

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (6): 1252.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20200026
收稿日期:2020-01-13
出版日期:2020-06-10
发布日期:2020-02-26
通讯作者:
马楠
E-mail:nan.ma@suda.edu.cn
基金资助:
BAI Cuiting,YUE Renye,LUO Liegao,MA Nan*( )
)
Received:2020-01-13
Online:2020-06-10
Published:2020-02-26
Contact:
Nan MA
E-mail:nan.ma@suda.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
癌细胞中microRNA(miRNA)的灵敏成像对于疾病的诊断治疗具有重要意义, 其中miRNA-21通常在多种癌细胞中异常表达. 本文将DNA功能化的金纳米颗粒与发射波长分离的荧光染料FAM和Cy5.5修饰的DNA通过含有光控基团PC-linker的DNA4作为桥梁进行自组装, 构建了纳米传感器GDC. 将302 nm紫外光作为启动开关, 用其照射该体系时, Cy5.5修饰的DNA3被释放, 其荧光强度可作为内参比信号, 用于标定进入细胞的组装体含量; 细胞中miRNA-21作为催化分子, 与外加燃料Fuel DNA共同作用下可实现催化放大, FAM修饰的DNA2被释放且被猝灭的荧光信号得以恢复, 并作为检测信号. 通过2种荧光信号强度(FL)的检测及FLFAM/FLCy5.5比值的计算, 达到定量分析细胞中miRNA含量的目的. 该体系可扣除因细胞内组装体含量不同造成的背景信号误差, 不仅能显著提高检测准确度, 还因存在催化循环而大大降低了检出限, 比传统方法至少降低了3个数量级. 该传感器的检出限为23.1 pmol/L, 通过定量计算得出HeLa细胞中miRNA的含量为0.0236 nmol/L.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
白翠婷, 岳仁叶, 罗列高, 马楠. 基于双色荧光传感器的癌细胞成像及microRNA定量检测. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(6): 1252.
BAI Cuiting, YUE Renye, LUO Liegao, MA Nan. Quantitative Analysis of MicroRNA Content by Fluorescence Imaging in Cancer Cells Using Dual-color Fluorescence Nanosensor †. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1252.
| Name | DNA Sequence(5'→3') |
|---|---|
| DNA1(thiolated DNA) | SH-AAAAAAAAAATCTCACTAACTTACGG |
| DNA2(FAM) | FAM-CCCTATAGCTTATCAGACT |
| DNA3(Cy5.5) | Cy5.5-GATGTTGACTCGAGAC |
| DNA4(PC Linker DNA) | GTCTCGAG//TCAACATCAGTCTGATAAGCTATAGGGCCGTAAGTTAGTGAGA |
| Fuel DNA(F) | CTAACTTACGGCCCTATAGCTTATCAGACT |
| Catalyst DNA(C') | TAGCTTATCAGACTGATGTTGA |
| MiRNA-21(C) | UAGCUUAUCAGACUGAUGUUGA |
| FAM-DNA1 | SH-AAAAAAAAAATCTCACTAACTTACGG-FAM |
| FAM-DNA4 | GTCTCGAGTCAACATCAGTCTGATAAGCTATAGGGCCGTAAGTTAGTGAGA-FAM |
| 1-Mismatch[C'(mis-1)] | TAGCTTATCAGACTGATCTTGA |
| 2-Mismatches[C'(mis-2)] | TAGCTTATCAGTCTGATCTTGA |
| 3-Mismatches[C'(mis-3)] | TAGCTAATCAGTCTGATCTTGA |
Table 1 DNA sequences*
| Name | DNA Sequence(5'→3') |
|---|---|
| DNA1(thiolated DNA) | SH-AAAAAAAAAATCTCACTAACTTACGG |
| DNA2(FAM) | FAM-CCCTATAGCTTATCAGACT |
| DNA3(Cy5.5) | Cy5.5-GATGTTGACTCGAGAC |
| DNA4(PC Linker DNA) | GTCTCGAG//TCAACATCAGTCTGATAAGCTATAGGGCCGTAAGTTAGTGAGA |
| Fuel DNA(F) | CTAACTTACGGCCCTATAGCTTATCAGACT |
| Catalyst DNA(C') | TAGCTTATCAGACTGATGTTGA |
| MiRNA-21(C) | UAGCUUAUCAGACUGAUGUUGA |
| FAM-DNA1 | SH-AAAAAAAAAATCTCACTAACTTACGG-FAM |
| FAM-DNA4 | GTCTCGAGTCAACATCAGTCTGATAAGCTATAGGGCCGTAAGTTAGTGAGA-FAM |
| 1-Mismatch[C'(mis-1)] | TAGCTTATCAGACTGATCTTGA |
| 2-Mismatches[C'(mis-2)] | TAGCTTATCAGTCTGATCTTGA |
| 3-Mismatches[C'(mis-3)] | TAGCTAATCAGTCTGATCTTGA |
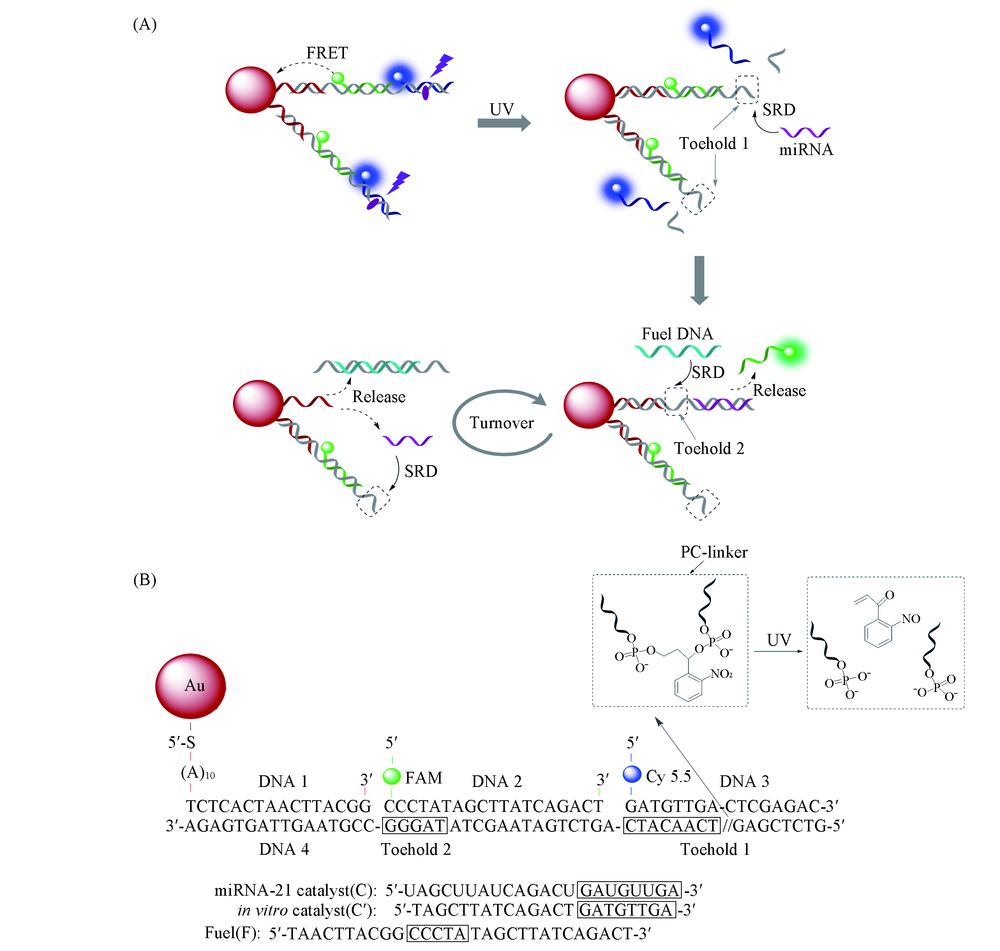
Scheme 1 Schematic illustration of dual-color GDC sensor for quantitative analysis of microRNA (A) Photo-activated and miRNA-catalyzed disassemble of DNA2, DNA3 with GNP through two-step DNA strand displacement reactions(SDR); (B) DNA sequences for GDC and chemical structure of the photocleavage group(PC-linker).
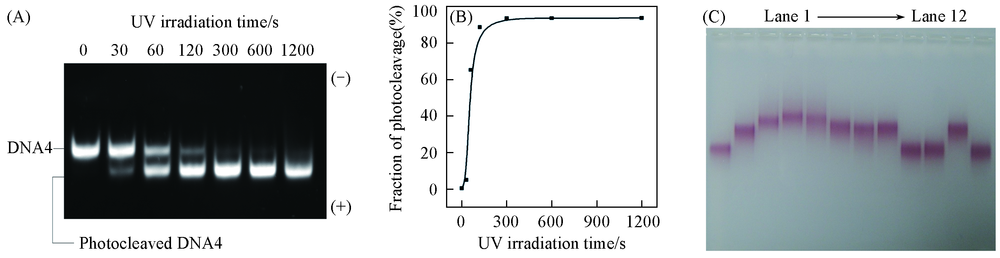
Fig.2 Characterization of photocleavage DNA4 with UV irradiation(302 nm, 6 W) (A) Native PAGE of DNA4 with different UV irradiation time; (B) fraction of photocleaved products with different UV irradiation time; (C) agarose Gel Electrophoresis characterization of GNP assembly with DNA1, DNA4, DNA2 and DNA3, and the catalytic disassembly of GDC in the present or absence of UV irradiation, catalyst DNA(C') and Fuel DNA. Line 1: GNP-DNA1; line 2: GNP-DNA1+DNA4; lane 3: GNP-DNA1+DNA4+DNA2; lane 4: GNP-DNA1+DNA4+DNA2+DNA3(GDC); lane 5: GDC+1×F+1×C'; lane 6: GDC+hv; lane 7: GDC+ hv+1×F; lane 8: GDC+ hv+1×C'; lane 9: GDC+ hv+1×F+1×C'; lane 10: GDC+hv+1×F+0.1×C'; lane 11: GDC+ hv+0.1×C'; lane 12: GNP-DNA1+DNA4+DNA2+1×F+0.1×C'.
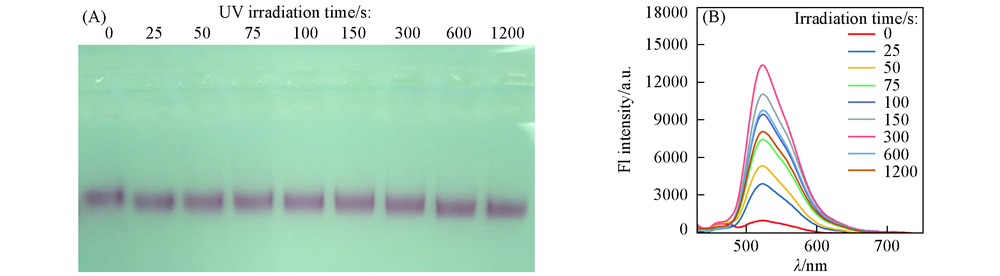
Fig.3 Agarose Gel electrophoresis characterization of disassembled products(A) and photoluminescence spectra of disassembled FAM-DNA2(B) with different UV irradiation time
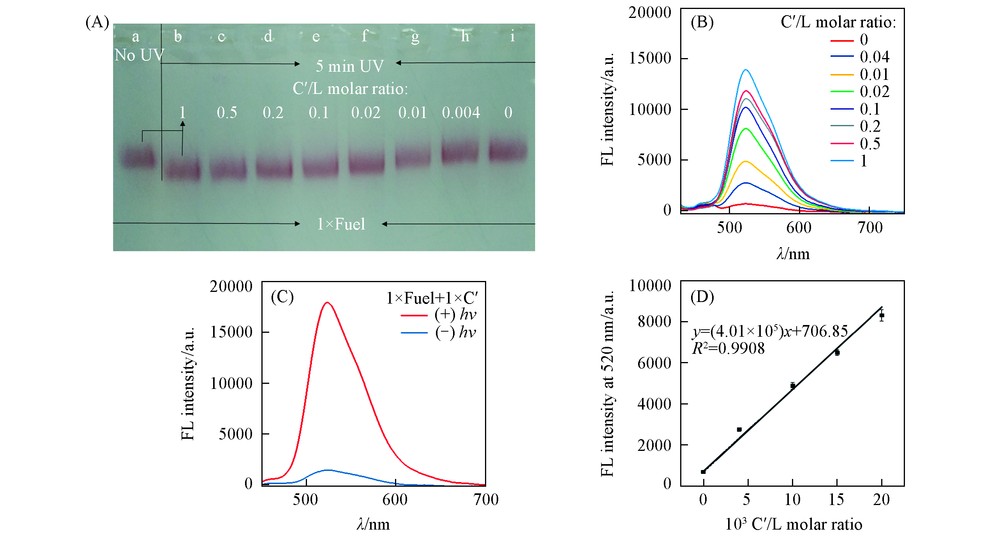
Fig.4 Agarose gel electrophoresis characterization of disassembled products with different C'/DNA4 molar ratios(A) and photoluminescence spectra of released FAM-DNA2 with different C'/DNA4 molar ratios(B), photoluminescence spectra of GNP-DNA sensor for C' detection with or without UV irradiation(C) and calibration curve for quantitative analysis of miRNA(D) (A) a. GDC+1×F+1×C'(NO UV); b. GDC+1×F+1×C'(UV 5 min); c. GDC+1×F+0.5×C'(UV 5 min); d. GDC+1×F+0.2×C'(UV 5 min); e. GDC+1×F+0.1×C'(UV 5 min); f. GDC+1×F+0.02×C'(UV 5 min); g. GDC+1×F+0.01×C'(UV 5 min); h. GDC+1×F+0.004×C'(UV 5 min); i. GDC+1×F+0×C'(UV 5 min).
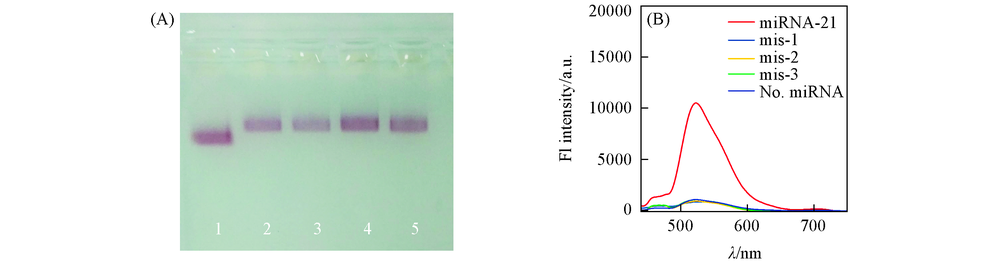
Fig.5 Specificity evaluation of GDC sensor (A) Agarose gel electrophoresis of catalytic DNA C' and three mutation sequences[C'(mis-1), C'(mis-2) and C'(mis-3)] containing one, two, three mismatches respectively. The sample without catalyst DNA is used as the control. All samples are irradiated with UV light in the presence of Fuel DNA; (B) corresponding photoluminescence spectra of the above-mentioned samples.
| 103 C'/L molar ratio | FL intensity/a.u. | 103 C'/L molar ratio | FL intensity/a.u. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAM | Cy5.5 | FAM | Cy5.5 | ||
| 0 | 1298 | 20635 | 15 | 26138 | 23284 |
| 4 | 7351 | 24341 | 20 | 33258 | 22946 |
| 10 | 16737 | 23975 | |||
Table 2 FL intensity of FAM and Cy 5.5
| 103 C'/L molar ratio | FL intensity/a.u. | 103 C'/L molar ratio | FL intensity/a.u. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAM | Cy5.5 | FAM | Cy5.5 | ||
| 0 | 1298 | 20635 | 15 | 26138 | 23284 |
| 4 | 7351 | 24341 | 20 | 33258 | 22946 |
| 10 | 16737 | 23975 | |||
| [1] |
Lim L. P., Lau N. C., Garrettengele P., Grimson A., Schelter J. M., Castle J., Bartel D. P., Linsley P. S., Johnson J. M., Nature, 2005, 433, 769—773
doi: 10.1038/nature03315 URL |
| [2] |
He L., Hannon G. J., Nat. Rev. Genet., 2004, 5, 522—531
doi: 10.1038/nrg1379 URL |
| [3] |
Ambros V., Nature, 2004, 431, 350—355
doi: 10.1038/nature02871 URL |
| [4] |
Liu H. Y., Bei X. Q., Xia Q. T., Fu Y., Zhang S., Liu M. C., Fan K., Zhang M. Z., Yang Y., Microchimica Acta, 2015, 183(1), 297—304
doi: 10.1007/s00604-015-1636-z URL |
| [5] |
Rajesha R., Frank. J. S., Nat. Rev. Drug Discov., 2017, 16(3), 203—222
doi: 10.1038/nrd.2016.246 URL |
| [6] |
Chen Y. X., Huang K. J., Niu K. X., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2018, 99, 612—624
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2017.08.036 URL |
| [7] |
Cullen B. R., Nature, 2009, 457(7228), 421—425
doi: 10.1038/nature07757 URL |
| [8] |
Matsumura T., Sugimachi K., Iinuma H., Takahashi Y., Kurashige J., Sawada G., Ueda M., Uchi R., Ueo H., Takano Y., Shinden Y., Eguchi H., Yamamoto H., Doki Y., Mori M., Ochiya T., Mimori K., Br. J. Cancer, 2015, 113(2), 275—281
doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.201 URL |
| [9] |
Nelson P. T., Baldwin D. A., Scearce L. M., Oberholtzer J. C., Tobias J. W., Mourelatos Z., Nat. Methods, 2004, 1, 155—161
doi: 10.1038/nmeth717 URL |
| [10] |
Markou A., Tsaroucha E. G., Kaklamanis L., Fotinou M., Georgoulias V., Lianidou E. S., Clin. Chem., 2008, 54, 1696—1704
doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2007.101741 URL |
| [11] |
Varkonyi-Gasic E., Wu R., Wood M., Walton E. F., Hellens R. P., Plant Methods, 2007, 3, 12
doi: 10.1186/1746-4811-3-12 URL |
| [12] |
Cheng Y., Lei J. P., Chen Y. L., Ju H. X., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2014, 51, 431—436
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2013.08.014 URL |
| [13] |
Zhang P., Wu X. Y., Yuan R., Chai Y. Q., Anal. Chem., 2015, 87, 3202—3207
doi: 10.1021/ac504455z URL |
| [14] |
Zhang D. C., Yan Y. R., Cheng W., Zhang W., Li Y. H., Ju H. X., Ding S. J., Microchim. Acta., 2013, 180, 397—403
doi: 10.1007/s00604-013-0945-3 URL |
| [15] |
Gao X. F., Xu H., Baloda M., Gurung A. S., Xu L. P., Wang T., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2014, 54, 578—584
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2013.10.055 URL |
| [16] |
Liu L. Z., Jiang S. T., Wang L., Zhang Z., Xie G. M., Microchim. Acta, 2015, 182, 77—84
doi: 10.1007/s00604-014-1273-y URL |
| [17] |
Sztandera K., Gorzkiewicz M., Klajnert-Maculewicz B., Mol. Pharm., 2019, 16(1), 1—23
doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00810 URL |
| [18] |
Reinhard B. M., Siu M., Agarwal H., Alivisatos A. P., Liphardt J., Nano Lett., 2005, 5(22), 2246—2252
doi: 10.1021/nl051592s URL |
| [19] |
Yun C. S., Javier A., Jennings T., Fisher M., Hira S., Peterson S., Hopkins B., Reich N. O., Strouse G. F., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127(23), 3115—3119
doi: 10.1021/ja043940i URL |
| [20] |
Gaylord B. S., Heeger A. J., Bazan G. C., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2002, 99, 10954—10957
doi: 10.1073/pnas.162375999 URL |
| [21] |
Niikura K., Matsunaga T., Suzuki T., Kobayashi S., Yamaguchi H., Orba Y., Kawaguchi A., Hasegawa H., Kajino K., Ninomiya T., Ijiro K., Sawa H., ACS Nano, 2013, 7(5), 3926—3938
doi: 10.1021/nn3057005 URL |
| [22] |
Jain P. K., Lee K. S., El-Sayed I. H., El-Sayed M. A., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110(14), 7238—7248
doi: 10.1021/jp057170o URL |
| [23] |
Huang K. J., Liu Y. J., Wang H. B., Wang Y. Y., Liu Y. M., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2014, 55, 195—202
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2013.11.061 URL |
| [24] |
Huang K. J., Liu Y. J., Shi G. W., Yang X. R., Liu Y. M., Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 2014, 201, 579—585
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2014.05.055 URL |
| [25] |
Komarala E. P., Tyagi H., Thiyagatajan S., Pradhan L., Aslam M., Bahadur D., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2017, 5(21), 3852—3861
doi: 10.1039/C7TB00015D URL |
| [26] |
Zhang J., Li C., Zhang X., Huo S., Jin S., An F. F., Wang X., Xue X., Okeke C. I., Duan G., Guo F., Zhang X., Hao J., Wang P. C., Zhang J., Liang X. J., Biomaterials, 2015, 42, 103—111
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.11.053 URL |
| [27] | Jin X. T., Liu G., Li J. Z., Sun L. L., Wang J. R., Li J. F., Li P., Chen W. Q., Wang Q., Tong T., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(2), 224—231 |
| 金新天, 刘刚, 李君哲, 孙丽丽, 王俊荣, 李俊锋, 李沛, 陈文庆, 王强, 佟倜 . 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(2), 224—231) | |
| [28] |
Wang J., Wang D. X., Tang A. N., Kong D. M., Anal. Chem., 2019, 91, 5244—5251
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b00007 URL |
| [29] |
Jiang L., Zhou Q., Mu K., Xie H., Zhu Y., Zhu W., Zhao Y., Xu H., Yang X., Biomaterials, 2013, 34(30), 7418—7428
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.05.078 URL |
| [30] |
Dong H. F., Zhang J., Ju H. X., Lu H. T., Wang S. Y., Jin S., Hao K. H., Du H. W., Zhang X. J., Anal. Chem., 2012, 84, 4587—4593
doi: 10.1021/ac300721u URL |
| [31] |
Dong H. F., Hao K. H., Tian Y. P., Jin S., Lu H. T., Zhou S. F., Zhang X. J., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2014, 53, 377—383
doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2013.09.061 URL |
| [32] | Wang Z. Y., Liu M., Zhang C. Y. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities 2017, 38(1), 1—11 |
| ( 王子月, 刘萌, 张春阳 . 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(1) 1—11) | |
| [33] |
Yang J. M., Dou B. T., Yuan R., Xiang Y., Anal. Chem., 2017, 89, 5138—5143
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b00827 URL |
| [34] |
Liu J. T., Du P., Zhang J., Shen H., Lei J. P., Chem. Commun., 2018, 54(20), 2550—2553
doi: 10.1039/C7CC09579A URL |
| [35] |
Zhang D. Y., Turberfield A. J., Yurke B., Winfree E., Science, 2007, 318(5853), 1121—1125
doi: 10.1126/science.1148532 URL |
| [36] |
He X. W., Zeng T., Li Z., Wang G. L., Ma N., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55, 3073—3076
doi: 10.1002/anie.201509726 URL |
| [37] | Luo X. C., Li Z., Wang G. L., He X. W., Shen X. Q., Sun Q. H., Wang L., Yue R. Y., Ma N., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 10, 1021 |
| [38] |
Shen Y., Li Z., Wang G. L., Ma N., ACS Sens., 2018, 3, 494—503
doi: 10.1021/acssensors.7b00922 URL |
| [39] |
Jin R., Wu G., Li Z., Mirkin C. A., Schatz G. C., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 1643—1654
doi: 10.1021/ja021096v URL |
| [1] | 刘苗, 刘瑞波, 刘巴蒂, 钱鹰. 溶酶体靶向吲哚氟硼二吡咯光敏剂的合成、 双光子荧光成像及光动力治疗[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220326. |
| [2] | 陈宏达, 张婳, 王振新. 用于小动物活体的荧光-光热双模成像系统[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(3): 725. |
| [3] | 王萌萌, 栾天骄, 杨铭焱, 吕佳佳, 高杰, 李洪玉, 卫钢, 袁泽利. 肿瘤乏氧靶向响应的罗丹明荧光探针及其成像介导手术治疗[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(10): 3071. |
| [4] | 梁钰昕, 赵容, 梁馨月, 方晓红. 细胞膜上信号转导蛋白的单分子成像与分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(6): 1127. |
| [5] | 邵伟, LEE Jiyoung, 李方园, 凌代舜. 有机小分子纳米粒子的光学诊疗应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(11): 2356. |
| [6] | 张怡萌, 张慧欣, 刘洋. 外泌体生物分析及其临床应用研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(11): 2306. |
| [7] | 张勇,申城,幸志荣,陈归柒,卢资,侯志兵,陈雪梅. 可视化检测次氯酸的苯并咪唑类荧光增强型探针[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(12): 2480. |
| [8] | 刘晔, 姚顺雨, 方超, 赵外欧, 王静媛, 李亚鹏. 靶向髓过氧化酶的双模态探针分子的合成与表征[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(7): 1573. |
| [9] | 张婵婵, 张方辉, 丁磊, 倪振杰, 江浪, 董焕丽, 张小涛, 李荣金, 胡文平. 基于表面等离子共振效应的有机光敏晶体管[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(1): 102. |
| [10] | 王子月, 刘萌, 张春阳. MicroRNA的超灵敏检测研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(1): 1. |
| [11] | 张涛, 汤永嘉, 徐亮, 刘克良. 新型可用于荧光标记的α-氰基丙烯酸酯单体的合成及在小鼠活体成像中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(6): 1168. |
| [12] | 米小龙, 焦晓洁, 刘畅, 何松, 曾宪顺. 基于罗丹明荧光信号报告基团的细胞通透性铜离子荧光探针[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(10): 1784. |
| [13] | 向军, 张雄辉, 叶芹, 李佳乐, 沈湘黔. Fe-Ni/C复合纳米纤维的原位制备与微波吸收性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(7): 1379. |
| [14] | 姜娜, 樊江莉, 张帅, 彭孝军. 活细胞线粒体中S |
| [15] | 李广, 陈龙聪, 陈萌梦, 高斌, 熊兴良. 基于金纳米颗粒生长的液晶生物传感器检测酪氨酸[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(11): 2493. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||