

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 279.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180673
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHENG Yingying, LIU Haiying*( ), TIAN Yigeng, LIU Zhongqi, LI Qingxin
), TIAN Yigeng, LIU Zhongqi, LI Qingxin
Received:2018-10-08
Online:2019-02-10
Published:2018-11-26
Contact:
LIU Haiying
E-mail:ss_liuhy@ujn.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
CHENG Yingying,LIU Haiying,TIAN Yigeng,LIU Zhongqi,LI Qingxin. Theoretical Study on Enhancement Effect of Amino Modification of Adenine on Conductivity of DNA†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 279.
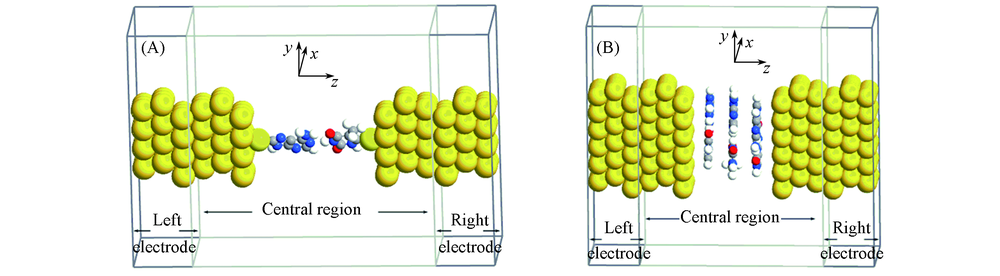
Fig.2 Schematic illustration of two-probe systems in charge transport calculation(A) The transverse charge transport model; (B) the longitudinal charge transport model.
| Base and base pair | VIP/eV | AIP/eV | Edef/eV | Eb/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 8.30 | 8.11 | 0.19 | - |
| D | 7.59 | 7.30 | 0.29 | - |
| G | 7.94 | 7.68 | 0.26 | - |
| AT | 7.87 | 7.70 | 0.17 | 0.46(0.52[ |
| DT | 7.16 | 6.90 | 0.26 | 0.55 |
| GC | 7.28 | 6.92(6.90[ | 0.36 | 1.00 |
Table 1 Comparison of the adiabatic ionization potentials(AIP), vertical ionization potentials(VIP), deformation energies(Edef) and binding energies(Eb)
| Base and base pair | VIP/eV | AIP/eV | Edef/eV | Eb/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 8.30 | 8.11 | 0.19 | - |
| D | 7.59 | 7.30 | 0.29 | - |
| G | 7.94 | 7.68 | 0.26 | - |
| AT | 7.87 | 7.70 | 0.17 | 0.46(0.52[ |
| DT | 7.16 | 6.90 | 0.26 | 0.55 |
| GC | 7.28 | 6.92(6.90[ | 0.36 | 1.00 |
| Base pair | EHOMO/eV | ELUMO/eV | Egap/eV | VIP/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAG | -6.35 | -0.86 | 5.49 | 6.89 |
| GDG | -5.89 | -0.95 | 4.94 | 6.40 |
Table 2 Comparison of HOMO-LUMO gaps, VIP of three-layer stacked base pairs GAG and GDG, calculated by M06-2X/B3LYP*
| Base pair | EHOMO/eV | ELUMO/eV | Egap/eV | VIP/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAG | -6.35 | -0.86 | 5.49 | 6.89 |
| GDG | -5.89 | -0.95 | 4.94 | 6.40 |
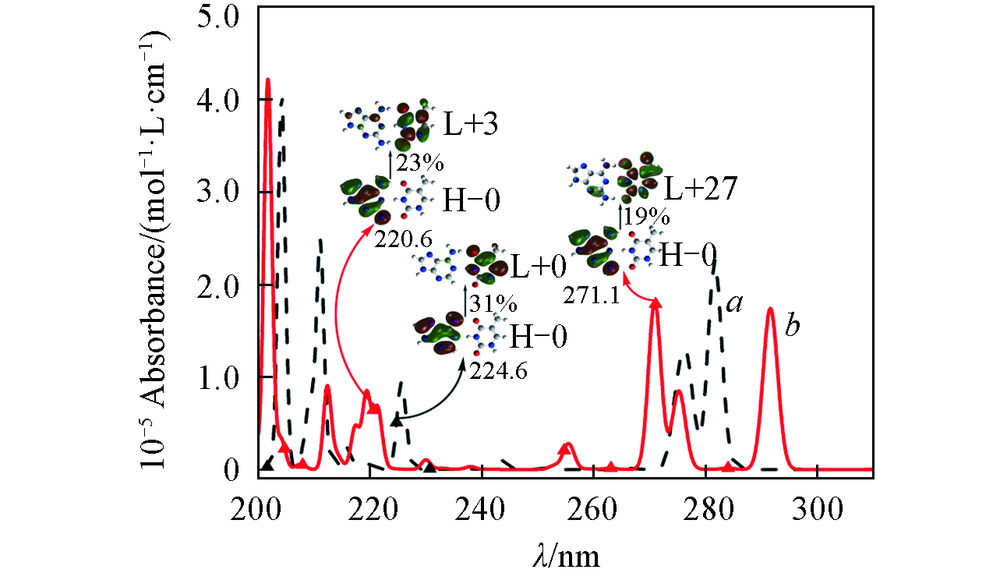
Fig.6 Absorption spectra of AT(a) and DT(b) in the ultraviolet region between 200 and 310 nm determined from the CIS resultsBlack and red solid triangles represent positions assigned to π→π* charge-transfer transition of AT and DT, respectively. H-0: HOMO, L+0: LUMO, L+3: LUMO+3, other markers are similar, and percentages represent proportions of transitions.
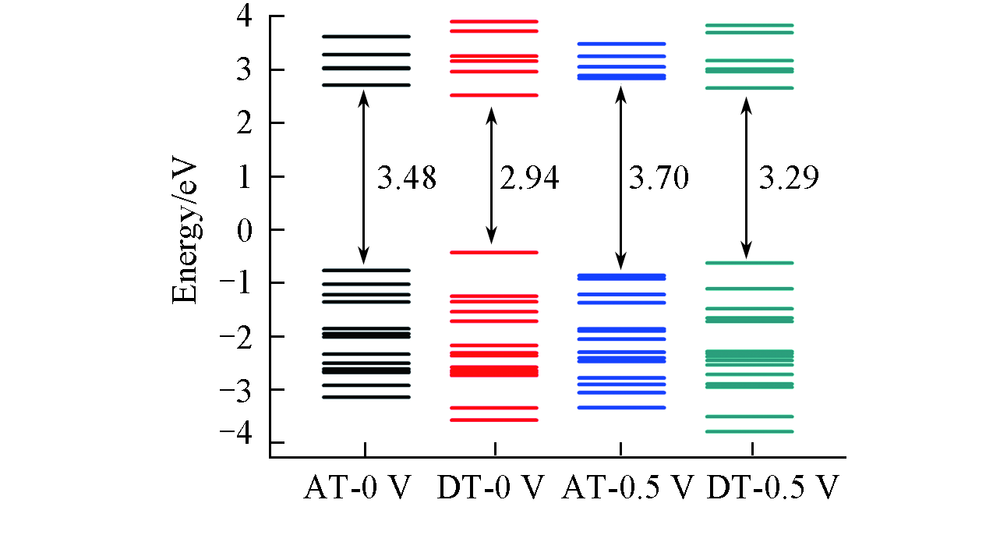
Fig.8 Energy levels of AT and DT junctions for the transverse transport model in the energy region of -4.0―4.0 eV under 0 and 0.5 V biasesThe average Fermi level is set as zero.
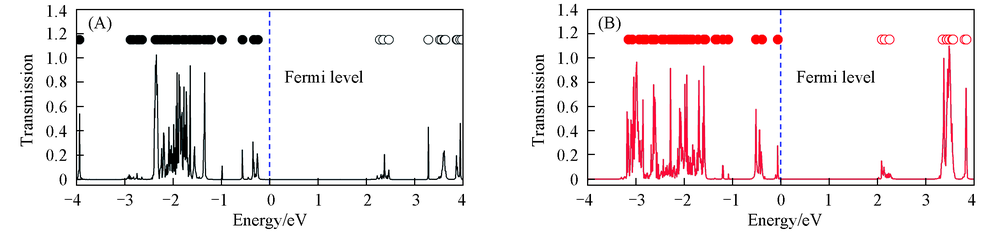
Fig.10 Transmission spectra of 3-layer stacked GAG(A) and GDG(B) junctions at zero bias for the longitudinal electronic transport modelThe dotted dots on the top of each picture represent the molecular projected self-consistent Hamiltonian(MPSH) eigenvalue positions. The solid dots represent the occupied molecular orbital energies and the hollow dots correspond to the unoccupied molecular orbital energies.
| [1] | Guo C. L., Wang K., Zerah-Harush E., Hamill J., Wang B., Dubi Y., Xu B. Q., Nat. Chem.,2016, 8(5), 484-490 |
| [2] | Xiang D., Wang X. L., Jia C. C., Lee T., Guo X. F., Chem. Rev.,2016, 116(7), 4318-4440 |
| [3] | Wang L., Li Z., Shen X. Q., Ma N., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2018, 39(1), 32-40 |
| (王莉, 李智, 沈晓琴, 马楠. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(1), 32-40) | |
| [4] | Behnia S., Fathizadeh S., Akhshani A., J. Phys. Chem. C,2016, 120(5), 2973-2983 |
| [5] | Shipman S. L., Nivala J., Macklis J. D., Church G. M., Nature,2017, 547(7663), 345-349 |
| [6] | Lin M. H., Wen Y. L., Li L. Y., Pei H., Liu G., Song H. Y., Zuo X. L., Fan C. H., Huang Q., Anal. Chem.,2014, 86(5), 2285-2288 |
| [7] | Li M., Kong H. F., Guo Z. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2016, 37(7), 1269-1275 |
| (李敏, 孔慧芳, 郭志慧. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(7), 1269-1275) | |
| [8] | Kasumov A. Y., Kociak M., Guéron S., Reulet B., Volkov V. T., Klinov D. V., Bouchiat H., Science,2001, 291(5502), 280-282 |
| [9] | Porath D., Bezryadin A., de Vries S., Dekker C., Nature,2000, 403(6770), 635-638 |
| [10] | De Pablo P. J., Moreno-Herrero F., Colchero J., Gómez-Herrero J., Herrero P., Baró A. M., Ordejón P., Soler J. M., Artacho E., Phys. Rev. Lett.,2000, 85(23), 4992-4995 |
| [11] | Steinbrecher T., Koslowski T., Case D. A., J. Phys. Chem. B,2008, 112(51), 16935-16944 |
| [12] | Kawai K., Kodera H., Osakada Y., Majima T., Nat. Chem., 2009, 1(2), 156-159 |
| [13] | Nakatani K., Dohno C., Saito I., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2000, 122(24), 5893-5894 |
| [14] | Lee A. H. F., Kool E. T., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2006, 128(28), 9219-9230 |
| [15] | Hernández A. R., Kool E. T., Org. Lett., 2011, 13(4), 676-679 |
| [16] | Liu H. Y., Li G. Q., Zhao P., Chen G., Bu Y. X., Int. J. Quantum Chem., 2014, 114(14), 911-919 |
| [17] | Brancolini G., Felice R. D., J. Phys. Chem. B,2008, 112(45), 14281-14290 |
| [18] | Liu H. Y., Li G. Q., Ai H. Q., Li J. L., Bu Y. X., J. Phys. Chem. C,2011, 115(45), 22547-22556 |
| [19] | Kawai K., Kodera H., Majima T., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(2), 627-630 |
| [20] | Brancolini G., Migliore A., Corni S., Fuentes-Cabrera M., Luque F. J., Di Felice R., ACS Nano,2013, 7(10), 9396-9406 |
| [21] | Becke A. D., J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 98(7), 5648-5652 |
| [22] | Lee C., Yang W., Parr R. G., Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter,1988, 37(2), 785-789 |
| [23] | Frisch M. J., Pople J. A., Binkley J. S., J. Chem. Phys.,1984, 80(7), 3265-3269 |
| [24] | Frisch M.J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Scalmani G., Barone V., Mennucci B., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Caricato M., Li X., Hratchian H. P., Izmaylov A. F., Bloino J., Zheng G., Sonnenberg J. L., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Vreven T., Montgomery J. A., Peralta J. E., Ogliaro F., Bearpark M., Heyd J. J., Brothers E., Kudin K. N., Staroverov V. N., Kobayashi R., Normand J., Raghavachari K., Rendell A., Burant J. C., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Cossi M., Rega N., Millam J. M., Klene M., Knox J. E., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J. W., Martin R. L., Morokuma K., Zakrzewski V. G., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Farkas O., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cioslowski J., Fox D. J., Gaussian 09, Revision A.02, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, 2009 |
| [25] | Rappé A. K., Bernstein E. R., J. Phys. Chem. A,2000, 104(26), 6117-6128 |
| [26] | Boys S. F., Bernardi F., Mol. Phys.,1970, 19(4), 553-566 |
| [27] | Wang M., Wang J., Bu Y. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2015, 36(11), 2271-2282 |
| (王梅, 王军, 步宇翔. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(11), 2271-2282) | |
| [28] | Liu C., Wang Y., Zhao D., Gong L. D., Yang Z. Z., J. Mol. Graph. Model.,2014, 47, 62-76 |
| [29] | Yang B., Rodgers M. T., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2014, 136(1), 282-290 |
| [30] | Jissy A. K., Datta A., J. Phys. Chem. Lett.,2014, 5(1), 154-166 |
| [31] | Foresman J. B., Head-Gordon M., Pople J. A., Frisch M. J., J. Phys. Chem.,1992, 96(1), 135-149 |
| [32] | Dreuw A., Head-Gordon M., Chem. Rev.,2005, 105(11), 4009-4037 |
| [33] | Shukla M. K., Leszczynski J., J. Phys. Chem. B,2005, 109(36), 17333-17339 |
| [34] | Zhang L., Bu Y., J. Phys. Chem. B,2008, 112(34), 10723-10731 |
| [35] | Broo A., Holmén A., J. Phys. Chem. A,1997, 101(19), 3589-3600 |
| [36] | Holmén A., Broo A., Albinsson B., Nordén B., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1997, 119(50), 12240-12250 |
| [37] | Gorelsky S.I., SWizard Program, Revision 4.4, Centre for Catalysis Research and Innovation, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, 2010( |
| [38] | Atomistix Tool Kit Version 2015.1, Quantum Wise A/S, De nmark, 2015( Version 2015.1, Quantum Wise A/S, De nmark, 2015() |
| [39] | Brandbyge M., Mozos J. L., Ordejón P., Taylor J., Stokbro K., Phys. Rev. B,2002, 65, 165401 |
| [40] | Staykov A., Tsuji Y., Yoshizawa K., J. Phys. Chem. C,2011, 115(8), 3481-3490 |
| [41] | Smeu M., Wolkow R. A., Guo H., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2009, 131(31), 11019-11026 |
| [42] | Jiang L. M., Qiu W., Al-Dirini F., Hossain F. M., Evans R., Skafidas E., Appl. Phys., 2016, 120(2), 025501 |
| [43] | Liu H. M., Wang N., Zhao J. W., Guo Y., Yin X., Boey F. Y. C., Zhang H., Chem. Phys. Chem.,2008, 9(10), 1416-1424 |
| [44] | Cohen R., Stokbro K., Martin J. M. L., Ratner M. A., J. Phys. Chem. C,2007, 111(40), 14893-14902 |
| [45] | Tada T., Kondo M., Yoshizawa K., Chem. Phys. Chem.,2003, 4(11), 1256-1260 |
| [46] | Lukas M., Kelly R. E. A., Kantorovich L. N., Otero R., Xu W., Laegsgaard E., Stensgaard I., Besenbacher F., J. Chem. Phys.,2009, 130(2), 024705 |
| [47] | Perdew J. P., Burke K., Ernzerhof M., Phys. Rev. Lett.,1996, 77(18), 3865-3868 |
| [48] | Troullier N., Martins J. L., Phys. Rev. B,1991, 43(3), 1993-2006 |
| [49] | Soler J. M., Artacho E., Gale J. D., Garcia A., Junquera J., Ordejon P., Sanchez-Portal D., Physics,2002, 14(11), 2745-2779 |
| [50] | Monkhorst H. J., Pack J. D., Phys. Rev. B,1976, 13(12), 5188-5192 |
| [51] | Grimme S., Antony J., Ehrlich S., Krieg H., J. Chem. Phys.,2010, 132(15), 154104 |
| [52] | Piccirilli J. A., Krauch T., Moroney S. E., Benner S. A., Nature,1990, 343(6253), 33-37 |
| [53] | Okamoto A., Maeda Y., Tsukamoto T., Ishikawa Y., Kurita N., Comp. Mater. Sci.,2012, 53(1), 416-424 |
| [54] | Nakano S., Sugimoto N., Molecules,2014, 19(8), 11613-11627 |
| [55] | Gervasio F. L., Boero M., Parrinello M., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2006, 45(34), 5606-5609 |
| [56] | Reynisson J., Steenken S., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.,2002, 4, 5353-5358 |
| [57] | Zhao Y., Truhlar D. G., Acc. Chem. Res.,2008, 41(2), 157-167 |
| [58] | Zhao Y., Truhlar D. G., Theor. Chem. Acc.,2008, 120(1—3), 215-241 |
| [1] | LIU Tianshuo, LONG Shichuan, YAO Zhiyi, SHI Jia, YANG Yang, HONG Wenjing. Progress of Charge Transport Through Self-assembled Monolayers by Employing Eutectic Gallium-Indium Technique [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2629. |
| [2] | HAN Bin,YU Xi,HU Wenping. Study on the Mechanism of Charge Tunneling and Hopping Transport in Ferrocene Self-Assembled Molecular Junctions† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 298. |
| [3] | FAN Jianxun, JI Lifei, REN Aimin. Theoretical Study on Charge Transport Properties of Copolymers of Diketopyrrolopyrrole and Oligo-thiophene† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 2053. |
| [4] | ZHENG Jiawei, JIANG Ling, DING Yong, MO Lie, DING Youcai, HU Linhua, DAI Songyuan. Influence of Au Doping on the Surface States and Charge Transport in TiO2 Films† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 2038. |
| [5] | WANG Mei, WANG Jun, BU Yuxiang. Metastable Hydrogen-bonds Featuring Negative Dissociation Energies in Protein-bound DNA in Hole Migration [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(11): 2271. |
| [6] | ZHANG Pan-Pan, ZHU Feng, AI Xi-Cheng, FU Li-Min, XU Dong-Sheng, ZHANG Jian-Ping. Zinc-doping Effects on the Trap State Distribution and Charge Recombination in the Anode of TiO2 Dye-sensitized Solar Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(2): 418. |
| [7] | LI Shang, ZHU Guang-Wen, CHEN Rui-Xin, WANG Jia-Tang, ZHAO Wei, PAN Mu. Performance of Fe-Nx/C Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction and the Effect of Ligand Stucture on the Catalytic Activity [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(08): 1782. |
| [8] | DUAN Gui-Hua, WANG Li-Juan, ZHANG Hou-Yu*, GU Xin , Chen Jie, MA Yu-Guang*. Theoretical Study of Electronic and Charge Transport Properties of Cruciform π-Conjugated 3,6-Diphenyl-1,2,4,5-(2′,2″-diphenyl)-benzobisazole [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(5): 1029. |
| [9] | JIANG Xiao-Qing1*, HARIMA Yutaka2. Charge Transport Study of a Series of Monosilanylene-oligothienylene Copolymer Films [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(7): 1403. |
| [10] | YANG Chun-He, LI Yi-Jun, DONG Shao-Jun . Charge Transport of Indigo-Carmine Doped Polypyrrole [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1997, 18(1): 29. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||