

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 20230028.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20230028
王锡慧, 唐笑( ), 刘婷婷, 李艳虹, 荆川, 凌发令, 刘俊, 周贤菊, 姚璐, 周衡, 张家忠
), 刘婷婷, 李艳虹, 荆川, 凌发令, 刘俊, 周贤菊, 姚璐, 周衡, 张家忠
收稿日期:2023-01-20
出版日期:2023-06-10
发布日期:2023-03-21
通讯作者:
唐笑
E-mail:tangxiao@cqupt.edu.cn
基金资助:
WANG Xihui, TANG Xiao( ), LIU Tingting, LI Yanhong, JING Chuan, LING Faling, LIU Jun, ZHOU Xianju, YAO Lu, ZHOU Heng, ZHANG Jiazhong
), LIU Tingting, LI Yanhong, JING Chuan, LING Faling, LIU Jun, ZHOU Xianju, YAO Lu, ZHOU Heng, ZHANG Jiazhong
Received:2023-01-20
Online:2023-06-10
Published:2023-03-21
Contact:
TANG Xiao
E-mail:tangxiao@cqupt.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
氮化碳材料固有的导电性差、 电子迁移率低等问题导致高光生电荷复合率, 阻碍了其光生电荷存储性能的提高. 为此, 构建了TiO2富碳氮化碳共轭聚合物(CPCN)界面异质结, 以提高光生电荷分离率. 采用具有高比表面积(220.03 m2/g)的TiO2纳米晶介孔薄膜作为电子传输物质, 通过增大TiO2与CPCN之间的界面面积提高了电极反应活性, 促进了光生空穴的高效抽取, 获得了197 C/g的光生电荷存储容量.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
王锡慧, 唐笑, 刘婷婷, 李艳虹, 荆川, 凌发令, 刘俊, 周贤菊, 姚璐, 周衡, 张家忠. TiO2提高富碳氮化碳的光生电荷存储性能. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(6): 20230028.
WANG Xihui, TANG Xiao, LIU Tingting, LI Yanhong, JING Chuan, LING Faling, LIU Jun, ZHOU Xianju, YAO Lu, ZHOU Heng, ZHANG Jiazhong. Photocharging Storage Capacity of C-rich Polymeric Carbon Nitrides Enhanced by TiO2. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(6): 20230028.
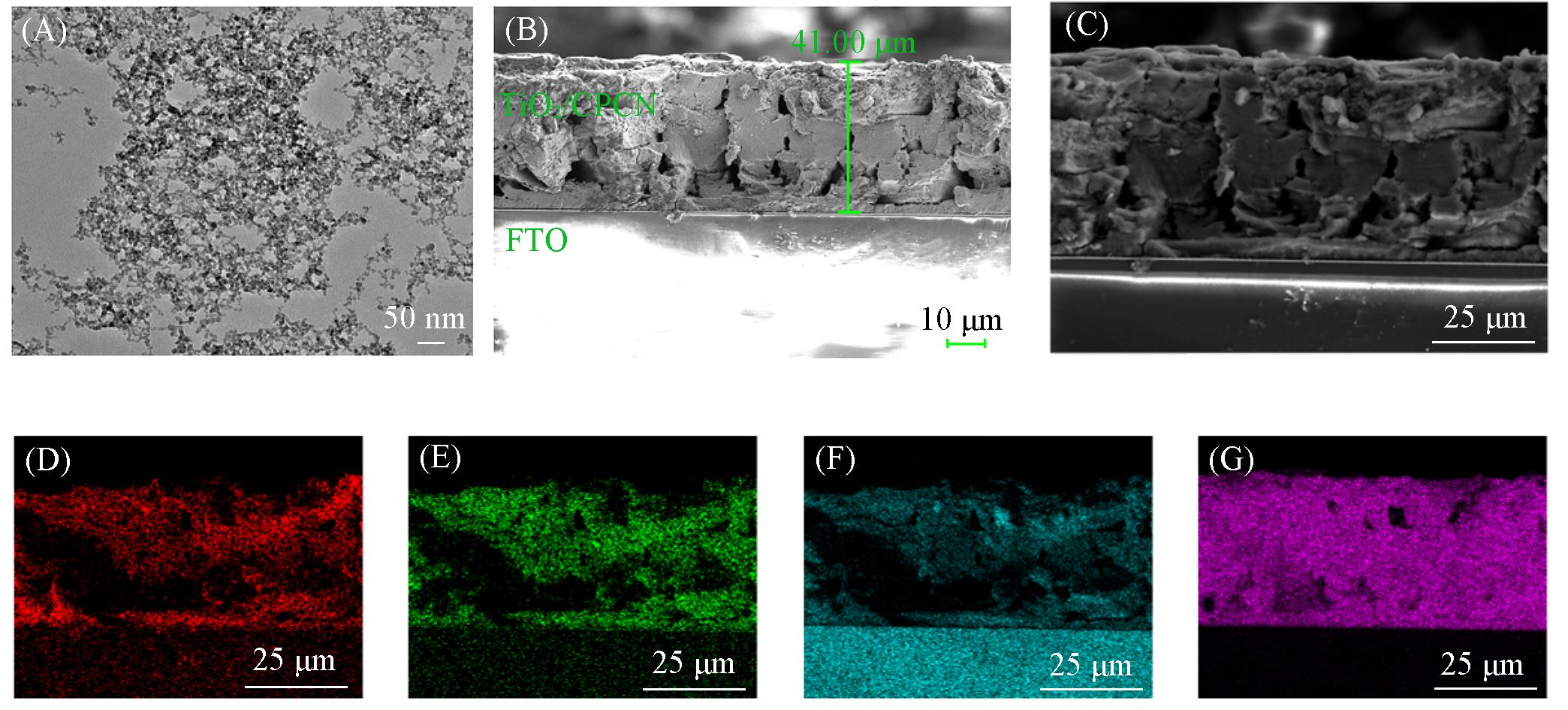
Fig.2 TEM image of the prepared TiO2 nanoparticles(A), FESEM image of the cross section(B) and an enlarged part(C), EDS elemental mapping of C(D), N(E), O(F) and Ti(G) of the TiO2/CPCN thin film electrode
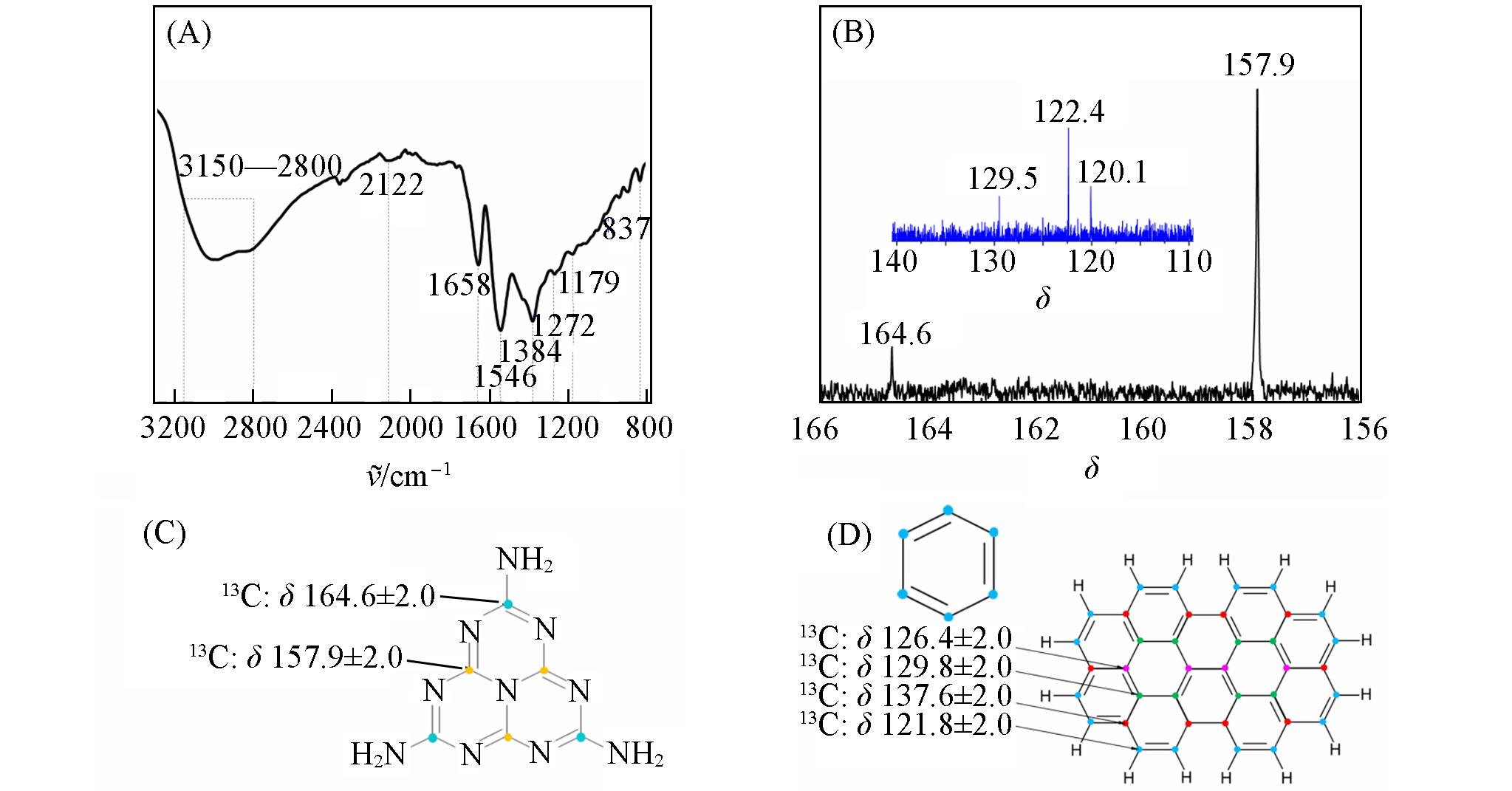
Fig.3 FTIR spectrum(A) and 13C liquid⁃state NMR spectrum(B) of the synthesized CPCN sample, schematic diagram of the NMR chemical shift of heptazine rings(C) and conjugate carbon frameworks(D)(B) The inset is 13C chemical shifts of conjugated carbon frameworks.
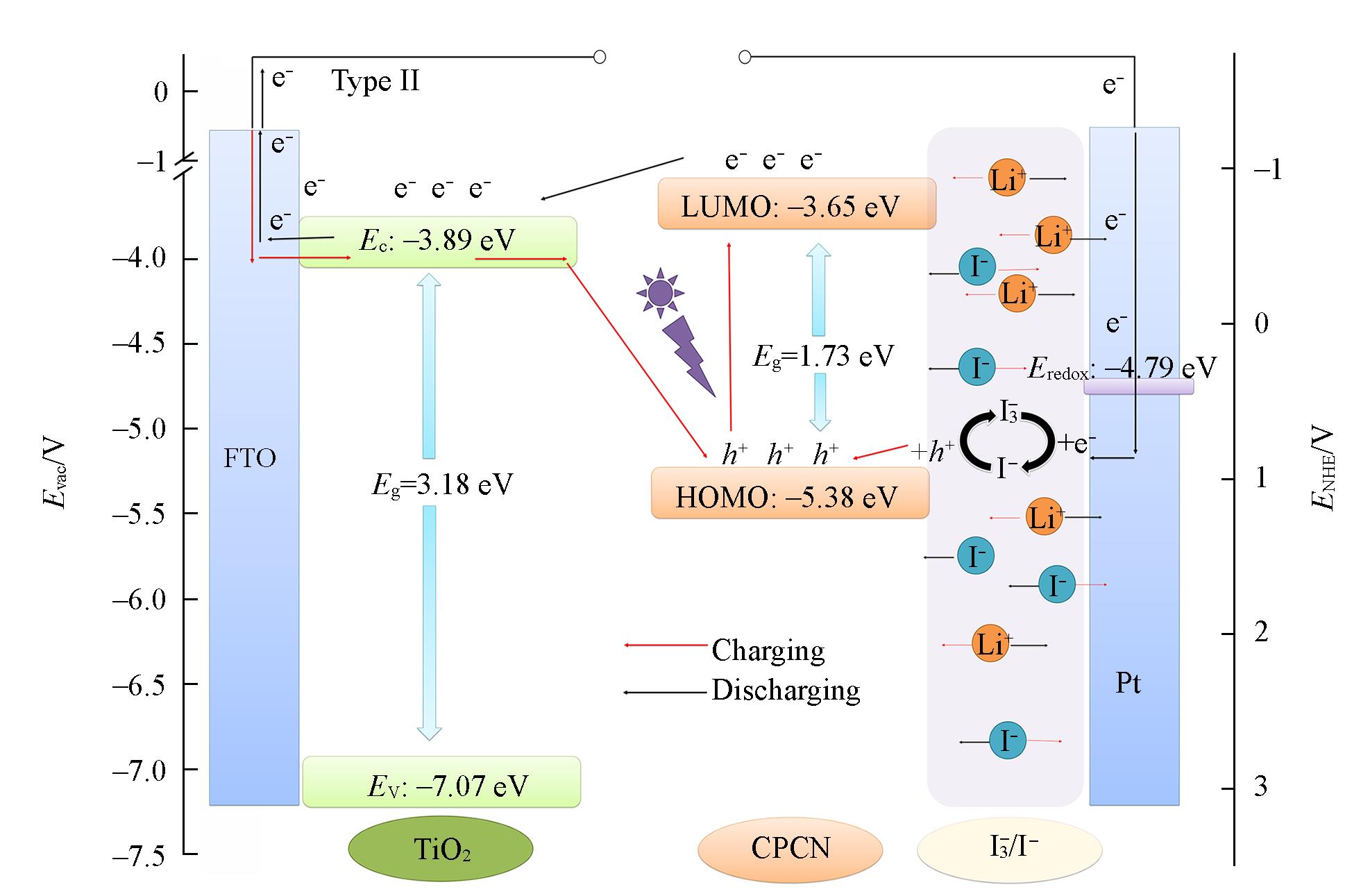
Fig.7 Band diagram for the energy levels of the CPCN and TiO2, as well as the schematic illustration of working mechanism of the TiO2/CPCN cellEvac: the vacuum level.
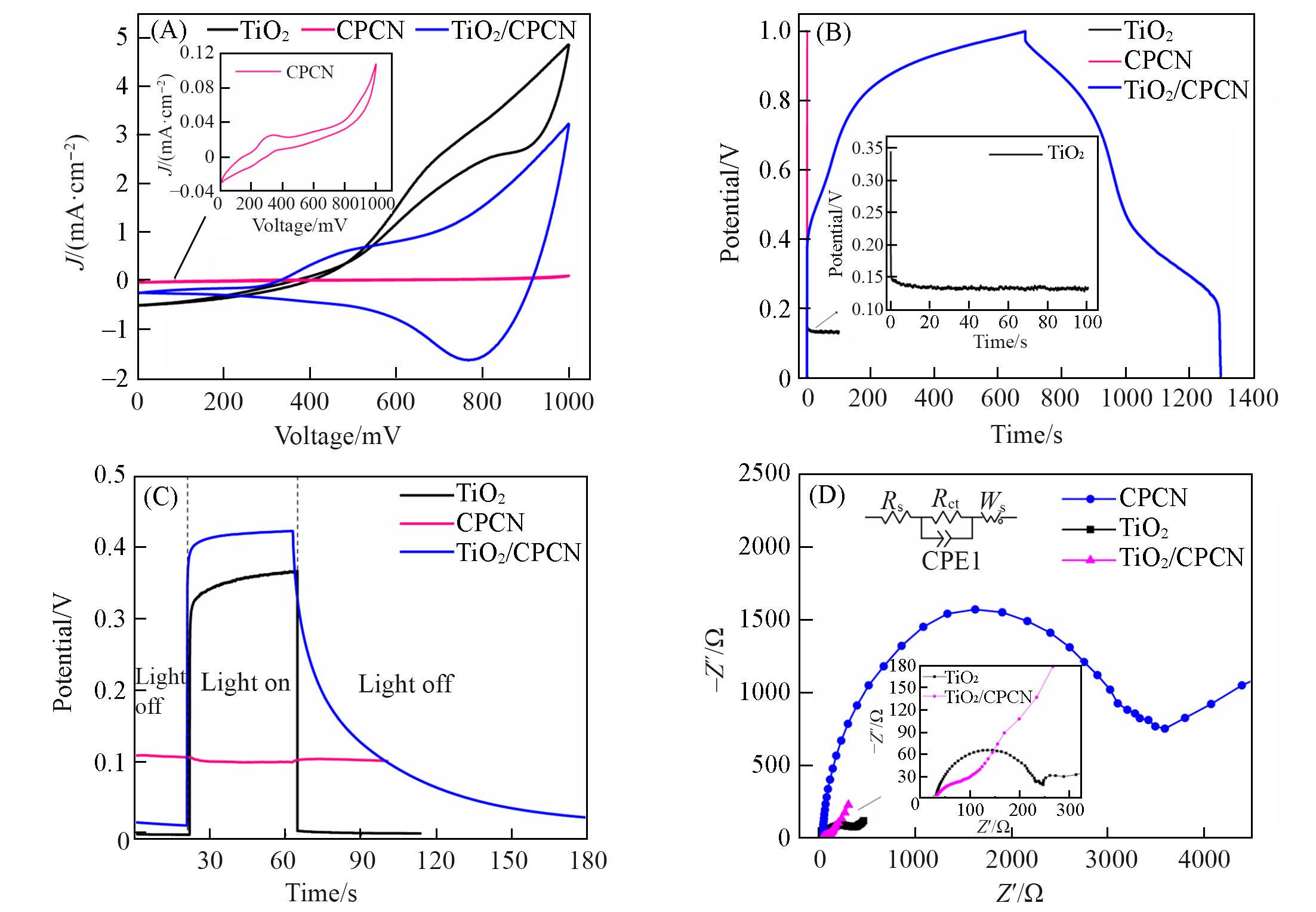
Fig.8 CV curves at a scan rate of 10 mV/s(A), GCD curves at a current of 0.4 mA and in a potential window of 0—1 V(B), OCPT curves(C) and EIS spectroscopies(D) of TiO2, CPCN and TiO2/CPCN electrodes(D) The inset is the Nyquist plots amplification of TiO2 and TiO2/CPCN heterojunction and equivalent circuit model, where RCT is the charge transfer resistance, CPE1 is the electric double layer capacitance, Ws is the Warburg component caused by diffusion of ions, Rs is the resistance of conductive substrate; the illumination condition is the simulated AM 1.5 solar light irradiation(100 mW/cm2) and the geometric area of the cell is 4 cm2.
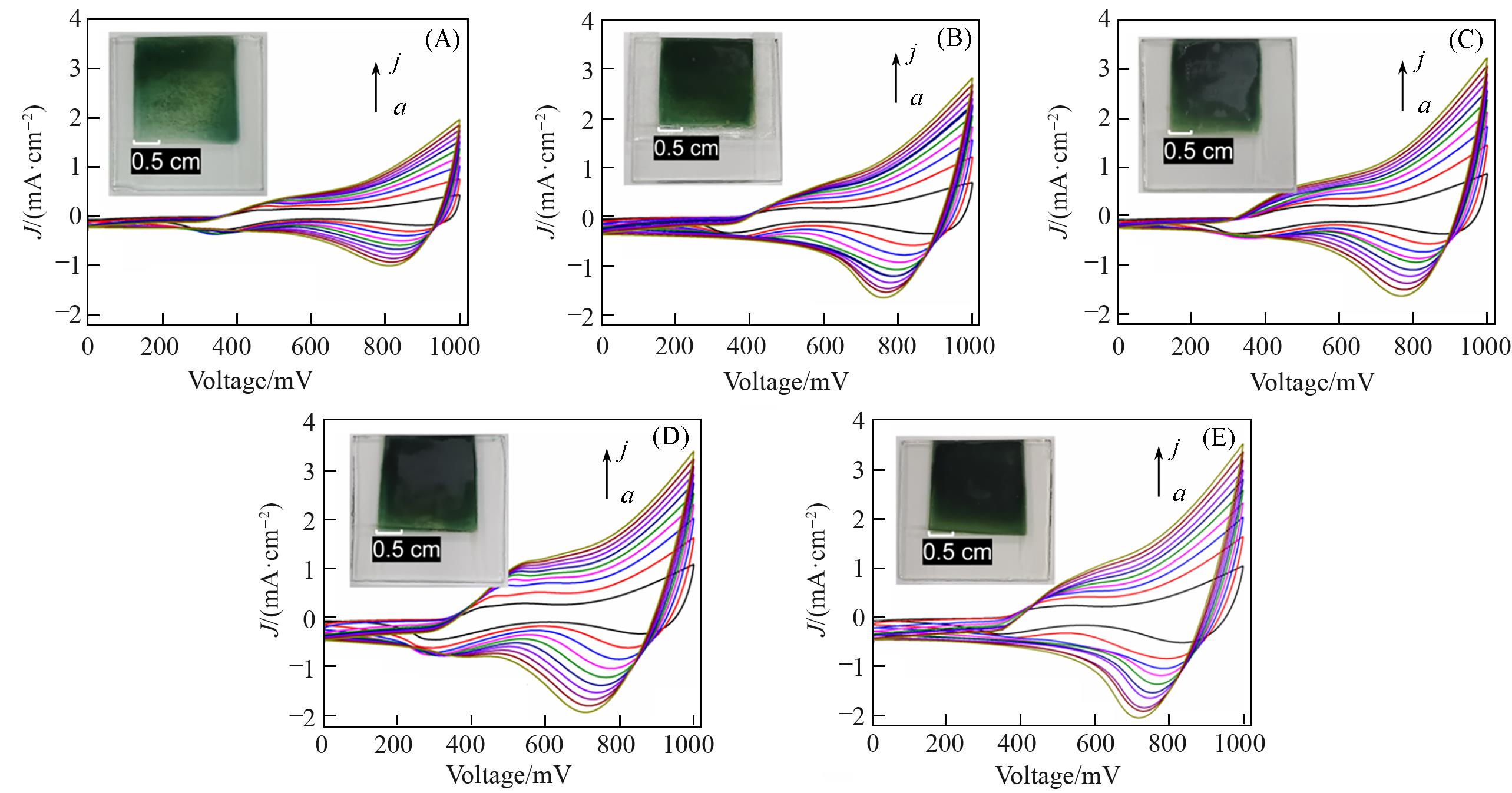
Fig.9 CV curves tested in different scan rates ranging from 1 mV/s to 10 mV/s under illumination(A) TiO2⁃1/CPCN; (B) TiO2⁃2/CPCN; (C) TiO2⁃3/CPCN; (D) TiO2⁃4/CPCN; (E) TiO2⁃5/CPCN.Scan rate: a.1 mV/s; b.2 mV/s; c.3 mV/s; d.4 mV/s; e.5 mV/s; f.6 mV/s; g.7 mV/s; h.8 mV/s; i.9 mV/s; j.10 mV/s. The insets show the prepared photoelectrodes.
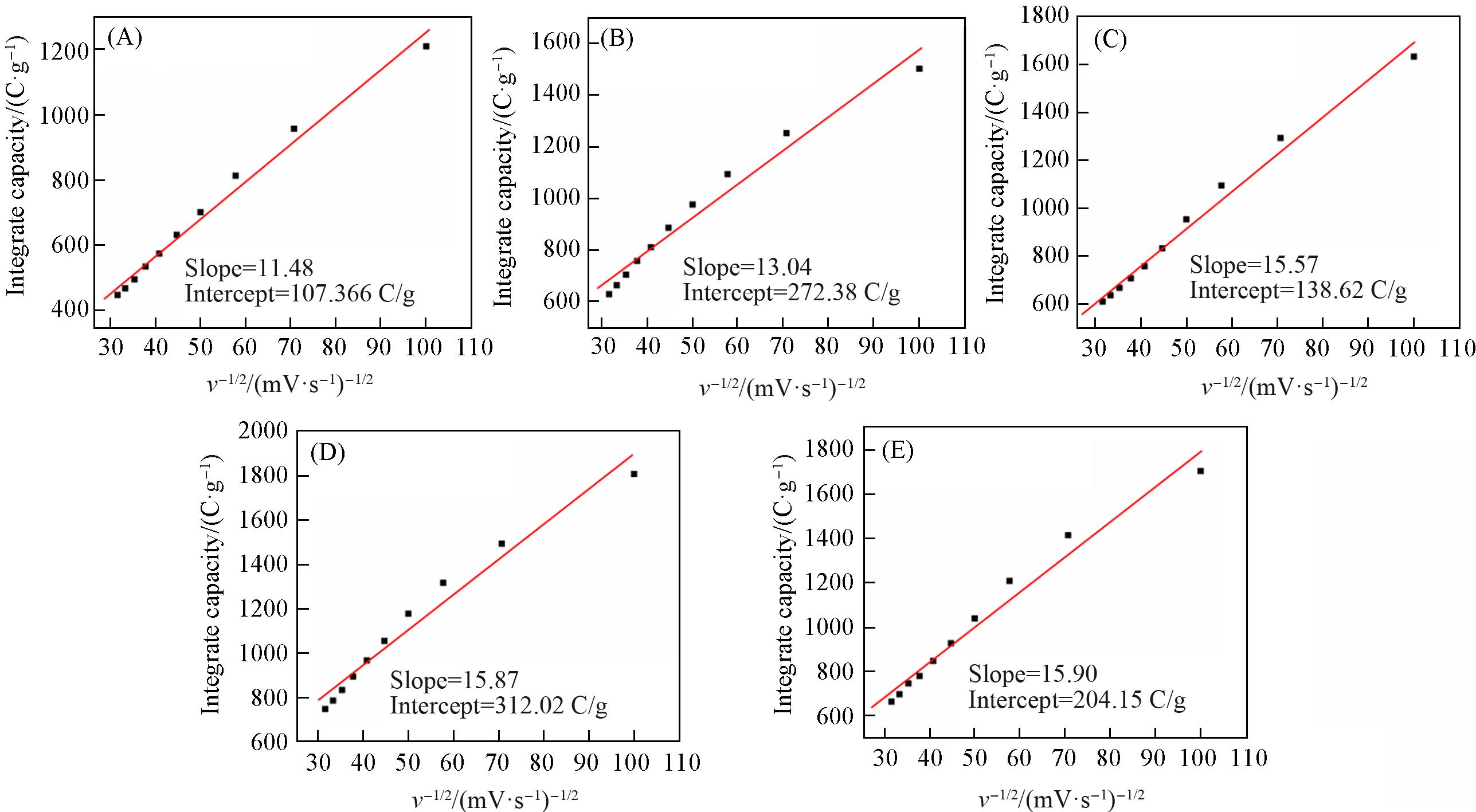
Fig.10 Linear fitting results of the relationship between total integral capacity and v-1/2(A) TiO2⁃1/CPCN; (B) TiO2⁃2/CPCN; (C) TiO2⁃3/CPCN; (D) TiO2⁃4/CPCN; (E) TiO2⁃5/CPCN.
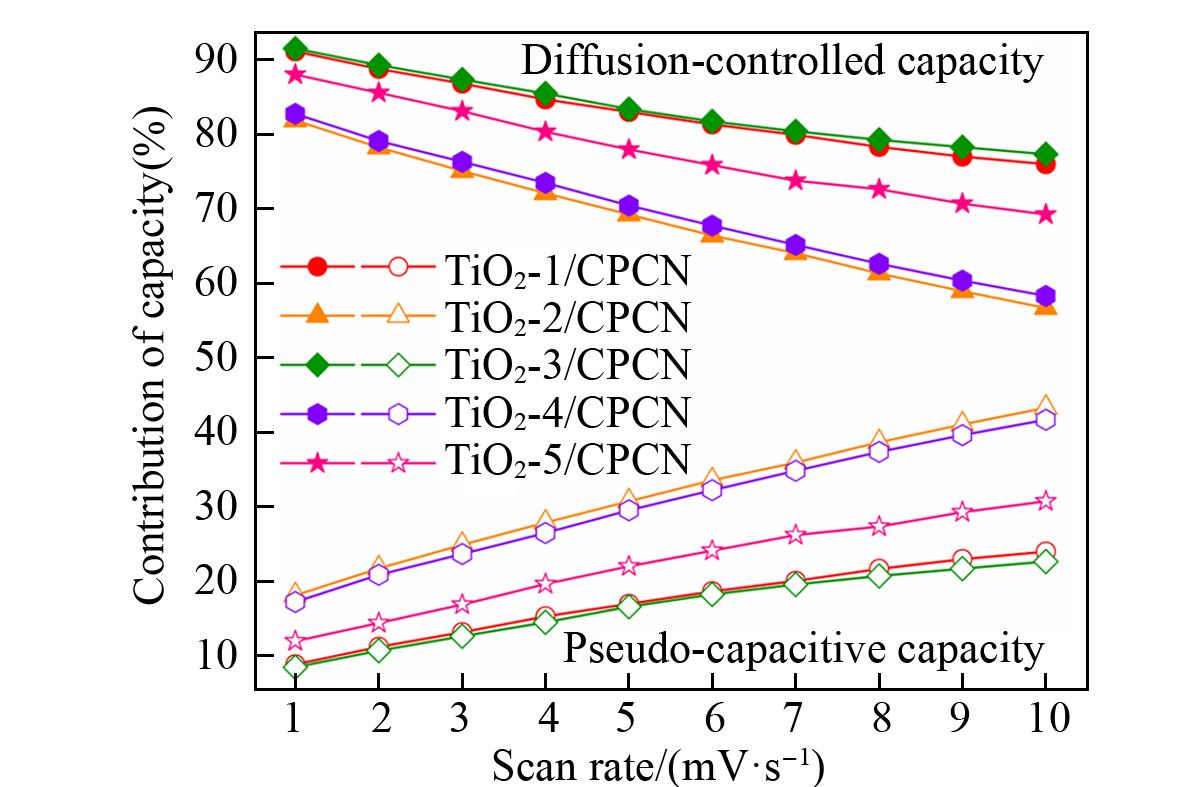
Fig.11 Contributions and properties of the capacities of TiO2⁃x/CPCN(x=1, 2, 3, 4, 5) electrodeIllumination condition is simulated sunlight AM 1.5(100 mW/cm2) irradiation, and the geometric area of the cell is 4 cm2.
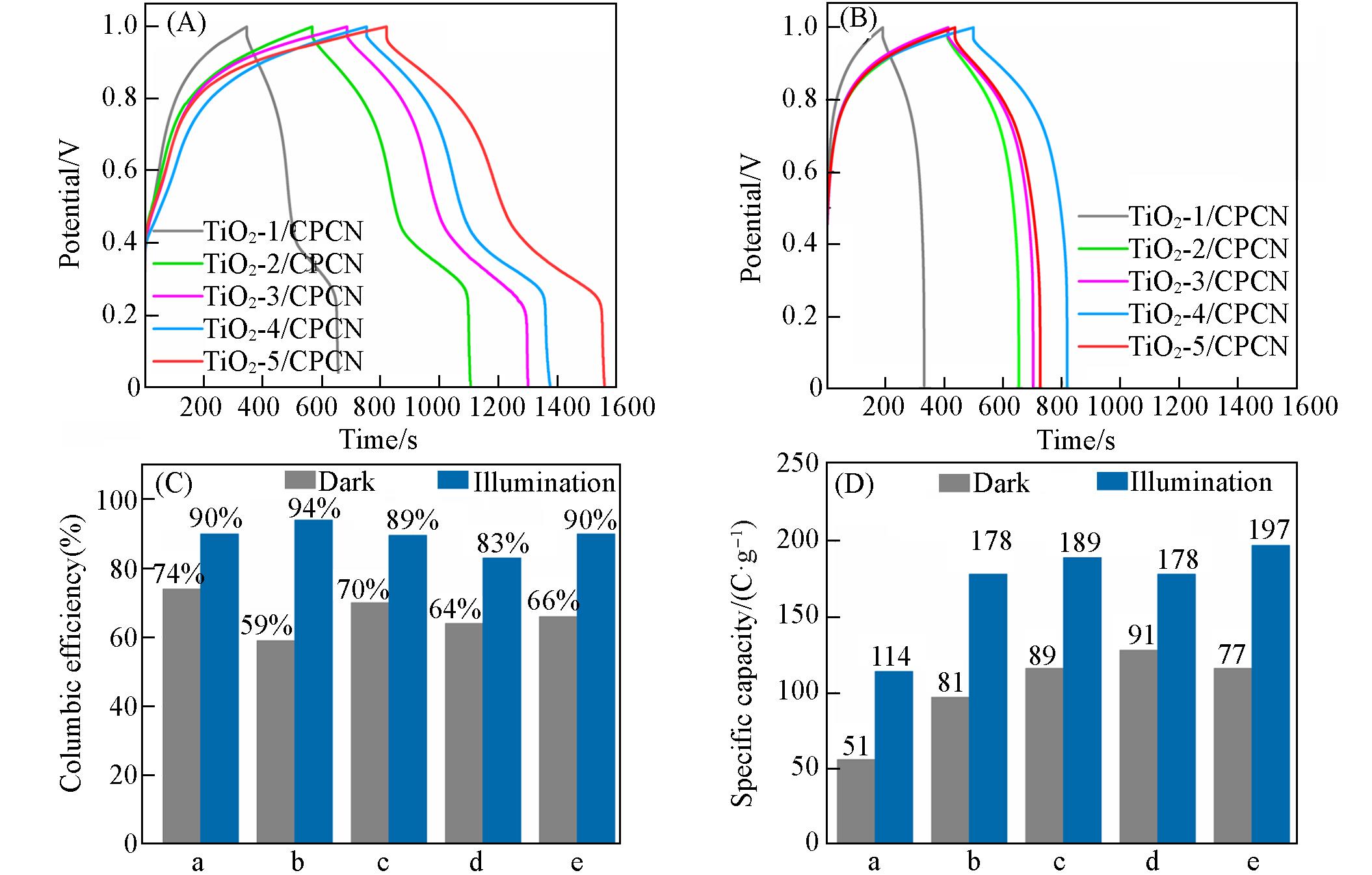
Fig.12 GCD curves under illumination(A) and dark condition(B), coulomb efficiency(C) and specific capacitance(D) of illumination and dark condition calculated from GCD curves of TiO2⁃x/CPCN(x= 1, 2, 3, 4, 5) electrodeIllumination condition is simulated sunlight AM 1.5(100 mW/cm2) irradiation, and the geometric area of the cell is 4 cm2. (C, D) a.TiO2⁃1/CPCN; b.TiO2⁃1/CPCN; c.TiO2⁃3/CPCN; d.TiO2⁃4/CPCN; e.TiO2⁃5/CPCN.
| 1 | Meng H., Pang S., Cui G., ChemSusChem, 2019, 12, 3431—3447 |
| 2 | Bae J., Park Y. J., Lee M., Cha S. N., Choi Y. J., Lee C. S., Kim J. M., Wang Z. L., Adv. Mater., 2011, 23, 3446—3449 |
| 3 | Li Q., Liu Y., Guo S., Zhou H., Nano Today, 2017, 16, 46—60 |
| 4 | Kelly N. A., J. Power Sources, 2012, 209, 105—119 |
| 5 | Kalasina S., Pattanasattayavong P., Suksomboon M., Phattharasupakun N., Wutthiprom J., Sawangphruk M., Chem. Commun., 2017, 53, 709—712 |
| 6 | Boruah B. D., Mathieson A., Wen B., Jo C., Deschler F., de Volder M., Nano Lett., 2020, 20, 5967—5974 |
| 7 | Safshekan S., Herraiz⁃Cardona I., Cardenas⁃Morcoso D., Ojani R., Haro M., Gimenez S., ACS Energy Lett., 2017, 2, 469—475 |
| 8 | Kumar A., Thakur P., Sharma R., Puthirath A. B., Ajayan P. M., Narayanan T. N., Small, 2021, 17, 2105029 |
| 9 | Wang J., Wang Y., Zhu C., Liu B., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14, 4071—4078 |
| 10 | Boruah B. D., Mathieson A., Wen B., Feldmann S., Dose W. M., de Volder M., Energy Environ. Sci., 2020, 13, 2414—2421 |
| 11 | Wang P., Chen X., Sun G., Wang C., Luo J., Yang L., Lv J., Yao Y., Luo W., Zou Z., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 1390—1395 |
| 12 | Su S. J., Lai Q. X., Liang Y. Y., Acta Chim. Sin., 2015, 73, 735 |
| 苏善金, 来庆学, 梁彦瑜. 化学学报, 2015, 73, 735 | |
| 13 | Li K. N., Zhang M. X., Ou X. Y., Li R. N., Li Q., Fan J. J., Lv K. L., Acta Phys⁃Chim. Sin., 2021, 37, 2008010 |
| 李开宁, 张梦曦, 欧小雨, 李睿娜, 李覃, 范佳杰, 吕康乐. 物理化学学报, 2021, 37, 2008010 | |
| 14 | Zhou L., Li Y. F., Zhang Y. K., Qiu L. W., Xing Y., Acta Phys⁃Chim. Sin., 2022, 38, 2112027 |
| 周亮, 李云锋, 张永康, 秋列维, 邢艳. 物理化学学报, 2022, 38, 2112027 | |
| 15 | Ma C., Wu J. W., Zhu L., Han X. X., Ruan W. D., Song W., Wang X., Zhao B., Acta Chim. Sin., 2019, 77, 1024 |
| 马超, 武佳炜, 朱琳, 韩晓霞, 阮伟东, 宋薇, 王旭, 赵冰. 化学学报, 2019, 77, 1024 | |
| 16 | Wang X., Maeda K., Thomas A., Takanabe K., Xin G., Carlsson J. M., Domen K.,Antonietti M., Nat. Mater., 2009, 8, 76—80 |
| 17 | Podjaski F., Lotsch B. V., Adv. Energy Mater., 2021, 11, 2003049 |
| 18 | Lau V. W. H., Lotsch B. V., Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12, 2101078 |
| 19 | Podjaski F., Kröger J., Lotsch B. V., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1705477 |
| 20 | Fang Z., Li Y., Li J., Shu C., Zhong L., Lu S., Mo C., Yang M., Yu D., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 17615—17621 |
| 21 | Zhang L., Tang X., Li Y., Wang X., Ling F., Jing C., Zhou X., Xiang G., Liu T., Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 9, 2102372 |
| 22 | Liu Y., Zeng X., Hu X., Hu J., Wang Z., Yin Y., Sun C., Zhang X., Catal. Today, 2019, 335, 243—251 |
| 23 | Liu D., Lu C., Wu J., Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32, 8287—8295 |
| 24 | Alcudia⁃Ramos M. A., Fuentez⁃Torres M. O., Ortiz⁃Chi F., Espinosa⁃González C. G., Hernández⁃Como N., García⁃Zaleta D. S., Kesarla M. K., Torres⁃Torres J. G., Collins⁃Martínez V., Godavarthi S., Ceram. Int., 2020, 46, 38—45 |
| 25 | Yu W., Chen J., Shang T., Chen L., Gu L., Peng T., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2017, 219, 693—704 |
| 26 | Vu N. N., Kaliaguine S., Do T. O., ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2020, 8, 853—863 |
| 27 | Ilies L., Isomura M., Yamauchi S. I., Nakamura T., Nakamura E., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 23—26 |
| 28 | Jürgens B., Irran E., Senker J., Kroll P., Müller H., Schnick W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 10288—10300 |
| 29 | Kröger J., Jiménez⁃Solano A., Savasci G., Rovó P., Moudrakovski I., Küster K., Schlomberg H., Vignolo⁃González H. A., Duppel V., Grunenberg L., Dayan C. B., Sitti M., Podjaski F., Ochsenfeld C., Lotsch B. V., Adv. Energy Mater., 2021, 11, 2003016 |
| 31 | Kitao T., MacLean M. W. A., Nakata K., Takayanagi M., Nagaoka M., Uemura T., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 5509—5514 |
| 32 | Kröger J., Jiménez⁃Solano A., Savasci G., Lau V. W. H., Duppel V., Moudrakovski I., Küster K., Scholz T., Gouder A., Schreiber M. L., Podjaski F., Ochsenfeld C., Lotsch B. V., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31, 2102468 |
| 33 | Papailias I., Todorova N., Giannakopoulou T., Ioannidis N., Dallas P., Dimotikali D., Trapalis C., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2020, 268, 118733 |
| 34 | Xie K., Fang J., Li L., Deng J., Liang Z., ChemistrySelect, 2021, 6, 11407—11416 |
| 35 | Sun J., Deng L., Sun J., Shen T., Wang X., Zhao R., Zhang Y., Wang B., RSC Adv., 2022, 12, 20206—20216 |
| 36 | Daeneke T., Kwon T. H., Holmes A. B., Duffy N. W., Bach U., Spiccia L., Nat. Chem., 2011, 3, 211—215 |
| 37 | Yang X., Rogach A. L., Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9, 1900747 |
| [1] | 时宇, 张榴, 国霞, 王阳, 肖海芹, 房进, 周祎, 张茂杰. 聚合物添加剂作为形貌调节剂提升全小分子有机太阳能电池的效率和稳定性[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(7): 20230047. |
| [2] | 赵明新, 姚志刚, 刘中原, 徐文婧, 马晓玲, 张福俊. 逐层沉积型有机太阳能电池的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(7): 20230120. |
| [3] | 韦晚霞, 周先敏, 董馨韵, 刘铁峰, 谢聪, 程靖宇, 陈建平, 陆鑫, 冯凯, 周印华. 交联PEDOT∶F空穴传输层提升柔性有机光伏电池性能的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(7): 20230069. |
| [4] | 司文钦, 李腾飞, 林禹泽. 非对称稠环光伏电子受体[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(7): 20230149. |
| [5] | 何韦, 陈飞, 李鸿祥, 王嘉宇, 秦家强, 崔宁博, 严岑琪, 程沛. 基于三氟苯甲酸自组装阳极界面层的高性能有机太阳能电池[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(7): 20230161. |
| [6] | 张有辉, 杨娜, 段娜, 程毓君, 游诗勇, 吴飞燕, 谌烈. 端基修饰聚合物给体制备高性能有机太阳能电池[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(7): 20230169. |
| [7] | 方海盛, 梁世洁, 肖承义, 夏冬冬, 李韦伟. 基于刚性连接单元的双缆共轭高分子材料的合成及在单组分有机太阳能电池中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(7): 20230146. |
| [8] | 陈海阳, 李欣琪, 丁俊源, 黄雨婷, 李耀文. 客体增塑剂调控非卤溶剂中聚合物给体预聚集行为制备高性能有机太阳能电池[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(7): 20230128. |
| [9] | 任毅, 阚媛媛, 孙延娜, 李建丰, 高珂. 石墨炔在光伏领域的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(7): 20220752. |
| [10] | 郭赟彤, 陈振宇, 葛子义. 不同卤化端基的非富勒烯受体对有机太阳能电池的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(7): 20230084. |
| [11] | 张永倩, 朱小玉, 苗俊辉, 刘俊, 王利祥. 烷基链支化位点对全稠环小分子受体聚集的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(7): 20230068. |
| [12] | 张亿, 单通, 王焱, 钟洪亮. 以锗为桥接原子的受体材料及其在有机太阳能电池中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(7): 20230050. |
| [13] | 张泽升, 邓宇鑫, 孔令晨, 罗妹, 王新康, 张连杰, 陈军武. 含9,10-二氟二噻吩并吩嗪杂环共轭聚合物的合成及有机太阳能电池性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(7): 20230148. |
| [14] | 姜珊, 申倩倩, 李琦, 贾虎生, 薛晋波. Pd增强缺陷态TiO2纳米管阵列的光催化产氢性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220206. |
| [15] | 苏英立, 任海生, 李象远. 非平衡溶剂化新理论在有机染料电子光谱中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2254. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||