

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (10): 2252.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140448
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHU Ruiwen, SUN Weixiang, LIU Xinxing, TONG Zhen*( )
)
Received:2014-05-12
Online:2014-10-10
Published:2014-09-17
Contact:
TONG Zhen
E-mail:mcztong@scut.edu.cn
Supported by:TrendMD:
SHU Ruiwen, SUN Weixiang, LIU Xinxing, TONG Zhen. Effect of Poly(ethylene glycol) Concentration on the Re-entrant Gelation and Yielding Behavior of Aqueous Hectorite Clay Dispersion†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(10): 2252.
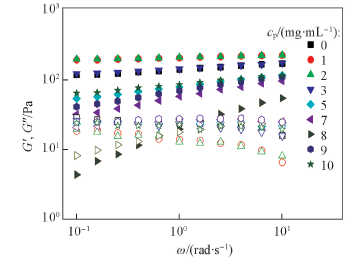
Fig.1 Dynamic storage modulus G'(filled symbols) and loss modulus G″(open symbols) as a function of ω for hectorite clay/PEG samples with cw=30 mg/mL and cp=0—10 mg/mL at γ0=0.5%
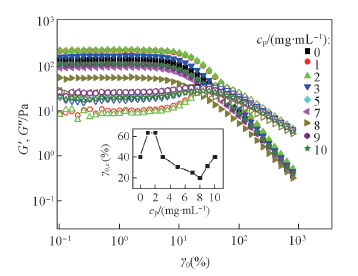
Fig.5 Strain amplitude γ0 dependence of the storage modulus G'(filled symbols) and loss modulus G″(open symbols) of hectorite clay/PEG samples L30Pcp with indicated cp at ω=6.28 rad/s Inset: cp dependence of the strain amplitude threshold γ0,c.
| [1] | Odom I. E., Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1984, 311(1517), 391—409 |
| [2] | Ruzicka B., Zaccarelli E., Soft Matter,2011, 7(4), 1268—1286 |
| [3] | Balnois E., Durand-Vidal S., Levitz P., Langmuir,2003, 19(17), 6633—6637 |
| [4] | Mourchid A., Delville A., Lambard J., LeColier E., Levitz P., Langmuir,1995, 11(6), 1942—1950 |
| [5] | Mourchid A., Levitz P., Physical Review E,1998, 57(5), R4887—R4890 |
| [6] | Yang Y. R., Sun W. X., Huang L. Z., Shu R. W., Tong Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2012, 33(4), 818—822 |
| (杨燕瑞, 孙尉翔, 黄丽浈, 疏瑞文, 童真. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(4), 818—822) | |
| [7] | Nelson A., Cosgrove T., Langmuir,2004, 20(6), 2298—2304 |
| [8] | Nelson A., Cosgrove T., Langmuir,2004, 20(24), 10382—10388 |
| [9] | Baghdadi H. A., Sardinha H., Bhatia S. R., Journal of Polymer Science, Part B: Polymer Physics,2005, 43(2), 233—240 |
| [10] | Baghdadi H., Jensen E., Easwar N., Bhatia S., Rheologica Acta,2008, 47(2), 121—127 |
| [11] | Baghdadi H., Parrella J., Bhatia S., Rheologica Acta,2008, 47(3), 349—357 |
| [12] | Sun W., Yang Y., Wang T., Huang H., Liu X., Tong Z., Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2012, 376(1), 76—82 |
| [13] | Tawari S. L., Koch D. L., Cohen C., Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2001, 240(1), 54—66 |
| [14] | Jabbari-Farouji S., Tanaka H., Wegdam G. H., Bonn D., Physical Review E,2008, 78(6), 061405 |
| [15] | Pathmamanoharan C., Slob C., Lekkerkerker H. N. W., Colloid and Polymer Science,1989, 267(5), 448—450 |
| [16] | Peng B., van der Wee E., Imhof A., van Blaaderen A., Langmuir,2012, 28(17), 6776—6785 |
| [17] | Jardine R. S., Bartlett P., Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2002, 211(2/3), 127—132 |
| [18] | Hu H., Larson R. G., Langmuir,2004, 20(18), 7436—7443 |
| [19] | Zulian L., Ruzicka B., Ruocco G., Philosophical Magazine,2008, 88(33), 4213—4221 |
| [20] | Dullens R. P. A., Claesson E. M., Kegel W. K., Langmuir,2003, 20(3), 658—664 |
| [21] | Wang Y., Eli W., Nueraimaiti A., Liu Y., Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2009, 48(8), 3749—3754. |
| [22] | Bonn D., Tanaka H., Wegdam G., Kellay H., Meunier J., Europhysics Letters,1999, 45(1), 52—57 |
| [23] | Gary L. H., EricR. W., Reports on Progress in Physics,2012, 75(6), 066501-1—066501-30 |
| [24] | Lattuada M., Wu H., Morbidelli M., Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2003, 268(1), 106—120 |
| [25] | Lattuada M., Sandkühler P., Wu H., Sefcik J., Morbidelli M., Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,2003, 103(1), 33—56 |
| [26] | Liu K. K., Williams D. R., Briscoe B. J., Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics,1998, 31(3), 294 |
| [27] | Del Gado E., Kob W., Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics,2008, 149(1—3), 28—33 |
| [28] | Perkins R., Brace R., Matijevic E., Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,1974, 48(3), 417—426 |
| [29] | Zhao X., Urano K., Ogasawara S., Colloid and Polymer Science,1989, 267(10), 899—906 |
| [30] | Koumakis N., Pamvouxoglou A., Poulos A. S., Petekidis G., Soft Matter,2012, 8(15), 4271—4284 |
| [1] | ZHANG Li,QIAN Mingchao,LIU Xueke,Gao Shuaitao,YU Jiang,XIE Haishen,WANG Hongbin,SUN Fengjiang,SU Xianghong. Dynamic Study of Oxidative Desulfurization by Iron-based Ionic Liquids/NHD † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 317. |
| [2] | GUO Zhaopei,LIN Lin,CHEN Jie,TIAN Huayu,CHEN Xuesi. Polyglutamic Acid Grafted Polyethylene Glycol@Calcium Carbonate Based Shielding System for Improving Polyethyleneimine Gene Transfection Efficiency † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 235. |
| [3] | LI Lin, XU Xinru, LI Yingqi, ZHANG Caifeng. Preparation of Targeting Nanodiamond-metaminopterone Drug System and Its Interaction with MCF-7 Cells † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1998. |
| [4] | ZHAO Yuxuan,CHEN Yanjun,PAN Guxin,WANG Chang,PENG Zhenbo,SUN Zongxu,LIANG Yongri,SHI Qisong. Preparation and Performance of Novel Tb-PEG+Eu-PEG/PANI/PAN Luminescent-electrical-phase Change Composite Fibers by Electrospinning† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 824. |
| [5] | LIU Bo,ZOU Nan,ZHANG Yuxia,SHI Haifeng. Structure and Properties of Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone)/Laponite Proton Exchange Membrane for All Vanadium Redox Flow Battery † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2186. |
| [6] | QIAN Yihao, ZHANG Dongjie, CHENG Zhongjun, KANG Hongjun, LIU Yuyan. Preparation of Hydrophilic Epoxy Resin and Its Wettability Regulation† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1823. |
| [7] | GAO Yan, ZHANG Hua, ZHANG Wen, LI Xiangpeng, YUE Pan, LI Wei. Preparation of Micro/Nano-fibers Membranes Encapsulated with Dual Drugs by Emulsion Electrospun and Controlled Release of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Drugs† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(3): 575. |
| [8] | LIU Jie, ZHOU Hao, HUANG Yufang, CHEN Xin. Soy Protein Isolate/Agar Composite Hydrogel† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(3): 591. |
| [9] | LIU Jie, ZHOU Hao, HUANG Yufang, CHEN Xin. Polyethylene Glycol Chemically Modified Soy Protein Isolate Hydrogel† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(2): 390. |
| [10] | CAO Xiaoqiang, YAN Bingqi, WANG Qian, WANG Yaping, QIU Jun, HUANG Yongqing, LI Lin, ZHANG Yan, HU Shugang, KANG Ling, LÜ Xianjun. Adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ) from Aqueous Solutions on Organic Modified Laponite† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(2): 173. |
| [11] | WANG Zhengguang, HU Duo, WU Dongwei, LU Lu, ZHOU Changren. Preparation and Properties of Double Network Hydrogels Based on Gellan Gum and Polyethylene Glycol Acrylate† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(2): 275. |
| [12] | QIU Chuanlong,LI Chunfang,LI Dongxiang,HOU Wanguo. Synthesis, Characterization and Aggregation Behavior of Polyethylene Glycol-conjugated Hydroxycamptothecin† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(8): 1535. |
| [13] | HU Qi, FANG Chao, ZHAO Wai’ou, LI Yapeng, CHEN Xia, WANG Jingyuan. Synthetic of PGMA-EDA-g-PEG-g-DS@IO as a Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agent for Atherosclerosis† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(10): 2061. |
| [14] | LI Xue-Quan, SUN Cheng-Yu, ZHAO Qian, WU Zhi-Shan, XU Dan-Ke, ZHONG Wen-Ying. Oxidation, Modification and Dispersibility of Single-walled Carbon Nanohorns [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(4): 763. |
| [15] | JIANG Xian-cai, SONG Jie, JIANG Ting, DAI Hua, ZHANG Xi. Melt Processing of PVA with Magnesium Chloride and Polyethylene Glycol as the Complex Plasticizer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(10): 2451. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||