

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 20210516.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20210516
靳科研1, 白璞1,4, 李小龙2( ), 张佳楠3, 闫文付1(
), 张佳楠3, 闫文付1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-07-19
出版日期:2022-02-10
发布日期:2021-09-16
通讯作者:
李小龙,闫文付
E-mail:free123orange@163.com;yanw@jlu.edu.cn
基金资助:
JIN Keyan1, BAI Pu1,4, LI Xiaolong2( ), ZHANG Jianan3, YAN Wenfu1(
), ZHANG Jianan3, YAN Wenfu1( )
)
Received:2021-07-19
Online:2022-02-10
Published:2021-09-16
Contact:
LI Xiaolong,YAN Wenfu
E-mail:free123orange@163.com;yanw@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
通过特定的焙烧过程制备了不含碳酸根的Mg-Al型层状双金属氧化物. 该层状双金属氧化物在废水中可水解为层状双金属氢氧化物, 从而能够通过四级串联吸附处理的方式将模拟核电厂含硼废水中的硼浓度由初始的2000 mg/L显著降低至10 mg/L, 满足内陆拟建核电厂需要将含硼废水硼浓度处理至30 mg/L以下的技术要求. 在pH=10.61, 固液比为1/40 g/mL, 吸附温度为20 ℃条件下, 吸附剂的硼吸附量可高达39.64 mg/g. 此外, 还在分子层次上讨论了中间氧化物的形成机理以及其水解生成层状双金属氢氧化物的机理, 探讨了核电厂高浓度含硼废水的pH值、 初始硼浓度、 吸附剂用量和搅拌时间等条件对吸附剂硼吸附性能的影响.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
靳科研, 白璞, 李小龙, 张佳楠, 闫文付. 新型Mg-Al吸附剂去除压水堆核电厂废水中高浓度硼. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210516.
JIN Keyan, BAI Pu, LI Xiaolong, ZHANG Jianan, YAN Wenfu. New Mg-Al Type Sorbent for Efficient Removal of Boron from Waste Water Containing High-concentration of Boron from Pressurized Water Reactor Nuclear Power Plants. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210516.
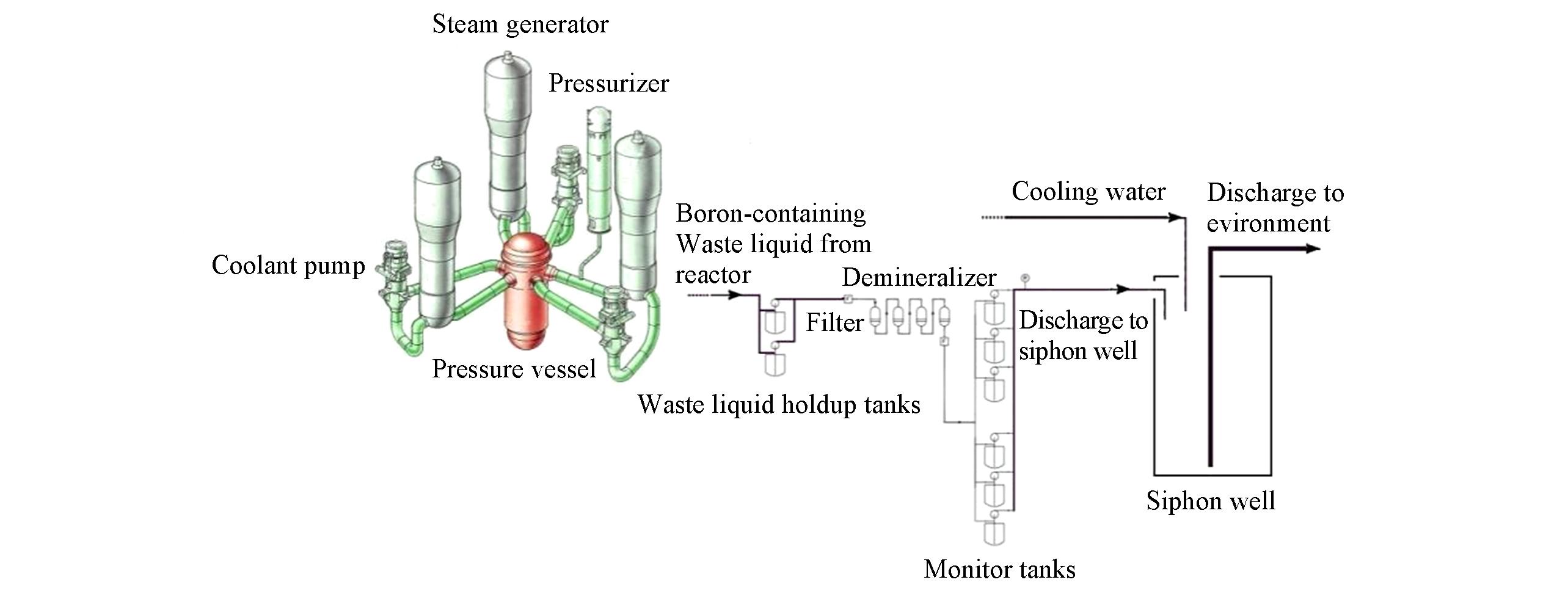
Scheme 1 Schematic diagram of the treatment and discharge of the boron?containing waste water generated from pressurized water reactor nuclear power plant
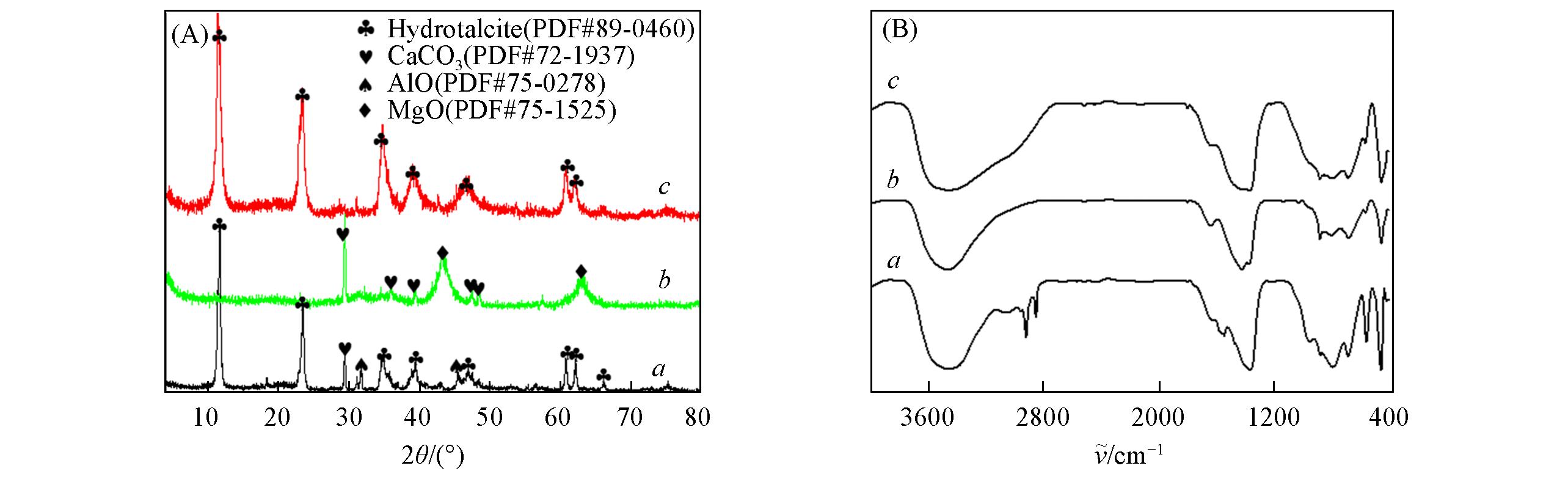
Fig.1 Experimental XRD patterns(A) and FTIR spectra(B) of raw Mg?Al LDH(a), intermediate oxide from the calcination of LDH(b), and layered double hydroxide after B?anions adsorption(c)
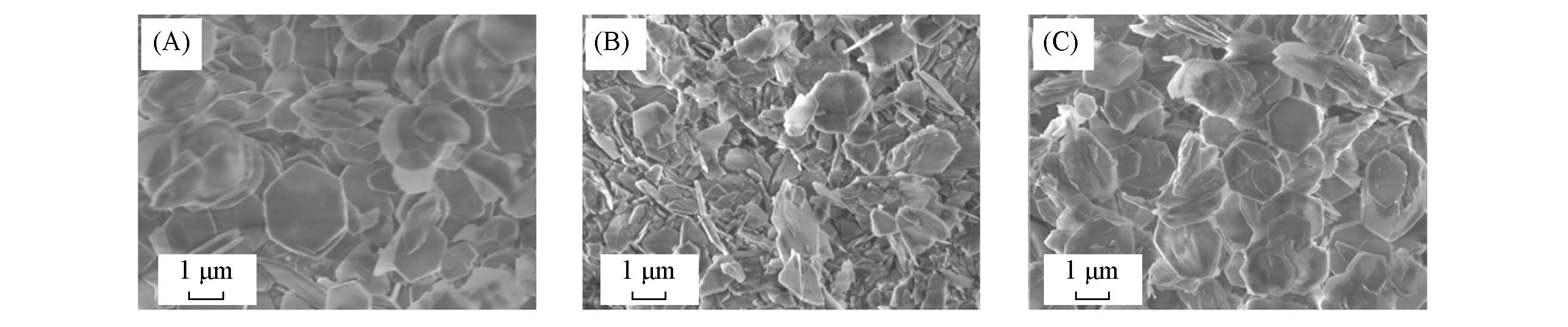
Fig.2 SEM images of the raw Mg?Al LDH(A), intermediate oxide from the calcination of LDH(B), and layered double hydroxide after B?anions adsorption(C)
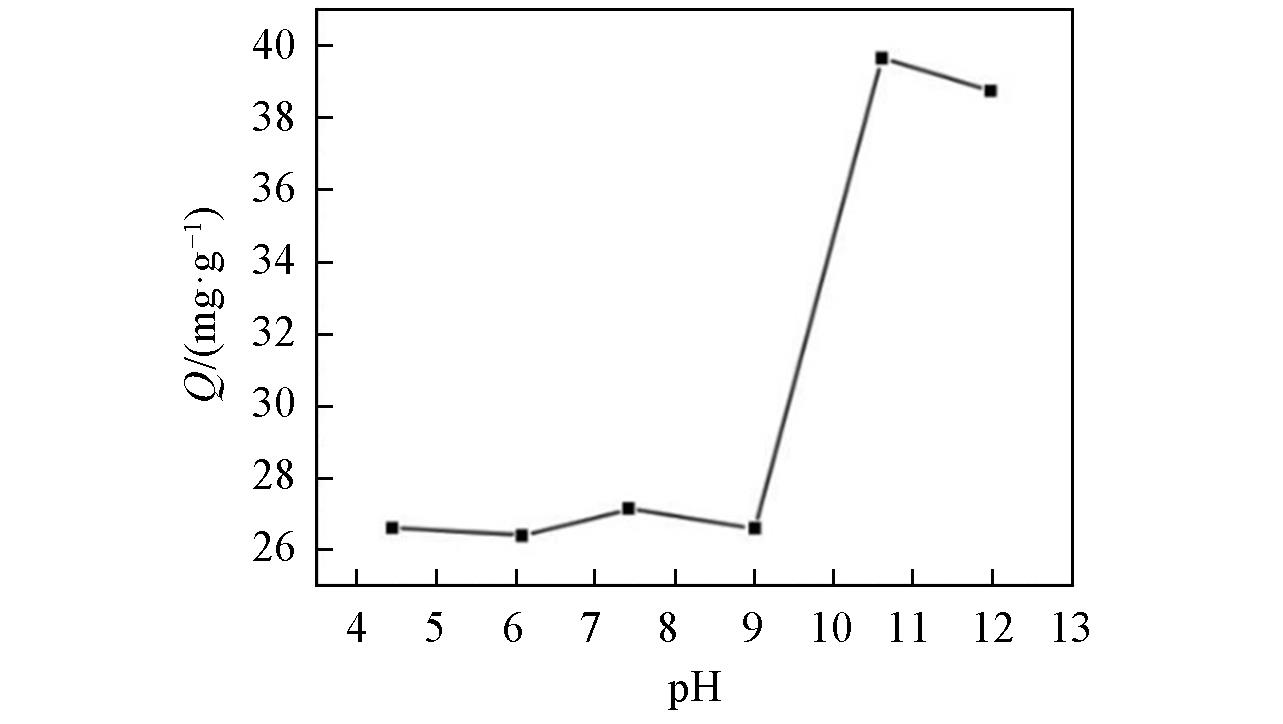
Fig.3 Influence of pH value on the removal of boron at an initial boron concentration of 2000 mg/LAdsorbent dose/solution volume ratio: 1/40 g/mL; temperature: 20 ℃; reaction time: 24 h.
| Run | c0/(mg·L-1) | ce/(mg·L-1) | Removal efficiency(%) | Qe/(mg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50 | 11.07 | 77.86 | 1.56 |
| 2 | 200 | 36.46 | 81.77 | 6.54 |
| 3 | 500 | 69.01 | 86.20 | 17.24 |
| 4 | 1000 | 453.4 | 54.66 | 21.86 |
| 5 | 2000 | 1277.4 | 54.66 | 28.90 |
Table 1 Boron adsorption on intermediate oxide from aqueous solution with various initial B concentrations(Adsorbent dose/solution volume ratio: 1/40 g/mL, pH=7.43, contact time: 24 h)
| Run | c0/(mg·L-1) | ce/(mg·L-1) | Removal efficiency(%) | Qe/(mg·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50 | 11.07 | 77.86 | 1.56 |
| 2 | 200 | 36.46 | 81.77 | 6.54 |
| 3 | 500 | 69.01 | 86.20 | 17.24 |
| 4 | 1000 | 453.4 | 54.66 | 21.86 |
| 5 | 2000 | 1277.4 | 54.66 | 28.90 |
| Material | qm,exp/(mg·g-1) | Langmuir model | Freundlich model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm/(mg·g-1) | b/(L·mg-1) | R2 | kF/(mg·g-1) | 1/n | R2 | |||
| Intermediate oxide | 28.90 | 32.01 | 0.0065 | 0.981 | 0.756 | 0.554 | 0.735 | |
Table 2 Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm parameters of B adsorption on intermediate oxide
| Material | qm,exp/(mg·g-1) | Langmuir model | Freundlich model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm/(mg·g-1) | b/(L·mg-1) | R2 | kF/(mg·g-1) | 1/n | R2 | |||
| Intermediate oxide | 28.90 | 32.01 | 0.0065 | 0.981 | 0.756 | 0.554 | 0.735 | |
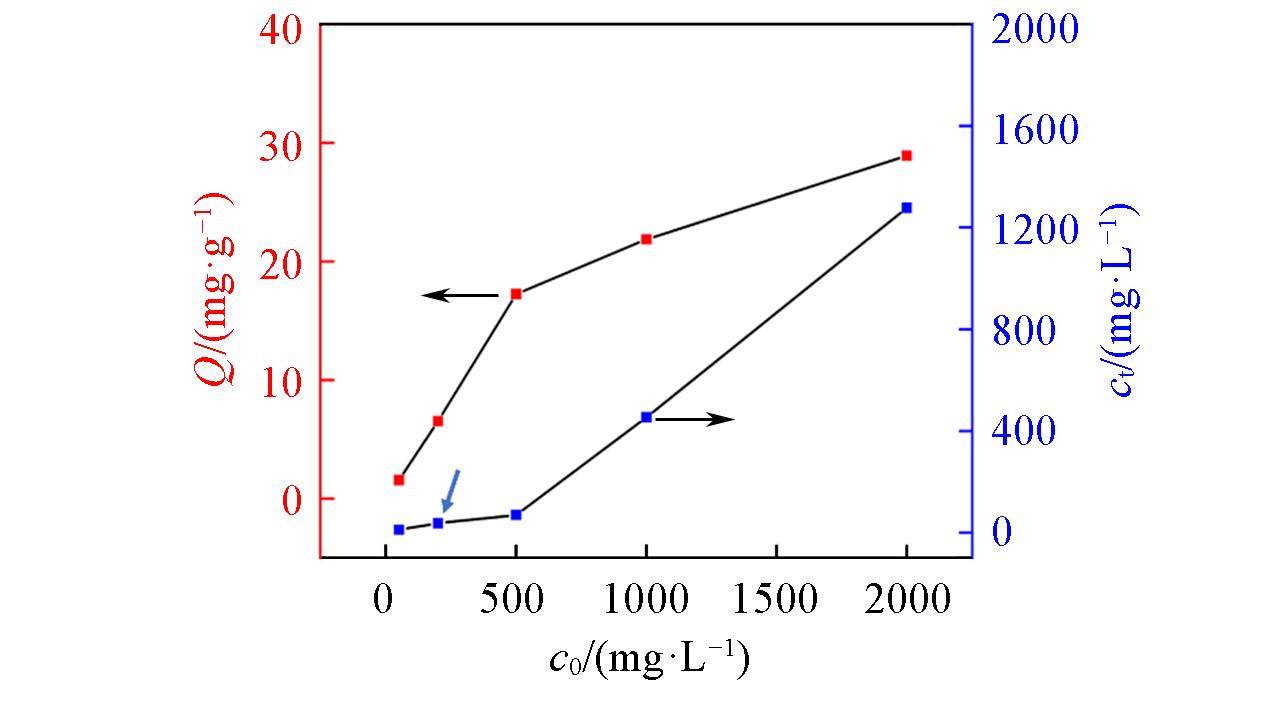
Fig.5 Influence of initial boron concentration(c0) on the removal of boron at pH of 7.43Adsorbent dose/solution volume ratio: 1/40 g/mL;temperature: 20 °C; reaction time: 24 h.
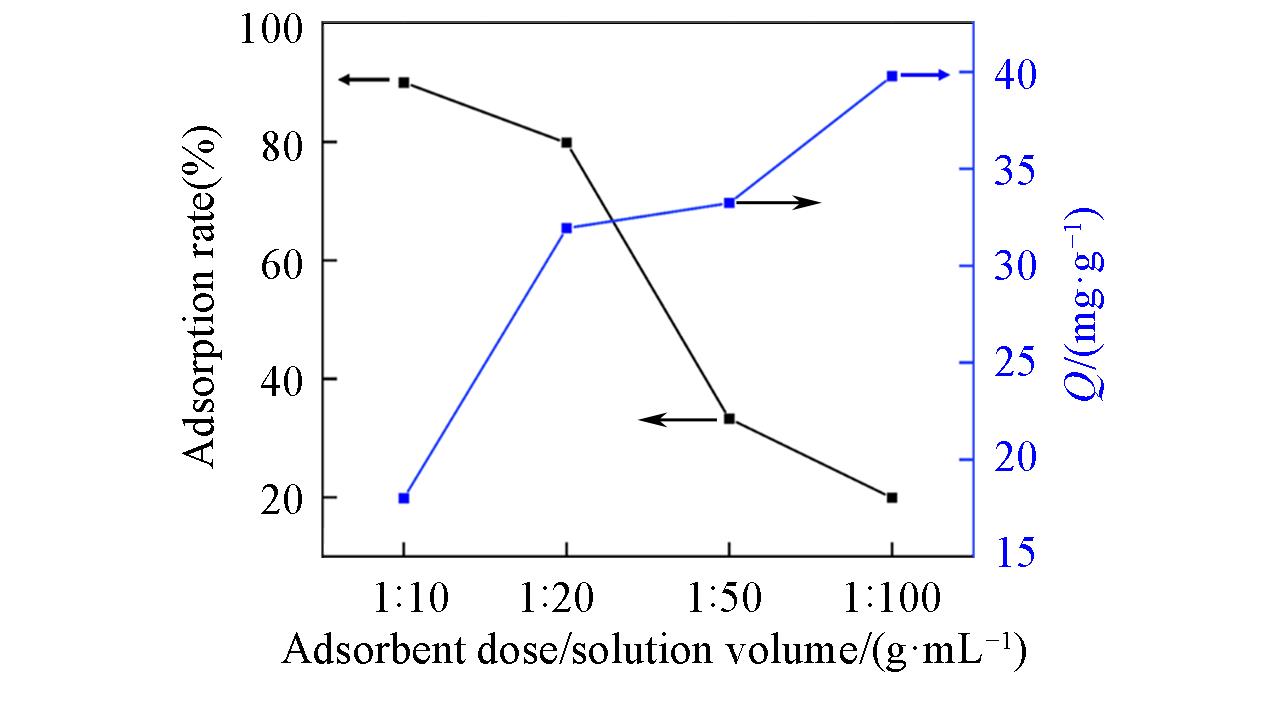
Fig.6 Influence of adsorbent dose/solution volume ratio on the removal of boron at an initial boron concentration of 2000 mg/L, pH=7.43, temperature of 20 ℃, and reaction time of 24 h
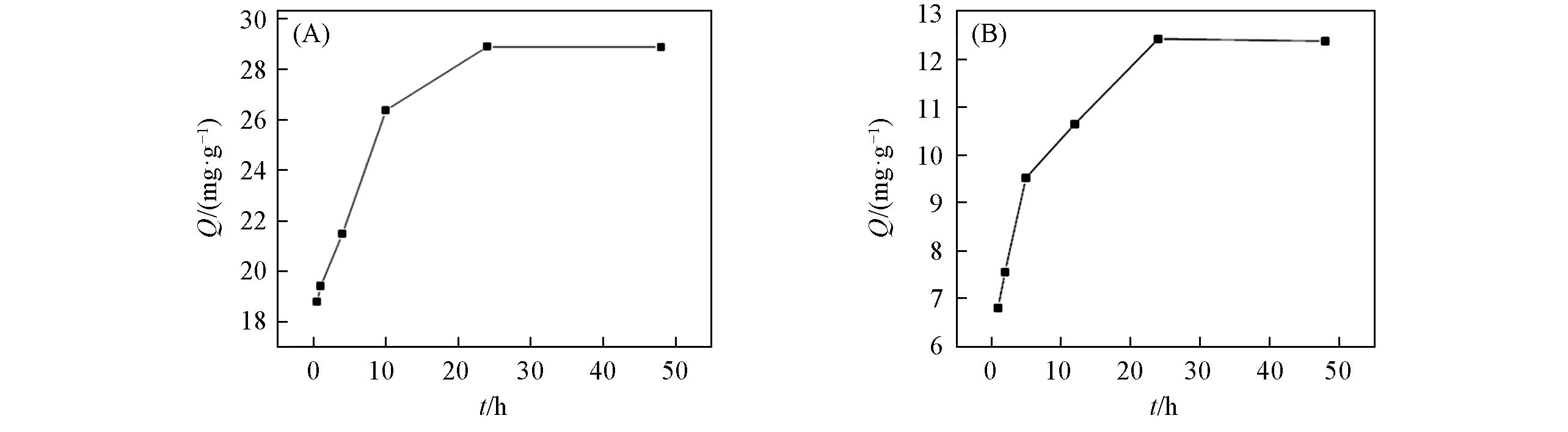
Fig.7 Influence of agitation time on the removal of boron of calcined Mg?Al LDH(A) and un?calcined Mg?Al LDH(B)Initial boron concentration: 2000 mg/L, pH=7.43, adsorbent dose: 1/40 g/mL for calcined Mg?Al LDH, 1/100 g/mL for un?calcined Mg?Al LDH, temperature: 20 ℃.
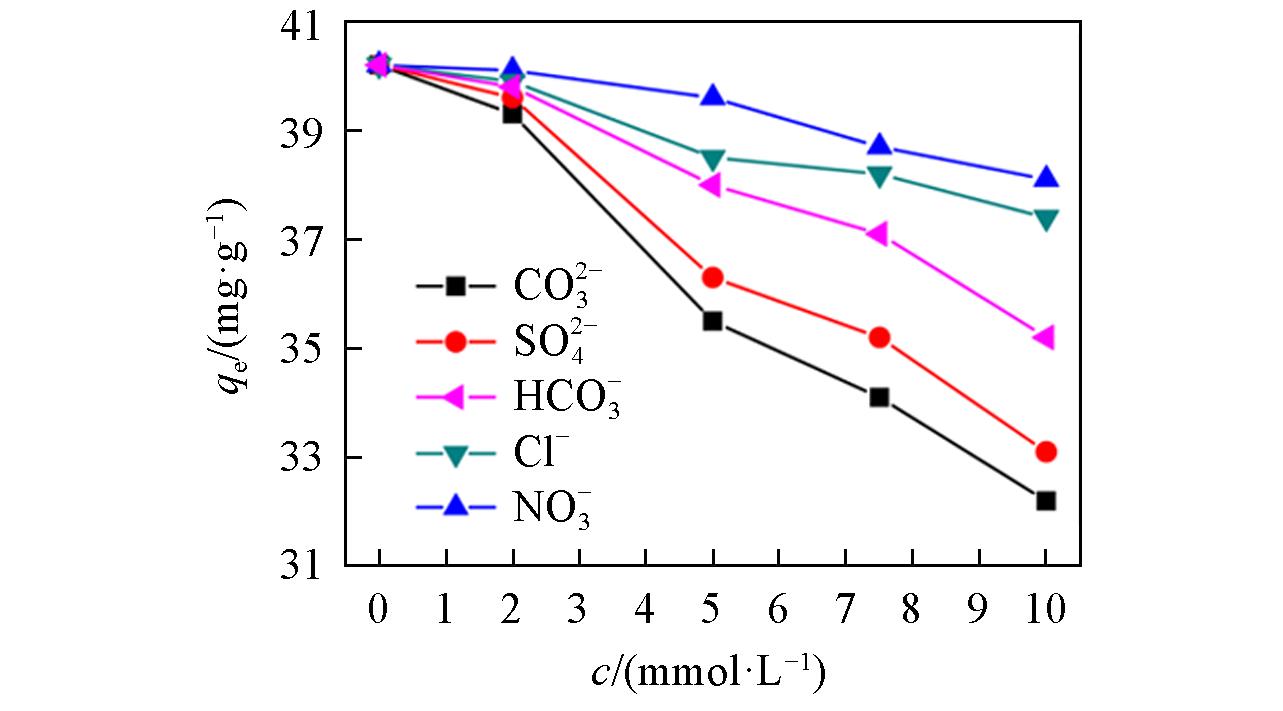
Fig.8 Influence of competition ion on the removal of boron at an initial boron concentration of 2000 mg/L, pH of 7.43, adsorbent dose/solution volume of 1/100 g/mL, and temperature of 20 ℃
| 1 | Ozturk N., Kavak D., J. Hazard. Mater., 2005, 127(1—3), 81—88 |
| 2 | Şahin S., Desalination, 2002, 143(1), 35—43 |
| 3 | Li G. Q., Yu J. S., Li G. W., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(3), 793—796(李广全, 于景生, 李国文. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(3), 793—796) |
| 4 | Fang F., Xu C. Y., Liu X. H., Wu H., Radiation Protection, 2012, 32(1), 8—14, 20(方岚, 徐春艳, 刘新华, 吴浩. 辐射防护, 2012, 32(1), 8—14, 20) |
| 5 | Zerze H., Özbelge H. Ö., Bıçak N., Yılmaz L., Sep. Sci. Technol., 2015, 50(13), 2004—2014 |
| 6 | Liu P., Hu W., Wu G. P., Wei F. S., World Sci⁃Tech R&D, 2003, 25(6), 6—11(刘平, 胡伟, 吴国平, 魏复盛. 世界科技研究与发展, 2003, 25(6), 6—11) |
| 7 | Kluczka J., Int. J. Environ. Res., 2015, 9(2), 711—720 |
| 8 | Ping Q., Abu⁃Reesh I. M., He Z., Desalination, 2015, 376, 55—61 |
| 9 | Zheng Z. Q., Bian S. P., Zheng J. M., Shang S. Y., Li B. J., Liu X. L., Environ. Sci., 1983, 4(3), 16—20(郑泽群, 边淑萍, 郑建民, 商寿岩, 李炳钧, 刘秀兰. 环境科学, 1983, 4(3), 16—20) |
| 10 | Rivas B. L., Sanchez J., Macromol. Symp., 2015, 351(1), 37—45 |
| 11 | Fang L., Liu X. H.,Wu H., Zhang Z. Y., Chin. J. Nucl. Sci. Eng., 2011, 31(1), 86—92(方岚, 刘新华, 吴浩, 张志银. 核科学与工程, 2011, 31(1), 86—92) |
| 12 | Wei X. Y., Ma H. B., Wang P., Yang D. J., Shang Z. R., Radiat. Prot. Bull., 2012, 32(5), 32—36(魏新渝, 马鸿宾, 汪萍, 杨端节, 商照荣. 辐射防护通讯, 2012, 32(5), 32—36) |
| 13 | Chang R. R., Wu J. Q., Wang G. Z., Liang L., Guo L. M., Appl. Chem. Ind., 2020, 49(11), 2718—2721(常瑞瑞, 吴家全, 王桂珠, 梁利, 郭丽梅. 应用化工, 2020, 49(11), 2718—2721) |
| 14 | Yoshikawa E., Sasaki A., Endo M., J. Hazard. Mater., 2012, 237(30), 277—282 |
| 15 | Goldberg S., Forster H. S., Lesch S. M., Heick E. L., Soil Sci., 1996, 161(2), 99—103 |
| 16 | Ozturk N., Kavak D., Fresenius Environ. Bull., 2003, 12(12), 1450—1456 |
| 17 | Xu X. Y., Liao Y. Q., Sun J. C., Wang X. H., Chen S. Q., Lv Z., Song J. Q., Acta Phys. ⁃Chim. Sin., 2019, 35(3), 317—326 |
| 18 | Gong F. F., Wang Y., Chen S. H., Zhang Y. Q., Liu Y. D., Meng T. Y., Lou Y. J., Li Y. Y., J. Nucl. Agric. Sci., 2020, 34(8), 1763—1769(龚芳芳, 王晔, 陈淑敏, 张玉琦, 刘英丹, 孟天宇, 娄永江, 李勇勇. 核农学报, 2020, 34(8), 1763—1769) |
| 19 | Wu X. X., Li Q. Q., Li M., Tang H., Hu B., Light Met., 1995, (7), 35—38(吴贤熙, 李琴琴, 黎曼, 汤辉, 胡波. 轻金属, 1995, (7), 35—38) |
| 20 | Gao C. K., Li R. H., Liu L. F., Song X. X., Xie X., Zhang X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9), 2033—2040(高从堦, 李蕊含, 刘立芬, 宋潇潇, 谢欣, 张潇. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(9), 2033—2040) |
| 21 | Wang J. Q., Zhou M. S., Lu D. N., Fei W. Y., Wu J. Z., Green Energy Environ., 2020, 5(3), 364—373 |
| 22 | Wang N., Wei R. Q., Cao F. T., Liu X. N., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(12), 2795—2800(王楠, 魏荣卿, 曹飞婷, 刘晓宁. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(12), 2795—2800) |
| 23 | Kluczka J., Ciba J., Trojanowska J., Zolotajkin M., Turek M., Dydo P., Environ. Prog., 2007, 26(1), 71—77 |
| 24 | Kluczka J., Trojanowska J., Zolotajkin M., Ciba J., Turek M., Dydo P., Environ. Technol., 2007, 28(1), 105—113 |
| 25 | Celik Z. C., Can B. Z., Kocakerim M. M., J. Hazard. Mater., 2008, 152(1), 415—422 |
| 26 | Halim A. A., Roslan N. A., Yaacub N. S., Latif M. T., Sains Malays., 2013, 42(9), 1293—1300 |
| 27 | Zohdi N., Mahdavi F., Abdullah L. C., Choong T. S. Y., J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng., 2014, 12, 3 |
| 28 | Rajaković L. V., Ristić M. D., Carbon, 1996, 34(6), 769—774 |
| 29 | Seyhan S., Seki Y., Yurdakoc M., Merdivan M., J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, 146(1/2), 180—185 |
| 30 | Cengeloglu Y., Tor A., Arslan G., Ersoz M., Gezgin S., J. Hazard. Mater., 2007, 142(1/2), 412—417 |
| 31 | Kameda T., Oba J., Yoshioka T., J. Hazard. Mater., 2015, 293, 54—63 |
| 32 | Yan C. Y., Yi W. T., Ma P. H., Li F. Q., Ion Exch. Adsorpt., 2009, 25(3), 233—240(闫春燕, 伊文涛, 马培华, 李法强. 离子交换与吸附. 2009, 25(3), 233—240) |
| 33 | Ferreira O. P., de Moraes S. G., Duran N., Cornejo L., Alves O. L., Chemosphere, 2006, 62(1), 80—88 |
| 34 | Kentjono L., Liu J. C., Chang W. C., Irawan C., Desalination, 2010, 262(1—3), 280—283 |
| 35 | Delazare T., Ferreira L. P., Ribeiro N. F. P., Souza M. M. V. M., Campos J. C., Yokoyama L., Environ. Eng., 2014, 49(8), 923—932 |
| 36 | Jiang J. Q., Xu Y., Quill K., Simon J., Shettle K., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2007, 46(13), 4577—4583 |
| 37 | Liu J., Guo X. L., Yuan J. S., Desalin. Water Treat., 2014, 52(10—12), 1919—1927 |
| 38 | Ay A. N., Zümreoglu⁃Karan B., Temel A., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2007, 98(1—3), 1—5 |
| 39 | Yan C. Y., Yi W. T., Environ. Prot. Chem. Ind., 2010, 30(2), 172—175(闫春燕, 伊文涛. 化工环保, 2010, 30(2), 172—175) |
| 40 | Qiu X. H., Sasaki K., Osseo⁃Asare K., Hirajima T., Ideta K., Miyawaki J., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2015, 445, 183—194 |
| 41 | Koilraj P., Srinivasan K., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2011, 50(11), 6943—6951 |
| 42 | García S. M. M. F., Muñoz C. E., Sep. Purif. Technol., 2006, 48(1), 36—44 |
| 43 | García S. M. M. F., Muñoz C. E., Desalination, 2009, 249(2), 626—634 |
| 44 | Dionisiou N., Matsi T., Misopolinos N. D., J. Environ. Qual., 2006, 35(6), 2222—2228 |
| 45 | Seki Y., Seyhan S., Yurdakoc M., J. Hazard. Mater., 2006, 138(1), 60—66 |
| 46 | Bouguerra W., Mnif A., Hamrouni B., Dhahbi M., Desalination, 2008, 223(1), 31—37 |
| 47 | Zhang G. F., Sun G. Q., Mar. Sci., 1995, (2), 58—61(张国防, 孙国清. 海洋科学. 1995, (2), 58—61) |
| 48 | Qiu X. H., Sasaki K., Osseo⁃Asare K., Hirajima T., Ideta K., Jin M., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2015, 445, 183—194 |
| 49 | Fan H. L., He W., Jiang Y. Y., Bao G. H., Ge T. J., Eng. Plast. Appl., 2011, 39(4), 10—14(范惠琳, 何伟, 姜莹莹, 保功辉, 葛铁军. 工程塑料应用, 2011, 39(4), 10—14) |
| 50 | Ma Z. Y., Spectrosc. Spectral Anal., 2012, 32(5), 1255—1258(马赵扬. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2012, 32(5), 1255—1258) |
| 51 | Wang X., Preparation of Hydrotalcite by Mechano⁃chemical Method and Study the Memory Effect of Structure, Dalian Jiaotong University, Dalian, 2014(王旭. 机械力化学法制备镁铝水滑石的结构记忆效应研究, 大连: 大连交通大学, 2014) |
| 52 | Sato T., Wakabayashi T., Shimada M., Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev., 1986, 25(1), 89—92 |
| 53 | Sasaki K., Qiu X. H., Moriyama S., Tokoro C., Ideta K., Miyawaki J., Mater. Trans., 2013, 54(9), 1809—1817 |
| 54 | Goh K. H., Lim T. T., Dong Z. L., Water Res., 2008, 42(6/7), 1343—1368 |
| 55 | Iyi N., Matsumoto T., Kaneko Y., Kitamura K., Chem. Lett., 2004, 33(9), 1122—1123 |
| 56 | Li L., Ma R. Z., Ebina Y., Iyi N., Sasaki T., Chem. Mater., 2005, 17(17), 4386—4391 |
| 57 | Zhang T., Li Q. R., Xiao H. Y., Lu H. X., Zhou Y. M., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2012, 51(35), 11490—11498 |
| [1] | 姜宏斌, 代文臣, 张娆, 徐晓晨, 陈捷, 杨光, 杨凤林. Co3O4/UiO-66@α-Al2O3陶瓷膜对VOCs废气的分离催化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220025. |
| [2] | 戴卫, 侯华, 王宝山. 七氟异丁腈负离子结构与反应活性的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220044. |
| [3] | 郝宏蕾, 孟繁雨, 李若钰, 李迎秋, 贾明君, 张文祥, 袁晓玲. 生物质基氮掺杂多孔炭材料的制备及对水中亚甲基蓝的吸附性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220055. |
| [4] | 王红宁, 黄丽, 清江, 马腾洲, 蒋伟, 黄维秋, 陈若愚. 香蒲基生物炭的活化及对VOCs吸附的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210824. |
| [5] | 孟祥龙, 杨歌, 郭海玲, 刘晨光, 柴永明, 王纯正, 郭永梅. 纳米分子筛的合成及硫化氢吸附性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210687. |
| [6] | 陈潇禄, 袁珍闫, 仲迎春, 任浩. 机械球磨制备三苯胺基PAF-106s及C2烃吸附性质[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210771. |
| [7] | 谭乐见, 仲宣树, 王锦, 刘宗建, 张爱英, 叶霖, 冯增国. β-环糊精的低临界溶解温度现象及其在有序纳米孔道片晶制备中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220405. |
| [8] | 郑美琪, 毛方琪, 孔祥贵, 段雪. 类水滑石材料在核废水处理领域的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220456. |
| [9] | 田晓康, 张青松, 杨舒淋, 白洁, 陈冰洁, 潘杰, 陈莉, 危岩. 微生物发酵诱导多孔材料: 制备方法和应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220216. |
| [10] | 张弛, 孙福兴, 朱广山. 双金属同构金属-有机框架材料CAU-21-Al/M的合成、 氮气吸附及复合膜性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(1): 20210578. |
| [11] | 马鉴新, 刘晓东, 徐娜, 刘国成, 王秀丽. 一种具有发光传感、 安培传感和染料吸附性能的多功能Zn(II)配位聚合物[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(1): 20210585. |
| [12] | 刘昌辉, 梁国俊, 李妍璐, 程秀凤, 赵显. NH3在硼纳米管表面吸附的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2263. |
| [13] | 王红宁, 黄丽, 宋夫交, 朱婷, 黄维秋, 钟璟, 陈若愚. 中空碳纳米球的制备及VOCs吸附性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1704. |
| [14] | 刘云鸿, 彭新艳. 新型蛋白结合类毒素血液灌流吸附剂的制备及吸附性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1952. |
| [15] | 王隆杰, 范鸿川, 秦渝, 曹秋娥, 郑立炎. 金属有机框架材料在分离分析领域的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(4): 1167. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||