

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (11): 2163.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150491
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2015-06-24
Online:2015-11-10
Published:2015-10-12
Contact:
LIU Yajun
E-mail:yajun.liu@bnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
SONG Yanli, LIU Yajun. Spin-orbit Coupling ab initio Investigation on the Photolysis Mechnism of CH2BrI†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(11): 2163.
| Solvent | CH2BrI | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d(C—I)/nm | d(C—Br)/nm | d(C—H)/nm | ∠H—C—H/(°) | ∠I—C—Br/(°) | ∠I—C—Br—H/(°) | ||
| Gas phase[ | 0.2130 | 0.1935 | 0.1091 | 112.3 | 113.2 | 119.3 | |
| Acetonitrile | 0.2130 | 0.1936 | 0.1094 | 112.6 | 112.8 | 119.0 | |
| 2-Butanol | 0.2130 | 0.1937 | 0.1094 | 112.6 | 112.6 | 119.0 | |
| Cyclohexane | 0.2129 | 0.1935 | 0.1092 | 112.2 | 113.0 | 119.2 | |
| Solvent | CH2Br—I | ||||||
| d(C—Br)/nm | d(Br—I)/nm | d(C—H)/nm | ∠H—C—H/(°) | ∠Br—C—H/(°) | ∠C—Br—I/(°) | ∠I—Br—C—H/(°) | |
| Gas phase[ | 0.1822 | 0.2924 | 0.1101 | 121.1 | 116.7 | 121.1 | 77.1 |
| Acetonitrile | 0.1803 | 0.2895 | 0.1090 | 122.5 | 117.0 | 121.8 | 79.6 |
| 2-Butanol | 0.1800 | 0.2898 | 0.1090 | 122.2 | 117.1 | 121.7 | 79.6 |
| Cyclohexane | 0.1807 | 0.2888 | 0.1090 | 121.4 | 117.0 | 122.0 | 78.1 |
| Solvent | CH2I—Br | ||||||
| d(C—I)/nm | d(Br—I)/nm | d(C—H)/nm | ∠H—C—H/(°) | ∠I—C—H/(°) | ∠C—I—Br/(°) | ∠Br—I—C—H/(°) | |
| Gas phase[ | 0.2009 | 0.2753 | 0.1101 | 119.7 | 117.0 | 121.9 | 76.1 |
| Acetonitrile | 0.1972 | 0.2831 | 0.1092 | 120.9 | 118.2 | 119.6 | 80.9 |
| 2-Butanol | 0.1967 | 0.2793 | 0.1091 | 121.7 | 117.7 | 117.5 | 80.7 |
| Cyclohexane | 0.1972 | 0.2753 | 0.1091 | 120.0 | 117.5 | 119.6 | 77.5 |
Table 1 CASPT2 optimized geometries of the CH2BrI, CH2Br—I, and CH2I—Br in acetonitrile, 2-butanol and cyclohexane in comparison with the results in the gas phase
| Solvent | CH2BrI | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d(C—I)/nm | d(C—Br)/nm | d(C—H)/nm | ∠H—C—H/(°) | ∠I—C—Br/(°) | ∠I—C—Br—H/(°) | ||
| Gas phase[ | 0.2130 | 0.1935 | 0.1091 | 112.3 | 113.2 | 119.3 | |
| Acetonitrile | 0.2130 | 0.1936 | 0.1094 | 112.6 | 112.8 | 119.0 | |
| 2-Butanol | 0.2130 | 0.1937 | 0.1094 | 112.6 | 112.6 | 119.0 | |
| Cyclohexane | 0.2129 | 0.1935 | 0.1092 | 112.2 | 113.0 | 119.2 | |
| Solvent | CH2Br—I | ||||||
| d(C—Br)/nm | d(Br—I)/nm | d(C—H)/nm | ∠H—C—H/(°) | ∠Br—C—H/(°) | ∠C—Br—I/(°) | ∠I—Br—C—H/(°) | |
| Gas phase[ | 0.1822 | 0.2924 | 0.1101 | 121.1 | 116.7 | 121.1 | 77.1 |
| Acetonitrile | 0.1803 | 0.2895 | 0.1090 | 122.5 | 117.0 | 121.8 | 79.6 |
| 2-Butanol | 0.1800 | 0.2898 | 0.1090 | 122.2 | 117.1 | 121.7 | 79.6 |
| Cyclohexane | 0.1807 | 0.2888 | 0.1090 | 121.4 | 117.0 | 122.0 | 78.1 |
| Solvent | CH2I—Br | ||||||
| d(C—I)/nm | d(Br—I)/nm | d(C—H)/nm | ∠H—C—H/(°) | ∠I—C—H/(°) | ∠C—I—Br/(°) | ∠Br—I—C—H/(°) | |
| Gas phase[ | 0.2009 | 0.2753 | 0.1101 | 119.7 | 117.0 | 121.9 | 76.1 |
| Acetonitrile | 0.1972 | 0.2831 | 0.1092 | 120.9 | 118.2 | 119.6 | 80.9 |
| 2-Butanol | 0.1967 | 0.2793 | 0.1091 | 121.7 | 117.7 | 117.5 | 80.7 |
| Cyclohexane | 0.1972 | 0.2753 | 0.1091 | 120.0 | 117.5 | 119.6 | 77.5 |
| Isomer | Symmetry | Description | Gas phase[ | Acetonitrile | 2-Butanol | Cyclohexane | Experiment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH2BrI | A' | CH2 sym.str. | 3122 | 3040 | 3055 | 3076 | 2978[ |
| CH2 def. | 1424 | 1439 | 1412 | 1421 | 1374[ | ||
| CH2 wag | 1221 | 1187 | 1192 | 1196 | 1150[ | ||
| C—Br str. | 647 | 577 | 644 | 652 | 616[ | ||
| C—I str. | 550 | 418 | 537 | 538 | 517[ | ||
| C—I—Br bend | 143 | 133 | 144 | 145 | 144[ | ||
| A″ | CH2 asym.str. | 3182 | 3077 | 3076 | 3102 | 3053[ | |
| CH2 twist | 1075 | 1005 | 1076 | 1085 | 1065[ | ||
| CH2 rock | 787 | 750 | 782 | 789 | 754[ | ||
| CH2Br—I | A' | CH2 sym.str. | 3118 | 3107 | 3107 | 3115 | |
| CH2 def. | 1399 | 1384 | 1385 | 1397 | |||
| CH2 wag | 785 | 795 | 793 | 787 | 839[ | ||
| C—Br str. | 661 | 660 | 666 | 661 | 628[ | ||
| C—I str. | 144 | 152 | 150 | 146 | 159[ | ||
| C—I—Br bend | 116 | 116 | 97 | 113 | 111[ | ||
| A″ | CH2 asym.str. | 3230 | 3200 | 3196 | 3181 | ||
| CH2 twist | 949 | 946 | 947 | 945 | |||
| CH2 rock | 380 | 422 | 409 | 417 | |||
| CH2I—Br | A' | CH2 sym.str. | 3115 | 3092 | 3112 | 3106 | |
| CH2 def. | 1387 | 1369 | 1388 | 1367 | |||
| CH2 wag | 741 | 769 | 756 | 755 | 730[ | ||
| C—Br str. | 641 | 666 | 656 | 668 | |||
| C—I str. | 174 | 158 | 177 | 167 | 173[ | ||
| C—I—Br bend | 109 | 94 | 107 | 100 | 118[ | ||
| A″ | CH2 asym.str. | 3224 | 3190 | 3194 | 3214 | ||
| CH2 twist | 886 | 866 | 877 | 873 | |||
| CH2 rock | 432 | 439 | 451 | 447 |
Table 2 CASPT2 calculated harmonic vibrational frequencies(cm-1) of the CH2BrI, CH2Br—I and CH2I—Br in solvents and gas phase in comparison with the experimental results
| Isomer | Symmetry | Description | Gas phase[ | Acetonitrile | 2-Butanol | Cyclohexane | Experiment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH2BrI | A' | CH2 sym.str. | 3122 | 3040 | 3055 | 3076 | 2978[ |
| CH2 def. | 1424 | 1439 | 1412 | 1421 | 1374[ | ||
| CH2 wag | 1221 | 1187 | 1192 | 1196 | 1150[ | ||
| C—Br str. | 647 | 577 | 644 | 652 | 616[ | ||
| C—I str. | 550 | 418 | 537 | 538 | 517[ | ||
| C—I—Br bend | 143 | 133 | 144 | 145 | 144[ | ||
| A″ | CH2 asym.str. | 3182 | 3077 | 3076 | 3102 | 3053[ | |
| CH2 twist | 1075 | 1005 | 1076 | 1085 | 1065[ | ||
| CH2 rock | 787 | 750 | 782 | 789 | 754[ | ||
| CH2Br—I | A' | CH2 sym.str. | 3118 | 3107 | 3107 | 3115 | |
| CH2 def. | 1399 | 1384 | 1385 | 1397 | |||
| CH2 wag | 785 | 795 | 793 | 787 | 839[ | ||
| C—Br str. | 661 | 660 | 666 | 661 | 628[ | ||
| C—I str. | 144 | 152 | 150 | 146 | 159[ | ||
| C—I—Br bend | 116 | 116 | 97 | 113 | 111[ | ||
| A″ | CH2 asym.str. | 3230 | 3200 | 3196 | 3181 | ||
| CH2 twist | 949 | 946 | 947 | 945 | |||
| CH2 rock | 380 | 422 | 409 | 417 | |||
| CH2I—Br | A' | CH2 sym.str. | 3115 | 3092 | 3112 | 3106 | |
| CH2 def. | 1387 | 1369 | 1388 | 1367 | |||
| CH2 wag | 741 | 769 | 756 | 755 | 730[ | ||
| C—Br str. | 641 | 666 | 656 | 668 | |||
| C—I str. | 174 | 158 | 177 | 167 | 173[ | ||
| C—I—Br bend | 109 | 94 | 107 | 100 | 118[ | ||
| A″ | CH2 asym.str. | 3224 | 3190 | 3194 | 3214 | ||
| CH2 twist | 886 | 866 | 877 | 873 | |||
| CH2 rock | 432 | 439 | 451 | 447 |
| Solvent | CH2BrI | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d(C—I)/nm | d(C—Br)/nm | d(C—H)/nm | ∠H—C—H/(°) | ∠I—C—Br/(°) | ∠I—C—Br—H/(°) | ||
| Gas phase[ | 0.4074 | 0.1865 | 0.1085 | 122.9 | 89.3 | 79.1 | |
| Acetonitrile | 0.4051 | 0.1872 | 0.1088 | 123.7 | 92.5 | 79.2 | |
| 2-Butanol | 0.4041 | 0.1872 | 0.1088 | 123.7 | 95.5 | 79.2 | |
| Cyclohexane | 0.4104 | 0.1867 | 0.1086 | 123.3 | 88.4 | 79.6 | |
| Solvent | CH2Br—I | ||||||
| d(C—Br)/nm | d(Br—I)/nm | d(C—H)/nm | ∠H—C—H/(°) | ∠Br—C—H/(°) | ∠C—Br—I/(°) | ∠I—Br—C—H/(°) | |
| Gas phase[ | 0.1864 | 0.3929 | 0.1085 | 123.5 | 117.0 | 179.2 | 98.5 |
| Acetonitrile | 0.1868 | 0.3949 | 0.1087 | 125.4 | 117.3 | 180.0 | 90.6 |
| 2-Butanol | 0.1869 | 0.3941 | 0.1087 | 125.4 | 117.3 | 180.0 | 90.7 |
| Cyclohexane | 0.1864 | 0.3928 | 0.1085 | 124.8 | 117.5 | 179.6 | 92.7 |
| Solvent | CH2I—Br | ||||||
| d(C—I)/nm | d(Br—I)/nm | d(C—H)/nm | ∠H—C—H/(°) | ∠I—C—H/(°) | ∠C—I—Br/(°) | ∠Br—I—C—H/(°) | |
| Gas phase[ | 0.2044 | 0.3899 | 0.1086 | 123.1 | 118.4 | 179.2 | 90.0 |
| Acetonitrile | 0.2051 | 0.3937 | 0.1088 | 124.1 | 117.9 | 180.0 | 90.6 |
| 2-Butanol | 0.2051 | 0.3926 | 0.1088 | 124.0 | 118.0 | 179.7 | 89.2 |
| Cyclohexane | 0.2048 | 0.3920 | 0.1087 | 123.6 | 118.2 | 180.0 | 89.7 |
Table 3 CASPT2 optimized geometries of the 11A″ excited state of CH2BrI, CH2Br—I and CH2I—Br in acetonitrile, 2-butanol and cyclohexane in comparison with gas-phase results
| Solvent | CH2BrI | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d(C—I)/nm | d(C—Br)/nm | d(C—H)/nm | ∠H—C—H/(°) | ∠I—C—Br/(°) | ∠I—C—Br—H/(°) | ||
| Gas phase[ | 0.4074 | 0.1865 | 0.1085 | 122.9 | 89.3 | 79.1 | |
| Acetonitrile | 0.4051 | 0.1872 | 0.1088 | 123.7 | 92.5 | 79.2 | |
| 2-Butanol | 0.4041 | 0.1872 | 0.1088 | 123.7 | 95.5 | 79.2 | |
| Cyclohexane | 0.4104 | 0.1867 | 0.1086 | 123.3 | 88.4 | 79.6 | |
| Solvent | CH2Br—I | ||||||
| d(C—Br)/nm | d(Br—I)/nm | d(C—H)/nm | ∠H—C—H/(°) | ∠Br—C—H/(°) | ∠C—Br—I/(°) | ∠I—Br—C—H/(°) | |
| Gas phase[ | 0.1864 | 0.3929 | 0.1085 | 123.5 | 117.0 | 179.2 | 98.5 |
| Acetonitrile | 0.1868 | 0.3949 | 0.1087 | 125.4 | 117.3 | 180.0 | 90.6 |
| 2-Butanol | 0.1869 | 0.3941 | 0.1087 | 125.4 | 117.3 | 180.0 | 90.7 |
| Cyclohexane | 0.1864 | 0.3928 | 0.1085 | 124.8 | 117.5 | 179.6 | 92.7 |
| Solvent | CH2I—Br | ||||||
| d(C—I)/nm | d(Br—I)/nm | d(C—H)/nm | ∠H—C—H/(°) | ∠I—C—H/(°) | ∠C—I—Br/(°) | ∠Br—I—C—H/(°) | |
| Gas phase[ | 0.2044 | 0.3899 | 0.1086 | 123.1 | 118.4 | 179.2 | 90.0 |
| Acetonitrile | 0.2051 | 0.3937 | 0.1088 | 124.1 | 117.9 | 180.0 | 90.6 |
| 2-Butanol | 0.2051 | 0.3926 | 0.1088 | 124.0 | 118.0 | 179.7 | 89.2 |
| Cyclohexane | 0.2048 | 0.3920 | 0.1087 | 123.6 | 118.2 | 180.0 | 89.7 |
| Isoner | State | Acetonitrile | 2-Butanol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ev/cm-1(eV) | f | Ev/cm-1(eV) | f | ||
| CH2BrI | X11A' | 0(0) | 0(0) | ||
| 11A″ | 38213(4.74) | 6.78×10-3 | 38236(4.74) | 6.77×10-3 | |
| 21A' | 38615(4.79) | 1.24×10-2 | 38582(4.78) | 1.26×10-2 | |
| 31A' | 48043(5.96) | 2.22×10-2 | 47974(5.95) | 2.13×10-2 | |
| 21A″ | 48229(5.98) | 1.48×10-3 | 48179(5.97) | 1.79×10-3 | |
| CH2Br—I | X11A' | 0(0) | 0(0) | ||
| 11A″ | 15591(1.93) | 4.04×10-5 | 15412(1.91) | 3.94×10-5 | |
| 21A' | 16956(2.10) | 4.21×10-4 | 16753(2.08) | 4.02×10-4 | |
| 31A' | 26368(3.27) | 6.50×10-1 | 26427(3.28) | 6.50×10-1 | |
| 21A″ | 36305(4.50) | 3.59×10-7 | 36416(4.52) | 2.84×10-7 | |
| CH2I—Br | X11A' | 0(0) | 0(0) | ||
| 11A″ | 20205(2.51) | 1.75×10-6 | 21188(2.63) | 1.93×10-6 | |
| 21A' | 22896(2.84) | 7.50×10-4 | 24144(2.99) | 9.38×10-4 | |
| 31A' | 29302(3.63) | 5.80×10-1 | 30567(3.79) | 6.00×10-1 | |
| 21A″ | 32852(4.07) | 5.55×10-4 | 34168(4.24) | 5.69×10-4 | |
Table 4 MS-CASPT2 calculated vertical excitation energies(Ev) and oscillator strength(f) of the five lowest-lying spin-orbital-free states of CH2BrI, CH2Br—I and CH2I—Br in acetonitrile and 2-butanol
| Isoner | State | Acetonitrile | 2-Butanol | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ev/cm-1(eV) | f | Ev/cm-1(eV) | f | ||
| CH2BrI | X11A' | 0(0) | 0(0) | ||
| 11A″ | 38213(4.74) | 6.78×10-3 | 38236(4.74) | 6.77×10-3 | |
| 21A' | 38615(4.79) | 1.24×10-2 | 38582(4.78) | 1.26×10-2 | |
| 31A' | 48043(5.96) | 2.22×10-2 | 47974(5.95) | 2.13×10-2 | |
| 21A″ | 48229(5.98) | 1.48×10-3 | 48179(5.97) | 1.79×10-3 | |
| CH2Br—I | X11A' | 0(0) | 0(0) | ||
| 11A″ | 15591(1.93) | 4.04×10-5 | 15412(1.91) | 3.94×10-5 | |
| 21A' | 16956(2.10) | 4.21×10-4 | 16753(2.08) | 4.02×10-4 | |
| 31A' | 26368(3.27) | 6.50×10-1 | 26427(3.28) | 6.50×10-1 | |
| 21A″ | 36305(4.50) | 3.59×10-7 | 36416(4.52) | 2.84×10-7 | |
| CH2I—Br | X11A' | 0(0) | 0(0) | ||
| 11A″ | 20205(2.51) | 1.75×10-6 | 21188(2.63) | 1.93×10-6 | |
| 21A' | 22896(2.84) | 7.50×10-4 | 24144(2.99) | 9.38×10-4 | |
| 31A' | 29302(3.63) | 5.80×10-1 | 30567(3.79) | 6.00×10-1 | |
| 21A″ | 32852(4.07) | 5.55×10-4 | 34168(4.24) | 5.69×10-4 | |
| Isoner | State | Cyclohexane | Gas phase[ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ev/cm-1(eV) | f | Ev/cm-1(eV) | f | ||
| CH2BrI | X11A' | 0(0) | 0(0) | ||
| 11A″ | 37879(4.70) | 6.81×10-3 | 38283(4.75) | 8.10×10-3 | |
| 21A' | 38163(4.73) | 1.23×10-2 | 38570(4.78) | 6.00×10-3 | |
| 31A' | 47584(5.90) | 2.14×10-2 | 46622(5.78) | 1.40×10-3 | |
| 21A″ | 47873(5.94) | 1.60×10-3 | 47184(5.85) | 1.80×10-2 | |
| CH2Br—I | X11A' | 0(0) | 0(0) | ||
| 11A″ | 13031(1.62) | 3.26×10-5 | 13229(1.64) | 3.70×10-5 | |
| 21A' | 14265(1.77) | 1.54×10-4 | 14363(1.78) | 1.70×10-4 | |
| 31A' | 28438(3.53) | 5.70×10-1 | 28771(3.57) | 5.60×10-1 | |
| 21A″ | 38295(4.75) | 2.96×10-6 | 38146(4.73) | 1.10×10-6 | |
| CH2I—Br | X11A' | 0(0) | 0(0) | ||
| 11A″ | 20249(2.51) | 3.85×10-6 | 19619(2.43) | 4.20×10-7 | |
| 21A' | 22757(2.82) | 6.92×10-4 | 22269(2.76) | 6.20×10-4 | |
| 31A' | 31533(3.91) | 5.50×10-1 | 31630(3.92) | 4.80×10-1 | |
| 21A″ | 35127(4.36) | 8.56×10-4 | 35054(4.35) | 9.30×10-4 | |
Table 5 MS-CASPT2 calculated vertical excitation energies(Ev) and oscillator strength(f) of the five lowest-lying spin-orbital-free states of CH2BrI, CH2Br—I and CH2I—Br in cyclohexane and gas phase
| Isoner | State | Cyclohexane | Gas phase[ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ev/cm-1(eV) | f | Ev/cm-1(eV) | f | ||
| CH2BrI | X11A' | 0(0) | 0(0) | ||
| 11A″ | 37879(4.70) | 6.81×10-3 | 38283(4.75) | 8.10×10-3 | |
| 21A' | 38163(4.73) | 1.23×10-2 | 38570(4.78) | 6.00×10-3 | |
| 31A' | 47584(5.90) | 2.14×10-2 | 46622(5.78) | 1.40×10-3 | |
| 21A″ | 47873(5.94) | 1.60×10-3 | 47184(5.85) | 1.80×10-2 | |
| CH2Br—I | X11A' | 0(0) | 0(0) | ||
| 11A″ | 13031(1.62) | 3.26×10-5 | 13229(1.64) | 3.70×10-5 | |
| 21A' | 14265(1.77) | 1.54×10-4 | 14363(1.78) | 1.70×10-4 | |
| 31A' | 28438(3.53) | 5.70×10-1 | 28771(3.57) | 5.60×10-1 | |
| 21A″ | 38295(4.75) | 2.96×10-6 | 38146(4.73) | 1.10×10-6 | |
| CH2I—Br | X11A' | 0(0) | 0(0) | ||
| 11A″ | 20249(2.51) | 3.85×10-6 | 19619(2.43) | 4.20×10-7 | |
| 21A' | 22757(2.82) | 6.92×10-4 | 22269(2.76) | 6.20×10-4 | |
| 31A' | 31533(3.91) | 5.50×10-1 | 31630(3.92) | 4.80×10-1 | |
| 21A″ | 35127(4.36) | 8.56×10-4 | 35054(4.35) | 9.30×10-4 | |
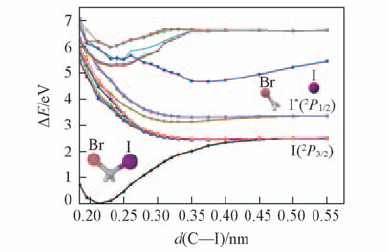
Fig.2 MS-CASPT2//CASPT2 calculated potential energy curevs of the spin-orbit-coupledstates with respect to the C—I bond coordinate of CH2BrI in cyclohexane
| [1] | Carpenter L. J., Wevill D. J., Palmer C. J., Michels J., Mar. Chem., 2007, 103(3/4), 227—236 |
| [2] | Class T. H., Ballschmiter K., J. Atmos. Chem., 1988, 6(1/2), 35—46 |
| [3] | Blomstro D., Herbig K., Simmons H. E., J. Org. Chem., 1965, 30(4), 959—964 |
| [4] | Pienta N. J., Kropp P. J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1978, 100(2), 655—656 |
| [5] | Kropp P. J., Pienta N. J., Sawyer J. A., Polniaszek R. P., Tetrahedron, 1981, 37(19), 3229—3236 |
| [6] | Kropp P. J., Acc. Chem. Res., 1984, 17(4), 131—137 |
| [7] | Phillips D. L., Fang W. H., Zheng X. M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2001, 123(18), 4197—4203 |
| [8] | Liu Y. J., Xiao H. Y., Sun M. T., Fang W. H., J. Comput. Chem., 2008, 29(15), 2513—2519 |
| [9] | Fang W. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1999, 121(36), 8376—8384 |
| [10] | He H. Y., Fang W. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125(51), 16139—16147 |
| [11] | Butler L. J., Hintsa E. J., Shane S. F., Lee Y. T., J. Chem. Phys., 1987, 86(4), 2051—2074 |
| [12] | Butler L. J., Hintsa E. J., Lee Y. T., J. Chem. Phys., 1986, 84(7), 4104—4106 |
| [13] | Lee S. J., Bersohn R., J. Phys. Chem., 1982, 86(5), 728—730 |
| [14] | Liu Y. J., Ajitha D., Krogh J. W., Tarnovsky A. N., Lindh R., Chemphyschem, 2006, 7(4), 955—963 |
| [15] | Tarnovsky A. N., Wall M., Gustafsson M., Lascoux N., Sundstrom V., Akesson E., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2002, 106(25), 5999—6005 |
| [16] | Zheng X. M., Phillips D. L., J. Chem. Phys., 2000, 113(8), 3194—3203 |
| [17] | Kwok W. M., Ma C. S., Phillips D., Parker A. W., Towrie M., Matousek P., Phillips D. L., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2001, 341(3/4), 292—298 |
| [18] | Anderson C. P., Spears K. G., Wilson K. R., Sension R. J., J. Chem. Phys., 2013, 139(19), 194307 |
| [19] | Podsiadlo M., Katrusiak A., Crystengcomm, 2008, 10(10), 1436—1442 |
| [20] | Tang K. C., Peng J., Spears K. G., Sension R. J., J. Chem. Phys., 2010, 132(14), 141102 |
| [21] | Andersson K., Malmqvist P. Å., Roos B. O., J. Chem. Phys., 1992, 96(2), 1218—1226 |
| [22] | Andersson K., Theor. Chim. Acta, 1995, 91(1/2), 31—46 |
| [23] | Malmqvist P. Å., Roos B. O., Chem. Phys. Lett., 1989, 155(2), 189—194 |
| [24] | Roos B.O., Andersson K., Fülscher M. P., Malmqvist P. Å., Serrano Andrés L., Pierloot K., Merchán M., Advances in Chemical Physics: New Methods in Computational Quantum Mechanics, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1996, 219—331 |
| [25] | Finley J., Malmqvist P. Å., Roos B. O., Serrano-Andrés L., Chem. Phys. Lett., 1998, 288(2—4), 299—306 |
| [26] | Malmqvist P. Å., Roos B. O., Schimmelpfennig B., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2002, 357(3/4), 230—240 |
| [27] | Roos B. O., Malmqvist P. Å., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2004, 6(11), 2919—2927 |
| [28] | Marian C. M., Wahlgren U., Chem. Phys. Lett., 1996, 251(5/6), 357—364 |
| [29] | Ghigo G., Roos B. O., Malmqvist P. Å., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2004, 396(1—3), 142—149 |
| [30] | Barone V., Cossi M., J. Phys. Chem. A, 1998, 102(11), 1995—2001 |
| [31] | Tarnovsky A. N., Pascher I., Pascher T., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2007, 111(46), 11814—11817 |
| [32] | Man S. Q., Kwok W. M., Phillips D. L., Johnson A. E., J. Chem. Phys., 1996, 105(14), 5842—5857 |
| [33] | Widmark P. O., Persson B. J., Roos B. O., Theor. Chim. Acta, 1991, 79(6), 419—432 |
| [34] | Widmark P. O., Malmqvist P. A., Roos B. O., Theor. Chim. Acta, 1990, 77(5), 291—306 |
| [35] | Roos B. O., Lindh R., Malmqvist P. Å., Veryazov V., Widmark P. O., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2004, 108(15), 2851—2858 |
| [36] | Karlstrom G., Lindh R., Malmqvist P. Å., Roos B. O., Ryde U., Veryazov V., Widmark P. O., Cossi M., Schimmelpfennig B., Neogrady P., Seijo L., Comput. Mater. Sci., 2003, 28(2), 222—239 |
| [37] | Veryazov V., Widmark P. O., Serrano-Andrés L., Lindh R., Roos B. O., Int. J. Quantum Chem., 2004, 100(4), 626—635 |
| [38] | Fang W. H., Acc. Chem. Res., 2008, 41(3), 452—457 |
| [39] | Fang W. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1998, 120(30), 7568—7576 |
| [40] | El-Sabban M. Z., J. Chem. Phys., 1966, 44(5), 1770—1779 |
| [41] | Liu Y. J., De Vico L., Lindh R., Fang W. H., Chemphyschem, 2007, 8(6), 890—898 |
| [42] | Donovan R.J.,J. Photochem., 1972, 75—78 |
| [1] | WANG Jian, ZHANG Hongxing. Theoretical Study on the Structural-photophysical Relationships of Tetra-Pt Phosphorescent Emitters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2245. |
| [2] | AN Feng, HU Xixi, XIE Daiqian. Research Advances on Nonadiabatic Energy Transfer Dynamics for Triatomic Molecules [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2103. |
| [3] | PENG Qin, FANG Yeguang, ZHANG Tengshuo, CUI Ganglong, FANG Weihai. Theoretical Study on the Excited State Properties and Photophysical Mechanism of Selenothymine and Adenine Base Pairs in DNA Environment [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2136. |
| [4] | ZHU Qichen, XIONG Ming, TAO Siyu, TANG Siwei, REN Qizhi. Effect of Light Source on the Photocatalytic Performance of Dihydroxynaphthalene by Water-soluble Sulfonated Porphyrins [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1933. |
| [5] | LI Qing, YI Pinggui, TAO Hongwen, LI Yangyang, ZHANG Zhiyu, PENG Wenyu, LI Yuru. Solvent and Substituent Effects on Spectral Characteristics and Excited-state Intramolecular Proton Transfer of 2-(2-Aminophenyl) Benzothiazole† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1425. |
| [6] | XU Yandong,YOU Jinglin,WANG Jian,GONG Xiaoye,DING Yani,CAO Peiming,ZHENG Shaobo,WU Yongquan,YU Zhongda. High-temperature in situ Raman Spectroscopic Study on the Micro-structure of Bi4B2O9 Crystal and Melt † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2143. |
| [7] | WU Zhidong,YOU Jinglin,WANG Jian,WANG Min,HE Yingxia,YANG Yejin. NMR Spectroscopic Study on Binary Sodium Silicate Glass Based on the Fine Structure† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 108. |
| [8] | ZHAO Xiaohui,CHU Zhenhua,LI Yu. Molecular Design of Lower Photodegradation Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics and Their Photolysis Paths Inference† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(12): 2707. |
| [9] | LI Xun,XUE Yurui,SONG Yu,ZHANG Wenke. Coordinate Interaction Between Monosulfide and Au Surfaces† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(12): 2774. |
| [10] | CHEN Deli, YANG Pengyong, WU Shengnan, HE Sihui, WANG Fangfang. Ab initio Molecular Dynamics Simulations on the Structures and Stabilities of Pd Clusters Encapsulated UiO-66 Materials† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1210. |
| [11] | CHEN Baiyan, KANG Chunli, WU Jiayu, WANG Yixue, GUO Zhixin, BAO Siqi, ZHONG Yubo, TIAN Tao, XUE Honghai. Rose Bengal-sensitized Photolysis of γ-Hexachlorocyclohexane in Ice† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5): 791. |
| [12] | WANG Yunming, CHANG Peiyang, GU Fang, WANG Haijun. Intramolecular Reaction in Self-condensing Vinyl Polymerization System with Solvent Effect† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(4): 660. |
| [13] | TANG Qian, SU Jinhong, CAO Hongyu, WANG Lihao, SHI Fei, WANG Ailing, GONG Tingting, JIN Xiaojun, ZHENG Xuefang. Interaction of Pyrimidine Derivatives with Human Serum Albumin† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 1982. |
| [14] | GAO Lijuan, WANG Li, WANG Shengyan, JING Shubo. Influence of Solvent on Structure of Ni(Ⅱ) Metal-organic Frameworks† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(9): 1589. |
| [15] | YU Yongbo,LIU Cui,GONG Lidong. Studies of (CH3OH)n(n=3—12) and [Na(CH3OH)n]+(n=3—6)via ab initio and ABEEMσπ/MM† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(8): 1468. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
