

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 1051.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180785
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHU Yuxin, HARAGIRIMANA Alphonse, LU Yao, BUREGEYA Ingabire Providence, NING Cong, LI Na, HU Zhaoxia*( ), CHEN Shouwen*
), CHEN Shouwen*
Received:2018-11-21
Online:2019-05-06
Published:2019-05-09
Contact:
HU Zhaoxia,CHEN Shouwen
E-mail:huzhaoxia@njust.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHU Yuxin,HARAGIRIMANA Alphonse,LU Yao,BUREGEYA Ingabire Providence,NING Cong,LI Na,HU Zhaoxia,CHEN Shouwen. Preparation and Properties of Filling-type Sulfonated Poly(arylene ether sulfone)/Poly(ether sulfone) Composite Membranes with Microporous Structures†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 1051.
| Sample | IECa/ (mmol·g-1) | WU(%) | SR(%) | σ/(mS·cm-1) | Mass lossb(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 ℃ | 80 ℃ | 30 ℃ | 30 ℃ | 90 ℃ | |||
| S30-20 | 0.21 | 64.1±5.0 | 198.4±12.6 | 0.20±0.01 | 5.0±0.2 | 16.2±0.4 | 0.20 |
| S30-30 | 0.36 | 86.2±7.0 | 209.8±12.8 | 0.90±0.07 | 10.1±0.3 | 26.7±0.8 | 0 |
| S30-40 | 0.42 | 91.3±11.3 | 205.9±11.8 | 1.70±0.07 | 16.0±0.5 | 32.1±1.4 | 0 |
| S40-20 | 0.30 | 83.3±6.8 | 161.7±11.4 | 0.43±0.05 | 6.3±0.2 | 24.8±1.2 | 0.07 |
| S40-30 | 0.41 | 116.6±12.5 | 226.5±13.5 | 1.22±0.09 | 9.9±0.2 | 37.0±1.6 | 0.15 |
| S40-40 | 0.58 | 122.8±7.1 | 201.6±12.3 | 2.15±0.10 | 16.9±0.6 | 32.1±1.5 | 0.20 |
| S50-20 | 0.32 | 102.8±8.3 | 244.8±15.4 | 0.58±0.06 | 7.7±0.3 | 19.2±0.6 | 0.05 |
| S50-30 | 0.51 | 136.2±9.5 | 270.4±17.5 | 1.39±0.10 | 1.5±0.1 | 5.8±0.1 | 0.13 |
| S50-40 | 0.69 | 151.1±13.9 | 283.2±18.6 | 3.50±0.14 | 5.4±0.1 | 8.7±0.2 | 0.17 |
| S30-20+F50 | 0.29 | 46.2±2.8 | 186.3±11.9 | 0.24±0.03 | 8.0±0.4 | 41.3±1.6 | 0.58 |
| S30-30+F50 | 0.84 | 50.8±3.4 | 196.2±12.5 | 0.97±0.07 | 26.6±0.9 | 43.2±1.7 | 0.62 |
| S30-40+F50 | 0.69 | 55.6±3.5 | 188.7±12.1 | 1.80±0.09 | 28.0±1.2 | 50.4±2.2 | 0.66 |
| S40-20+F50 | 0.58 | 48.8±2.9 | 148.6±8.9 | 0.54±0.04 | 13.1±0.6 | 30.1±1.4 | 0.67 |
| S40-30+F50 | 0.60 | 72.9±4.4 | 210.6±12.6 | 2.56±0.12 | 18.5±0.7 | 40.2±1.5 | 0.75 |
| S40-40+F50 | 0.66 | 87.7±4.7 | 187.4±11.6 | 4.47±0.31 | 18.0±0.7 | 33.3±1.4 | 0.87 |
| S50-20+F50 | 0.67 | 92.4±6.5 | 222.4±13.4 | 0.78±0.04 | 16.9±0.6 | 28.6±0.9 | 1.01 |
| S50-30+F50 | 0.72 | 93.7±6.8 | 262.1±14.5 | 1.88±0.16 | 5.1±0.2 | 12.1±0.6 | 1.19 |
| S50-40+F50 | 0.78 | 98.2±7.3 | 277.8±14.8 | 3.85±0.22 | 8.8±0.3 | 14.1±0.8 | 0.98 |
Table 1 Water uptake(WU), IEC, swelling rate(SR) and proton conductivity(σ) of microporous membranes and filling membranes
| Sample | IECa/ (mmol·g-1) | WU(%) | SR(%) | σ/(mS·cm-1) | Mass lossb(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 ℃ | 80 ℃ | 30 ℃ | 30 ℃ | 90 ℃ | |||
| S30-20 | 0.21 | 64.1±5.0 | 198.4±12.6 | 0.20±0.01 | 5.0±0.2 | 16.2±0.4 | 0.20 |
| S30-30 | 0.36 | 86.2±7.0 | 209.8±12.8 | 0.90±0.07 | 10.1±0.3 | 26.7±0.8 | 0 |
| S30-40 | 0.42 | 91.3±11.3 | 205.9±11.8 | 1.70±0.07 | 16.0±0.5 | 32.1±1.4 | 0 |
| S40-20 | 0.30 | 83.3±6.8 | 161.7±11.4 | 0.43±0.05 | 6.3±0.2 | 24.8±1.2 | 0.07 |
| S40-30 | 0.41 | 116.6±12.5 | 226.5±13.5 | 1.22±0.09 | 9.9±0.2 | 37.0±1.6 | 0.15 |
| S40-40 | 0.58 | 122.8±7.1 | 201.6±12.3 | 2.15±0.10 | 16.9±0.6 | 32.1±1.5 | 0.20 |
| S50-20 | 0.32 | 102.8±8.3 | 244.8±15.4 | 0.58±0.06 | 7.7±0.3 | 19.2±0.6 | 0.05 |
| S50-30 | 0.51 | 136.2±9.5 | 270.4±17.5 | 1.39±0.10 | 1.5±0.1 | 5.8±0.1 | 0.13 |
| S50-40 | 0.69 | 151.1±13.9 | 283.2±18.6 | 3.50±0.14 | 5.4±0.1 | 8.7±0.2 | 0.17 |
| S30-20+F50 | 0.29 | 46.2±2.8 | 186.3±11.9 | 0.24±0.03 | 8.0±0.4 | 41.3±1.6 | 0.58 |
| S30-30+F50 | 0.84 | 50.8±3.4 | 196.2±12.5 | 0.97±0.07 | 26.6±0.9 | 43.2±1.7 | 0.62 |
| S30-40+F50 | 0.69 | 55.6±3.5 | 188.7±12.1 | 1.80±0.09 | 28.0±1.2 | 50.4±2.2 | 0.66 |
| S40-20+F50 | 0.58 | 48.8±2.9 | 148.6±8.9 | 0.54±0.04 | 13.1±0.6 | 30.1±1.4 | 0.67 |
| S40-30+F50 | 0.60 | 72.9±4.4 | 210.6±12.6 | 2.56±0.12 | 18.5±0.7 | 40.2±1.5 | 0.75 |
| S40-40+F50 | 0.66 | 87.7±4.7 | 187.4±11.6 | 4.47±0.31 | 18.0±0.7 | 33.3±1.4 | 0.87 |
| S50-20+F50 | 0.67 | 92.4±6.5 | 222.4±13.4 | 0.78±0.04 | 16.9±0.6 | 28.6±0.9 | 1.01 |
| S50-30+F50 | 0.72 | 93.7±6.8 | 262.1±14.5 | 1.88±0.16 | 5.1±0.2 | 12.1±0.6 | 1.19 |
| S50-40+F50 | 0.78 | 98.2±7.3 | 277.8±14.8 | 3.85±0.22 | 8.8±0.3 | 14.1±0.8 | 0.98 |
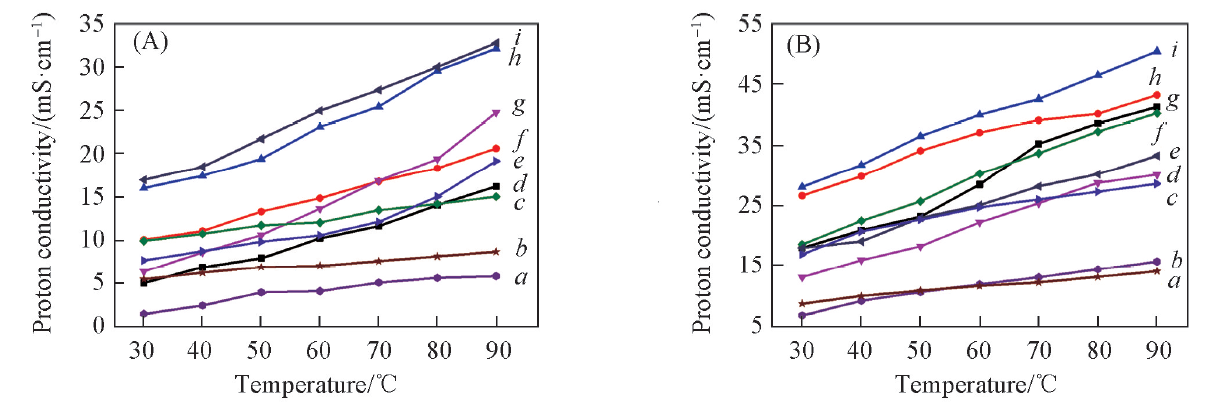
Fig.3 Relationship of proton conductivity and temperature in water of the microporous membranes of Sx-y(A) and Sx-y-F50(B)(A) a. S50-30; b. S50-40; c. S40-30; d. S30-20; e. S50-20; f. S30-30; g. S40-20; h. S30-40; i. S40-40. (B) a. S50-40+F50; b. S50-30+F50; c. S50-20+F50; d. S40-20+F50; e. S40-40+F50; f. S40-30+F50; g. S30-20+F50; h. S30-30+F50; i. S30-40+F50.
| Code | Mass loss(%) | IEC/(mmol·g-1) | σ/(mS·cm-1)(30 ℃) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 24 h | 0 h | 24 h | ||
| S30-20+F50 | 6.3 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 18.0±0.5 | 16.7±0.5 |
| S30-30+F50 | 7.5 | 0.84 | 0.39 | 26.6±0.9 | 20.4±0.8 |
| S30-40+F50 | 8.2 | 0.69 | 0.47 | 28.0±1.2 | 25.6±0.9 |
| S40-20+F50 | 3.2 | 0.58 | 0.35 | 13.1±0.4 | 11.1±0.6 |
| S40-30+F50 | 5.4 | 0.60 | 0.33 | 18.5±0.7 | 16.8±0.8 |
| S40-40+F50 | 21.5 | 0.66 | 0.58 | 18.0±0.9 | 10.7±0.5 |
| S50-20+F50 | 10.6 | 0.67 | 0.30 | 16.9±0.8 | 9.2±0.4 |
| S50-30+F50 | 8.9 | 0.72 | 0.46 | 6.8±0.5 | 5.2±0.3 |
| S50-40+F50 | 17.8 | 0.78 | 0.62 | 8.8±0.6 | 8.1±0.3 |
Table 2 Hydrolytic stability(140 ℃, 24 h) of the filling membranes
| Code | Mass loss(%) | IEC/(mmol·g-1) | σ/(mS·cm-1)(30 ℃) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 24 h | 0 h | 24 h | ||
| S30-20+F50 | 6.3 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 18.0±0.5 | 16.7±0.5 |
| S30-30+F50 | 7.5 | 0.84 | 0.39 | 26.6±0.9 | 20.4±0.8 |
| S30-40+F50 | 8.2 | 0.69 | 0.47 | 28.0±1.2 | 25.6±0.9 |
| S40-20+F50 | 3.2 | 0.58 | 0.35 | 13.1±0.4 | 11.1±0.6 |
| S40-30+F50 | 5.4 | 0.60 | 0.33 | 18.5±0.7 | 16.8±0.8 |
| S40-40+F50 | 21.5 | 0.66 | 0.58 | 18.0±0.9 | 10.7±0.5 |
| S50-20+F50 | 10.6 | 0.67 | 0.30 | 16.9±0.8 | 9.2±0.4 |
| S50-30+F50 | 8.9 | 0.72 | 0.46 | 6.8±0.5 | 5.2±0.3 |
| S50-40+F50 | 17.8 | 0.78 | 0.62 | 8.8±0.6 | 8.1±0.3 |
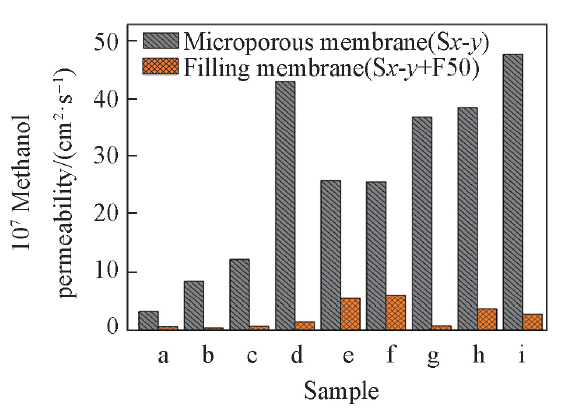
Fig.5 Methanol permeability of the microporous membranes and filling membranesa. S30-20; b. S30-30; c. S30-40; d. S40-20; e. S40-30; f. S40-40; g. S50-20; h. S50-30; i. S50-40.
| [1] | Fang Y., Miao R.Y., Wang T. T., Wang X. D., Fang S. B.,Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2009, (10), 992—1006 |
| (方勇, 苗睿瑛, 王同涛, 王新东, 方世璧. 高分子学报, 2009, (10), 992—1006) | |
| [2] | Yan X. M., Zheng W. J., Ruan X. H., Pan Y., Wu X. M., He G. H., Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering,2016, 24(5), 558—571 |
| [3] | Yuk J., Lee S., Nugraha A. F., Lee H., Park S. H., Yim S. D., Bae B., Journal of Membrane Science,2016, 518(15), 50—59 |
| [4] | Gloukhovski R., Tsur Y., Freger V., Fuel Cells,2017, 17(23), 56—66 |
| [5] | Hu Z. X., Lu Y., Zhang X. L., Gao Q., Yan X. B., Chen S. W., International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2017, 42(17), 12064—12075 |
| [6] | Lu Y., Zhang X. L., Yan X. B., Hu Z. X., Chen S. W., Journal of Membrane Science,2018, 555(1), 45—55 |
| [7] | Tao Y. Y., Zhang X. L., Hu Z. X., Zhang J. J., Geng H., Gao Y., Yuan Z. F., Bi H. P., Chen S. W., Wang L. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2016, 37(4), 793—800 |
| (陶应勇, 张虚略, 胡朝霞, 张晶晶, 耿慧, 高颖, 袁祖凤, 毕慧平, 陈守文, 王连军. 高等学校化学学报,2016, 37(4), 793—800) | |
| [8] | Jonghyun C., Kyung M. L., Ryszard W., Peter N. P., Patrick T. M., Macromolecules,2008, 41(13), 4569—4572 |
| [9] | Petreanua I., Marinoiua A., Sisua C., Varlama M., Fierascub R., Stanescuc P., Materials Research Bulletin,2017, 96, 136—142 |
| [10] | Cao N., Zhou C. F., Wang Y., Ju H., Tan D. Y., Li J., Materials,2018, 11, 516 |
| [11] | Parnian M. J., Rowshanzamir S., Prasad A. K., Journal of Membrane Science,2018, 556(15), 12—22 |
| [12] | Zhu K., Zhang S. L., Luan J. S., Mu Y. F., Du Y. L., Wang G. B., Journal of Membrane Science,2017, 539(1), 116—127 |
| [13] | Fang L. F., Yang H. Y., Cheng L., Kato N., Jeon S., Takagi R., Matsuyama H., Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2018, 57, 4430—4441 |
| [14] | Jiang Y. Y., Hao J. K., Hou M., Hong S. J., Song W., Yia B. L., Shao Z. G., Sustainable Energy & Fuels,2017, 1, 1405—1413 |
| [1] | QIU Xinsheng, WU Qin, SHI Daxin, ZHANG Yaoyuan, CHEN Kangcheng, LI Hansheng. Preparation and High Temperature Fuel Cell Performance of Ionic Crosslinked Sulfonated Polyimides for Proton Exchange Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220140. |
| [2] | CHEN Changli, MI Wanliang, LI Yujing. Research Progress of Single Atom Catalysts in Electrochemical Hydrogen Cycling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220065. |
| [3] | LUO Bian, ZHOU Fen, PAN Mu. Study on Preparation and Accessibility of Hierarchical Porous Carbon Supported Platinum Catalyst [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210853. |
| [4] | LIU Jie, LI Jinsheng, BAI Jingsen, JIN Zhao, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Constructing a Water-blocking Interlayer Containing Sulfonated Carbon Tubes to Reduce Concentration Polarization in Direct Methanol Fuel Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220420. |
| [5] | CAO Kaiyue, PENG JinWu, LI Hongbin, SHI Chengying, WANG Peng, LIU Baijun. High-temperature Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Cross-linked Polybenzimidazole/hyperbranched-polymer Blends [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2049. |
| [6] | PU Yangyang, NING Cong, LU Yao, LIU Lili, LI Na, HU Zhaoxia, CHEN Shouwen. Preparation and Characterizations of Cross-linked Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone)/Partially Fluorinated Sulfonated Poly(aryl ether sulfone) Blend Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2002. |
| [7] | LI Hongbin, ZHANG Shuai, LI Zheng, DING Changjiang, BEN Teng. Synthesis and Anisotropic Proton Conduction of Porous Organic Salt Single Crystal [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3047. |
| [8] | WANG Yuemin, MENG Qinglei, WANG Xian, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Enhancement of Performance of Fe-N-C Catalysts by Copper and Sulfur Doping for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1843. |
| [9] | LIANG Minhui, WANG Peng, LI Hongbin, LI Tianyang, CAO Kaiyue, PENG Jinwu, LIU Zhenchao, LIU Baijun. Preparation of High-temperature Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Semi-interpenetrating Polymer Networks [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2845. |
| [10] | HUA Tao, LI Shengnan, LI Fengxiang, WANG Haonan. Treatment of Naphthalene by Microbial Electrochemical System and the Analysis of Microbial Communities † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1964. |
| [11] | YU Yancun, WANG Xian, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Promoted Formic Acid Electrooxidation Using PdNx/C Catalyst Prepared with Hyperbranched Polymer† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1433. |
| [12] | SONG Xipeng, LIU Jinyu, WANG Lihua, HAN Xutong, HUANG Qinglin. Preparation of Polybenzimidazole/Polyvinylpyrrolidone Proton Exchange Membranes for Vanadium Redox Flow Battery† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1543. |
| [13] | LIN Zhouchen,HUANG Qiaoxi,LEI Ming. Fabrication and Electrocatalytic Performance of Graphene-fullerene Ammonium Iodide Composite Supported Pd Nanocatalyst for Ethanol Oxidation† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 1013. |
| [14] | LIU Jiaming,FU Kailin,ZHANG Ze,GUO Wei,PAN Mu. Ultra-low Pt Loading Cathodic Catalyst Layer Prepared on Textured Gas Diffusion Layer by Magnetron Sputtering Method for Hydrogen-oxygen Fuel Cells† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(3): 542. |
| [15] | SHI Yue,MAO Qing,XIAO Cheng,JING Weiyun,ZHANG Xueyuan. Nonlinear Spectroscopy Analysis for Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Methanol on PtRu/C Surface† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 2017. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||