

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 20250280.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20250280
收稿日期:2025-09-29
出版日期:2026-01-10
发布日期:2025-12-02
通讯作者:
卢晓峰
E-mail:xflu@jlu.edu.cn
Received:2025-09-29
Online:2026-01-10
Published:2025-12-02
Contact:
LU Xiaofeng
E-mail:xflu@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
电化学水分解是目前最具潜力的可持续制氢途径之一, 然而, 阴极析氢反应与阳极析氧反应所需的高过电位严重制约了其规模化应用. 过渡金属基催化剂因成本低、 组成可调和具有类贵金属催化活性, 可有效降低电极过电位, 被视为替代贵金属催化剂的理想材料, 因而备受关注. 本文总结了基于静电纺纳米纤维构筑的过渡金属双功能电催化剂的主要类型(金属、 氧化物、 磷化物、 硫化物及碳化物等体系), 重点讨论了提升其催化性能的关键策略(包括异质界面工程、 杂原子掺杂、 金属-非金属-金属桥接结构设计以及单原子位点调控等). 最后, 探讨了该领域面临的挑战与未来发展的方向, 以期为高性能全解水电催化剂的理性设计与开发提供参考.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
银泳婷, 卢晓峰. 静电纺纳米纤维过渡金属基双功能电催化剂及其在全解水中的应用. 高等学校化学学报, 2026, 47(1): 20250280.
YIN Yongting, LU Xiaofeng. Electrospun Nanofibrous Transition Metal-based Bifunctional Electrocatalysts Toward Overall Water Splitting. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2026, 47(1): 20250280.
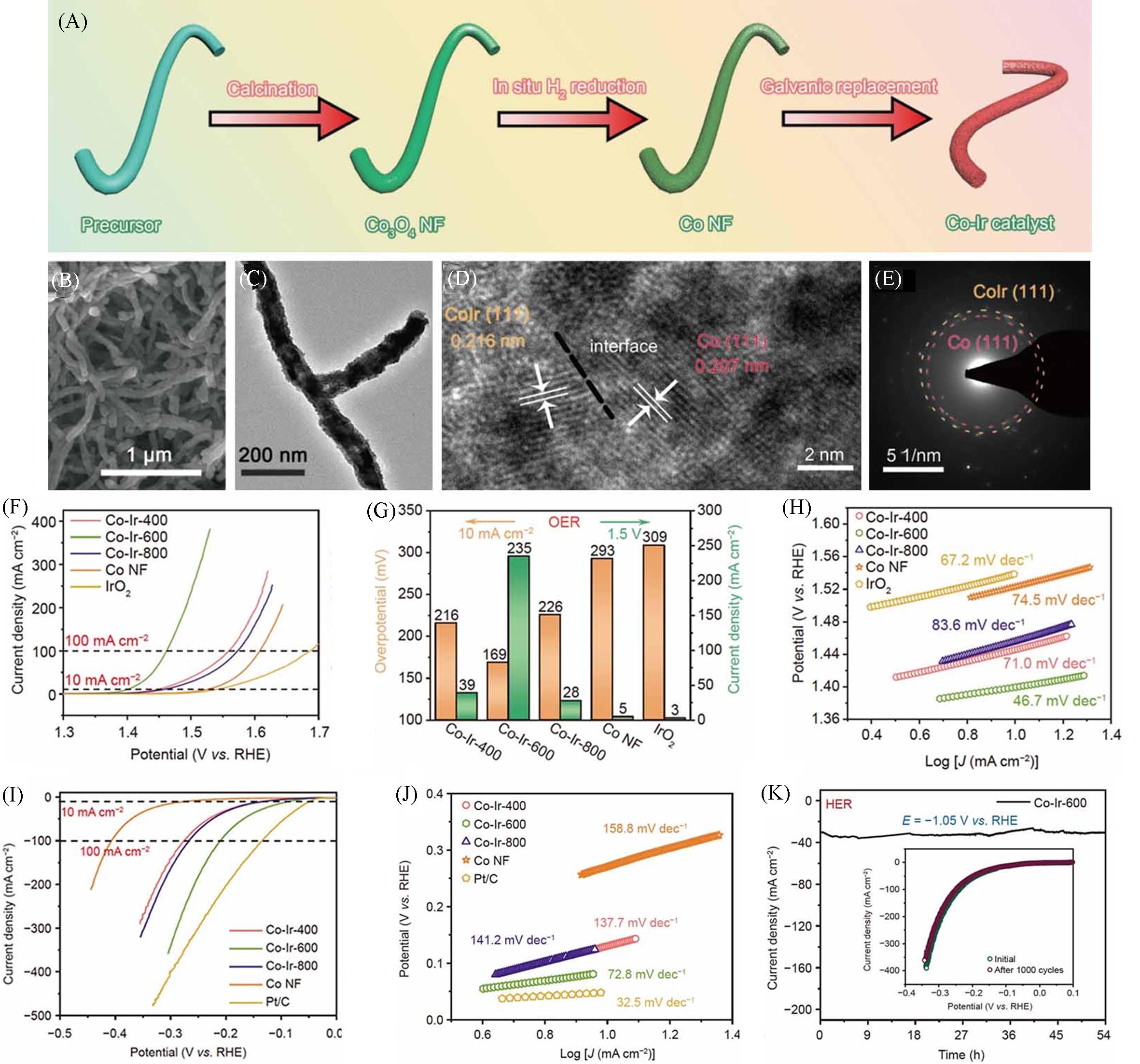
Fig.2 Scheme of the procedure to prepare the Co⁃Ir nanofibrous catalyst(A), SEM image(B), TEM image(C), HRTEM image(D) and SAED pattern(E) of the Co⁃Ir⁃600 NFs, LSV curves of varied electrocatalysts for OER(F), comparison of OER activity for varied catalysts(G), Tafel slopes of varied catalysts for OER(H), LSV curves(I) and Tafel slopes(J) of varied catalysts for HER and i⁃t curve and the LSV curves before and after 1000 CV cycles(inset) of Co⁃Ir⁃600 NFs for HER(K)[23]
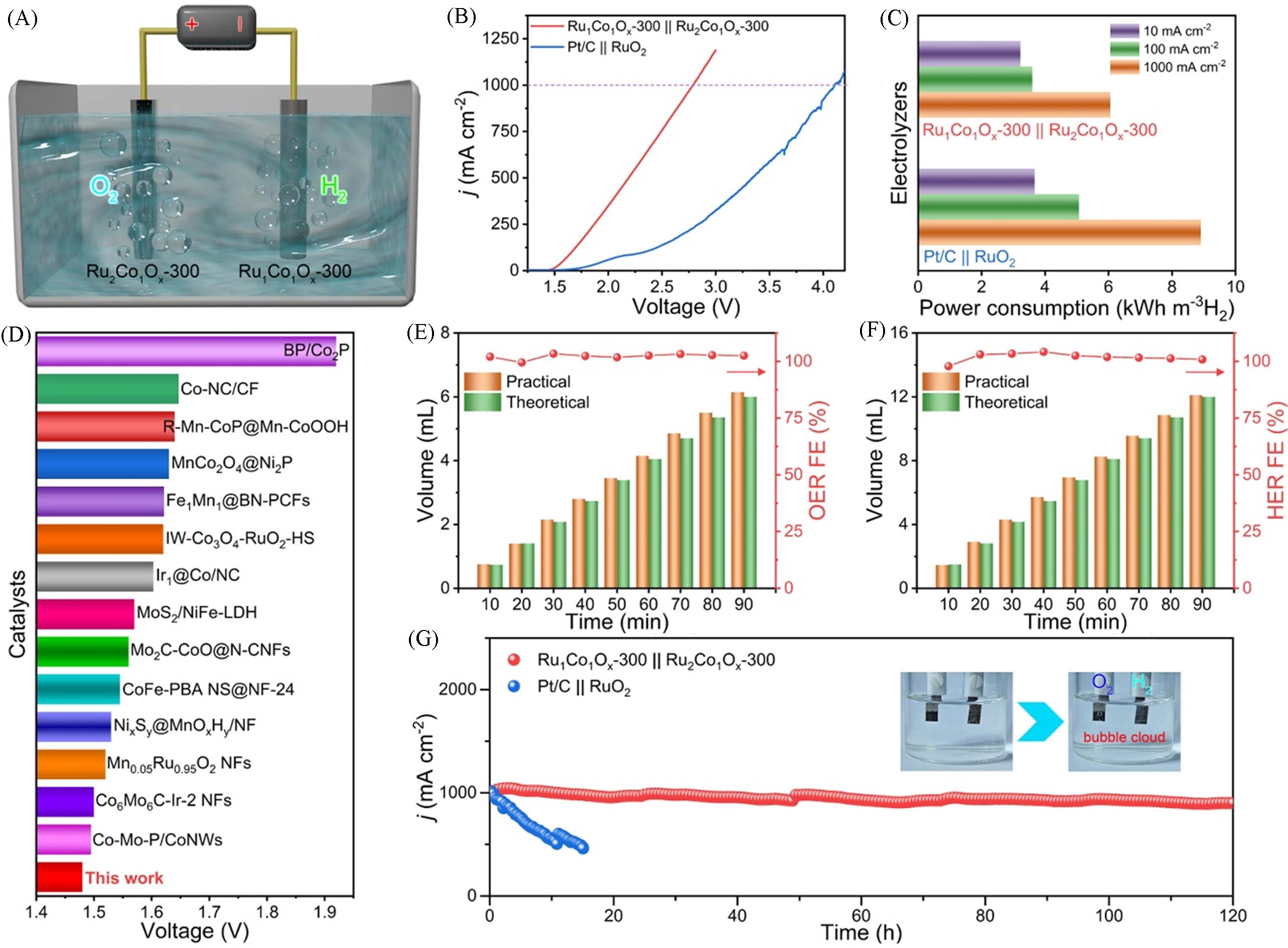
Fig.3 Schematic illustration of the alkaline two⁃electrode OWS system(A), LSV curves without iR correction(B) and power consumption for H2 generation at various current densities in two electrolysis systems(C), comparison of voltages at 10 mA/cm2 among various electrolysis systems(D), practical and theoretical O₂(E) and H₂(F) production as well as the FEs of the OWS system, stability test and the gas bubbles at the electrodes in the electrolyte(inset) of RuCoOₓ⁃300||Ru2CoOₓ⁃300 and Pt/C||RuO2 electrolysis systems(G)[26]
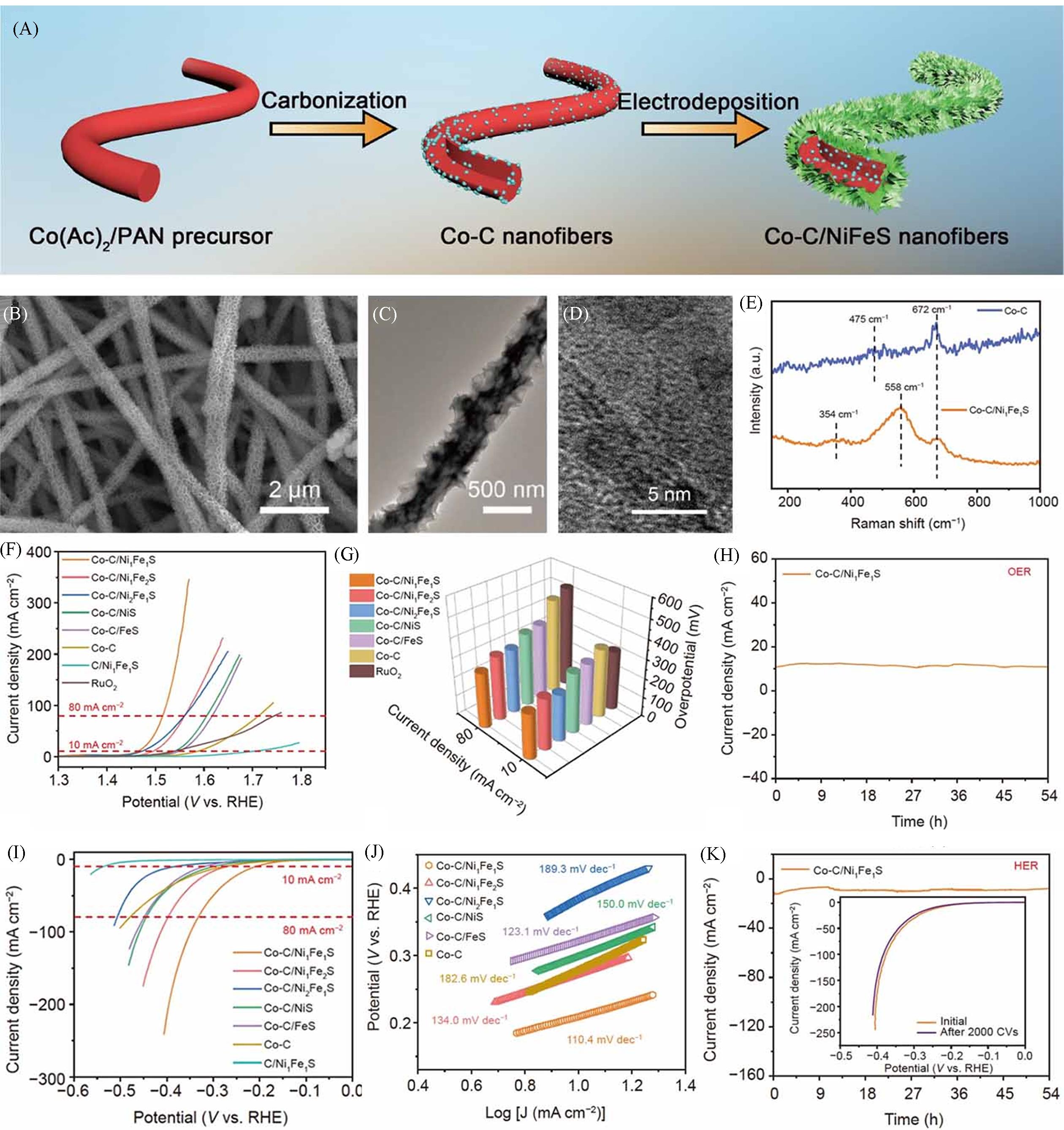
Fig.4 Illustration of the preparation process of Co⁃C/NiFeS NFs(A), SEM(B), TEM(C), HRTEM(D) images of Co⁃C/NiFeS NFs, Raman spectra of Co⁃C and Co⁃C/NiFeS NFs(E), LSV curves of varied electrocatalysts for OER(F), collections of overpotentials at 10 and 80 mA/cm2(G), OER durability at around 10 mA/cm2(H) of Co⁃C/NiFeS NFs, LSV curves(I) and Tafel slopes(J) of varied electrocatalysts for HER and i⁃t curve and the LSV curves before and after 2000 CV cycles(inset) of Co⁃C/NiFeS NFs for HER(K)[37]
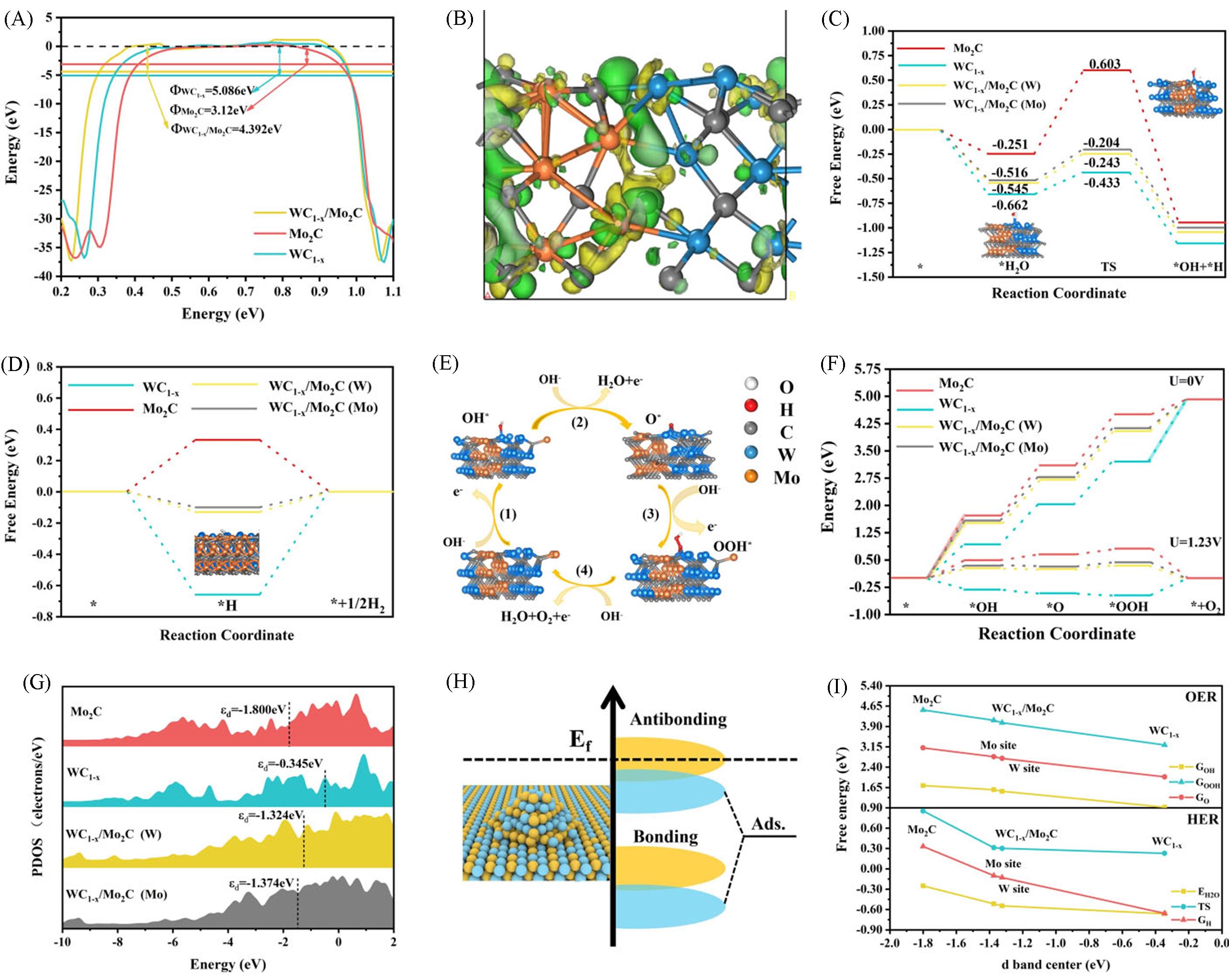
Fig.5 DFT calculation results of WC1⁃x /Mo2C, Mo2C and WC1⁃x [43](A) Calculated work function; (B) deformation charge density of catalyst; (C) calculated adsorption and dissociation energies of H2O on the catalysts; (D) computed Gibbs free energy; (E) proposed pathways for OER; (F) adsorption free energy of oxygen⁃containing intermediates on the catalysts; (G) the d⁃band centers of Mo and W; (H) schematic diagram illustrating the correlation between the d⁃band center and adsorption strength; (I) comparison of the free energy of key intermediates versusd⁃band center positions. Copyright 2024, John Wiley and Sons.
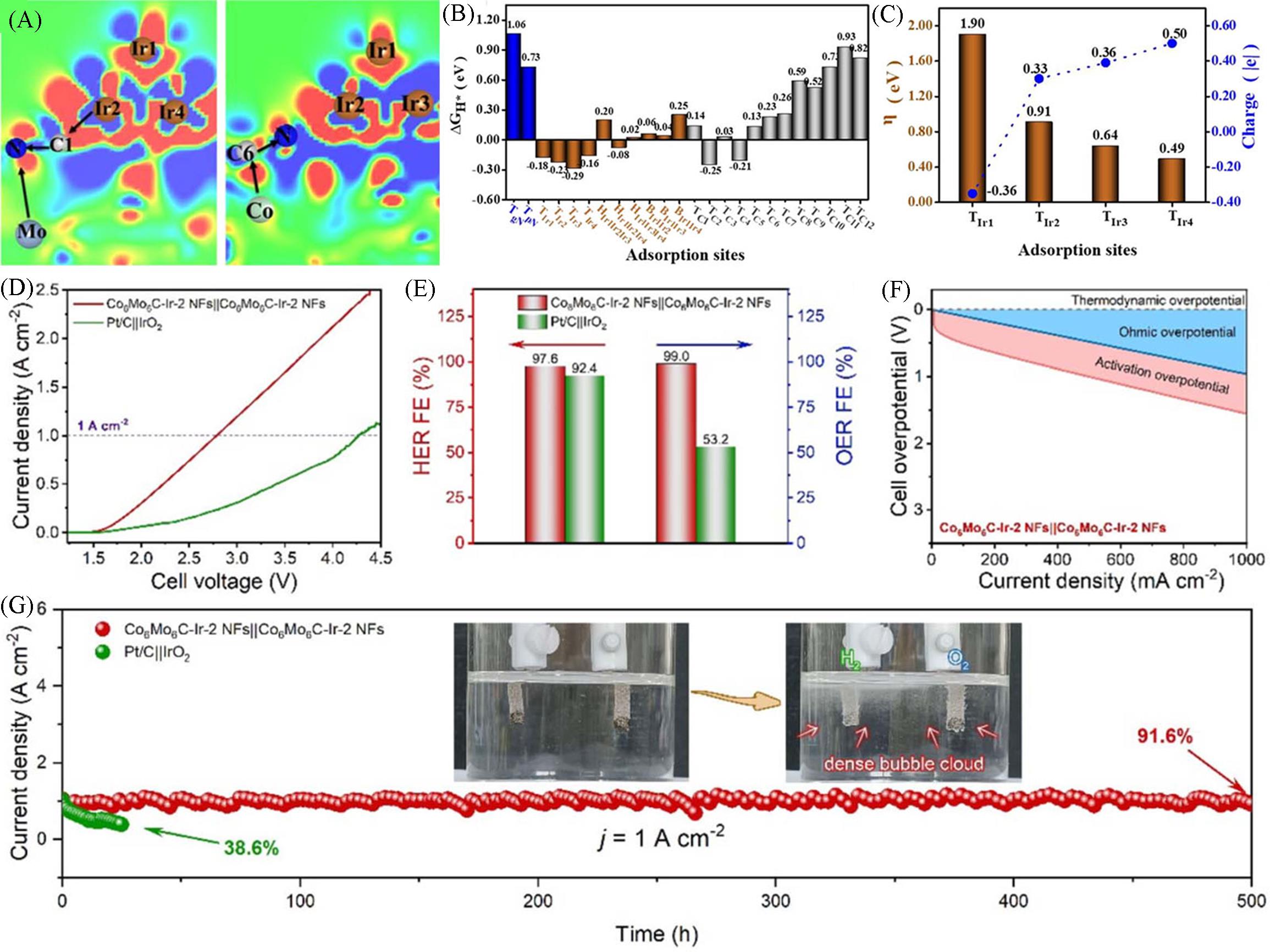
Fig.6 Charge density difference of Co6Mo6C⁃Ir NFs catalyst(A), ΔGH* at varied adsorption sites(B), OER overpotentials on Co6Mo6C⁃Ir NFs and Bader charge of various active sites(C), polarization curves of two electrolyzers(D), FEs of the two electrolyzers measured at 200 mA/cm2(E), the ohmic and activation overpotential analysis for Co6Mo6C⁃Ir⁃2 NFs||Co6Mo6C⁃Ir⁃2 NFs system(F) and the long⁃term stability test and the vigorous generation of H2 and O2 at the electrodes(insets) of two electrolyzers(G)[55]
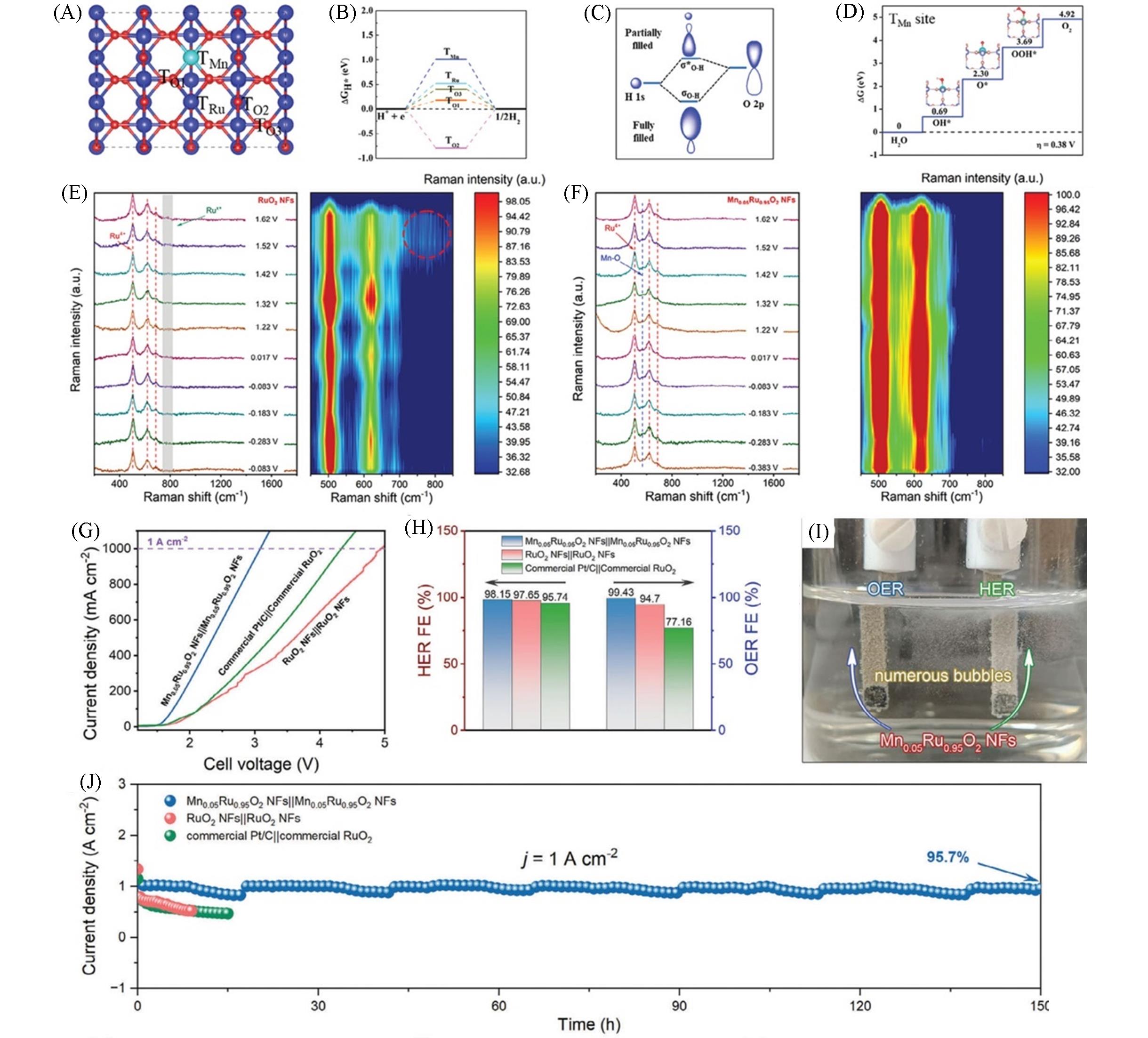
Fig.7 Adsorption sites for H* on Mn⁃doped RuO2(A), the calculated ΔGH* at varied adsorption sites(B), schematic illustration of the formed fully filled bonding orbital and a partially filled antibonding orbital for H* adsorption(C), free energy diagram of OER at the top site of Mn in Mn⁃doped RuO2(D), potential⁃dependent Raman spectra of RuO2 NFs Mn⁃doped RuO2 NFs(E, F), LSV curves(G) and FEs(H) of various electrolysis systems, digital photograph for generating H2 and O2 bubbles at cathode and anode(I) and the stability test of various electrolysis systems(J)[61]
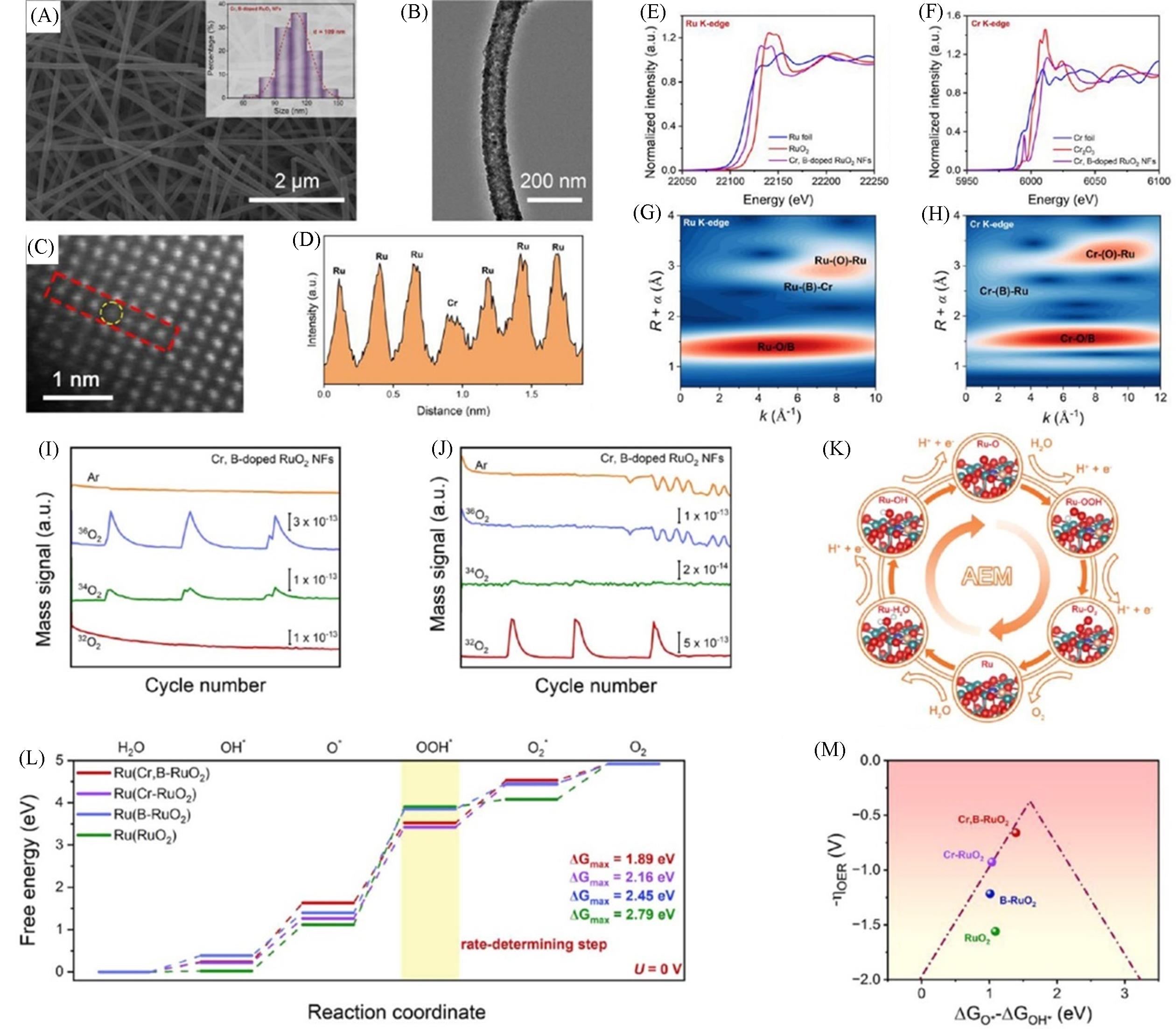
Fig.8 SEM image(A), TEM image(B), magnified spherical aberration⁃corrected HAADF⁃STEM image(C) and corresponding line scanning intensity profile of Cr, B⁃doped RuO2 NFs(D), XANES spectra for Ru K⁃edge(E) and Cr K⁃edge(F) for various samples, wavelet⁃transform EXAFS analysis at the Ru K⁃edge(G) and the Cr K⁃edge(H) of Cr, B⁃doped RuO2 NFs, operando DEMS spectra for Cr, B⁃doped RuO2 NFs using H218O solvent(I) and 18O⁃labeled Cr, B⁃doped RuO2 NFs with H216O solvent(J), schematic diagram of AEM mechanism for OER(K), free energy diagram of OER on various Ru sites(L) and correlation between the calculated negative overpotential(-ηOER) and the descriptor of ΔGO*-ΔGOH* for various catalysts(M)[67]
| [1] | Zhang J., Fu X., Kwon S., Chen K., Liu X., Yang J., Sun H., Wang Y., Uchiyama T., Uchimoto Y., Li S., Li Y., Fan X., Chen G., Xia F., Wu J., Li Y., Yue Q., Qiao L., Su D., Zhou H., Goddard W., Kang Y., Science, 2025, 387, 48—55 |
| [2] | Xia T., Ren Q., Yang J., Li Z., Shao M., Duan X., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2024, 40, 577—589 |
| [3] | Quan L., Jiang H., Mei G., Sun Y., You B., Chem. Rev., 2024, 124, 3694—3812 |
| [4] | Zhou Y., Yu W., Liu H., Fan R., Han G., Dong B., Chai Y., EcoEnergy, 2023, 1, 425—436 |
| [5] | Li W., Wang C., Lu X., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9, 3786—3827 |
| [6] | Cao X., Wang T., Jiao L., Adv. Fiber Mater., 2021, 3, 210—228 |
| [7] | Song W., Li M., Wang C., Lu X., Carbon Energ., 2021, 3, 101—128 |
| [8] | Song N., Ren S., Zhang Y., Wang C., Lu X., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32, 2204751 |
| [9] | Shi B., Lu X., Chem. Sci., 2025, 16, 17568—17594 |
| [10] | Wang C., Wang W., Qi H., Dai Y., Jiang S., Ding B., Wang X., Li C., Zeng J., Wu T., Li H., Wang Y., Zhao Y., Wang W., Li Z., Mo X., Hou H., Dong L., Ma H., Liu Y., Su C., Bai J., Wu W., Guo G., Nie G., Wang N., Zhu H., Bai J., Fang J., Liang D., Ba Z., Han G., Lu X., Wang K., Zhang X., Kang W., Deng N., Hu W., Chen W., Zhang X., Yang D., Wang F., Bian Y., Liu Z., Zhang L., Li X., Li L., Li Y., Huang H., Jia X., Li X., Yang D., Jin X., Li S., Zhang X., Tang N., Hao R., Tian F., Mai L., Wei Y., Xue J., Prog. Mater. Sci., 2025, 154, 101494 |
| [11] | Zhu Y., Tang Z., Yuan L., Li B., Shao Z., Guo W., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2025, 54, 1027—1092 |
| [12] | Fu X., Shi R., Jiao S., Li M., Li Q., J. Energy Chem., 2022, 70, 129—153 |
| [13] | Lu X., Li M., Wang H., Wang C., Inorg. Chem. Front., 2019, 6, 3012—3040 |
| [14] | Ni J., Shi Z., Wang Y., Yang J., Wu H., Wang P., Xiao M., Liu C., Xing W., eScience, 2025, 5, 100295 |
| [15] | Gao X., Chen Y., Wang Y., Zhao L., Zhao X., Du J., Wu H., Chen A., Nano-Micro Lett., 2024, 16, 237 |
| [16] | Ghouri Z. K., Badreldin A., Ehaled K., Kumar D., Youssef K., Abdel-Wahab A., J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2021, 96, 243—253 |
| [17] | Chen J., Chen J., Yu D., Zhang M., Zhu H., Du M., Electrochim. Acta, 2017, 246, 17—26 |
| [18] | Li T., Li S., Liu Q., Yin J., Sun D., Zhang M., Xu L., Tang Y., Zhang Y., Adv. Sci., 2020, 7, 1902371 |
| [19] | Liu X., Zhang M., Yang T., Wan L., Zhu H., Wang S., Du M., Mater. Des., 2016, 109, 162—170 |
| [20] | Gebremariam T. T., Chen F., Jin Y., Wang Q., Wang J., Wang J., Catal. Sci. Technol., 2019, 9, 2532—2542 |
| [21] | Wang L., Wang C., Mu Y., Fan J., Yang X., Yu C., Guo B., Zeng G., Fuel, 2025, 391, 134800 |
| [22] | Kwon T., Yu A., Kim S. J.,Kim M. H., Lee C., Lee Y., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2021, 563, 150293 |
| [23] | Li W., Li M., Wang C., Lu X., Sci. China Mater., 2023, 66(3), 1024—1032 |
| [24] | Zhang B., Shan J., Yu J., Wang W., Li W., Li N., Li Y., Int. J. Hydrog. Energy, 2021, 46, 8871—8884 |
| [25] | Hua B., Li M., Zhang Y., Sun Y., Luo J., Adv. Energy Mater., 2017, 7, 1700666 |
| [26] | Yu X., Qi R., Zhang L., Deng L., Zhong M., Chen Z., Lu X., Acta Mater., 2025, 294, 121165 |
| [27] | Ding M., Wei Z., Zhao W., Lu Q., Lu C., Zhou M., Liu D., Yang H., Green Chem., 2024, 26, 7789—7798 |
| [28] | Cao M., Li B., Cao Y., Li Y., Tian R., Shen Q., Xie W., Gu W., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2025, 17, 15259—15273 |
| [29] | Huang T., Xu G., Ding H., Liu X., Zhang L., Sep. Purif. Technol., 2025, 354, 129094. |
| [30] | Huang T., Xu G., Ding H., Zhang L., Wei B., Liu X., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2022, 625, 956—964 |
| [31] | Chang X., Yan J., Ding X., Jia Y., Li S., Zhang M., Nanomaterials, 2022, 12, 3886 |
| [32] | Xie X., Liu J., Gu C., Li J., Zhao Y., Liu C., J. Energy Chem., 2022, 64, 503—510 |
| [33] | Chen J., Huang F., Ke S., Shen J., Li Y., Zheng F., Li S., Dalton Trans., 2022, 51, 5168—5174 |
| [34] | Liu X., Xu G., Ding H., Zhang L., Huang T., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48, 35064—35074 |
| [35] | Meng D., Ran S., Gao L., Zhang Y., San X., Zhang L., Li R., Jin Q., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2024, 40, 490—498 |
| [36] | Wang F., Xu L., Wang P., Zhang Y., Electrochim. Acta, 2019, 306, 437—445 |
| [37] | Li W., Zhong M., Chen X., Ren S., Yan S., Wang C., Lu X., Sci. China Mater., 2023, 66, 2235—2245 |
| [38] | Shah M., Jang G., Zhang K., Park J., EcoEnergy, 2023, 1, 344—374 |
| [39] | Xu S., Sun X., Cui W., Bai J., Li C., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 49, 309—321 |
| [40] | Zhang J., Sun X., Peng W., Lu G., Sun S., Xu Y., Fang C., Li Q., Han J., ChemCatChem, 2020, 12, 3737—3745 |
| [41] | Li M., Zhu Y., Wang H., Wang C., Pinna N., Lu X., Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9, 1803185 |
| [42] | Zhang S., Le F., Jia W., Yang X., Hu P., Wu X., Shu W., Xie Y., Xiao W., Jia D., Small Methods, 2025, 9, 2401103 |
| [43] | Zhang W., Yang L., Li Z., Nie G., Cao X., Fang Z., Wang X., Ramakrishna S., Long Y., Jiao L., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2024, 63, e202400888 |
| [44] | Zhang X., Liang Z., Zhang X., Guo Q., Xie Y., Wang L., Fu H., Chin. Chem. Lett., 2025, 36, 109935 |
| [45] | Kumar M. R., Thiruvengadam D., Kumar K. S., Rajan K., Jayabharathi J., Padmavathy M., Energy Fuels, 2025, 39, 6605—6619 |
| [46] | Xia M., Shi B., Li W., Yu X., Qi R., Mu M., Wang C., Lu X., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2026, 702, 138880 |
| [47] | Zhong M., Yan S., Xu J., Wang C., Lu X., Inorg. Chem. Front., 2022, 9, 4881—4891 |
| [48] | Nagappan S., Minhas H., Urkude R. R., Pathak B., Kundu S., Small, 2025, 21, 2500081 |
| [49] | Nagappan S., Jayan R., Rajagopal N., Krishnan A., Islam M. M., Kundu S., Small, 2024, 20, 2403908 |
| [50] | Gong T., Zhang J., Liu Y., Hou L., Deng J., Yuan C., Chem. Eng. J., 2023, 451, 139025 |
| [51] | Cui W., Sun X., Xu S., Li C., Bai J., Sustain. Energy Fuels, 2024, 8, 4962 |
| [52] | Zhang Y., Shi W., Bo L., Shen Y., Ji X., Xia L., Guan X., Wang Y., Tong J., Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 431, 134188 |
| [53] | Thiruvengadam D., Nithiasri R., Sangamithirai M., Kumar K. S., Jayabharathi J., ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2025, 8, 1266—1281 |
| [54] | Li T., Yin J., Sun D., Zhang M., Pang H., Xu L., Zhang Y., Yang J., Tang Y., Xue J., Small, 2022, 18, 2106592 |
| [55] | Li W., Guo W., Zhang L., Zhong M., Ren S., Yu G., Wang C., Chen W., Lu X., Chem. Sci., 2024, 15, 11890—11901 |
| [56] | Zhao X., Liu M., Shang Z., Lu Q., Han X., Ji X., Zhang H., Energy Fuels, 2024, 38, 17939—17947 |
| [57] | Zhu H., Zhang J., Yanzhang R., Du M., Wang Q., Gao G., Wu J., Wu G., Zhang M., Liu B., Yao J., Zhang X., Adv. Mater., 2015, 27, 4752—4759 |
| [58] | Wang T., Shi Y., Fei J., Zhu J., Song L., Li C., Zhan T., Lai J., Wang L., App. Catal. B: Environ., 2024, 358, 124367 |
| [59] | Chae S. H., Muthurasu A., Kim T., Kim J. S.,Khil M. S., Lee M., Kim H., Lee J. Y.,Kim H. Y., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2021, 293, 120209 |
| [60] | Yu X., Zhang L., Qi R., Xia M., Wang Y., Zhong M., Song W., Lu X., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2025, 699, 138225 |
| [61] | Li W., Liu R., Yu G., Chen X., Yan S., Ren S., Chen J., Chen W., Wang C., Lu X., Small, 2024, 20, 2307164 |
| [62] | Zhang L., Li W., Ren S., Song W., Wang C., Lu X., Adv. Energy Mater., 2025, 15, 2403136 |
| [63] | Surendran S., Jesudass S. C., Janani G., Kim J. Y., Lim Y., Park J., Han M. K.,Cho I. S., Sim U., Adv. Mater. Technol., 2023, 8, 2200572 |
| [64] | Wang X., Chen X., Huang M., Liu Z., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 63, 556—565 |
| [65] | Li W., Wang C., Lu X., Nano Lett., 2024, 24, 11779—11792 |
| [66] | Li Y., Zhou B., Ding W., Luo Q., Wang L., Kim I., Zhang T., Ji D., Qin X., Appl. Catal. B: Environ. Energy, 2025, 380, 125776 |
| [67] | Li W., Zhang L., Ma L., Wang J., Qi R., Pang Y., Xu C., Wang C., Gao M., Lu X., Nano Lett., 2025, 25, 443—452 |
| [68] | Yu J., Li J., Xu C., Li Q., Liu Q., Liu J., Chen R., Zhu J., Wang J., Nano Energy, 2022, 98, 107266 |
| [69] | Li J., Zhu J., Jia Z., Li R., Yu J., Chem. Asian J., 2023, 18, e202300393 |
| [70] | Wang Y., Jiang Q., Ren S., Xu J., Wang Y., Zhong M., Lu X., Adv. Mater., 2025, 37, 2504922 |
| [71] | Xu M., Xu J., Zhang L., Yu X., Ren S., Zhang S., Gao M., Zhong M., Lu X., Adv. Energy Mater., 2025, 15, e01970 |
| [72] | Zhong M., Xu M., Ren S., Li W., Wang C., Gao M., Lu X., Energy Environ. Sci., 2024, 17, 1984—1996 |
| [1] | 王圣程, 王存民, 郝雅馨, 朱桂英, 李欣雨, 宋欣译, 张明明, 徐欢, 何新建. PLA/ZIF-8-NS纳米纤维膜的制备及高效滤除超细颗粒物性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2025, 46(2): 20240426. |
| [2] | 陈鑫, 刘婧媛, 于静. 多孔碳纳米纤维负载铜铂合金催化剂的制备及电催化析氢性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(6): 20240042. |
| [3] | 曹铁平, 李跃军, 孙大伟. 双S型YVO4/TiO2/BiVO4 异质结的构筑及光催化CO2还原性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(12): 20240298. |
| [4] | 李轩, 亓帅, 周伟良, 李小杰, 景玲胭, 冯超, 蒋兴星, 杨恒攀, 胡琪, 何传新. 纤维基氧化还原电催化剂的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(5): 20220770. |
| [5] | 胡诗颖, 沈佳艳, 韩峻山, 郝婷婷, 李星. CoO纳米颗粒/石墨烯纳米纤维复合材料的制备及电化学性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(2): 20220462. |
| [6] | 李小川, 唐梦珂, 朱金佗, 何新建, 徐欢. 界面立构复合化电活性聚乳酸纳纤膜的制备及高效过滤性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(12): 20230311. |
| [7] | 马文龙, 郭状, 张威, 陈明星. PP/PMIA@PVDF-HFP纳米纤维复合滤材的制备及性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(12): 20230344. |
| [8] | 高冲, 周全, 杨帆, 任瑞鹏, 吕永康. 乳液电纺制备微囊型聚己内酯纳米纤维及其封装蛋白性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(10): 20230199. |
| [9] | 李怀科, 岳贵初, 谢海韵, 刘静, 高松伟, 侯兰兰, 李帅, 苗贝贝, 王女, 白杰, 崔志民, 赵勇. 静电纺丝中空纳米纤维在催化领域的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(1): 20220625. |
| [10] | 吴玉, 李轩, 杨恒攀, 何传新. 钴单原子的双重限域制备策略及高效CO2电还原性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220343. |
| [11] | 张宏伟, 陈雯, 赵美淇, 马超, 韩云虎. 单原子催化剂在电化学中的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(5): 20220129. |
| [12] | 谢璠, 陈珊珊, 卓龙海, 陆赵情, 高坤, 代啓阳. 聚对二甲苯纳米纤维阵列的CVD液晶模板法制备及降解性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2643. |
| [13] | 李敏, 赵纯, 冯钦忠, 冯建, 孟晓静. 硫脲基纳米螯合纤维对水溶液中Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附和密度泛函理论计算[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(12): 3680. |
| [14] | 赵子一,郑洪芝,徐雁. 晶态纳米纤维素的多色圆偏振荧光性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(5): 1120. |
| [15] | 秦春萍, 王先流, 唐寒, 易兵成, 刘畅, 张彦中. 含骨脱细胞基质电纺纤维的成骨性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(4): 780. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
