jian. Effects of Glass Fiber on Electrical Conductivities of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube-filled Polymer/Thermoplastic Polyurethane Blends[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(6): 1216.
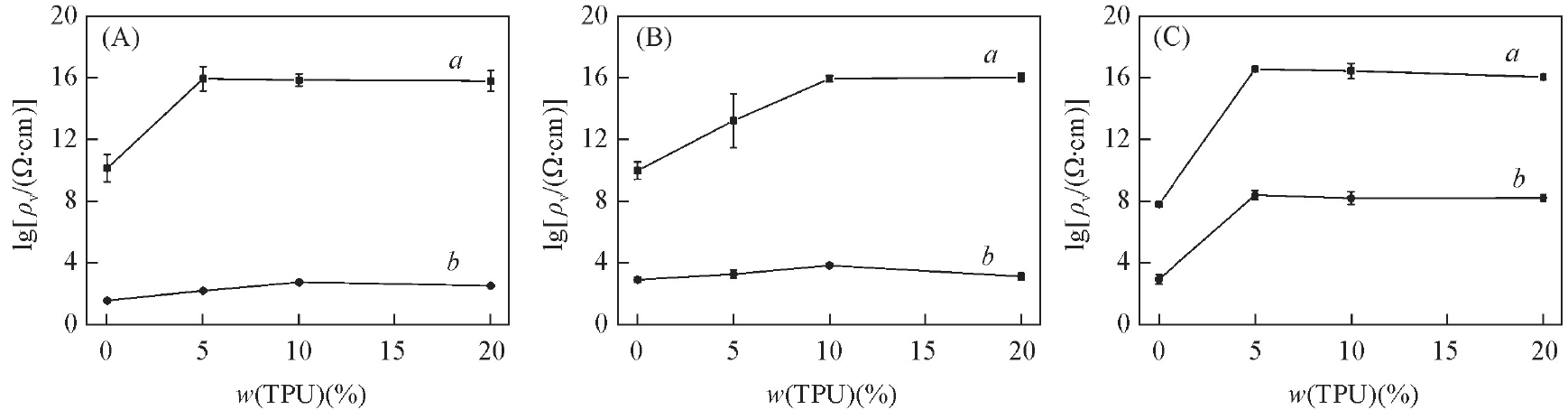
Fig.1 Effects of GF on electrical resistivities of PP/TPU/MWCNT(A), PMMA/TPU/MWCNT(B) and PLA/TPU/MWCNT(C) composites(A) a. PP/TPU/4%MWCNT, b. PP/TPU/4%MWCNT/20%GF; (B) a. PMMA/TPU/1.5%MWCNT,b. PMMA/TPU/1.5%MWCNT/20%GF; (C) a. PLA/TPU/1%MWCNT, b. PLA/TPU/1%MWCNT/20%GF.
| Sample | Contact angle/(°) | γ/(mN·m-1) | γd/(mN·m-1) | γp/(mN·m-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Diiodomethane | ||||
| PP | 97.3 | 49.5 | 38.1 | 37.9 | 0.2 |
| PMMA | 66.6 | 26.5 | 46.2 | 36.1 | 10.1 |
| PLA | 74.3 | 39.8 | 40.0 | 32.5 | 7.5 |
| TPU | 102.4 | 73.4 | 21.5 | 20.4 | 1.1 |
Table 1 Contact angles in water and diiodomethane and surface tensions of all polymers at 20 ℃
| Sample | Contact angle/(°) | γ/(mN·m-1) | γd/(mN·m-1) | γp/(mN·m-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Diiodomethane | ||||
| PP | 97.3 | 49.5 | 38.1 | 37.9 | 0.2 |
| PMMA | 66.6 | 26.5 | 46.2 | 36.1 | 10.1 |
| PLA | 74.3 | 39.8 | 40.0 | 32.5 | 7.5 |
| TPU | 102.4 | 73.4 | 21.5 | 20.4 | 1.1 |
| Sample | Temperature/℃ | γ/(mN·m-1) | γd/(mN·m-1) | γp/(mN·m-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP | 200 | 26.5 | 26.4 | 0.1 |
| PMMA | 200 | 32.3 | 25.2 | 7.1 |
| PLA | 190 | 28.5 | 23.2 | 5.3 |
| TPU | 200 | 15.0 | 14.2 | 0.8 |
| TPU | 190 | 15.3 | 14.5 | 0.8 |
| MWCNTs[ | 45.3 | 18.4 | 26.9 | |
| MWCNTs[ | 27.8 | 17.6 | 10.2 |
Table 2 Surface tensions of all polymers at processing temperature
| Sample | Temperature/℃ | γ/(mN·m-1) | γd/(mN·m-1) | γp/(mN·m-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP | 200 | 26.5 | 26.4 | 0.1 |
| PMMA | 200 | 32.3 | 25.2 | 7.1 |
| PLA | 190 | 28.5 | 23.2 | 5.3 |
| TPU | 200 | 15.0 | 14.2 | 0.8 |
| TPU | 190 | 15.3 | 14.5 | 0.8 |
| MWCNTs[ | 45.3 | 18.4 | 26.9 | |
| MWCNTs[ | 27.8 | 17.6 | 10.2 |
| System | ωa | Predicted location of MWCNTs | System | ωa | Predicted location of MWCNTs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP/TPU/MWCNT[ | 0.7 | Interface | PMMA/TPU/MWCNT[ | -0.8 | Interface |
| PP/TPU/MWCNT[ | 0.8 | Interface | PLA/TPU/MWCNT[ | -1.9 | PLA phase |
| PMMA/TPU/MWCNT[ | -1.5 | PMMA phase | PLA/TPU/MWCNT[ | -1.1 | PLA phase |
Table 3 Wetting coefficients and predicted locations of MWCNTs
| System | ωa | Predicted location of MWCNTs | System | ωa | Predicted location of MWCNTs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP/TPU/MWCNT[ | 0.7 | Interface | PMMA/TPU/MWCNT[ | -0.8 | Interface |
| PP/TPU/MWCNT[ | 0.8 | Interface | PLA/TPU/MWCNT[ | -1.9 | PLA phase |
| PMMA/TPU/MWCNT[ | -1.5 | PMMA phase | PLA/TPU/MWCNT[ | -1.1 | PLA phase |
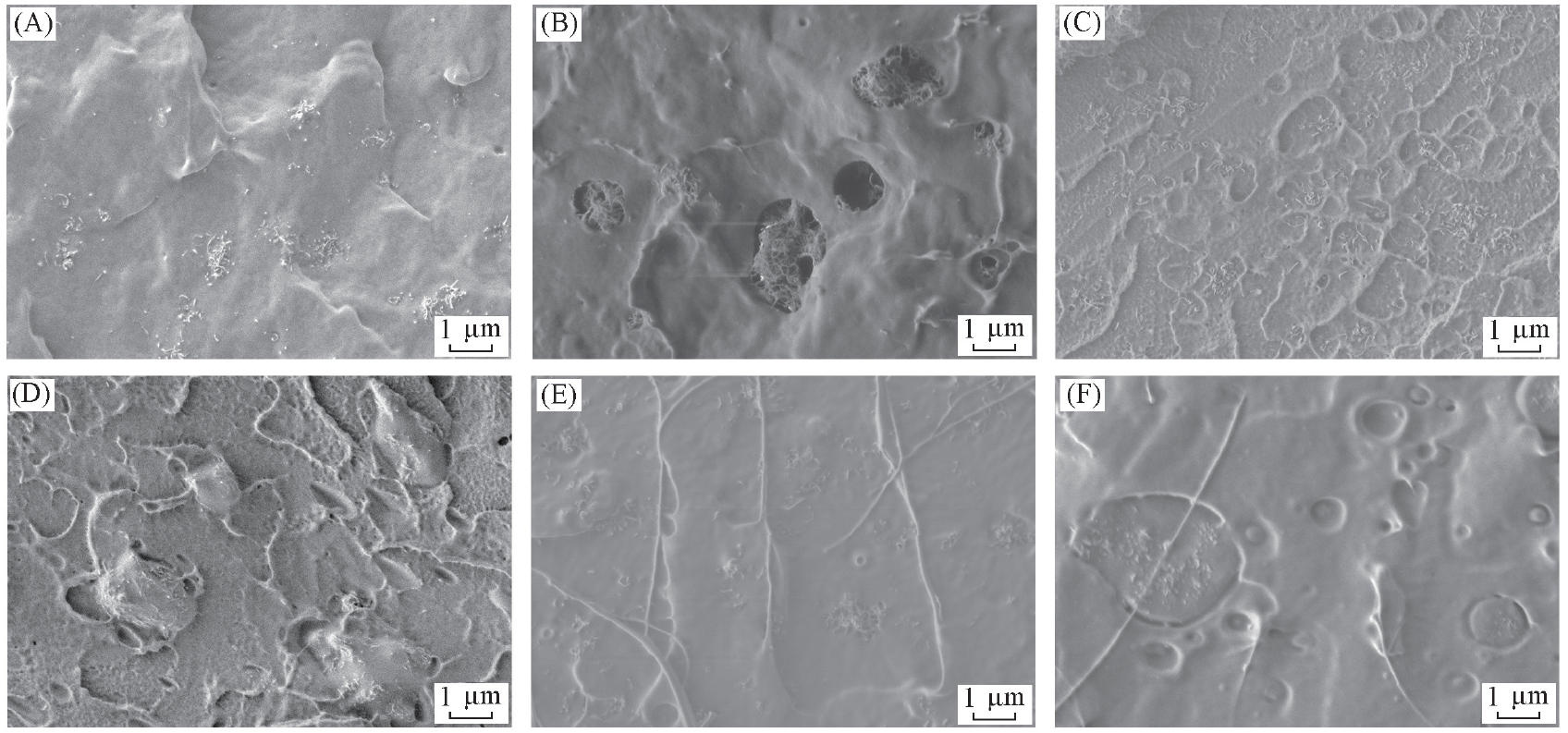
Fig.2 FESEM images of PP/4%MWCNT(A), PP/10%TPU/4%MWCNT after etching(B), PMMA/1.5%MWCNT(C), PMMA/10%TPU/1.5%MWCNT(D), PLA/1%MWCNT(E) and PLA/10%TPU/1%MWCNT(F) composites

Fig.3 FESEM images of PP/4%MWCNT/20%GF(A), PP/10%TPU/4%MWCNT/20%GF(B) and PP/20%TPU/4%MWCNT/20%GF(C) compositesTop inset of (B): PP matrix; bottom inset of (B): GF surface.
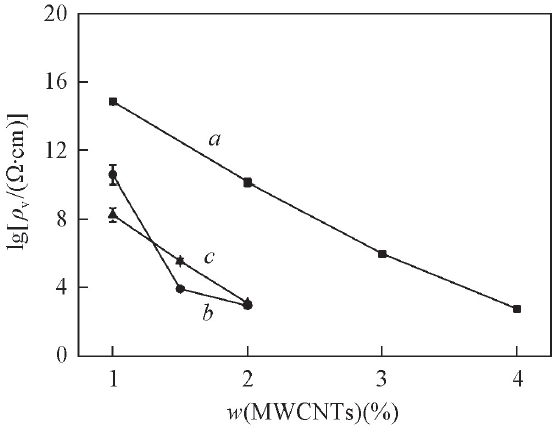
Fig.7 Effects of MWCNTs contents on electrical resistivities of polymer/10%TPU/MWCNT/20%GF compositesa. PP/10%TPU/MWCNT/20%GF;b. PMMA/10%TPU/MWCNT/20%GF;c. PLA/10%TPU/MWCNT/20%GF.
| [1] | Baughman R. H., Zakhidov A. A., de Heer W. A., Science, 2002, 297, 787—792 |
| [2] | Spitalsky Z., Tasis D., Papagelis K., Galiotis C., Prog. Polym. Sci., 2010, 35, 357—401 |
| [3] | Deng H., Lin L., Ji M. Z., Zhang S. M., Yang M. B., Fu Q., Prog. Polym. Sci., 2014, 39, 627—655 |
| [4] | Bauhofer W., Kovacs J. Z., Compos. Sci. Tech., 2009, 69, 1486—1498 |
| [5] | Göldel A., Marmur A., Kasaliwal G. R., Pötschke P., Heinrich G., Macromolecules, 2011, 44, 6094—6102 |
| [6] | Göldel A., Kasaliwal G., Pötschke P., Macromol. Rapid. Commun., 2009, 30, 423—429 |
| [7] | Pötschke P., Bhattacharyya A. R., Janke A., Polymer, 2003, 44, 8061—8069 |
| [8] | Gubbels F., Blacher S., Vanlathem E., Jerome R., Deltour R., Brouers F., Teyssie Ph., Macromolecules, 1995, 28, 1559—1566 |
| [9] | Gubbels F., Jerome R., Teyssie P., Vanlathem E., Deltour R., Calderone A., Parente V., Parente J.L., Macromolecules, 1994, 27, 1972—1974 |
| [10] | Sumita M., Sakata K., Hayakawa Y., Asai S., Miyasaka K., Tanemura M., Colloid. Polym. Sci., 1992, 270, 134—139 |
| [11] | Sumita M., Sakata K., Asai S., Miyasaka K., Nakagawa H., Polym. Bull., 1991, 25, 265—271 |
| [12] | Fenouillot F., Cassagnau P., Majeste J. C., Polymer, 2009, 50, 1333—1350 |
| [13] | Xiong Z. Y., Zhang B. Y., Wang L., Yu J., Guo Z. X., Carbon, 2014, 70, 233—240 |
| [14] | Xiong Z. Y., Wang L., Sun Y., Guo Z. X., Yu J., Polymer, 2013, 54, 447—455 |
| [15] | Sun Y., Jia M. Y., Guo Z. X., Yu J., Nagai S., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2011, 120, 3224—3232 |
| [16] | Sun Y., Guo Z. X., Yu J., Macromol. Mater. Eng., 2010, 295, 263—268 |
| [17] | Xiong Z. Y., Sun Y., Wang L., Guo Z. X., Yu J., Sci. China Chem., 2012, 55, 808—813 |
| [18] | Xu Z. B., Zhao C., Gu A. J., Fang Z. P., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2007, 103, 1042—1047 |
| [19] | Zhang B. Y., Xu L., Guo Z. X., Yu J., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2015, 132, 41794 |
| [20] | Zhang B.Y., Xu l., Guo Z. X., Yu J.,Polym. Composite, 2015, DOI: 10.1002/pc.23697 |
| [21] | Narkis M., Lidor G., Vaxman A., Zuri L., Electronics Packaging Manufacturing, IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf., 2000, 23, 239—245 |
| [22] | Narkis M., Lidor G., Vaxman A., Zuri L., J. Electrostat., 1999, 47, 201—214 |
| [23] | Li Y., Wang S. F., Zhang Y., Zhang Y. X., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2005, 98, 1142—1149 |
| [24] | Liu Y. K., Tan X. L., Chen J. Z., Niu M. J., Liu X. Y., Guan L. F., Li X. F., Pack. Eng., 2007, 28, 39—41 |
| (刘玉坤, 谭晓莉, 陈金周, 牛明军, 刘雪莹, 管兰芳, 李新法. 包装工程, 2007, 28, 39—41) | |
| [25] | Fan M., Chen J. Z., Liu X. Y., Liu Y. K., Li L. F., Wang J. W., Chin. Plast. Ind., 2004, 32, 43—45 |
| (樊敏, 陈金周, 刘雪莹, 刘玉坤, 李新法, 王经武. 塑料工业, 2004, 32, 43—45) | |
| [26] | Poomalai P., Siddaramaiah, J. Macromol. Sci. A, 2005, 42, 1399—1407 |
| [27] | Jing X., Mi H. Y., Peng X. F., Turng L. S., Polym. Eng. Sci., 2015, 55, 70—80 |
| [28] | Han J. J., Huang H. X., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2011, 120, 3217—3223 |
| [29] | Han J. J., Huang H. X., Chin. Plast. Ind., 2010, 38, 67—71 |
| (韩娟娟, 黄汉雄. 塑料工业, 2010, 38, 67—71) | |
| [30] | Tavana H., Lam C. N. C., Grundke K., Friedel P., Kwok D. Y., Hair M. L., Neumann A. W., J. Colloid. Interf. Sci., 2004, 279, 493—502 |
| [31] | Shimizu R. N., Demarquette N. R., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2000, 76, 1831—1845 |
| [32] | Wu S., Surface and Interfacial Tensions of Polymers, Oligomers, Plasticizers, and Organic Pigments, Wiley Database of Polymer Properties, 2003, 521—522 |
| [33] | Nuriel S., Liu L., Barber A. H., Wagner H. D., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2005, 404, 263—266 |
| [34] | Barber A. H., Cohen S. R., Wagner H. D., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2004, 92, 186103 |
| [1] | LUO Xinyan, JIA Ruonan, XIANG Yong, ZHANG Xiaokun. Progress on the Stretchable Composite Solid Polymer Electrolytes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220149. |
| [2] | YAN Jiasen, HAN Xianying, DANG Zhaohan, LI Jiangang, HE Xiangming. Preparation and Performance of Paraffin/Expanded Graphite/Graphene Composite Phase Change Heat Storage Material [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220054. |
| [3] | YANG Junge, GAO Chengqian, LI Boxin, YIN Dezhong. Preparation of High Thermal Conductivity Phase Change Monolithic Materials Based on Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Surface Modified Graphene Oxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210593. |
| [4] | WAN Ren, SONG Fan, PENG Changjun, LIU Honglai. Group Contribution Method for Infinite Dilution Molar Conductivity of Unconventional Ions in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3672. |
| [5] | ZHANG Ruqiang, ZHANG Guoliang, LONG Zhu, ZHANG Dan, LI Zhiqiang, WANG Shihua, HU Ailin. Preparation and Properties of Light-weight Flexible Polyimide Paper-based Electromagnetic Shielding Composites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3211. |
| [6] | LI Hongbin, ZHANG Shuai, LI Zheng, DING Changjiang, BEN Teng. Synthesis and Anisotropic Proton Conduction of Porous Organic Salt Single Crystal [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3047. |
| [7] | XIE Fan,WANG Yafang,ZHUO Longhai,QIN Panliang,NING Doudou,WANG Danni,LU Zhaoqing. Preparation and Properties of High Thermal Conductivity Hexagonal Boron Nitride/Aramid Fibrid Composite Film † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 582. |
| [8] | LING Xuxia, LONG Zhu, WANG Shihua, LI Zhiqiang, GUO Shuai, ZHANG Dan. Surface Modified Aramid Pulp with Polyaniline and Conductivity of Its Paper-based Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2553. |
| [9] | SONG Xipeng, LIU Jinyu, WANG Lihua, HAN Xutong, HUANG Qinglin. Preparation of Polybenzimidazole/Polyvinylpyrrolidone Proton Exchange Membranes for Vanadium Redox Flow Battery† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1543. |
| [10] | ZHU Yuxin,HARAGIRIMANA Alphonse,LU Yao,BUREGEYA Ingabire Providence,NING Cong,LI Na,HU Zhaoxia,CHEN Shouwen. Preparation and Properties of Filling-type Sulfonated Poly(arylene ether sulfone)/Poly(ether sulfone) Composite Membranes with Microporous Structures† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 1051. |
| [11] | CHENG Yingying,LIU Haiying,TIAN Yigeng,LIU Zhongqi,LI Qingxin. Theoretical Study on Enhancement Effect of Amino Modification of Adenine on Conductivity of DNA† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 279. |
| [12] | GUAN Mingming,CHEN Jia,TANG Shaokun. Synthesis and Performance of Novel Bis-functional Cross-linked Anion Exchange Membranes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 2054. |
| [13] | GAO Feilong, LI Yongcun, LUAN Yunbo, XUE Zhicheng, GUO Zhangxin, ZHANG Qi, WU Guiying. Enhancement Mechanisms of Mechanical and Self-Healing Properties of Thermoplastic Polyurethane Composites Induced by Different G-CNT Hybridization Systems† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(4): 832. |
| [14] | YAN Fei, ZHANG Min, ZHANG Lu, LI Chengtao, LI Yichen. Interfacial Interaction and Compatibilizing Mechanism of PVDF/TPU Blends [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5): 888. |
| [15] | XU Yixin, ZHANG Dengji, YE Niya, YANG Jingshuai, HE Ronghuan. Phosphonium-based Crosslinked Poly(aryl ether ketone) Anion Exchange Membranes with 1,4-Bis(diphenylphosphino)butane as the Crosslinker† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(10): 1872. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||