

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 20230410.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20230410
王佳瑞1, 李春丽1,2( ), 程佳豪1, 郝亚玲1, 周楠1, 杨鹏1
), 程佳豪1, 郝亚玲1, 周楠1, 杨鹏1
收稿日期:2023-09-15
出版日期:2024-01-10
发布日期:2023-10-26
通讯作者:
李春丽
E-mail:lichunli16@163.com
基金资助:
WANG Jiarui1, LI Chunli1,2( ), CHENG Jiahao1, HAO Yaling1, ZHOU Nan1, YANG Peng1
), CHENG Jiahao1, HAO Yaling1, ZHOU Nan1, YANG Peng1
Received:2023-09-15
Online:2024-01-10
Published:2023-10-26
Contact:
LI Chunli
E-mail:lichunli16@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
针对氧化石墨烯(GO)制备过程中插层阶段的调控及机理研究对GO功能化应用于电极材料具有重要的研究意义. 本文在改进Hummers法的基础上, 向H2SO4插层剂中加入不同体积的H3PO4, 制备了不同氧化程度的GO. 利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、 X射线光电子能谱(XPS)和傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)等表征手段, 分析了不同氧化程度的GO的微观形貌、 元素组成、 氧化程度, 以探究H3PO4在插层石墨过程中的作用机理; 并采用循环伏安法(CV)和交流阻抗法(EIS)对不同H2SO4/H3PO4体积比下的GO进行电化学性能测试, 分析了H3PO4对GO电化学性能的影响, 以达到调控石墨的插层氧化从而提升GO导电性的目的. 结果表明, 单一的H2SO4使GO基面上的邻位二醇过度氧化造成孔洞, H3PO4的加入会扩大石墨层间距, 使氧化剂更易进入石墨层间, 并与1,2-二醇反应生成环状结构以起到保护基面的作用, 从而提高GO的导电性. H3PO4作为辅助酸会协助H2SO4制备基面更加完整且氧化程度更高的GO, 但其酸性较弱, 不可完全代替H2SO4在氧化过程中的作用.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
王佳瑞, 李春丽, 程佳豪, 郝亚玲, 周楠, 杨鹏. 磷酸在GO插层阶段的功能化调控及机理. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(1): 20230410.
WANG Jiarui, LI Chunli, CHENG Jiahao, HAO Yaling, ZHOU Nan, YANG Peng. Functional Regulation and Mechanism of Phosphoric Acid in GO Intercalation Stage. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(1): 20230410.
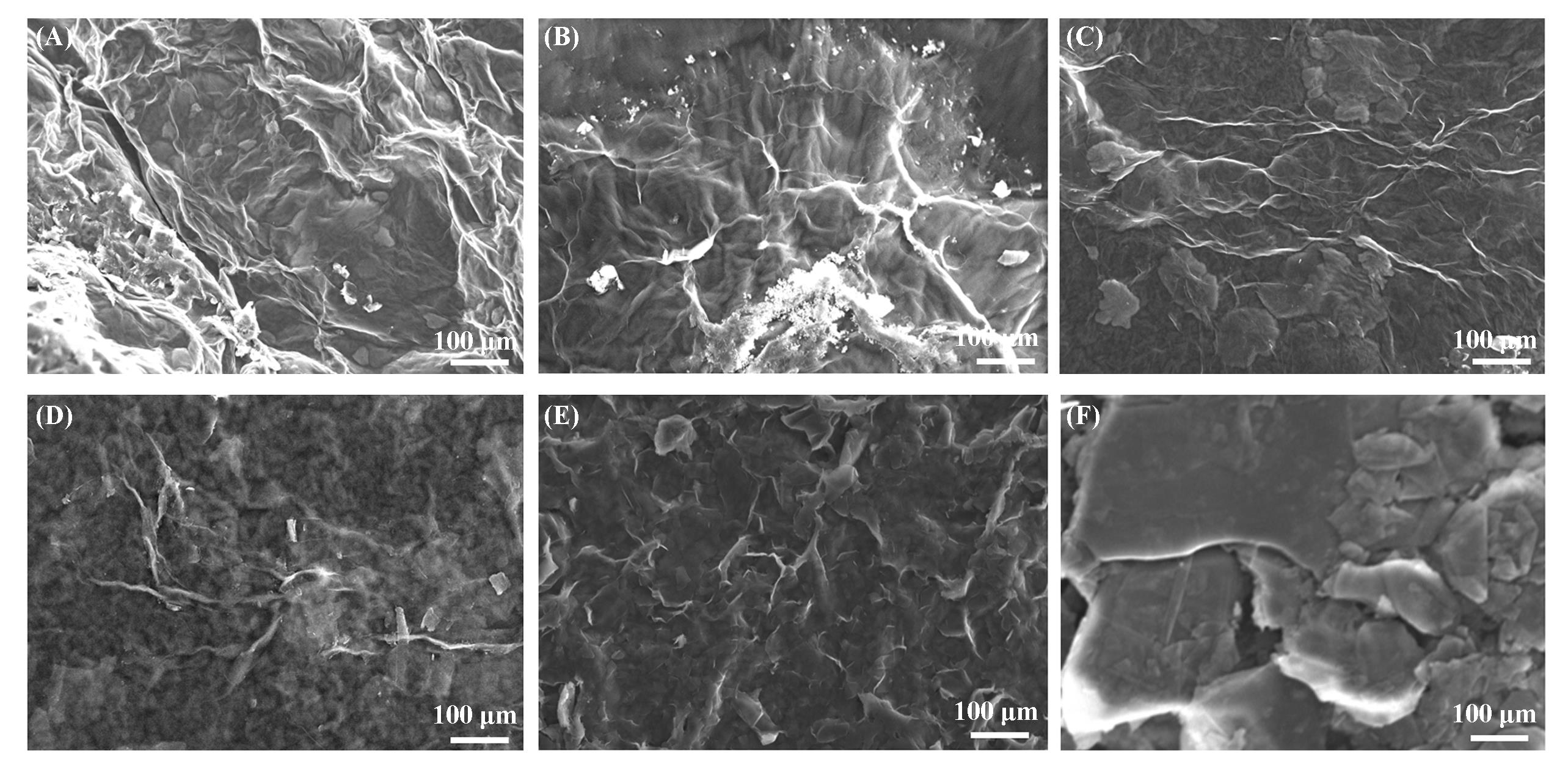
Fig.1 SEM images of GO prepared by H2SO4/H3PO4 with different volume ratios(A—E) and graphite(F)V(H2SO4)∶V(H3PO4): (A) 10∶0; (B) 9∶1; (C) 8∶2; (D) 5∶5; (E) 2∶8.
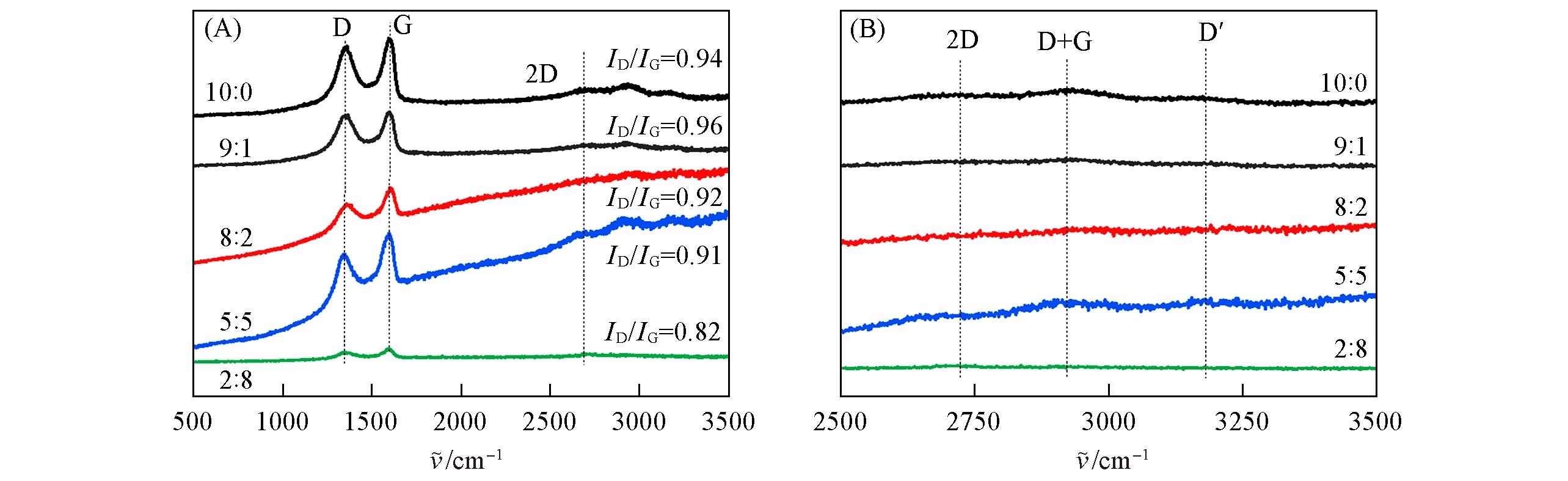
Fig.3 Raman spectra of samples prepared by H2SO4/H3PO4 with different volume ratios(A), zoomed⁃in image of Raman spectra in the range of 2500—3500 cm-1 representing the intensity of 2D, D+G, and D′ bands(B)
| V(H2SO4)∶V(H3PO4) | 10∶0 | 9∶1 | 8∶2 | 5∶5 | 2∶8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La./nm | 20.851 | 20.025 | 20.496 | 21.125 | 23.443 |
Table 1 La. parameters of GO prepared under different volume ratios of H2SO4/H3PO4
| V(H2SO4)∶V(H3PO4) | 10∶0 | 9∶1 | 8∶2 | 5∶5 | 2∶8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La./nm | 20.851 | 20.025 | 20.496 | 21.125 | 23.443 |
| V(H2SO4)∶V(H3PO4) | 10∶0 | 9∶1 | 8∶2 | 5∶5 | 2∶8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d/nm | 0.704 | 0.750 | 0.785 | 0.829 | 0.346 |
Table 2 Interlayer spacing(d) of samples prepared by H2SO4/H3PO4 with different volume ratios
| V(H2SO4)∶V(H3PO4) | 10∶0 | 9∶1 | 8∶2 | 5∶5 | 2∶8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d/nm | 0.704 | 0.750 | 0.785 | 0.829 | 0.346 |
| V(H2SO4)∶V(H3PO4) | C/O | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | P | ||
| 10∶0 | 63.38 | 28.2 | — | 2.24 |
| 9∶1 | 66.18 | 32.01 | — | 2.07 |
| 8∶2 | 66.63 | 31.68 | 0.55 | 2.10 |
| 5∶5 | 60.15 | 26.66 | 0.88 | 2.26 |
| 2∶8 | 83.79 | 13.78 | 1.38 | 6.08 |
Table 3 Fitting results of the elemental composition of samples prepared by H2SO4 /H3PO4 with different volume ratios
| V(H2SO4)∶V(H3PO4) | C/O | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | P | ||
| 10∶0 | 63.38 | 28.2 | — | 2.24 |
| 9∶1 | 66.18 | 32.01 | — | 2.07 |
| 8∶2 | 66.63 | 31.68 | 0.55 | 2.10 |
| 5∶5 | 60.15 | 26.66 | 0.88 | 2.26 |
| 2∶8 | 83.79 | 13.78 | 1.38 | 6.08 |
| V(H2SO4)∶V(H3PO4) | 104ΔIp/A | 102ΔEp/V | Ipa/Ipc |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10∶0 | 1.387 | 0.075 | 1.767 |
| 9∶1 | 2.847 | 0.083 | 1.714 |
| 8∶2 | 2.644 | 0.087 | 1.499 |
| 5∶5 | 3.243 | 0.091 | 1.581 |
| 2∶8 | 1.785 | 0.074 | 2.412 |
Table 4 Results of CV curves of samples prepared by H2SO4 /H3PO4 with different volume ratios
| V(H2SO4)∶V(H3PO4) | 104ΔIp/A | 102ΔEp/V | Ipa/Ipc |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10∶0 | 1.387 | 0.075 | 1.767 |
| 9∶1 | 2.847 | 0.083 | 1.714 |
| 8∶2 | 2.644 | 0.087 | 1.499 |
| 5∶5 | 3.243 | 0.091 | 1.581 |
| 2∶8 | 1.785 | 0.074 | 2.412 |
| V(H2SO4)∶V(H3PO4) | Rs/(Ω·cm-2) | Rct/(Ω·cm-2) |
|---|---|---|
| 10∶0 | 2.506 | 44.31 |
| 9∶1 | 2.556 | 32.13 |
| 8∶2 | 2.447 | 38.11 |
| 5∶5 | 2.523 | 34.31 |
| 2∶8 | 2.306 | 28.90 |
Table 5 Impedance fitting parameters of samples prepared by H2SO4 /H3PO4 with different volume ratios
| V(H2SO4)∶V(H3PO4) | Rs/(Ω·cm-2) | Rct/(Ω·cm-2) |
|---|---|---|
| 10∶0 | 2.506 | 44.31 |
| 9∶1 | 2.556 | 32.13 |
| 8∶2 | 2.447 | 38.11 |
| 5∶5 | 2.523 | 34.31 |
| 2∶8 | 2.306 | 28.90 |
| 1 | Xu B., Li C. L., Zhang H. Y., Gong Z., Yu Y., Qiu G. M., Membrane Sci. Technology, 2021, 41(6), 18—26 |
| 徐博, 李春丽, 张浩月, 弓哲, 于颖, 邱广明. 膜科学与技术, 2021, 41(6), 18—26 | |
| 2 | Zhang Z. H., Schnieqq H. C., Adamson D. H., Carbon, 2019, 154, 510—521 |
| 3 | Meng C. F., Hu P. F., Chen H. T., Cai Y. J., Zhou H., Jiang Z. H., Xiang Z., Liu Z. Y., Wang C. Y., Yuan A. H., Nanoscale, 2021, 13(16), 7751—7760 |
| 4 | Štengl V., Bakardjieva S., Grygar T. M., Bludská J., Kormunda M., Chem. Cent. J., 2013, 7(41), 1—12 |
| 5 | Li D., Müller M. B., Gilje S., Kaner R. B., Wallace G. G., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2008, 3(2), 101—105 |
| 6 | Alkhouzaam A., Qiblawey H., Khraishes M., Atieh M., Al⁃Ghouti M., Ceram. Int., 2020, 46(15), 23997—24007 |
| 7 | Contreras J. G., Briones C. F., Mater. Chem. Phys., 2015, 153, 209—220 |
| 8 | Sun L., Miyakai T., Seki S., Dincă M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(22), 8185—8188 |
| 9 | Hummers W. S. Jr., Offeman R. E., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1958, 80(6), 1339 |
| 10 | Marcano D. C., Kosynkin D. V., Berlin J. M., Sinitskii A., Sun Z. Z., Slesarev A. S., Alemany L. B., Lu W., Tour J. M., ACS Nano, 2010, 4(8), 4806—4814 |
| 11 | Kovtyukhova N. I., Wang Y., Berkdemir A., Cruz⁃Silva R., Terrones M., Crespi V. H., Mallouk T. E., Nat. Chem., 2014, 6(11), 957—963 |
| 12 | Panwar V., Chattree A., Pal K., Physica E: Low⁃dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, 2015, 73, 235—241 |
| 13 | Tan P., Bi Q., Hu Y., Fang Z., Chen Y., Cheng J., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 423, 1141—1151 |
| 14 | Shuai S., Liu Y., Zhao C., Zhu H., Li Y., Zhou K., Ge W., Hao J., Chem. Phys., 2020, 539, 110938 |
| 15 | Zhang H. Y., Li C. L., Xu B., Li X. H., Tong L., Qiu G. M., Prog. Chem., 2023, 42(5), 2606—2615 |
| 张浩月, 李春丽, 徐博, 李筱贺, 仝铃, 邱广明. 化工进展, 2023, 42(5), 2606—2615 | |
| 16 | Chen J., Yao B., Li C., Shi G., Carbon, 2013, 64, 225—229 |
| 17 | Shao G., Lu Y., Wu F., Yang C., Zeng F., Wu Q., J. Mater. Sci., 2012, 47, 4400—4409 |
| 18 | Al⁃Gaashani R., Najjar A., Zakaria Y., Mansour S., Atieh M. A., Ceramics International, 2019, 45(11), 14439—14448 |
| 19 | Kim D., Yang S. J., Kim Y. S., Jung H., Park C. R., Carbon, 2012, 50(9), 3229—3232 |
| 20 | Dimiev A. M., Tour J. M., ACS Nano, 2014, 8(3), 3060—3068 |
| 21 | Yadav N., Kallur V., Chakraborty D., Johari P., Lochab B., ACS Omega, 2019, 4(5), 9407—9418 |
| 22 | Cançado L. G., Takai K., Enoki T., Endo M., Kim Y. A., Mizusaki H., Jorio A., Coelho L. N., Magalhães⁃Paniago R., Pimenta M. A., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2006, 88(16), 163106 |
| 23 | Samsonidze G. G., Barros E. B., Saito R., Jiang J., Dresselhaus G., Dresselhaus M. S., Phys. Rev. B, 2007, 75(15), 155420 |
| 24 | Dresselhaus M. S., Dresselhaus G., Adv. Phys., 2002, 51(1), 1—186 |
| 25 | Liu Z., Duan X. Z., Zhou X. G., Qian G., Zhou J. H., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2014, 53(1), 253—258 |
| 26 | Matsumoto R., Okabe Y., Synthetic. Met., 2016, 212, 62—68 |
| 27 | Lai Q., Luo X. P., J. Mater. Res., 2015, 29(2), 155—160 |
| 赖奇, 罗学萍. 材料研究学报, 2015, 29(2), 155—160 | |
| 28 | Jeong H. K., Jin M. H., So K. P., Lim S. C., Lee Y. H., J. Phys. D, 2009, 42(6), 065418 |
| 29 | Liang Y., Zhang R. L., Liu B. H., Wang J. P., Wang S. H., Han M. Y., Zhang Z. P., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53(38), 10109—10113 |
| 30 | Yu H. T., Zhang B. W., Bulin C. K., Li R. H., Xing R. G., Sci. Rep., 2016, 6(1), 36143 |
| 31 | Becerra⁃Paniagua D. K., Sotelo⁃Lerma M., Hu H. L., J. Mater. Sci. Mater. E, 2019, 30,3973—3983 |
| 32 | Dimiev A. M., Bachilo S. M., Saito R., Tour J. M., ACS Nano, 2012, 6(9), 7842—7849 |
| 33 | Narayanan Kutty T. R., Vasudeva Murthy A. R., Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem., 1970, 379(2), 218—224 |
| 34 | Shan H., Xin B. J., Chen Z. M., Liu Y., Text. Res. J., 2019, 89(6), 1038—1050 |
| 35 | Fu L., The Research on Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Graphite Oxide and Polypyrrole/Graphite Oxide Nanocomposites, Hunan University, Changsha, 2005 |
| 傅玲. 氧化石墨和聚吡咯/氧化石墨纳米复合材料的制备、 表征及应用研究, 长沙: 湖南大学, 2005 | |
| 36 | Zubair N. A., Rahman N. A., Lim H. N., Sulaiman Y., Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2017, 12, 1—13 |
| 37 | Jiang B., Wu L. T., Yu L. H., Qiu X. P., Xi J.Y., J. Membr. Sci., 2016, 510, 18—26 |
| 38 | Mohan V. B., Jayaraman K., Stamm M., Bhattacharyya D., Thin Solid Films, 2016, 616, 172—182 |
| 39 | Hou M., Hong X. H., Tang Y. J., Jin Z. M., Zhu C. Y., Tao C., Wan J. M., Dong Y. B., Text. Res. J., 2021, 91(19/20), 2169—2183 |
| 40 | Narayanan Kutty T. R., Vasudeva Murthy A. R., Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem., 1970, 379(2), 218—224 |
| 41 | Zhu Y. H., Zhu X. M., Wang X. X., Zhang X., Zheng H. L., Deng H. P., Zhao C., China Environ. Sci., 2020, 40(3), 1139—1145 |
| 朱云华, 朱轩墨, 王旭旭, 张轩, 郑怀礼, 邓慧萍, 赵纯. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(3), 1139—1145 |
| [1] | 秦海敬, 贺乾军, 徐敏敏, 袁亚仙, 姚建林. 离子液体中PMBA脱羧反应及界面水影响的电化学SERS研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(1): 20230349. |
| [2] | 赵环宇, 米洪田, 常月琪, 周冬雪, 张立国, 杨穆. Ni/TiO2-VO纳米线自支撑薄膜的界面工程与电催化产氢性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(8): 20230057. |
| [3] | 陈亚锋, 曾刘莉, 郭伟. 质子交换膜燃料电池阴极侧不同部位水淹对性能的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(6): 20230003. |
| [4] | 王斯阳, 敬稳, 常江伟, 卢思宇. 碳点的制备及电化学能源应用进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(5): 20220733. |
| [5] | 杜磊, 刘兆清. 非贵金属催化剂在羟甲基糠醛电氧化增值中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(5): 20220710. |
| [6] | 巴迪迪, 赵海洲, 张志明, 于良民. 电纺聚苯胺涂层表面浸润性和表面荷电对微生物附着的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(4): 20220615. |
| [7] | 孔好, 徐菲洋, 王依香, 张艳. 基于小分子化学反应工具构建CRISPR-Cas9功能调控体系的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(3): 20220346. |
| [8] | 孙竹梅, 傅杰, 李鑫, 王海芳, 卢静, 童天星, 朱明飞, 舒余德, 王云燕. 电吸附除氯过程的电化学阻抗谱及动力学研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(2): 20220528. |
| [9] | 胡诗颖, 沈佳艳, 韩峻山, 郝婷婷, 李星. CoO纳米颗粒/石墨烯纳米纤维复合材料的制备及电化学性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(2): 20220462. |
| [10] | 陈珊, 陈劲虎, 徐郭海林, 柳军, 钱明艳, 陈敬文, 方一民. 基于铂修饰丝网印刷电极检测土壤中铵态氮的电化学传感器[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(12): 20230390. |
| [11] | 王前, 魏祎, 贾洪声. Mo2C/PE隔膜对锂硫电池性能的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(11): 20230223. |
| [12] | 范建玲, 唐灏, 秦凤娟, 许文静, 谷鸿飞, 裴加景, 陈文星. 氮掺杂超薄碳纳米片复合铂钌单原子合金催化剂的电化学析氢性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220366. |
| [13] | 江博文, 陈敬轩, 成永华, 桑微, 寇宗魁. 单原子材料在电化学生物传感中的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220334. |
| [14] | 王瑞娜, 孙瑞粉, 钟添华, 池毓务. 大尺寸石墨烯量子点组装体的制备及电化学发光性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220161. |
| [15] | 李玉龙, 谢发婷, 管燕, 刘嘉丽, 张贵群, 姚超, 杨通, 杨云慧, 胡蓉. 基于银离子与DNA相互作用的比率型电化学传感器用于银离子的检测[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220202. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||