

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 791.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160933
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Baiyan1, KANG Chunli1, WU Jiayu1,3, WANG Yixue1, GUO Zhixin1, BAO Siqi1, ZHONG Yubo1, TIAN Tao1,*( ), XUE Honghai2
), XUE Honghai2
Received:2016-12-23
Online:2017-05-10
Published:2017-04-20
Contact:
TIAN Tao
E-mail:tiantao@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
CHEN Baiyan, KANG Chunli, WU Jiayu, WANG Yixue, GUO Zhixin, BAO Siqi, ZHONG Yubo, TIAN Tao, XUE Honghai. Rose Bengal-sensitized Photolysis of γ-Hexachlorocyclohexane in Ice†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5): 791.
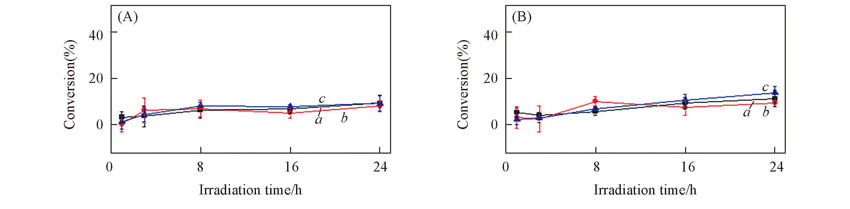
Fig.1 Effects of different phosphate buffer concentrations on the direct photolysis of γ-HCH in icec0(γ-HCH)=60 μg/L. (A) c(PBS)=0.005 mol/L;(B) c(BPS)=0.05 mol/L. a. pH=6; b. pH=8; c. no adjustment.
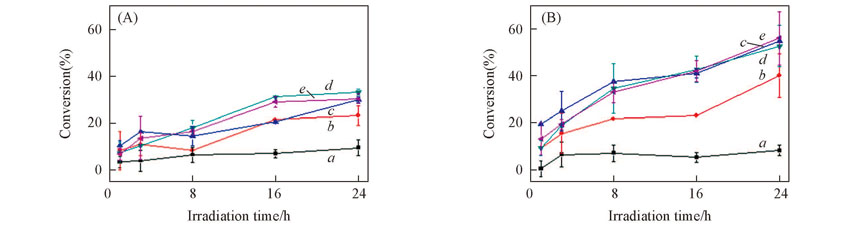
Fig.2 Effects of the initial concentration of RB on the photolysis of γ-HCH in icec0(γ-HCH)=60 μg/L, c(PBS)=0.005 mol/L. (A) pH=6; (B) pH=8.c(RB)/(mg·L-1): a. 0; b. 2.5; c. 5.0; d. 10.0; e. 20.0.
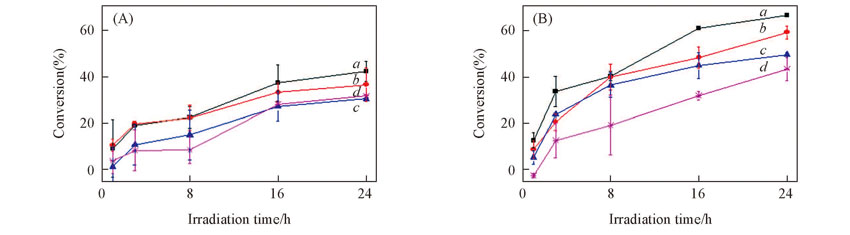
Fig.3 Effects of the initial concentration of γ-HCH on its photolysis in icec(RB)=10 mg/L, c(PBS)=0.005 mol/L. (A) pH=6; (B) pH=8. c0(γ-HCH)/(μg·L-1): a. 20; b. 60; c. 200; d. 600.
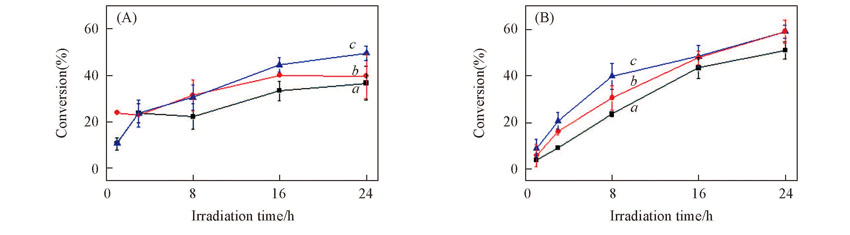
Fig.4 Effects of the phosphate buffer concentration on the photolysis of γ-HCH in icec0(γ-HCH)=60 μg/L, c(RB)=10 mg/L. (A) pH=6; (B) pH=8. c(PBS)/(mol·L-1): a. 0.005; b. 0.010; c. 0.055.
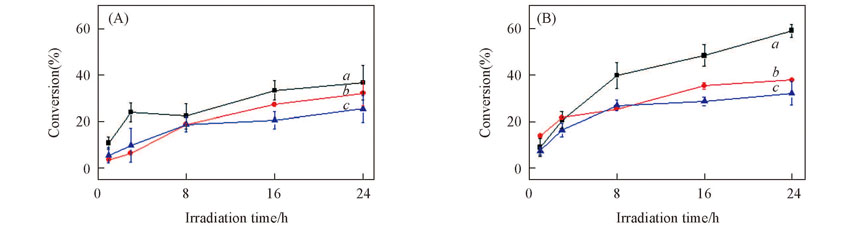
Fig.5 Effects of the sodium sulfate concentration on the photolysis of γ-HCH in icec0(γ-HCH)=60 μg/L, c(RB)=10 mg/L, c(PBS)=0.005 mol/L. (A) pH=6; (B) pH=8.c(Na2SO4)/(mol·L-1): a. 0; b. 0.005; c. 0.050.
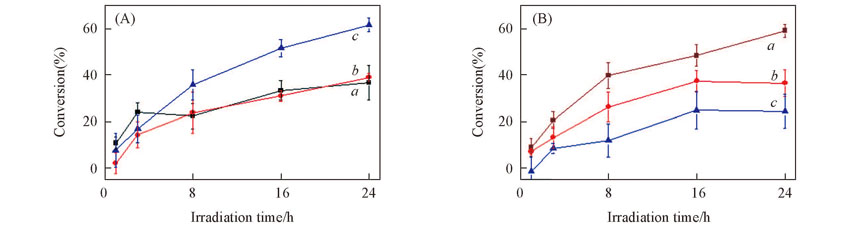
Fig.6 Effects of the sodium azide concentration on the photolysis of γ-HCH in ice at normal and deoxygenated conditionsc0(γ-HCH)=60 μg/L, c(RB)=10 mg/L, c(PBS)=0.005 mol/L. (A) pH=6; (B) pH=8. c(NaN3)/(mol·L-1): a. 0; b. 0.005; c. 0.050.
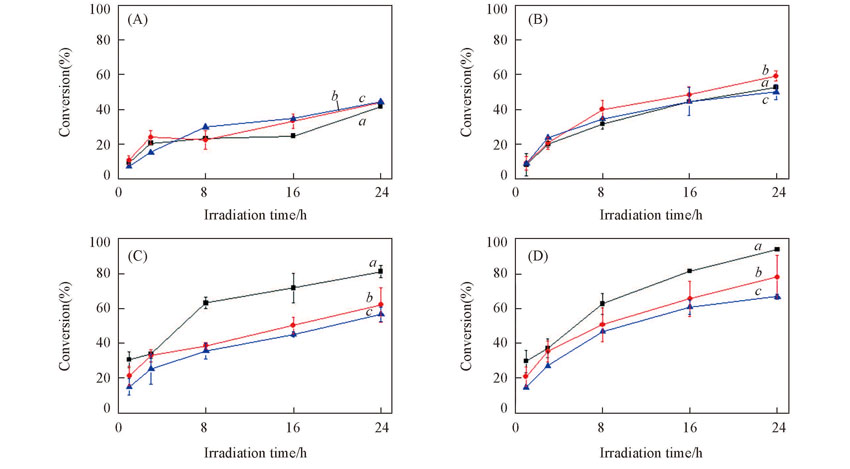
Fig.7 Effects of temperature on the photolysis of γ-HCH in ice at normal(A, B) and deoxygenated(C, D) conditionsc0(γ-HCH)=60 μg/L, c(RB)=10 mg/L, c(PBS)=0.005 mol/L. (A),(C) pH=6; (B), (D) pH=8.Temperature/K: a. 263; b. 256; c. 248.
| [1] | Gregor D. J., Gummer W. D., Environ. Sci. Technol., 1989, 23(5), 561—565 |
| [2] | Wania F., Hoff J. T., Jia C. Q., Mackay D., Environ. Pollut., 1998, 102(1), 25—41 |
| [3] | Yu Y., Li H., Piao L., Chen H., Wang W., Xia J., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2016, 32(1), 1—7 |
| [4] | Chen T, Sun C., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2016, 32(2), 261—267 |
| [5] | Grannas A. M., Bausch A. R., Mahanna K. M., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2007, 111(43), 11043—11049 |
| [6] | O’Concubhair R., Sodeau J. R., Accounts Chem. Res., 2013, 46(11), 2716—2724 |
| [7] | Beine H., Colussi A. J., Amoroso A., Esposito G., Montagnoli M., Hoffmann M. R., Environ. Res. Lett., 2008, 3(4), 045005 |
| [8] | Guzman M. I., Colussi A. J., Hoffmann M. R., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2006, 110(3), 931—935 |
| [9] | Kahan T. F., Donaldson D. J., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2007, 111(7), 1277—1285 |
| [10] | Dong X., Ma L. Q., Gress J., Harris W., Li Y., J. Hazard. Mater., 2014, 267, 62—70 |
| [11] | Peng F., Xue H. H., Tang X. J., Kang C. L., Li L. L., Li Z., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2012, 28(1), 47—52 |
| [12] | Liu H. F., Yang T., Kang C. L., Li L. L., Li Z., Liu J., Chen B. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(8), 1971—1978 |
| (刘汉飞, 杨婷, 康春莉, 李林璘, 李哲, 刘佳, 陈柏言.高等学校化学学报, 2013,34(8), 1971—1978) | |
| [13] | Tang X. J., Wang Y. X., Kang C. L., Liu H. F., Chen B. Y., Qiu S. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9), 1719—1723 |
| (唐晓剑, 王依雪, 康春莉, 刘汉飞, 陈柏言, 裘式纶.高等学校化学学报, 2015,36(9), 1719—1723) | |
| [14] | Niu J., Li Y., Wang W., Chemosphere, 2013, 92(11), 1423—1429 |
| [15] | Bower J. P., Anastasio C., Atmos. Environ., 2013, 75, 188—195 |
| [16] | King M. D., France J. L., Fisher F. N., Beine H. J., J. Photochem. Photobiol. A, 2005, 176(1), 39—49 |
| [17] | Shimizu O., Watanabe J., Naito S., Shibata Y., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2006, 110(5), 1735—1739 |
| [18] | Chu L., Anastasio C., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2003, 107(45), 9594—9602 |
| [19] | Bower J. P., Anastasio C., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2013, 117(30), 6612—6621 |
| [20] | Liu H. F., Kang C. L., Xue H. H., He C., Bao S. Q., Zhong Y. B., Tian T., Science Technology & Engineering, 2016,16(14), 9—11) |
| (刘汉飞, 康春莉, 薛洪海, 何冲, 包思琪, 钟宇博, 田涛.科学技术与工程, 2016,16(14), 9—11) | |
| [21] | Bao S. Q., Kang C. L., Zhong Y. B., Zhou L., Yao Z. F., Huang D. M., Wang Y. H., Tian T., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(12), 2253—2259 |
| (包思琪, 康春莉, 钟宇博, 周林, 姚志富, 黄冬梅, 王宇寒, 田涛.高等学校化学学报, 2016,37(12), 2253—2259) | |
| [22] | Xue H. H., Tang X. J., Kang C. L., Liu J., Shi L., Wang H. L., Yang T., Water Sci. Technol., 2013, 68(11), 2479—2484 |
| [23] | Bancirova M., Luminescence, 2011, 26(6), 685—688 |
| [24] | Chen Z. H., Dai C. M., Environ. Chem., 1984, 2, 11—18 |
| [25] | Miller J. S., Water Res., 2005, 39(2), 412—422 |
| [1] | CUI Shaoli, ZHANG Weijia, SHAO Xueguang, CAI Wensheng. Revealing the Effect of Threonine on the Binding Ability of Antifreeze Proteins with Ice Crystals by Free-energy Calculations [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210838. |
| [2] | GAO Huiling, CAO Zhenzhen, GU Fang, WANG Haijun. Monte Carlo Simulation on Self-healing Behaviour of Hydrogen-bonded Hydrogel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220482. |
| [3] | WU Zexin, ZHU Yuanjie, WANG Hongzhong, WANG Junan, HE Ying. Methyl-modified Carbazole/Diphenyl Sulfone-based AIE-TADF Blue Emitter and Its OLEDs [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220371. |
| [4] | YUAN Bo, QI Chaochao, ZHANG Xiangting, LUAN Guoyan, ZOU Haifeng. Luminescence Property and LED Device Application for Color-tunable Ca2LaTaO6∶Dy3+,Sm3+ Phosphor Based on Energy Transfer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2717. |
| [5] | PAN Xiaojun, BAO Rongrong, PAN Caofeng. Research Progress of Flexible Tactile Sensors Applied to Wearable Electronics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2359. |
| [6] | HAN Yixiu, WU Dianguo, LI Hongpu, YIN Hongyao, MEI Yongjun, FENG Yujun, ZHONG Zuqin. Interactions Between Hydrophobic Associating Poly(sodium acrylate) and a Zwitterionic Surfactant in Non-aqueous Media and Low Temperature Environment [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2056. |
| [7] | DING Hui, ZHOU Xuanxuan, ZHANG Zihui, XIA Kunlin, ZHAO Yunpeng. Solvent-free and High-yielding Synthesis of Highly Efficient Red-emitting Carbon Dots and Their Application in White Light Devices [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2080. |
| [8] | HU Xueyi, HAN Lulu, FANG Yun, XIA Yongmei. Admicelles and Adsolubilization of Extended Surfactants on Alumina [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 843. |
| [9] | FAN Juanjuan, HAN Yuanyuan, CUI Jie. Monte Carlo Simulation of the Transformation Control of ABC Triblock Copolymer Micelles from Multicompartment Structure to Multicore Structure [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 857. |
| [10] | WANG Wei, LU Xiangchao, ZHOU Lijun, LU Yizhen, CAO Yang. Design, Construction and Performance Research of Functional Devices Based on Two-dimensional Piezoelectric Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 595. |
| [11] | ZHANG Miao, PENG Jinlei, LIU Ying, LIU Fangjun, MA Wei, WEI Hua. Synthesis of Crosslinked Micelles and Ring-like Colloids via a Cyclic Template with Multivalency [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3526. |
| [12] | WANG Zhiqing, CHEN Binbin, SHEN Jie, CHEN Wen, LIU Yueli, GONG Shaokang, ZHOU Jing. Light Assisted Resistive Switching Characteristics of Cu12Sb4S13 Quantum Dots [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1908. |
| [13] | HUANG Jialing,LIU Fengjiao,WANG Tingting,LIU Cuie,ZHENG Fengying,WANG Zhenhong,LI Shunxing. Nitrogen and Sulfur co-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Accurate Detection of pH in Gastric Juice† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1513. |
| [14] | SHENG Hui, XUE Bin, QIN Meng, WANG Wei, CAO Yi. Preparation and Applications of Stretchable and Tough Hydrogels † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1194. |
| [15] | GAO Naiwei, MA Qiang, HE Yonglin, WANG Yapei. Green Electronic Devices Based on Ionic Liquids † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 901. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||