

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (12): 2584.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140333
• Organic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Hongliang1, XU Guoxing1, BAO Meiying2, ZHANG Dapeng1, LI Zhiwei1,*( ), PEI Yazhong1,*(
), PEI Yazhong1,*( )
)
Received:2014-04-09
Online:2014-12-10
Published:2014-11-06
Contact:
LI Zhiwei,PEI Yazhong
E-mail:zwl.jida@gmail.com;peiyz@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
YANG Hongliang, XU Guoxing, BAO Meiying, ZHANG Dapeng, LI Zhiwei, PEI Yazhong. Design and Synthesis of Pyridinylisoxazoles and Their Anticancer Activities†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(12): 2584.
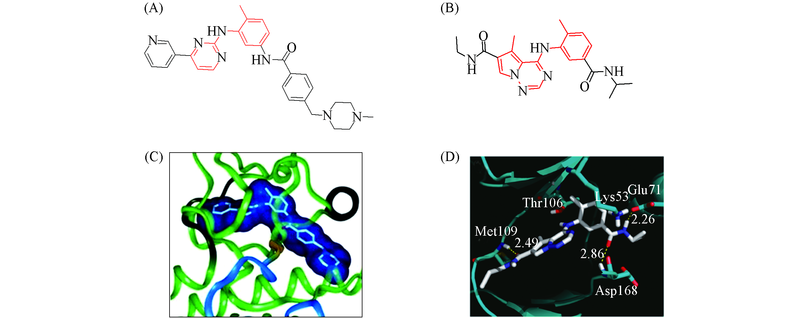
Fig.1 Structures of imatinib(A) and p38 inhibitor(B) and the X-ray co-crystal structures of known allosteric kinase inhibitors(C, D) (C) Imatinib binds to Abl kinase;(D) p38 inhibitor binds to p38 kinase.
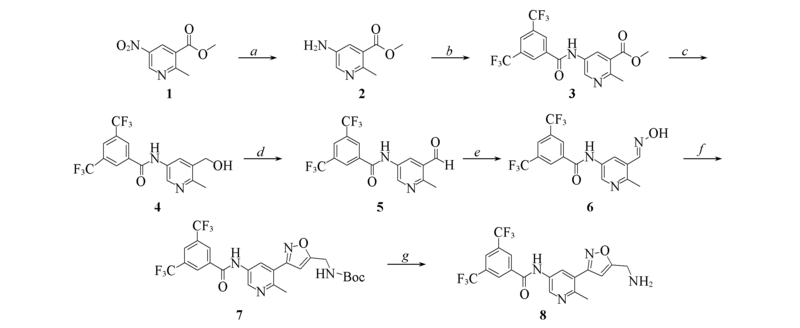
Scheme 1 Synthetic routes of intermediate 8 Reagents and conditions: a. H2, Pd/C, MeOH; b. 3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl) benzoic acid, DMAP, EDCI, DCM; c. LAH, THF, 0 ℃; d. Py·SO3, TEA, DMSO, DCM; e. NH2OH·HCl, EtOH, 70 ℃; f: (i). NCS, DMF, 0—50 ℃, (ii) N-Boc-propargylamine, TEA, DCM, 0 ℃; g. TFA, DCM, 0 ℃.
| Compd. | R1 | m.p./℃ | MS, m/z [M+H+] | Compd. | R2/NR3R4 | m.p./℃ | MS, m/z [M+H+] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | — | 116—118 | 167.2 | 10b |  | 184—185 | 598.7 |
| 3 | — | 56—58 | 406.9 | 10c |  | 176—178 | 614.7 |
| 4 | — | 191—193 | 378.8 | 10d |  | 199—201 | 602.7 |
| 5 | — | 227—229 | 10e |  | 153—155 | 652.7 | |
| 6 | — | 213—215 | 391.8 | 10f |  | 159—161 | 614.7 |
| 7 | — | 107—109 | 544.8 | 10g |  | 199—201 | 602.6 |
| 8 | — | 125—127 | 444.8 | 10h |  | 91—93 | 602.7 |
| 9a |  | 195—197 | 528.9 | 10i |  | 98—100 | 598.7 |
| 9b |  | 163—165 | 542.8 | 10j |  | 202—204 | 550.7 |
| 9c |  | 161—163 | 528.8 | 11 | — | 91—93 | 556.8 |
| 9d |  | 130—132 | 554.8 | 12a |  | 121—123 | 620.7 |
| 9e |  | 75—77 | 590.8 | 12b |  | 185—186 | 627.7 |
| 9f |  | 96—98 | 578.7 | 12c |  | 106—108 | 551.7 |
| 9g |  | 121—123 | 598.8 | 12d |  | 154—156 | 659.7 |
| 10a |  | 201—203 | 584.7 |
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of compounds 2—12
| Compd. | R1 | m.p./℃ | MS, m/z [M+H+] | Compd. | R2/NR3R4 | m.p./℃ | MS, m/z [M+H+] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | — | 116—118 | 167.2 | 10b |  | 184—185 | 598.7 |
| 3 | — | 56—58 | 406.9 | 10c |  | 176—178 | 614.7 |
| 4 | — | 191—193 | 378.8 | 10d |  | 199—201 | 602.7 |
| 5 | — | 227—229 | 10e |  | 153—155 | 652.7 | |
| 6 | — | 213—215 | 391.8 | 10f |  | 159—161 | 614.7 |
| 7 | — | 107—109 | 544.8 | 10g |  | 199—201 | 602.6 |
| 8 | — | 125—127 | 444.8 | 10h |  | 91—93 | 602.7 |
| 9a |  | 195—197 | 528.9 | 10i |  | 98—100 | 598.7 |
| 9b |  | 163—165 | 542.8 | 10j |  | 202—204 | 550.7 |
| 9c |  | 161—163 | 528.8 | 11 | — | 91—93 | 556.8 |
| 9d |  | 130—132 | 554.8 | 12a |  | 121—123 | 620.7 |
| 9e |  | 75—77 | 590.8 | 12b |  | 185—186 | 627.7 |
| 9f |  | 96—98 | 578.7 | 12c |  | 106—108 | 551.7 |
| 9g |  | 121—123 | 598.8 | 12d |  | 154—156 | 659.7 |
| 10a |  | 201—203 | 584.7 |
| Compd. | 1H NMR(300 MHz, CDCl3), δ | 13C NMR(75 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ |
|---|---|---|
| 2a | 8.13(d, J=3.0 Hz, 1H), 7.52(d, J=2.7 Hz, 1H), 3.90(s, 3H), 3.65(s, 2H), 2.70(s, 3H) | 167.9, 148.9, 140.3, 139.2, 124.8, 123.6, 52.0, 23.4 |
| 3a | 8.90(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.74(d, J=2.1 Hz, 1H), 8.39(s, 2H), 8.30(s, 1H), 8.10(s, 1H), 3.95(s, 3H), 2.86(s, 3H) | 166.3, 163.6, 156.1, 143.6, 135.8, 132.4(q, J=34.1 Hz), 132.2 , 130.6, 127.7, 125.7, 125.3, 122.7(q, J=271.4 Hz), 52.5, 23.9 |
| 4b | 10.75(s, 1H), 8.76(s, 1H), 8.63(s, 2H), 8.39(s, 1H), 8.12(s, 1H), 5.40(t, J=5.1 Hz, 1H), 4.53(d, J=5.1 Hz, 2H), 2.37(s, 3H) | 162.5, 150.6, 139.0, 136.6, 135.4, 133.2, 130.5(q, J=33.2 Hz), 128.5, 125.9, 125.1, 123.1(q, J=271.4 Hz), 59.8, 20.8 |
| 5b | 9.15(s, 1H), 8.92(s, 1H), 8.70(s, 2H), 8.45(s, 1H), 8.42(s, 1H), 2.74(s, 3H) | 163.2, 147.3, 143.2, 135.6, 133.3, 130.6(q, J=33.3 Hz), 130.5, 129.7, 128.8, 125.8, 122.9(q, J=271.3 Hz), 17.7 |
| 6b | 11.63(s, 1H), 10.83(s, 1H), 8.85(s, 1H), 8.64(s, 2H), 8.48(d, J=2.1 Hz, 1H), 8.41(s, 1H), 8.35(s, 1H), 2.56(s, 3H) | 162.9, 150.9, 145.2, 141.5, 136.4, 132.9, 131.0, 130.4(q, J=33.2 Hz), 128.1, 124.6, 124.5(q, J=278.1 Hz), 21.3 |
| 7 | 9.00(s, 1H), 8.80(d, J=2.7 Hz, 1H), 8.43(s, 2H), 8.24(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.04(s, 1H), 6.39(s, 1H), 5.23(t, J=5.4 Hz, 1H), 4.47(d, J=6.0 Hz, 2H), 2.61(s, 3H), 1.45(s, 9H) | 162.8, 160.9, 155.6, 151.2, 145.4, 141.9, 136.3, 133.2, 130.5(q, J=33.2 Hz), 128.5, 125.3, 124.9, 124.3(q, J=270.5 Hz), 123.5, 102.0, 78.5, 36.1, 28.1, 23.3 |
| 8 | 8.73(s, 1H), 8.65(s, 1H), 8.39(s, 2H), 8.29(d, J=1.8 Hz, 1H), 8.07(s, 1H), 6.41(s, 1H), 4.07(s, 3H), 2.65(s, 3H) | 175.7, 162.8, 160.8, 151.1, 142.0, 136.4, 133.4, 130.5(q, J=32.9 Hz), 128.7, 128.2, 125.3, 123.7, 123.1(q, J=271.6 Hz), 101.2, 37.8, 23.4 |
| 9a | 9.78(s, 1H), 8.83(s, 1H), 8.50(s, 2H), 8.27(s, 1H), 8.03(s, 1H), 6.61(s, 1H), 6.35(s, 1H), 4.57(d, J=5.4 Hz, 2H), 2.57(s, 3H), 1.24(s, 9H) | 177.8, 171.7, 162.8, 160.9, 151.3, 141.8, 136.4, 133.3, 130.6(q, J=33.2 Hz), 128.6, 128.4, 125.4, 123.7, 123.1(q, J=268.9 Hz), 101.8, 35.1, 27.3, 23.3 |
| 9ba | 9.13(s, 1H), 8.83(s, 1H), 8.48(s, 2H), 8.19(s, 1H), 8.07(s, 1H), 7.37(d, J=6.0 Hz, 1H), 6.37(s, 1H), 4.62(t, J=5.4 Hz, 2H), 4.40(dd, J=6.0 Hz, 1H), 4.06—3.84(m, 2H), 2.29(m, 1H), 2.11—1.82(m, 3H) | 169.3, 164.1, 158.5, 156.2, 147.8, 137.2, 131.1, 127.7, 127.2(q, J=33.7 Hz), 124.0, 123.2, 120.6, 119.1, 118.0(q, J=266.0 Hz), 97.7, 64.7, 29.8, 25.3, 20.6, 18.5 |
| 9ca | 9.49(s, 1H), 8.79(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.48(s, 2H), 8.09(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.05(s, 1H), 6.53(t, J=6.0 Hz, 1H), 6.32(s, 1H), 4.58(d, J=5.7 Hz, 2H), 2.52(s, 3H), 2.11(s, 2H), 1.14(dd, J=6.9 Hz, 1H), 1.03—0.87(m, 6H) | 173.8, 169.8, 163.9, 161.2, 152.7, 142.3, 136.1, 133.0, 132.3(q, J=33.7 Hz), 129.2, 128.3, 125.9, 124.3, 123.1(q, J=271.4 Hz), 102.8, 45.8, 35.5, 26.4, 23.4, 22.5 |
| 9db | 8.79(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.66(s, 2H), 8.44(t, J=6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.35(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.26(s, 1H), 6.64(s, 1H), 4.47(d, J=5.7 Hz, 2H), 2.56(s, 3H), 2.18(m, 1H), 1.72(s, 4H), 1.63(s, 1H), 1.33(m, 3H), 1.20(m, 2H) | 175.4, 171.1, 163.0, 161.1, 150.4, 142.6, 137.7, 135.0, 130.3(q, J=32.9 Hz), 128.5, 124.7, 123.4, 123.1(q, J=271.4 Hz), 102.0, 43.7, 34.5, 29.0, 25.4, 25.1, 23.2 |
| 9e | 9.04(s, 1H), 8.81(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.47(s, 1H), 8.12(d, J=2.1 Hz, 1H), 8.07(s, 1H), 7.24—7.23(m, 1H), 7.22(s, 1H), 7.19—7.11(m, 2H), 6.25(t, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 6.21(s, 1H), 4.55(d, J=6.0 Hz, 2H), 2.96(t, J=7.5 Hz, 2H), 2.59(s, 3H), 2.56(d, J=7.5 Hz, 2H) | 171.7, 171.1, 162.8, 160.9, 151.3, 142.0, 141.1, 136.4, 133.2, 130.6(q, J=33.3 Hz), 128.6, 128.2, 125.8, 125.4, 123.5, 123.1(q, J=271.1 Hz), 102.2, 36.7, 34.5, 30.9, 23.3 |
| 9f | 9.25(s, 1H), 8.85(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.46(s, 2H), 8.03(s, 1H), 8.00(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.32(t, J=6.0 Hz, 2H), 7.04(d, J=6.6 Hz, 1H), 6.34(s, 1H), 4.77(d, J=6.0 Hz, 2H), 3.78(s, 3H), 2.57(s, 3H) | 176.2, 171.8, 168.0, 164.4, 156.6, 147.2, 140.2, 138.4, 137.4, 135.8(q, J=33.8 Hz), 134.8, 134.7, 133.8, 133.5, 128.7, 125.4(q, J=251.4 Hz), 124.8, 122.6, 119.1, 117.7, 107.6, 60.4, 41.5, 28.6 |
| 9g | 9.33(s, 1H), 8.87(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.47(s, 2H), 8.32(s, 1H), 8.02(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.00(s, 1H), 7.91—7.77(m, 4H), 7.61—7.50(m, 2H), 7.47(t, J=5.7 Hz, 2H), 6.35(s, 1H), 4.82(d, J=5.7 Hz, 2H), 2.54(s, 3H) | 171.0, 166.5, 162.7, 161.1, 151.4, 142.0, 136.3, 134.3, 133.2, 132.1, 131.0, 130.6(q, J=33.2 Hz), 128.9, 128.5, 128.3, 128.0, 127.8, 127.7, 127.6, 126.7, 125.3, 124.1, 123.5, 123.1(q, J=271.3 Hz), 102.5, 35.4, 23.4 |
| 10ab | 10.93(s, 1H), 8.92(d, J=1.8 Hz, 1H), 8.65(s, 2H), 8.57(t, J=6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.43(s, 1H), 8.30(d, J=2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.99—7.83(m, 2H), 7.63—7.55(m, 3H), 6.63(s, 1H), 4.33(d, J=6.0 Hz, 2H), 2.53(s, 3H) | 169.2, 162.8, 160.7, 151.2, 141.9, 140.3, 136.3, 133.2, 132.5, 130.5(q, J=33.3 Hz), 129.1, 128.5, 128.1, 126.4, 125.3, 123.3, 123.0(q, J=271.4 Hz), 103.2, 23.2 |
| 10b | 8.92(s, 1H), 8.63(s, 1H), 8.43(s, 2H), 8.17(s, 1H), 8.07(s, 1H), 7.76(d, J=8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.32(d, J=8.1 Hz, 2H), 6.37(s, 1H), 4.37(d, J=6.3 Hz, 2H), 2.61(s, 3H), 2.40(s, 3H) | 169.3, 162.8, 160.8, 151.3, 142.8, 142.1, 137.6, 136.4, 133.2, 130.8(q, J=33.2 Hz), 129.6, 128.6, 128.2, 126.5, 125.3, 124.9(q, J=271.4 Hz), 123.3, 103.2, 38.0, 23.2, 20.8 |
| 10c | 8.93(d, J=2.1 Hz, 1H), 8.69(s, 1H), 8.41(s, 2H), 8.06(d, J=2.1 Hz, 1H), 8.04(s, 1H), 7.78(d, J=9.0 Hz, 2H), 6.95(d, J=9.0 Hz, 2H), 6.32(s, 1H), 4.32(d, J=6.3 Hz, 2H), 3.80(s, 3H), 2.57(s, 3H) | 162.8, 162.2, 160.7, 151.2, 142.0, 136.4, 133.1, 132.0, 131.4, 130.6(q, J=33.3 Hz), 128.7, 128.6, 128.2, 125.3, 123.3, 123.1(q, J=271.4 Hz), 114.2, 103.1, 55.5, 38.0, 23.2 |
| 10db | 10.93(s, 1H), 8.92(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.65(s, 2H), 8.43(s, 1H), 8.30(d, J=2.7 Hz, 1H), 7.96—7.78(m, 2H), 7.41(t, J=9.0 Hz, 2H), 6.65(s, 1H), 4.35(d, J= 3.3 Hz, 2H), 2.54(s, 3H) | 169.2, 165.8, 162.9, 162.5, 160.8, 151.3, 142.0, 136.9, 134.8(d, J=235.1 Hz), 130.6(q, J=33.2 Hz), 129.6(d, J=7.4 Hz), 128.6, 128.2, 125.5, 123.3, 123.1(q, J=271.1 Hz), 116.3(d, J=22.6 Hz), 103.3, 37.9, 23.3 |
| 10eb | 10.93(s, 1H), 8.91(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.85(s, 1H), 8.65(s, 2H), 8.44(s, 1H), 8.28(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.18—8.04(m, 2H), 8.01(d, J=8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.83(t, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 6.66(s, 1H), 4.43(s, 2H), 2.51(s, 3H) | 168.8, 162.9, 160.8, 151.2, 142.1, 141.7, 136.4, 133.2, 130.6(q, J=30.3 Hz), 130.6(q, J=33.8 Hz), 129.3, 128.6, 128.1, 125.6, 125.5(q, J=181.2 Hz), 123.6(q, J=271.6 Hz), 123.2, 103.4, 37.8, 23.3 |
| 10fb | 10.92(s, 1H), 8.92(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.65(s, 2H), 8.55(t, J=6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.42(s, 1H), 8.31(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.49(t, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.41—7.35(m, 1H), 7.33—7.28(m, 1H), 7.17(m, 1H), 6.64(s, 1H), 4.33(d, J=6.0 Hz, 2H), 3.79(s, 3H), 2.53(s, 3H) | 174.4, 168.0, 165.9, 164.5, 156.4, 147.2, 146.7, 141.5, 138.3, 135.9(q, J=33.0 Hz), 135.5, 133.7, 133.3, 130.5, 128.4, 128.2(q, J=271.6 Hz), 123.7, 123.6, 116.6, 108.4, 60.6, 43.1, 28.4 |
| 10gb | 10.93(s, 1H), 8.92(d, J=2.7 Hz, 1H), 8.73(t, J=6.3 Hz, 1H), 8.65(s, 2H), 8.43(s, 1H), 8.30(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.67—7.57(m, 3H), 7.55—7.45(m, 1H), 6.68(s, 1H), 4.38(d, J=6.0 Hz, 2H), 2.53(s, 3H) | 174.2, 168.0, 166.8(d, J=247.1 Hz), 166.0, 156.4, 147.7(d, J=6.45 Hz), 147.2, 141.6, 138.4, 136.8(d, J=7.95 Hz), 135.7(q, J=33.1 Hz), 133.8, 133.3, 130.6, 128.5, 128.2(q, J=268.9 Hz), 127.9(d, J=2.9 Hz), 125.1(d, J=20.9 Hz), 118.7(d, J=24.3 Hz), 108.6, 43.1, 28.4 |
| 10hb | 10.91(s, 1H), 8.91(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.86(t, J=6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.65(s, 2H), 8.41(s, 1H), 8.28(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.78(td, J=7.5, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.72—7.60(m, 1H), 7.46—7.28(m, 2H), 6.63(s, 1H), 4.43(d, J=6.3 Hz, 2H), 2.52(s, 3H) | 169.3, 163.2, 160.9, 158.4(d, J=252.2 Hz), 151.5, 142.2, 136.5, 135.8, 135.7(d, J=8.5 Hz), 133.4, 130.8(q, J=33.4 Hz), 129.8, 128.7(d, J=19.5 Hz), 128.4(d, J=9.9 Hz), 125.6, 125.2(q, J=271.0 Hz), 123.5, 123.0(d, J=3.7 Hz), 117.3(d, J=20.7 Hz), 103.5, 37.9, 23.4 |
| 10ib | 10.93(s, 1H), 8.92(d, J=2.1 Hz, 1H), 8.66(s, 2H), 8.42(s, 1H), 8.29(d, J=2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.83(d, J=7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.51—7.46(m, 1H), 7.41—7.27(m, 2H), 6.54(s, 1H), 4.34(d, J=6.3 Hz, 2H), 3.36(s, 3H), 2.59(s, 3H) | 169.3, 162.8, 160.7, 151.2, 142.0, 138.4, 136.6, 136.4, 134.8, 133.2, 132.9, 132.6, 132.4, 130.1(q, J=33.4 Hz), 128.5, 128.1, 126.1, 123.3, 123.1(q, J=271.3 Hz), 103.1, 37.6, 23.2, 19.7 |
| 10jb | 10.94(s, 1H), 8.96(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.65(s, 2H), 8.43(s, 1H), 8.38(d, J=2.7 Hz, 1H), 7.93(t, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 6.85(s, 1H), 4.45(d, J=4.8 Hz, 2H), 3.22(m, 1H), 2.62(s, 3H), 1.25(s, 3H), 1.23(s, 3H) | 170.7, 162.8, 161.0, 151.3, 142.0, 136.3, 133.2, 130.6(q, J=33.3 Hz), 128.5, 128.2, 125.6, 123.4, 123.0(q, J=274.7 Hz), 103.0, 52.1, 38.0, 23.3, 16.2 |
| 11b | 10.90(s, 1H), 8.94(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.64(s, 2H), 8.41(s, 1H), 8.39—8.33(m, 3H), 6.81(d, J=5.4 Hz, 1H), 6.76(s, 1H), 4.73(d, J=5.7 Hz, 2H), 2.60(s, 3H) | 162.8, 161.9, 161.0, 160.9, 154.8, 151.3, 142.0, 136.3, 133.1, 130.5(q, J=33.2 Hz), 128.5, 128.2, 125.4, 123.5, 123.0(q, J=275.6 Hz), 110.4, 102.7, 102.6, 23.3, 13.2 |
| 12ab | 10.94(s, 1H), 8.93(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.65(s, 2H), 8.41(s, 1H), 8.36(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.78(d, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 7.72(s, 1H), 6.73(s, 1H), 5.88(d, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 4.69(d, J=5.4 Hz, 2H), 3.62(t, J=4.5 Hz, 4H), 2.60(s, 3H), 2.32(t, J=4.8 Hz, 4H), 2.15(s, 3H) | 171.8, 162.8, 162.0, 161.0, 160.9, 155.4, 151.3, 141.9, 136.3, 133.2, 130.6(q, J=33.3 Hz), 128.6, 128.2, 125.5, 123.5, 123.1(q, J=271.8 Hz), 102.1, 54.4, 45.6, 43.1, 35.9, 23.4 |
| 12bb | 10.91(s, 1H), 8.95(s, 1H), 8.65(s, 2H), 8.42(s, 1H), 8.32(s, 1H), 7.71(d, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 7.64(s, 1H), 7.28—7.20(m, 4H), 7.11(s, 1H), 6.62(s, 1H), 5.85(d, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 4.68(d, J=4.8 Hz, 2H), 4.42(d, J=5.4 Hz, 2H), 2.58(s, 3H) | 162.7, 162.3, 161.4, 157.3, 156.0, 154.5, 151.7, 141.2, 136.3, 133.0, 130.6(q, J=32.9 Hz), 128.5, 128.0, 125.4, 123.9, 123.0(q, J=271.2 Hz), 113.1, 98.0, 43.4, 25.0, 13.0 |
| 12cb | 10.91(s, 1H), 8.95(d, J=2.7 Hz, 1H), 8.64(s, 2H), 8.41(s, 1H), 8.34(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.72(d, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 7.58(s, 1H), 6.73(s, 1H), 6.45(d, J=4.5 Hz, 1H), 5.83(d, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 4.70(d, J=6.0 Hz, 2H), 2.72(d, J=4.8 Hz, 3H), 2.61(s, 3H) | 171.9, 162.8, 162.4, 162.2, 160.9, 155.3, 151.3, 141.9, 136.4, 133.2, 130.6(q, J=33.2 Hz), 128.6, 128.2, 125.4, 124.9(q, J=271.4 Hz), 123.6, 102.2, 35.1, 27.7, 23.4 |
| 12db | 11.77(s, 1H), 10.89(s, 1H), 8.94(d, J=2.7 Hz, 1H), 8.63(s, 2H), 8.40(s, 1H), 8.31(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.86(d, J=5.4 Hz, 2H), 6.74(s, 1H), 6.19(s, 1H), 6.02(d, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 4.77(d, J=5.4 Hz, 2H), 2.57(s, 3H), 1.21(s, 9H) | 171.7, 162.8, 162.2, 160.9, 159.0, 151.3, 142.0, 136.4, 133.2, 130.6(q, J=33.1 Hz), 128.6, 128.2, 125.4, 123.5, 123.1(q, J=267.8 Hz), 102.3, 36.0, 30.8, 30.0, 23.4 |
Table 2 Spectral data of compounds 2—12
| Compd. | 1H NMR(300 MHz, CDCl3), δ | 13C NMR(75 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ |
|---|---|---|
| 2a | 8.13(d, J=3.0 Hz, 1H), 7.52(d, J=2.7 Hz, 1H), 3.90(s, 3H), 3.65(s, 2H), 2.70(s, 3H) | 167.9, 148.9, 140.3, 139.2, 124.8, 123.6, 52.0, 23.4 |
| 3a | 8.90(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.74(d, J=2.1 Hz, 1H), 8.39(s, 2H), 8.30(s, 1H), 8.10(s, 1H), 3.95(s, 3H), 2.86(s, 3H) | 166.3, 163.6, 156.1, 143.6, 135.8, 132.4(q, J=34.1 Hz), 132.2 , 130.6, 127.7, 125.7, 125.3, 122.7(q, J=271.4 Hz), 52.5, 23.9 |
| 4b | 10.75(s, 1H), 8.76(s, 1H), 8.63(s, 2H), 8.39(s, 1H), 8.12(s, 1H), 5.40(t, J=5.1 Hz, 1H), 4.53(d, J=5.1 Hz, 2H), 2.37(s, 3H) | 162.5, 150.6, 139.0, 136.6, 135.4, 133.2, 130.5(q, J=33.2 Hz), 128.5, 125.9, 125.1, 123.1(q, J=271.4 Hz), 59.8, 20.8 |
| 5b | 9.15(s, 1H), 8.92(s, 1H), 8.70(s, 2H), 8.45(s, 1H), 8.42(s, 1H), 2.74(s, 3H) | 163.2, 147.3, 143.2, 135.6, 133.3, 130.6(q, J=33.3 Hz), 130.5, 129.7, 128.8, 125.8, 122.9(q, J=271.3 Hz), 17.7 |
| 6b | 11.63(s, 1H), 10.83(s, 1H), 8.85(s, 1H), 8.64(s, 2H), 8.48(d, J=2.1 Hz, 1H), 8.41(s, 1H), 8.35(s, 1H), 2.56(s, 3H) | 162.9, 150.9, 145.2, 141.5, 136.4, 132.9, 131.0, 130.4(q, J=33.2 Hz), 128.1, 124.6, 124.5(q, J=278.1 Hz), 21.3 |
| 7 | 9.00(s, 1H), 8.80(d, J=2.7 Hz, 1H), 8.43(s, 2H), 8.24(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.04(s, 1H), 6.39(s, 1H), 5.23(t, J=5.4 Hz, 1H), 4.47(d, J=6.0 Hz, 2H), 2.61(s, 3H), 1.45(s, 9H) | 162.8, 160.9, 155.6, 151.2, 145.4, 141.9, 136.3, 133.2, 130.5(q, J=33.2 Hz), 128.5, 125.3, 124.9, 124.3(q, J=270.5 Hz), 123.5, 102.0, 78.5, 36.1, 28.1, 23.3 |
| 8 | 8.73(s, 1H), 8.65(s, 1H), 8.39(s, 2H), 8.29(d, J=1.8 Hz, 1H), 8.07(s, 1H), 6.41(s, 1H), 4.07(s, 3H), 2.65(s, 3H) | 175.7, 162.8, 160.8, 151.1, 142.0, 136.4, 133.4, 130.5(q, J=32.9 Hz), 128.7, 128.2, 125.3, 123.7, 123.1(q, J=271.6 Hz), 101.2, 37.8, 23.4 |
| 9a | 9.78(s, 1H), 8.83(s, 1H), 8.50(s, 2H), 8.27(s, 1H), 8.03(s, 1H), 6.61(s, 1H), 6.35(s, 1H), 4.57(d, J=5.4 Hz, 2H), 2.57(s, 3H), 1.24(s, 9H) | 177.8, 171.7, 162.8, 160.9, 151.3, 141.8, 136.4, 133.3, 130.6(q, J=33.2 Hz), 128.6, 128.4, 125.4, 123.7, 123.1(q, J=268.9 Hz), 101.8, 35.1, 27.3, 23.3 |
| 9ba | 9.13(s, 1H), 8.83(s, 1H), 8.48(s, 2H), 8.19(s, 1H), 8.07(s, 1H), 7.37(d, J=6.0 Hz, 1H), 6.37(s, 1H), 4.62(t, J=5.4 Hz, 2H), 4.40(dd, J=6.0 Hz, 1H), 4.06—3.84(m, 2H), 2.29(m, 1H), 2.11—1.82(m, 3H) | 169.3, 164.1, 158.5, 156.2, 147.8, 137.2, 131.1, 127.7, 127.2(q, J=33.7 Hz), 124.0, 123.2, 120.6, 119.1, 118.0(q, J=266.0 Hz), 97.7, 64.7, 29.8, 25.3, 20.6, 18.5 |
| 9ca | 9.49(s, 1H), 8.79(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.48(s, 2H), 8.09(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.05(s, 1H), 6.53(t, J=6.0 Hz, 1H), 6.32(s, 1H), 4.58(d, J=5.7 Hz, 2H), 2.52(s, 3H), 2.11(s, 2H), 1.14(dd, J=6.9 Hz, 1H), 1.03—0.87(m, 6H) | 173.8, 169.8, 163.9, 161.2, 152.7, 142.3, 136.1, 133.0, 132.3(q, J=33.7 Hz), 129.2, 128.3, 125.9, 124.3, 123.1(q, J=271.4 Hz), 102.8, 45.8, 35.5, 26.4, 23.4, 22.5 |
| 9db | 8.79(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.66(s, 2H), 8.44(t, J=6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.35(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.26(s, 1H), 6.64(s, 1H), 4.47(d, J=5.7 Hz, 2H), 2.56(s, 3H), 2.18(m, 1H), 1.72(s, 4H), 1.63(s, 1H), 1.33(m, 3H), 1.20(m, 2H) | 175.4, 171.1, 163.0, 161.1, 150.4, 142.6, 137.7, 135.0, 130.3(q, J=32.9 Hz), 128.5, 124.7, 123.4, 123.1(q, J=271.4 Hz), 102.0, 43.7, 34.5, 29.0, 25.4, 25.1, 23.2 |
| 9e | 9.04(s, 1H), 8.81(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.47(s, 1H), 8.12(d, J=2.1 Hz, 1H), 8.07(s, 1H), 7.24—7.23(m, 1H), 7.22(s, 1H), 7.19—7.11(m, 2H), 6.25(t, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 6.21(s, 1H), 4.55(d, J=6.0 Hz, 2H), 2.96(t, J=7.5 Hz, 2H), 2.59(s, 3H), 2.56(d, J=7.5 Hz, 2H) | 171.7, 171.1, 162.8, 160.9, 151.3, 142.0, 141.1, 136.4, 133.2, 130.6(q, J=33.3 Hz), 128.6, 128.2, 125.8, 125.4, 123.5, 123.1(q, J=271.1 Hz), 102.2, 36.7, 34.5, 30.9, 23.3 |
| 9f | 9.25(s, 1H), 8.85(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.46(s, 2H), 8.03(s, 1H), 8.00(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.32(t, J=6.0 Hz, 2H), 7.04(d, J=6.6 Hz, 1H), 6.34(s, 1H), 4.77(d, J=6.0 Hz, 2H), 3.78(s, 3H), 2.57(s, 3H) | 176.2, 171.8, 168.0, 164.4, 156.6, 147.2, 140.2, 138.4, 137.4, 135.8(q, J=33.8 Hz), 134.8, 134.7, 133.8, 133.5, 128.7, 125.4(q, J=251.4 Hz), 124.8, 122.6, 119.1, 117.7, 107.6, 60.4, 41.5, 28.6 |
| 9g | 9.33(s, 1H), 8.87(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.47(s, 2H), 8.32(s, 1H), 8.02(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.00(s, 1H), 7.91—7.77(m, 4H), 7.61—7.50(m, 2H), 7.47(t, J=5.7 Hz, 2H), 6.35(s, 1H), 4.82(d, J=5.7 Hz, 2H), 2.54(s, 3H) | 171.0, 166.5, 162.7, 161.1, 151.4, 142.0, 136.3, 134.3, 133.2, 132.1, 131.0, 130.6(q, J=33.2 Hz), 128.9, 128.5, 128.3, 128.0, 127.8, 127.7, 127.6, 126.7, 125.3, 124.1, 123.5, 123.1(q, J=271.3 Hz), 102.5, 35.4, 23.4 |
| 10ab | 10.93(s, 1H), 8.92(d, J=1.8 Hz, 1H), 8.65(s, 2H), 8.57(t, J=6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.43(s, 1H), 8.30(d, J=2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.99—7.83(m, 2H), 7.63—7.55(m, 3H), 6.63(s, 1H), 4.33(d, J=6.0 Hz, 2H), 2.53(s, 3H) | 169.2, 162.8, 160.7, 151.2, 141.9, 140.3, 136.3, 133.2, 132.5, 130.5(q, J=33.3 Hz), 129.1, 128.5, 128.1, 126.4, 125.3, 123.3, 123.0(q, J=271.4 Hz), 103.2, 23.2 |
| 10b | 8.92(s, 1H), 8.63(s, 1H), 8.43(s, 2H), 8.17(s, 1H), 8.07(s, 1H), 7.76(d, J=8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.32(d, J=8.1 Hz, 2H), 6.37(s, 1H), 4.37(d, J=6.3 Hz, 2H), 2.61(s, 3H), 2.40(s, 3H) | 169.3, 162.8, 160.8, 151.3, 142.8, 142.1, 137.6, 136.4, 133.2, 130.8(q, J=33.2 Hz), 129.6, 128.6, 128.2, 126.5, 125.3, 124.9(q, J=271.4 Hz), 123.3, 103.2, 38.0, 23.2, 20.8 |
| 10c | 8.93(d, J=2.1 Hz, 1H), 8.69(s, 1H), 8.41(s, 2H), 8.06(d, J=2.1 Hz, 1H), 8.04(s, 1H), 7.78(d, J=9.0 Hz, 2H), 6.95(d, J=9.0 Hz, 2H), 6.32(s, 1H), 4.32(d, J=6.3 Hz, 2H), 3.80(s, 3H), 2.57(s, 3H) | 162.8, 162.2, 160.7, 151.2, 142.0, 136.4, 133.1, 132.0, 131.4, 130.6(q, J=33.3 Hz), 128.7, 128.6, 128.2, 125.3, 123.3, 123.1(q, J=271.4 Hz), 114.2, 103.1, 55.5, 38.0, 23.2 |
| 10db | 10.93(s, 1H), 8.92(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.65(s, 2H), 8.43(s, 1H), 8.30(d, J=2.7 Hz, 1H), 7.96—7.78(m, 2H), 7.41(t, J=9.0 Hz, 2H), 6.65(s, 1H), 4.35(d, J= 3.3 Hz, 2H), 2.54(s, 3H) | 169.2, 165.8, 162.9, 162.5, 160.8, 151.3, 142.0, 136.9, 134.8(d, J=235.1 Hz), 130.6(q, J=33.2 Hz), 129.6(d, J=7.4 Hz), 128.6, 128.2, 125.5, 123.3, 123.1(q, J=271.1 Hz), 116.3(d, J=22.6 Hz), 103.3, 37.9, 23.3 |
| 10eb | 10.93(s, 1H), 8.91(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.85(s, 1H), 8.65(s, 2H), 8.44(s, 1H), 8.28(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.18—8.04(m, 2H), 8.01(d, J=8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.83(t, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 6.66(s, 1H), 4.43(s, 2H), 2.51(s, 3H) | 168.8, 162.9, 160.8, 151.2, 142.1, 141.7, 136.4, 133.2, 130.6(q, J=30.3 Hz), 130.6(q, J=33.8 Hz), 129.3, 128.6, 128.1, 125.6, 125.5(q, J=181.2 Hz), 123.6(q, J=271.6 Hz), 123.2, 103.4, 37.8, 23.3 |
| 10fb | 10.92(s, 1H), 8.92(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.65(s, 2H), 8.55(t, J=6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.42(s, 1H), 8.31(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.49(t, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.41—7.35(m, 1H), 7.33—7.28(m, 1H), 7.17(m, 1H), 6.64(s, 1H), 4.33(d, J=6.0 Hz, 2H), 3.79(s, 3H), 2.53(s, 3H) | 174.4, 168.0, 165.9, 164.5, 156.4, 147.2, 146.7, 141.5, 138.3, 135.9(q, J=33.0 Hz), 135.5, 133.7, 133.3, 130.5, 128.4, 128.2(q, J=271.6 Hz), 123.7, 123.6, 116.6, 108.4, 60.6, 43.1, 28.4 |
| 10gb | 10.93(s, 1H), 8.92(d, J=2.7 Hz, 1H), 8.73(t, J=6.3 Hz, 1H), 8.65(s, 2H), 8.43(s, 1H), 8.30(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.67—7.57(m, 3H), 7.55—7.45(m, 1H), 6.68(s, 1H), 4.38(d, J=6.0 Hz, 2H), 2.53(s, 3H) | 174.2, 168.0, 166.8(d, J=247.1 Hz), 166.0, 156.4, 147.7(d, J=6.45 Hz), 147.2, 141.6, 138.4, 136.8(d, J=7.95 Hz), 135.7(q, J=33.1 Hz), 133.8, 133.3, 130.6, 128.5, 128.2(q, J=268.9 Hz), 127.9(d, J=2.9 Hz), 125.1(d, J=20.9 Hz), 118.7(d, J=24.3 Hz), 108.6, 43.1, 28.4 |
| 10hb | 10.91(s, 1H), 8.91(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.86(t, J=6.0 Hz, 1H), 8.65(s, 2H), 8.41(s, 1H), 8.28(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.78(td, J=7.5, 1.8 Hz, 1H), 7.72—7.60(m, 1H), 7.46—7.28(m, 2H), 6.63(s, 1H), 4.43(d, J=6.3 Hz, 2H), 2.52(s, 3H) | 169.3, 163.2, 160.9, 158.4(d, J=252.2 Hz), 151.5, 142.2, 136.5, 135.8, 135.7(d, J=8.5 Hz), 133.4, 130.8(q, J=33.4 Hz), 129.8, 128.7(d, J=19.5 Hz), 128.4(d, J=9.9 Hz), 125.6, 125.2(q, J=271.0 Hz), 123.5, 123.0(d, J=3.7 Hz), 117.3(d, J=20.7 Hz), 103.5, 37.9, 23.4 |
| 10ib | 10.93(s, 1H), 8.92(d, J=2.1 Hz, 1H), 8.66(s, 2H), 8.42(s, 1H), 8.29(d, J=2.1 Hz, 1H), 7.83(d, J=7.2 Hz, 1H), 7.51—7.46(m, 1H), 7.41—7.27(m, 2H), 6.54(s, 1H), 4.34(d, J=6.3 Hz, 2H), 3.36(s, 3H), 2.59(s, 3H) | 169.3, 162.8, 160.7, 151.2, 142.0, 138.4, 136.6, 136.4, 134.8, 133.2, 132.9, 132.6, 132.4, 130.1(q, J=33.4 Hz), 128.5, 128.1, 126.1, 123.3, 123.1(q, J=271.3 Hz), 103.1, 37.6, 23.2, 19.7 |
| 10jb | 10.94(s, 1H), 8.96(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.65(s, 2H), 8.43(s, 1H), 8.38(d, J=2.7 Hz, 1H), 7.93(t, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 6.85(s, 1H), 4.45(d, J=4.8 Hz, 2H), 3.22(m, 1H), 2.62(s, 3H), 1.25(s, 3H), 1.23(s, 3H) | 170.7, 162.8, 161.0, 151.3, 142.0, 136.3, 133.2, 130.6(q, J=33.3 Hz), 128.5, 128.2, 125.6, 123.4, 123.0(q, J=274.7 Hz), 103.0, 52.1, 38.0, 23.3, 16.2 |
| 11b | 10.90(s, 1H), 8.94(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.64(s, 2H), 8.41(s, 1H), 8.39—8.33(m, 3H), 6.81(d, J=5.4 Hz, 1H), 6.76(s, 1H), 4.73(d, J=5.7 Hz, 2H), 2.60(s, 3H) | 162.8, 161.9, 161.0, 160.9, 154.8, 151.3, 142.0, 136.3, 133.1, 130.5(q, J=33.2 Hz), 128.5, 128.2, 125.4, 123.5, 123.0(q, J=275.6 Hz), 110.4, 102.7, 102.6, 23.3, 13.2 |
| 12ab | 10.94(s, 1H), 8.93(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.65(s, 2H), 8.41(s, 1H), 8.36(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.78(d, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 7.72(s, 1H), 6.73(s, 1H), 5.88(d, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 4.69(d, J=5.4 Hz, 2H), 3.62(t, J=4.5 Hz, 4H), 2.60(s, 3H), 2.32(t, J=4.8 Hz, 4H), 2.15(s, 3H) | 171.8, 162.8, 162.0, 161.0, 160.9, 155.4, 151.3, 141.9, 136.3, 133.2, 130.6(q, J=33.3 Hz), 128.6, 128.2, 125.5, 123.5, 123.1(q, J=271.8 Hz), 102.1, 54.4, 45.6, 43.1, 35.9, 23.4 |
| 12bb | 10.91(s, 1H), 8.95(s, 1H), 8.65(s, 2H), 8.42(s, 1H), 8.32(s, 1H), 7.71(d, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 7.64(s, 1H), 7.28—7.20(m, 4H), 7.11(s, 1H), 6.62(s, 1H), 5.85(d, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 4.68(d, J=4.8 Hz, 2H), 4.42(d, J=5.4 Hz, 2H), 2.58(s, 3H) | 162.7, 162.3, 161.4, 157.3, 156.0, 154.5, 151.7, 141.2, 136.3, 133.0, 130.6(q, J=32.9 Hz), 128.5, 128.0, 125.4, 123.9, 123.0(q, J=271.2 Hz), 113.1, 98.0, 43.4, 25.0, 13.0 |
| 12cb | 10.91(s, 1H), 8.95(d, J=2.7 Hz, 1H), 8.64(s, 2H), 8.41(s, 1H), 8.34(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.72(d, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 7.58(s, 1H), 6.73(s, 1H), 6.45(d, J=4.5 Hz, 1H), 5.83(d, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 4.70(d, J=6.0 Hz, 2H), 2.72(d, J=4.8 Hz, 3H), 2.61(s, 3H) | 171.9, 162.8, 162.4, 162.2, 160.9, 155.3, 151.3, 141.9, 136.4, 133.2, 130.6(q, J=33.2 Hz), 128.6, 128.2, 125.4, 124.9(q, J=271.4 Hz), 123.6, 102.2, 35.1, 27.7, 23.4 |
| 12db | 11.77(s, 1H), 10.89(s, 1H), 8.94(d, J=2.7 Hz, 1H), 8.63(s, 2H), 8.40(s, 1H), 8.31(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.86(d, J=5.4 Hz, 2H), 6.74(s, 1H), 6.19(s, 1H), 6.02(d, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 4.77(d, J=5.4 Hz, 2H), 2.57(s, 3H), 1.21(s, 9H) | 171.7, 162.8, 162.2, 160.9, 159.0, 151.3, 142.0, 136.4, 133.2, 130.6(q, J=33.1 Hz), 128.6, 128.2, 125.4, 123.5, 123.1(q, J=267.8 Hz), 102.3, 36.0, 30.8, 30.0, 23.4 |
| Compd. | Inhibition*(%) | IC50/(μmol·L-1) | Compd. | Inhibition*(%) | IC50/(μmol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9a | 15.5 | 10e | 17.3 | ||
| 9b | 9.7 | 10f | 10.0 | ||
| 9c | 22.5 | 10g | 51.8 | 8.5 | |
| 9d | 24.1 | 10h | 56.7 | 13.4 | |
| 9e | 16.1 | 10i | 72.2 | 6.7 | |
| 9f | 20.6 | 10j | 12.8 | ||
| 9g | 28.3 | 12a | 65.0 | 15.6 | |
| 10a | 59.8 | 9.4 | 12b | 100.0 | 7.3 |
| 10b | 20.4 | 12c | 63.0 | 15.2 | |
| 10c | 21.9 | 12d | 82.0 | 11.3 | |
| 10d | 47.2 | INK128 | 0.36 |
Table 3 Anti-tumor activities against human breast cancer cell line(MCF-7)
| Compd. | Inhibition*(%) | IC50/(μmol·L-1) | Compd. | Inhibition*(%) | IC50/(μmol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9a | 15.5 | 10e | 17.3 | ||
| 9b | 9.7 | 10f | 10.0 | ||
| 9c | 22.5 | 10g | 51.8 | 8.5 | |
| 9d | 24.1 | 10h | 56.7 | 13.4 | |
| 9e | 16.1 | 10i | 72.2 | 6.7 | |
| 9f | 20.6 | 10j | 12.8 | ||
| 9g | 28.3 | 12a | 65.0 | 15.6 | |
| 10a | 59.8 | 9.4 | 12b | 100.0 | 7.3 |
| 10b | 20.4 | 12c | 63.0 | 15.2 | |
| 10c | 21.9 | 12d | 82.0 | 11.3 | |
| 10d | 47.2 | INK128 | 0.36 |
| [1] | Zhang J. M., Yang P. L., Gray N. S., Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2009, 9, 28—39 |
| [2] | Philip C., Nat. Rev. Drug Discov., 2002, 1, 309—315 |
| [3] | Liu D., Zhu X. J., Jiang M., Chen H., Lan S. P., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(10), 2249—2255 |
| (刘丹, 朱秀杰, 姜梦, 陈虹, 兰帅鹏. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(10), 2249—2255) | |
| [4] | Lu H. B., Wang S. H., Li Q. M., Wang Y. S., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2013, 29(1), 67—70 |
| [5] | Sun X. X., Sun T., Wang T. Y., Zhang Y., Liu H. J., Wang Q., Niu G. J., Liu W., Zhou H. G., Yang C., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2013, 29(6), 1098—1103 |
| [6] | Zhang C., Bollag G., Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev., 2010, 20, 79—86 |
| [7] | Pargellis C., Tong L., Churchill L., Cirillo P. F., Gilmore T., Graham A. G., Grob P. M., Hickey E. R., Moss N., Pav S., Regan J., Nat. Struct. Biol., 2002, 9, 268—272 |
| [8] | Yang H. L., Chen T., Bai X., Pei Y. Z., J. Chin. Pharma. Sci., 2012, 21, 531—543 |
| [9] | Liu Y., Gray N. S., Nat. Chem. Biol., 2006, 2, 358—364 |
| [10] | Fang Z.Z., Grütter G., Rauh D., ACS Chem. Biol., 2012, 8(1), 58—70 |
| [11] | Vandana L., Indraneel G., Current Pharm. Design, 2012, 18, 2936—2945 |
| [12] | Dietrich J., Hulme C., Hurley L. H., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2010, 18, 5738—5748 |
| [13] | Nagar B., Bornmann W. G., Pellicena P., Schindler T., Veach D. R., Miller W. T., Clarkson B., Kuriyan J., Cancer Res., 2002, 62, 4236—4243 |
| [14] | Liu C. J., Lin J., Wrobleski S. T., Lin S. Q., Hynes J. J., Wu H., Dyckman A. J., Li T. L., Wityak J., Gillooly K. M., Pitt S., Shen D. R., Zhang R. F., McIntyre K. W., Salter-Cid L., Shuster D. J., Zhang H. J., Marathe P. H., Doweyko A. M., Sack J. S., Kiefer S. E., Kish K. F., Newitt J. A., McKinnon M., Dodd J. H., Barrish J. C., Schieven G. L., Leftheris K., J. Med. Chem., 2010, 53, 6629—6639 |
| [15] | Stockmann V., Bakke J. M., Bruheim P., Fiksdahl A., Tetrahedron,2009, 65, 3668—3672 |
| [16] | Yapi A. D., Desbois N., Chezal J. M., Chavignon O., Teulade J. C., Valentin A., Blache Y., Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2010, 45, 2854—2859 |
| [17] | Tanis S. P., Parker T. T., Colca J. R., Fisher R. M., Kletzein R. F., J. Med. Chem., 1996, 39, 5053—5063 |
| [18] | Parikh J. R., Doering W. V. E., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1967, 89, 5505—5507 |
| [19] | Yano J. K., Denton T. T., Cerny M. A., Zhang X. D., Johnson E. F., Cashman J. R., J. Med. Chem., 2006, 49, 6987—7001 |
| [20] | Kamal A., Dastagiri D., Ramaiah M. J., Reddy J. S., Bharathi E. V., Reddy M. K., Sagar M. V. P., Reddy T. L., Pushpavalli S. N. C. V. L., Pal-Bhadra M., Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2011, 46, 5817—5824 |
| [21] | Altmann E., Aichholz R., Betschart C., Buhl T., Green J., Irie O., Teno N., Lattmann R., Tintelnot-Blomley M., Missbach M., J. Med. Chem., 2002, 50, 591—594 |
| [22] | Zhang X. Q., Hufnagel H., Hou C. F., Opas E., McKenney S., Crysler C., O’Neill J., Johnson D., Sui Z. H., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2011, 21, 6042—6048 |
| [23] | Choi H. G., Ren P. D., Adrian F., Sun F. X., Lee H. S., Wang X., Ding Q., Zhang G. B., Xie Y. P., Zhang J. M., Liu Y., Tuntland T., Warmuth M., Manley P. W., Mestan J., Gray N. S., Sim T., J. Med. Chem., 2010, 53, 5439—5448 |
| [24] | Bogoyevitch M. A., Fairlie D. P., Drug Discov. Today, 2007, 12, 622—633 |
| [25] | Badrinarayan P., Sastry G. N., J. Mol. Graphics Modell., 2012, 34, 89—100 |
| [1] | XIAO Yanhua, ZHANG Guangjie, ZONG Liang, LIU Guohong, REN Lijun, DONG Junxing. Chemical Constituents and Antitumor Activity of Tupistra chinensis † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1897. |
| [2] | LÜ Mingjun,LI Wen,YANG Xinying,FANG Hao. Synthesis and Antitumor Activity of N9 Position Aromatic Substituted Purine-8-one Derivatives† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 254. |
| [3] | FANG Fang,XUE Liangmin,CONG Jing,TIAN Chao,WANG Xiaowei,LIU Junyi,ZHANG Zhili. Synthesis and Anti-tumor Activity Evaluation of a Series of 2- or 4-Substituted Pyrido[3,2-d]pyrimidines as Nonclassical Antifolates † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2111. |
| [4] | ZHANG Peiquan,YANG Qianqian,LONG Huidan,CHEN Xin. Synthesis and Antitumor Activity of Auranofin Derivatives † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2097. |
| [5] | BAI Xinfa, MA Xuan, XIE Xiaoxia, SHAO Mingsha, GUO Ningning, YAN Ning, YAO Lei. Synthesis and Anti-tumor Activity of Tubulysins Analogues† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(1): 47. |
| [6] | GUO Liang, CAO Rihui, FAN Wenxi, GAN Ziyun, MA Qin. Design, Synthesis and in vitro Antitumor Activities of Novel Bivalent β-Carbolines† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(6): 1093. |
| [7] | ZHANG Jie, ZHOU Changjian, XIE Jianwei, DAI Bin. Synthesis and Antitumor Activities of Rhein-Valine Adducts† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(12): 2159. |
| [8] | ZHOU Hao, DUAN Zhigang, ZHAO Shuang, BAO Meiying, LI Zhiwei, PEI Yazhong. Design and Synthesis of Phenylpyrimidine and Their Anticancer Activity† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9): 1694. |
| [9] | WANG Gang, HAN Leiqiang, FANG Hao. Syntheses and Antitumor Activities of Phenylpiperazine Derivatives† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(12): 2435. |
| [10] | GUO Hua, YANG Chengling, WANG Wei, LAI Quanyong, YUAN Zhi. Preparation of Liver-targeted Nano-prodrug Based on Sodium Alginate Derivative and the Study on Antitumor Activity† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(8): 1835. |
| [11] | SONG Xiudao, HE Jun, MA Jin, LIU Yunmei, ZHENG Xing, LEI Xiaoyong, GUO Yu. Syntheses and Anticancer Activities of Glycine Derivatives of Chrysin† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(7): 1465. |
| [12] | WANG Junhua, WANG Quande, DUN Yanyan, FANG Hao. Syntheses and Antitumor Activities of Purine-sulfonamides Derivatives† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(6): 1189. |
| [13] | YANG Haikui, XU Wanfu, DUAN Anna, YOU Wenwei, ZHAO Peiliang. Syntheses and Biological Activities of Novel Imine and Imide Derivatives Bearing 1,2,4-Triazole Moiety† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(3): 555. |
| [14] | GUO Liang, CAO Rihui, FAN Wenxi, MA Qin. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of 1,2,7,9-Tetrasubstituted Harmine Derivatives as Potential Antitumor Agents† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(3): 518. |
| [15] | DING Guobin, LI Binchun, GUO Yi, XU Li. Spectral Properties and Antitumor Activity of 10-Hydroxycamptothecin and Its Application in Cell Labeling† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(11): 2324. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||