

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (12): 20220383.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220383
收稿日期:2022-05-30
出版日期:2022-12-10
发布日期:2022-07-26
基金资助:
XU Xinyu, ZHANG Letian, CAO Hui, MA Yuan, LIU Liuhui, SONG Guosheng( ), ZHANG Xiaobing(
), ZHANG Xiaobing( )
)
Received:2022-05-30
Online:2022-12-10
Published:2022-07-26
Contact:
SONG Guosheng, ZHANG Xiaobing
E-mail:songgs@hnu.edu.cn;xbzhang@hnu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
动脉粥样硬化是心血管疾病的主要威胁之一, 可能导致如急性心肌梗死在内的急性冠状动脉综合征、 卒中, 甚至猝死等一系列严重的不良后果. 脂质的异常积累是动脉粥样硬化的标志之一, 有必要观察它们在体内的数量、 定位和分布. 荧光探针具有可操作性强、 高时空分辨率和与活体生物相容性佳的优点, 有望成为了解动脉粥样硬化中的脂质功能的有利工具. 本文综合评述了基于罗丹明、 香豆素、 氟化硼二吡咯(BODIPY)、 1,8-萘酰亚胺等有机框架结构以及金属配合物的脂滴特异性光学成像探针的研究进展, 并重点介绍了其在动脉粥样硬化斑块成像、 手术导航及治疗等领域的应用. 最后, 对该研究领域进行了总结和展望, 希望可为相关研究提供有益参考.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
徐心昱, 张乐天, 曹晖, 马原, 刘柳卉, 宋国胜, 张晓兵. 脂质响应型探针用于动脉粥样硬化成像及治疗的研究进展. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(12): 20220383.
XU Xinyu, ZHANG Letian, CAO Hui, MA Yuan, LIU Liuhui, SONG Guosheng, ZHANG Xiaobing. Recent Advances in Lipid-responsive Probes in the Imaging and Treatment of Atherosclerosis. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(12): 20220383.
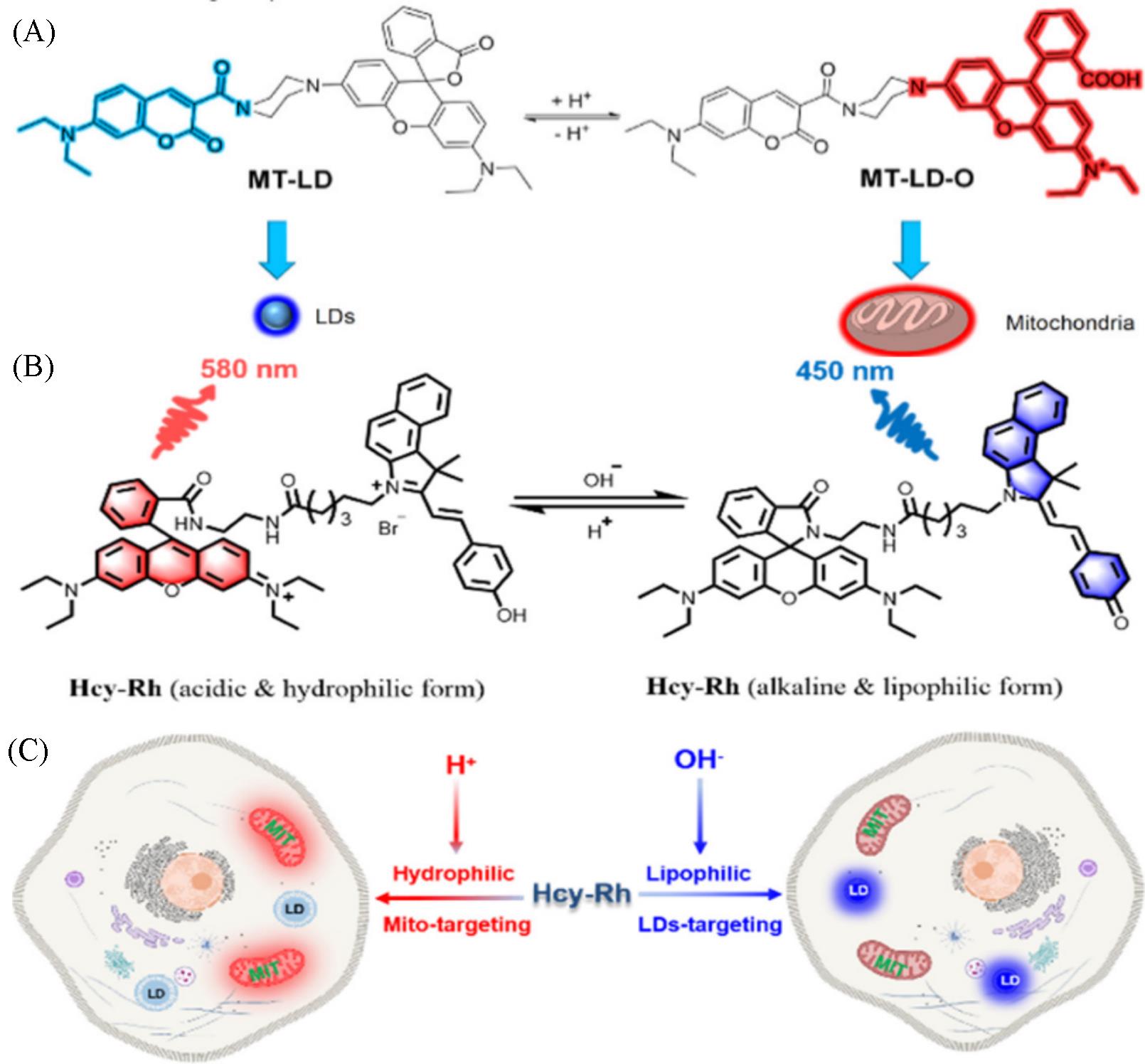
Fig.2 Chemical structure and the targeting mechanism of the probe MT⁃LD(A)[28], chemical structure of Hcy⁃Rh and the proposed polarity⁃reversible and ratiometric pH⁃sensing mechanism(B) and targeting mechanism of Hcy⁃Rh(C)[29](A) Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society; (B, C) Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society.
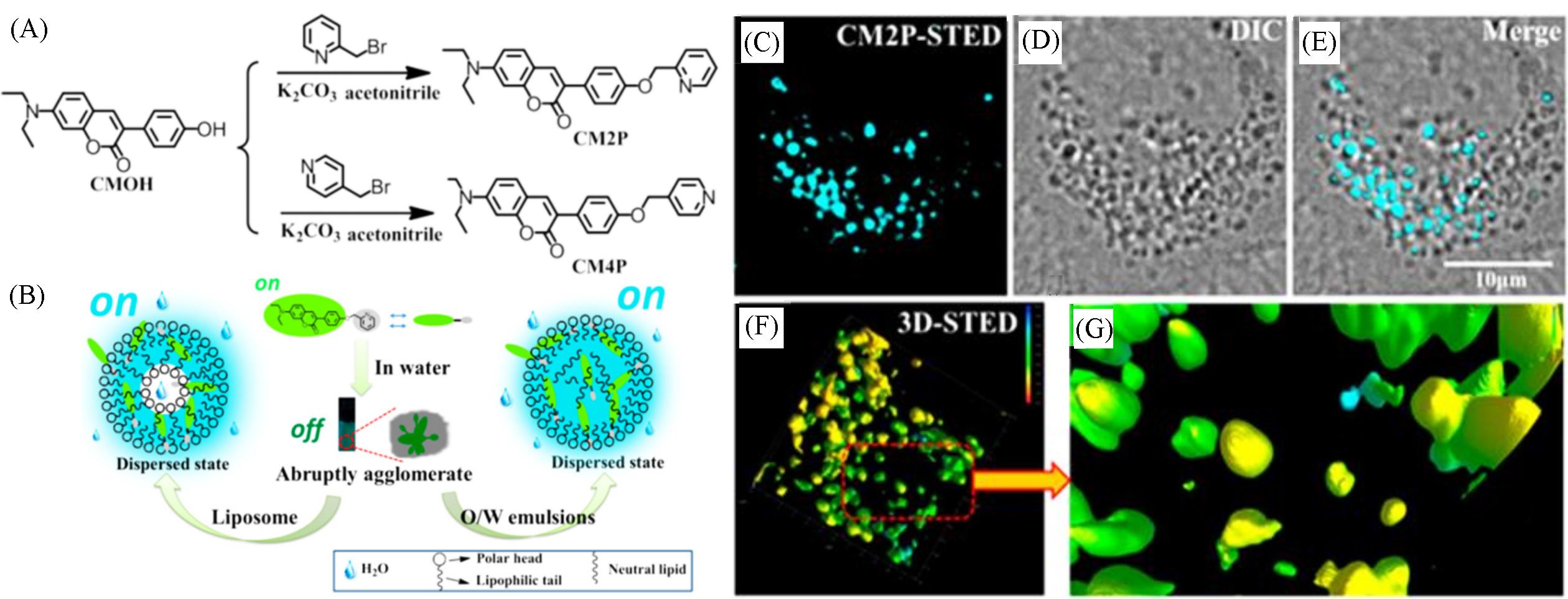
Fig.3 Synthetic route for CM2P and CM4P(A), simulation of interaction between CM2P and liposome, O/W emulsions(B), and fluorescent images of LDs stained with CM2P in live HeLa cells(C—G)[31] (C) STED image; (D) bright⁃field image; (E) merged image of (C) and (D); (F) 3D⁃STED image; (G) zoomed⁃in region from Fig.(F). Rainbow calibration bar, Z scale(0—10 μm).
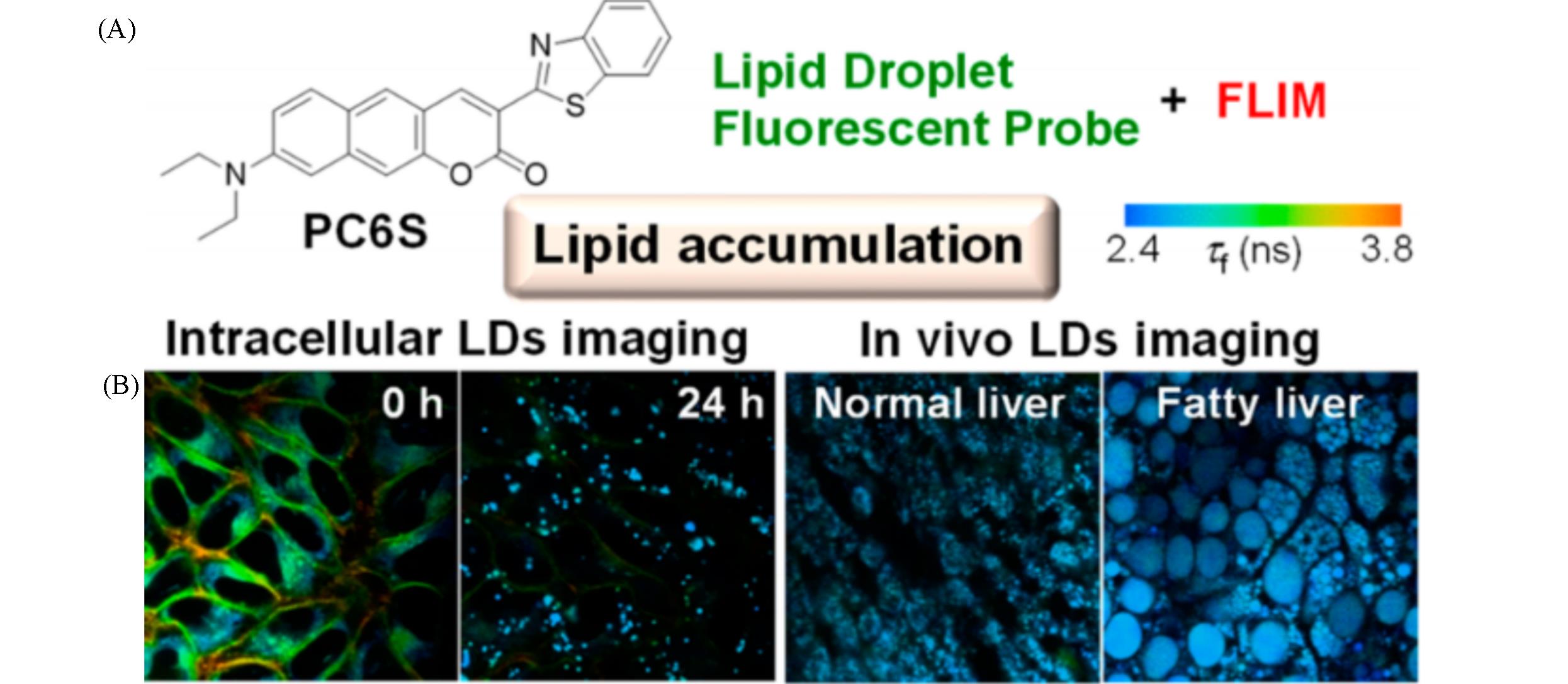
Fig.4 Chemical structure of PC6S(A) and FLIM images of HeLa cells stained with PC6S(2 μmol/L) for 30 min at 37 ℃, then treated with oleic acid(400 μmol/L) and FLIM images of the livers of living mice(B)[32](B) Excitation wavelength: 488 nm, collected emission wavelength range: 510—560 nm.
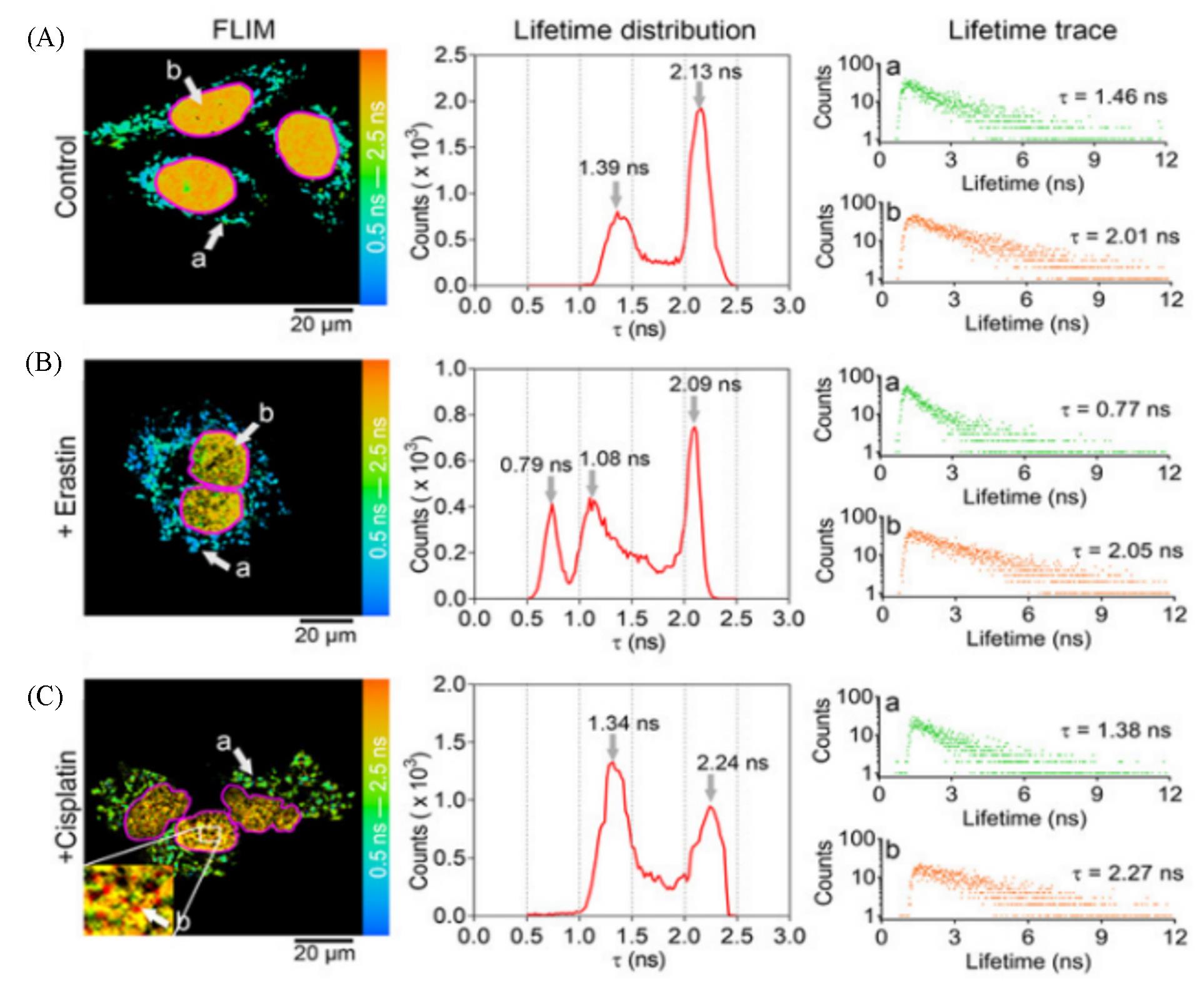
Fig.5 Application of CQPP(5 μmol/L) to monitoring the polarity changes of LDs and nucleus in living cells under different conditions by fluorescence lifetime imaging(FLIM)[33](A) HT-1080 cells under normal conditions (Control); (B) HT-1080 cells incubated with Erastin(10 μmol/L) for 6 h; (C) HT-1080 cells incubated with cisplatin(20 μmol/L) for 12 h. The solid pink line represents the shape of the nucleus. Lifetime distribution: the fluorescence lifetime(τ) distribution collected from FLIM. Lifetime trace: Fluorescence lifetime spectra of region a and b from FLIM. FLIM images were pulsed two-photon excitation at 810 nm. Images shown are representatives of replicate experiments.Copyright 2021, Wiley-VCH GmbH.
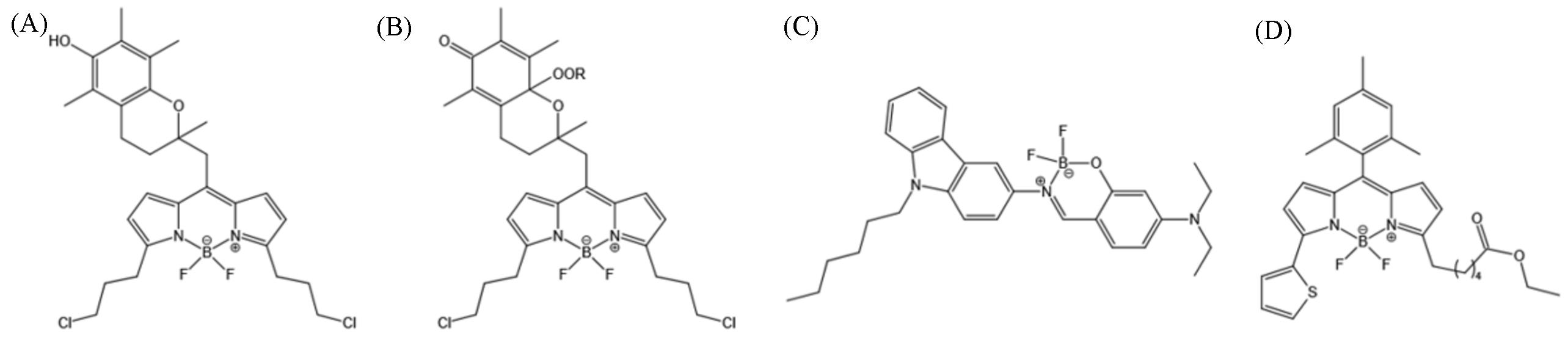
Fig.6 BODIPY⁃based LD probes(A) H4BPMHC; (B) H4BPMHCox[35]; (C) BoCz⁃Lip[36]; (D) BODIPYs 9.(A, B) Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society; (C) Copyright 2020, Elsevier B.V.;(D) Copyright 2020, the Royal Society of Chemistry.
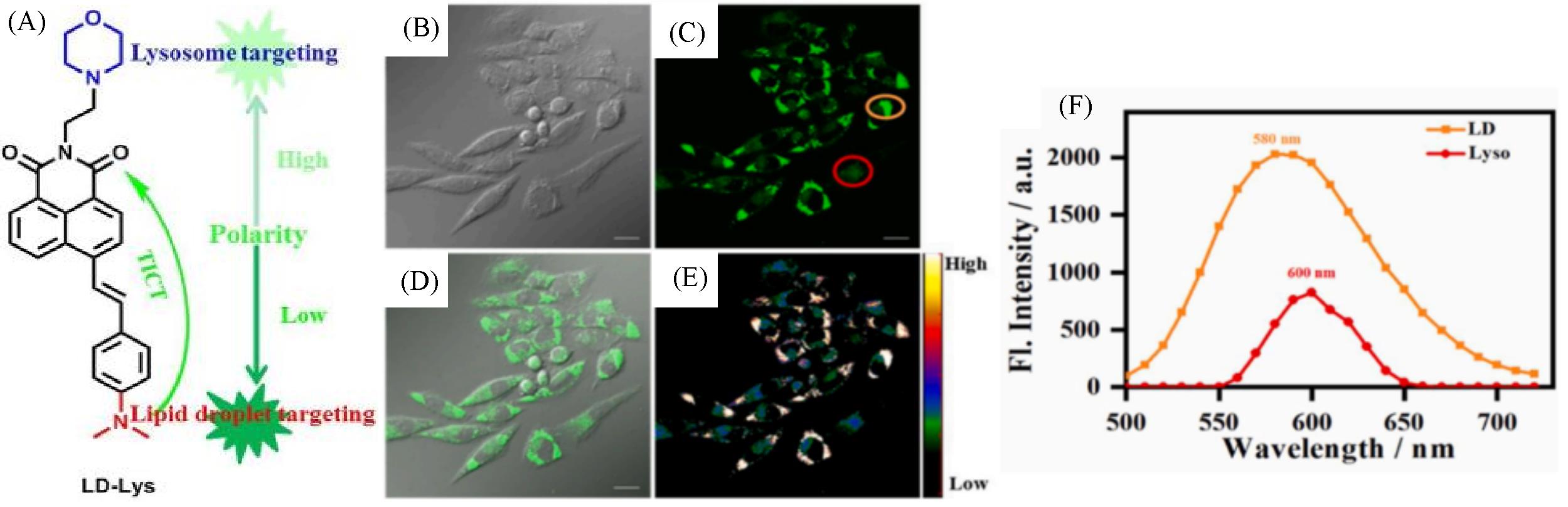
Fig.7 Molecular design and structure of LD⁃Lys(A) and fluorescent images(B—E) and spectra(F) of live SiHa cells stained with LD⁃Lys(5 μmol/L, 30 min)[39]
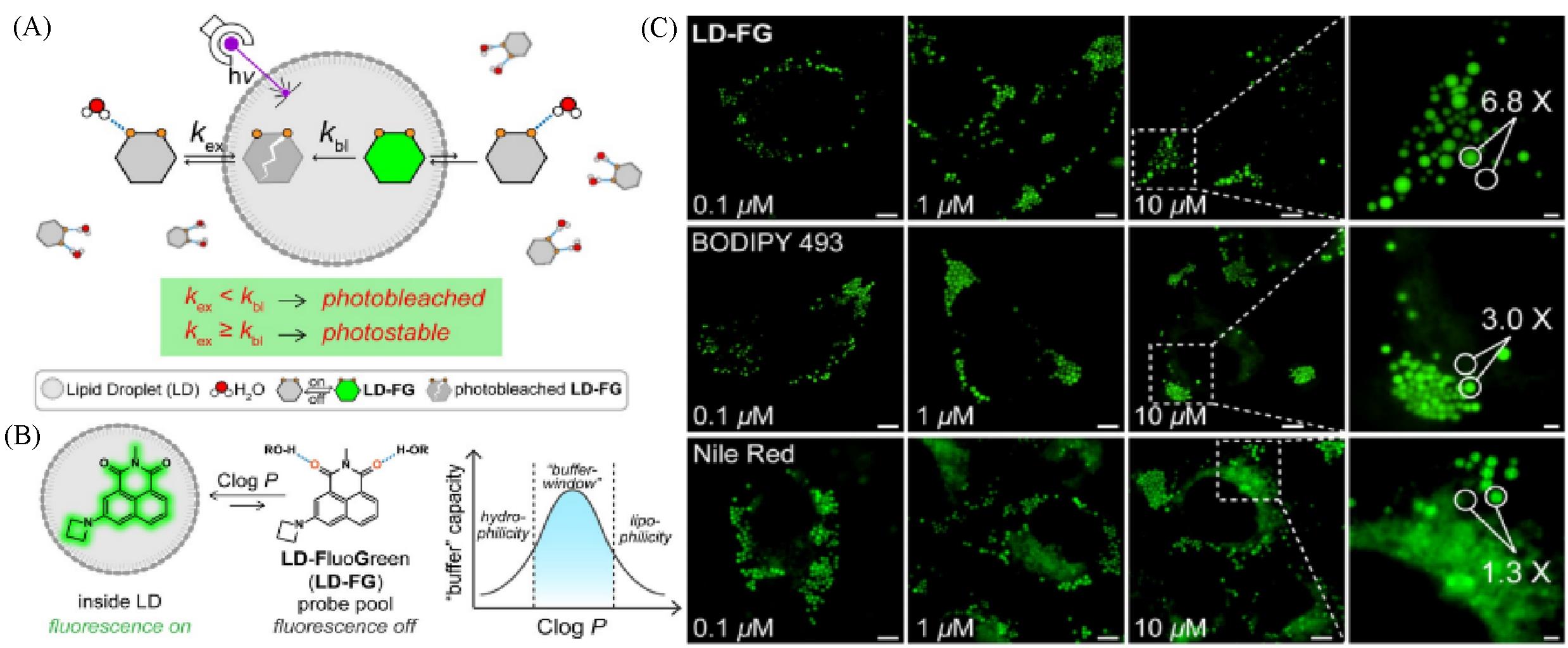
Fig.8 Super⁃resolution lipid droplet imaging probe LD⁃FG[40](A) The buffer strategy enables stable imaging of lipid droplets using LD-FG; (B) mechanism of LD-FG for LD fluorogenic and dynamic imaging; (C) fluorescent image of HeLa cells incubated with LD-FG, BODIPY 493, and Nile Red in different concentrations.Copyright 2021, Wiley-VCH GmbH.
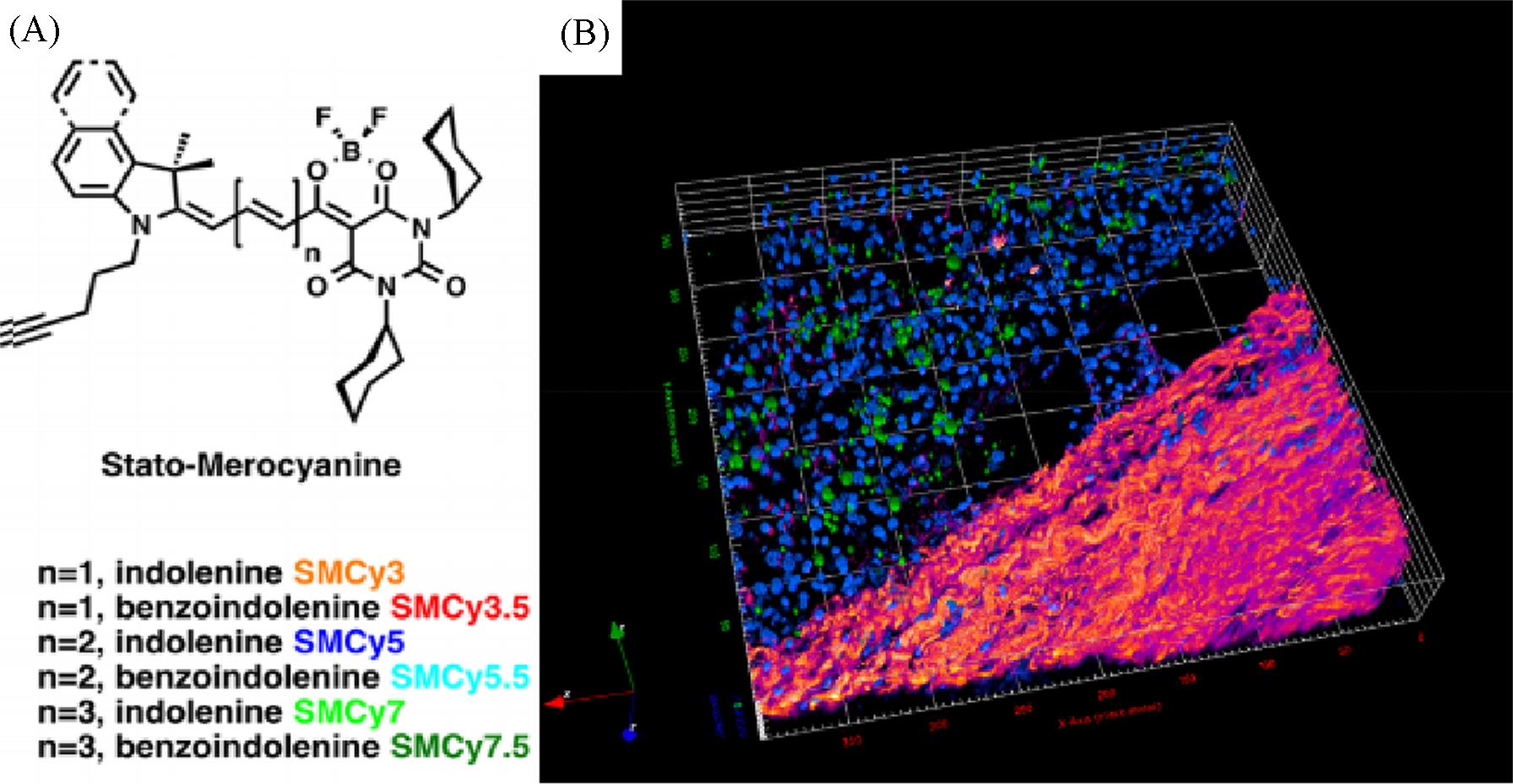
Fig.9 The six members of the StatoMerocyanines family(A) and two⁃photon excitation 3D imaging(52 μm depth) of a mouse liver slice, incubated with Hoechst(5 μg/mL) and SMCy5.5(5 μmol/L)(B)[42](B) The nuclei are displayed in blue, the lipid droplets in green, and the collagen fibers in fire color. The two⁃photon excitation wavelength was 810 nm.
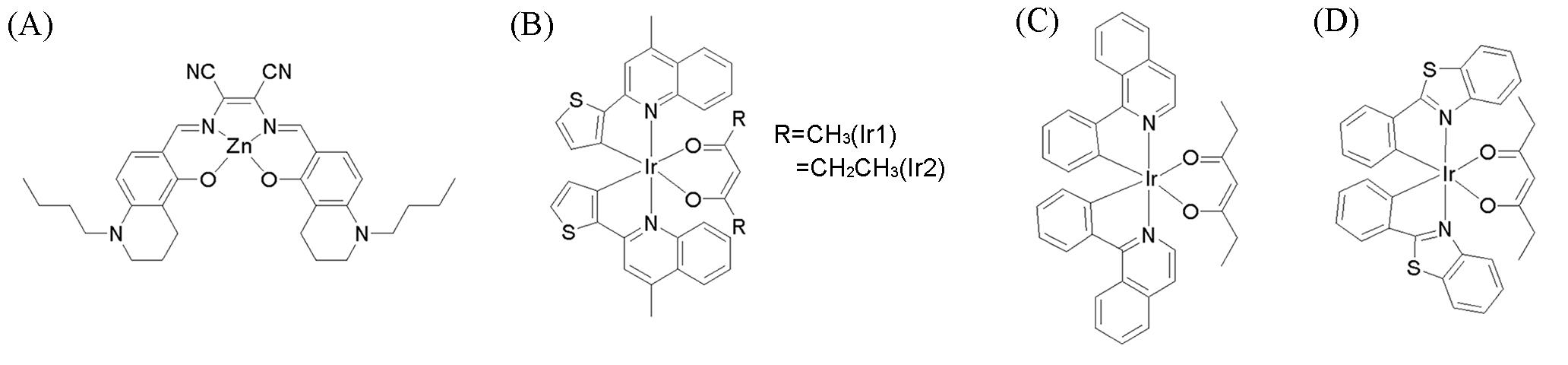
Fig.10 Chemical structures of some metal complex LD probes(A) LD⁃TPZn[43]; (B) lipophilic neutral phosphorescentIr(III) complexes(Ir1 and Ir2)[44]; (C, D) neutral cyclometalated iridium(III) complexes.(A) Copyright 2017, Wiley⁃VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA; (B) Copyright 2018, Elsevier B.V.; (C, D) Copyright 2022, Elsevier Ltd.
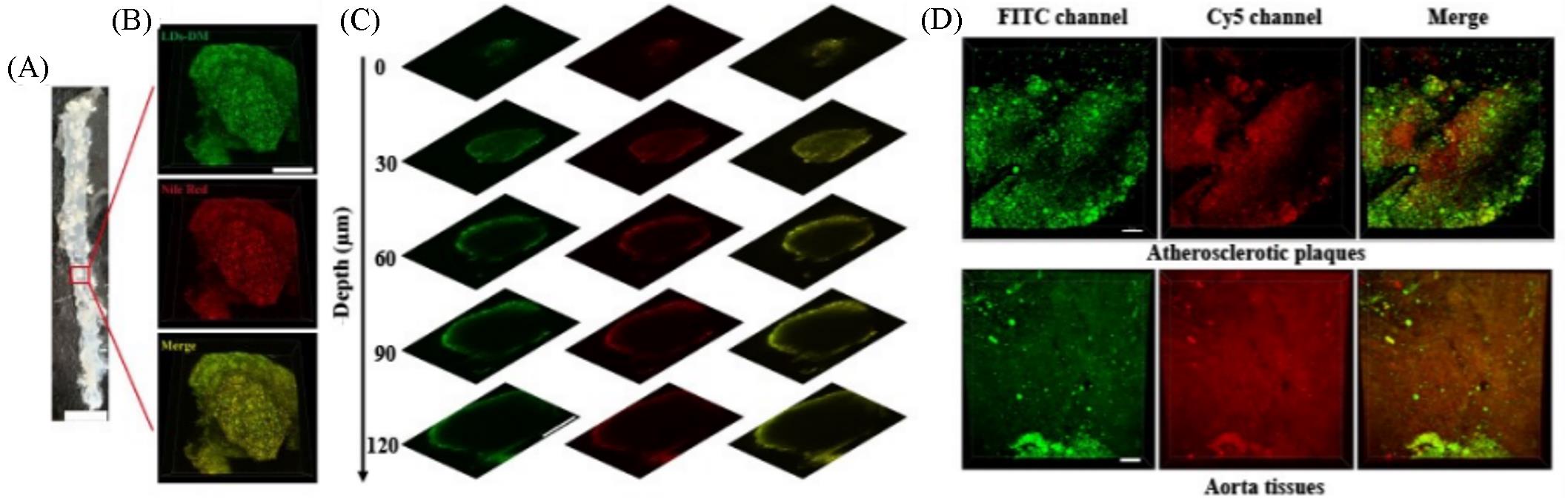
Fig.11 Simultaneous dual⁃color 3D imaging in atherosclerosis[46](A) En face photograph of the opened aorta from an ApoE-/- mouse, scale bar: 5 mm; (B) simultaneous 3D imaging of the microstructures of atherosclerotic plaques stained with LDs-DM(500 nmol/L) and Nile red (1 μmol/L), scale bar: 200 μm; (C) images of the atherosclerotic plaques stained with LDs-DM(500 nmol/L) and Nile red(1 μmol/L) at different imaging depths, scale bar: 200 μm; (D) simultaneous dual-color 3D imaging of the microstructures of atherosclerotic plaques and aorta tissue stained with 500 nmol/L LDs-DM within lumen(500—550 nm for FITC channel and 663—738 nm for Cy5 channel) under single excitation at 488 nm, scale bar: 70 μm.
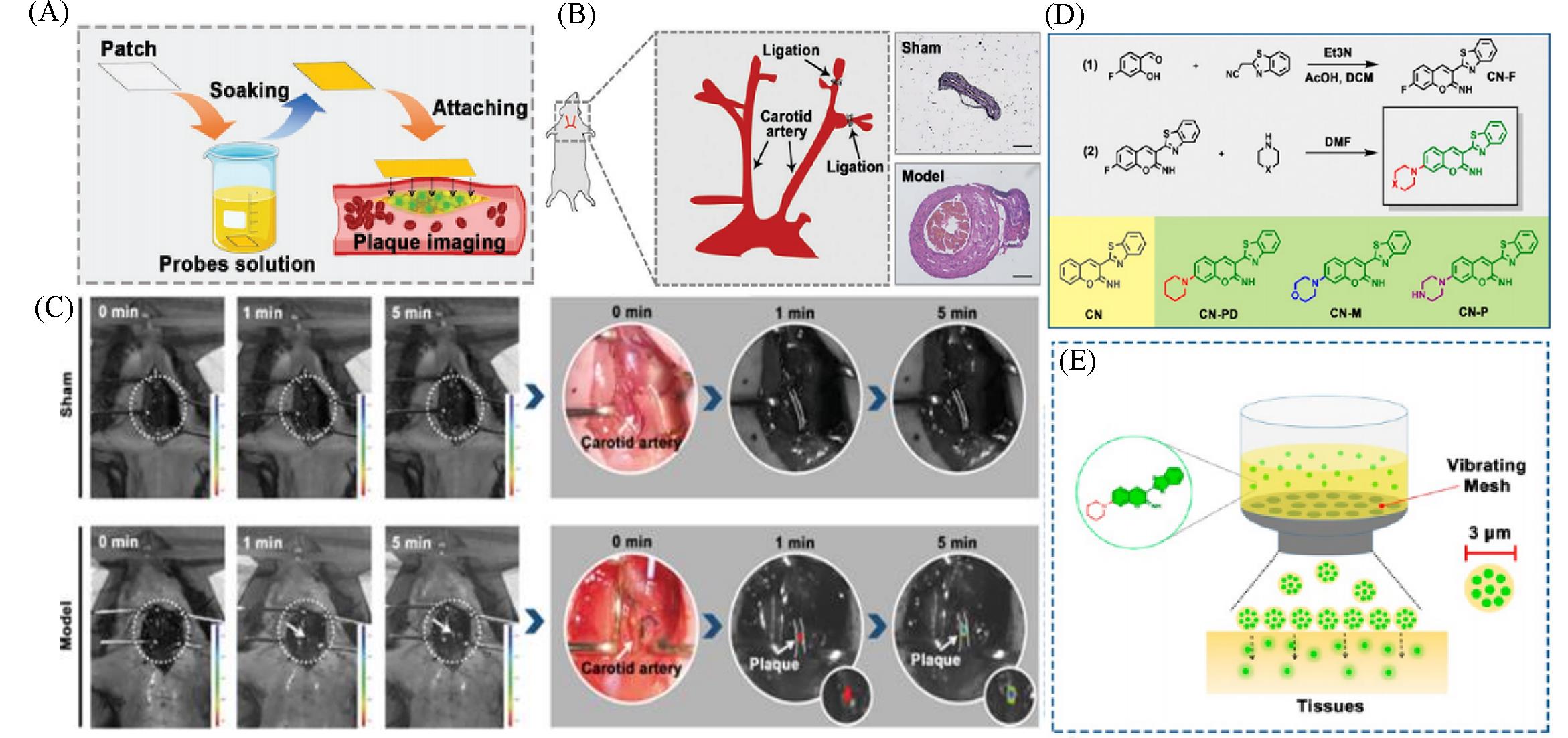
Fig.14 Lipid⁃activatable fluorescent probes for intraoperative imaging of atherosclerotic plaque(A) Schematic showing target artery surface attachment to CN-N2-soaked filter paper to realize rapid penetration of the probe into the plaque[49]; (B) Carotid ligation model of atherosclerosis illustrated using HE-stained tissue images[49]; (C) atherosclerosis model imaging procedure: the left carotid artery is exposed to CN-N2-soaked filter paper(1×10-5 mol/L) with in vivo imaging performed at 1 and 5 min[49]; (D) synthesis route, structure, and the corresponding abbreviation of the synthesized probes[50]; (E) vibrating mesh nebulized the aqueous solution of the probe into small droplets with a diameter of 3 μm to achieve rapid tissue permeation[50].(A—C) Copyright 2021, Wiley-VCH GmbH; (D, E) Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society.
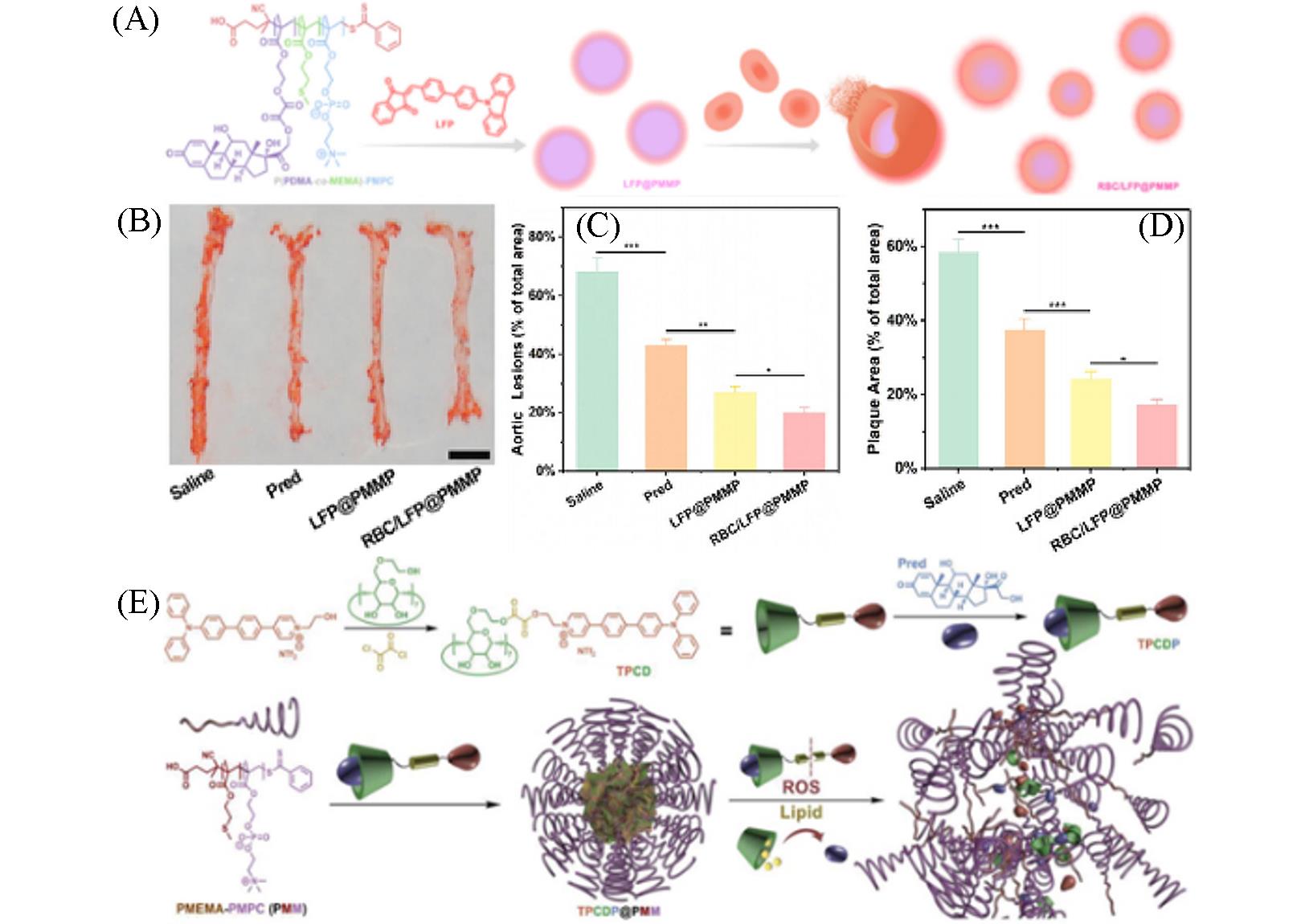
Fig.15 Nanoplatform with lipid⁃specific imaging for atherosclerosis⁃targeted therapy(A) Illustration of RBC/LFP@PMMP formation[54]; (B, C) photographs(B) and quantitative data(C) of the plaques on the en face of the aortas stained by ORO(n=6)[54], scale bar: 5 mm; (D) quantitative results of the aortic arch plaque areas[54]; (E) illustration of TPCDP@PMM preparation and its responsive behaviors under overexpressed ROS and rich lipid[55].(A—D) Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society; (E) Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH GmbH.
| 1 | Kawanishi K., Dhar C., Do R., Varki N., Gordts P., Varki A., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2019, 116(32), 16036—16045 |
| 2 | Tabas I., Garcia C. G., Owens G. K., J. Cell Biol., 2015, 209(1), 13—22 |
| 3 | Kobiyama K., Ley K., Circ. Res., 2018, 123(10), 1118—1120 |
| 4 | Ridker P. M., Circulation, 2003, 107(3), 363—369 |
| 5 | Moore K. J., Tabas I., Cell, 2011, 145(3), 341—355 |
| 6 | Soehnlein O., Drechsler M., Doring Y., Lievens D., Hartwig H., Kemmerich K., Ortega G. A., Mandl M., Vijayan S., Projahn D., Garlichs C. D., Koenen R. R., Hristov M., Lutgens E., Zernecke A., Weber C., EMBO Mol. Med., 2013, 5(3), 471—481 |
| 7 | Kojima Y., Volkmer J. P., Mckenna K., Civelek M., Lusis A. J., Miller C. L., Direnzo D., Nanda V., Ye J., Connolly A. J., Schadt E. E., Quertermous T., Betancur P., Maegdefessel L., Matic L. P., Hedin U., Weissman I. L., Leeper N. J., Nature, 2016, 536(7614), 86—90 |
| 8 | Kunjathoor V. V., Febbraio M., Podrez E. A., Moore K. J., Andersson L., Koehn S., Rhee J. S., Silverstein R., Hoff H. F., Freeman M. W., J. Biol. Chem., 2002, 277(51), 49982—49988 |
| 9 | Ji A., Meyer J. M., Cai L., Akinmusire A., de Beer M. C., Webb N. R., van der Westhuyzen D. R., Atherosclerosis, 2011, 217(1), 106—112 |
| 10 | Endemann G., Stanton L. W., Madden K. S., Bryant C. M., White R. T., Protter A. A., J. Biol. Chem., 1993, 268(16), 11811—11816 |
| 11 | Libby P., Ridker P. M., Hansson G. K., Nature, 2011, 473(7347), 317—325 |
| 12 | Thorp E., Tabas I., J. Leukoc. Biol., 2009, 86(5), 1089—1095 |
| 13 | Schrijvers D. M., de Meyer G. R., Kockx M. M., Herman A. G., Martinet W., Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 2005, 25(6), 1256—1261 |
| 14 | Thorp E., Cui D., Schrijvers D. M., Kuriakose G., Tabas I., Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 2008, 28(8), 1421—1428 |
| 15 | Beller M., Thiel K., Thul P. J., Jackle H., FEBS Lett., 2010, 584(11), 2176—2182 |
| 16 | Farese R. V. Jr., Walther T. C., Cell, 2009, 139(5), 855—860 |
| 17 | Walther T. C., Farese R. V. Jr., Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids, 2009, 1791(6), 459—466 |
| 18 | Onal G., Kutlu O., Gozuacik D., Dokmeci Emre S., Lipids Health Dis., 2017, 16(1), 128 |
| 19 | Yin J., Huang L., Wu L., Li J., James T. D., Lin W., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021, 50(21), 12098—12150 |
| 20 | Greenspan. P., Mayer. E. P., Fowler. S. D., J. Cell Biol., 1985, 100(3), 965—973 |
| 21 | Fam T. K., Klymchenko A. S., Collot M., Materials, 2018, 11(9), 1768 |
| 22 | Danylchuk D. I., Jouard P. H., Klymchenko A. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021,143(2), 912—924 |
| 23 | Zhao Y., Shi W., Li X., Ma H., Chem. Commun., 2022, 58(10), 1495—1509 |
| 24 | Rumin J., Bonnefond H., Saint⁃Jean B., Rouxel C., Sciandra A., Bernard O., Cadoret J. P., Bougaran G., Biotechnol Biofuels, 2015, 8, 42 |
| 25 | Lavis. L. D., Raines. R. T., ACS Chem. Biol., 2008, 3(3), 142—155 |
| 26 | Tian H., Sedgwick A. C., Han H.H., Sen S., Chen G.R., Zang Y., Sessler J. L., James T. D., Li J., He X. P., Coord. Chem. Rev., 2021, 427, 213577 |
| 27 | Beija M., Afonso C. A., Martinho J. M., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38(8), 2410—2433 |
| 28 | Tian M., Ge E., Dong B., Zuo Y., Zhao Y., Lin W., Anal. Chem., 2021, 93(7), 3602—3610 |
| 29 | Bai Q., Yang C., Yang M., Pei Z., Zhou X., Liu J., Ji H., Li G., Wu M., Qin Y., Wang Q., Wu L., Anal. Chem., 2022, 94(6), 2901—2911 |
| 30 | Mota A. A. R., Correa J. R., de Andrade L. P., Assumpcao J. A. F., de Souza Cintra G. A., Freitas⁃Junior L. H., Da Silva W. A., de Oliveira H. C. B., Neto B. A. D., ACS Omega, 2018, 3(4), 3874—3881 |
| 31 | Xu H., Zhang H., Liu G., Kong L., Zhu X., Tian X., Zhang Z., Zhang R., Wu Z., Tian Y., Zhou H., Anal. Chem., 2019, 91(1), 977—982 |
| 32 | Yoshihara T., Maruyama R., Shiozaki S., Yamamoto K., Kato S. I., Nakamura Y., Tobita S., Anal. Chem., 2020, 92(7), 4996—5003 |
| 33 | Wang K. N., Liu L. Y., Mao D., Xu S., Tan C. P., Cao Q., Mao Z. W., Liu B., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60(27), 15095—15100 |
| 34 | Chen S., Chen W., Shi W., Ma H., Chem. Eur. J., 2012, 18(3), 925—930 |
| 35 | Greene L. E., Lincoln R., Cosa G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(44), 15801—15811 |
| 36 | Liu X. L., Lu X., Zhu T., Du W. L., Yang Z. H., Cao H. Z., Wang S. Y., Tian Y. P., Zhang Z. P., Zhang R. L., de Souza S. C., Tian X. H., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2021, 175, 112871 |
| 37 | Tabero A., Garcia G. F., Prieto C. A., Palao E., Agarrabeitia A. R., Garcia M. I., Villanueva A., Moya S., Ortiz M. J., Chem. Commun., 2020, 56(6), 940—943 |
| 38 | Pan Y. H., Chen X. X., Dong L., Shao N., Niu L.Y., Yang Q. Z., Chin. Chem. Lett., 2021, 32(12), 3895—3898 |
| 39 | Meng F., Niu J., Zhang H., Yang R., Lu Q., Yu Y., Liu Z., Niu G., Yu X., Sens. Actuators B⁃Chem., 2021, 329, 129148 |
| 40 | Chen J., Wang C., Liu W., Qiao Q., Qi H., Zhou W., Xu N., Li J., Piao H., Tan D., Liu X., Xu Z., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60(47), 25104—25113 |
| 41 | Sun W., Guo S., Hu C., Fan J., Peng X., Chem. Rev., 2016, 116(14), 7768—7817 |
| 42 | Collot M., Fam T. K., Ashokkumar P., Faklaris O., Galli T., Danglot L., Klymchenko A. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140(16), 5401—5411 |
| 43 | Tang J., Zhang Y., Yin H. Y., Xu G., Zhang J. L., Chem. Asian J., 2017, 12(19), 2533—2538 |
| 44 | He L., Cao J. J., Zhang D. Y., Hao L., Zhang M. F., Tan C. P., Ji L. N., Mao Z. W., Sens. Actuators B Chem., 2018, 262, 313—325 |
| 45 | Pan Z. Y., Feng W. W., Liu Q. Y., He L., Yao D. H., He Z. D., Dyes Pigm., 2022, 203, 110387 |
| 46 | Zhan Z., Zhuang W., Lei Q., Li S., Mao W., Chen M., Li W., Chem. Commun., 2022, 58(25), 4020—4023 |
| 47 | Li S., Zhuang W., Chen J., Li L., Li G., Li J., Liao Y., Chen M., Wang Y., Sens. Actuators B Chem., 2021, 346, 130458 |
| 48 | Wang S., Li X., Chong S. Y., Wang X., Chen H., Chen C., Ng L. G., Wang J. W., Liu B., Adv. Mater., 2021, 33(11), 2007490 |
| 49 | Zheng J., Zhao S., Mao Y., Du Z., Li G., Sang M., Small, 2022, 18(5), 2104471 |
| 50 | Sang M., Cai B., Qin S., Zhao S., Mao Y., Wang Y., Yu X., Zheng J., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces., 2021, 13(49), 58369—58381 |
| 51 | Libby P., Bornfeldt K. E., Tall A. R., Circ. Res., 2016, 118(4), 531—534 |
| 52 | Abdel⁃Maksoud M. S., El⁃Gamal M. I., Benhalilou D. R., Ashraf S., Mohammed S. A., Oh C. H., Med. Res. Rev., 2019, 39(2), 631—664 |
| 53 | Lewis D. R., Petersen L. K., York A. W., Zablocki K. R., Joseph L. B., Kholodovych V., Prud'homme R. K., Uhrich K. E., Moghe P. V., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2015, 112(9), 2693—2698 |
| 54 | Ma B., Xu H., Wang Y., Yang L., Zhuang W., Li G., Wang Y., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13(30), 35410—35421 |
| 55 | Ma B., Xu H., Zhuang W., Wang Y., Li G., Wang Y., Small, 2020, 16(45), 2003253 |
| [1] | 赵永梅, 穆叶舒, 洪琛, 罗稳, 田智勇. 双萘酰亚胺衍生物用于检测水溶液中的苦味酸[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210765. |
| [2] | 唐倩, 但飞君, 郭涛, 兰海闯. 喹啉酮-香豆素类Hg2+比色荧光探针的合成及应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210660. |
| [3] | 李成, 周森森, 蒋锡群. 乏氧光学影像探针的设计与应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(12): 20220558. |
| [4] | 杨燕玲, 叶德举. 碳酸酐酶靶向探针的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(12): 20220557. |
| [5] | 姚善昆, 丁伟忠, 吴延平, 陈韵聪, 郭子建. 硫代部花菁类染料生物成像及诊疗的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(12): 20220568. |
| [6] | 叶卓, 吉墨轩, 刘定斌. 动脉粥样硬化光学成像探针研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(12): 20220556. |
| [7] | 王迪, 钟克利, 汤立军, 侯淑华, 吕春欣. 席夫碱共价有机框架的合成及对I ‒ 的识别[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220115. |
| [8] | 黄珊, 姚建东, 宁淦, 肖琦, 刘义. 石墨烯量子点荧光探针对碱性磷酸酶活性的高效检测[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2412. |
| [9] | 李安然, 赵冰, 阚伟, 宋天舒, 孔祥东, 卜凡强, 孙立, 殷广明, 王丽艳. 基于菲并咪唑的ON⁃OFF⁃ON双比色荧光探针及细胞成像[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2403. |
| [10] | 杨新杰, 赖艳琼, 李秋旸, 张艳丽, 王红斌, 庞鹏飞, 杨文荣. 基于环状DNA-银纳米簇荧光探针对微囊藻毒素-LR的传感检测[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(12): 3600. |
| [11] | 谌委菊, 陈诗雅, 薛曹叶, 刘波, 郑晶. 缺氧响应荧光探针的成像及治疗应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3433. |
| [12] | 黄加玲,刘凤娇,王婷婷,刘翠娥,郑凤英,王振红,李顺兴. 氮硫共掺杂碳量子点对胃液pH值的精确检测[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(7): 1513. |
| [13] | 吴倩, 程丹, 吕芸, 袁林, 张晓兵. 大斯托克斯位移远红光至近红外荧光探针用于检测肝损伤过程中过氧化亚硝酸盐的动态变化[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(11): 2426. |
| [14] | 王金金, 戚少龙, 杜建时, 杨清彪, 宋岩, 李耀先. 苯并噻唑类荧光探针的合成及对N2H4·H2O和HS |
| [15] | 张勇,申城,幸志荣,陈归柒,卢资,侯志兵,陈雪梅. 可视化检测次氯酸的苯并咪唑类荧光增强型探针[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(12): 2480. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
