

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 108.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180558
收稿日期:2018-08-06
出版日期:2019-01-10
发布日期:2018-12-19
作者简介:联系人简介: 尤静林, 男, 博士, 教授, 博士生导师, 主要从事结构表征和计算方面的研究. E-mail:
基金资助:
WU Zhidong, YOU Jinglin*( ), WANG Jian, WANG Min, HE Yingxia, YANG Yejin
), WANG Jian, WANG Min, HE Yingxia, YANG Yejin
Received:2018-08-06
Online:2019-01-10
Published:2018-12-19
Contact:
YOU Jinglin
E-mail:jlyou@staff.shu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
利用精细结构表征系列(
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
吴志东, 尤静林, 王建, 王敏, 何莹霞, 杨冶金. 基于精细结构对二元钠硅酸盐玻璃核磁共振波谱的研究. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(1): 108.
WU Zhidong,YOU Jinglin,WANG Jian,WANG Min,HE Yingxia,YANG Yejin. NMR Spectroscopic Study on Binary Sodium Silicate Glass Based on the Fine Structure†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 108.
| Chemical formula | Chemical shift, δ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6-311G(2df,2pd) | 6-311G++(3df,2pd) | |||
| Na4SiO4(a) | Q0 | Q0 | -36.9 | -36.1 |
| Na2Si7O6(b) | 2Q1 | 2Q1 | -66.2 | -64.0 |
| Na12Si18O6(c) | -89.8 | -87.3 | ||
| Na8Si12O4(d) | -86.4 | -84.2 | ||
| Na6Si9O3(e) | -80.3 | -78.4 | ||
| Na12Si30O12(f) | -98.2 | -95.0 | ||
| Na8Si20O8(g) | -96.2 | -93.2 | ||
| Na8Si28O12(h) | -96.1, -103.3 | -93.6, -101.2 | ||
| Na6Si18O12(i) | -87.1 | -84.7 | ||
| Na6Si21O9(j) | -87.7, -95.5 | -85.3, -92.1 | ||
| Na4Si10O4(k) | -83.0 | -81.3 | ||
| Na6Si19O8(l) | -85.5, -81.8 | -83.6, -80.2 | ||
| Na6Si27O12(m) | -88.8, -89.3 | -87.0, -87.4 | ||
| Na4Si34O16(n) | -91.2, -87.6 | -89.2, -85.6 | ||
Table 1 Structural characteristics of fine structure in binary sodium silicate and chemical shift
| Chemical formula | Chemical shift, δ | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6-311G(2df,2pd) | 6-311G++(3df,2pd) | |||
| Na4SiO4(a) | Q0 | Q0 | -36.9 | -36.1 |
| Na2Si7O6(b) | 2Q1 | 2Q1 | -66.2 | -64.0 |
| Na12Si18O6(c) | -89.8 | -87.3 | ||
| Na8Si12O4(d) | -86.4 | -84.2 | ||
| Na6Si9O3(e) | -80.3 | -78.4 | ||
| Na12Si30O12(f) | -98.2 | -95.0 | ||
| Na8Si20O8(g) | -96.2 | -93.2 | ||
| Na8Si28O12(h) | -96.1, -103.3 | -93.6, -101.2 | ||
| Na6Si18O12(i) | -87.1 | -84.7 | ||
| Na6Si21O9(j) | -87.7, -95.5 | -85.3, -92.1 | ||
| Na4Si10O4(k) | -83.0 | -81.3 | ||
| Na6Si19O8(l) | -85.5, -81.8 | -83.6, -80.2 | ||
| Na6Si27O12(m) | -88.8, -89.3 | -87.0, -87.4 | ||
| Na4Si34O16(n) | -91.2, -87.6 | -89.2, -85.6 | ||
| Type of Si—Ob | Length of Si—Ob/nm | Bond angle of Si—Ob/(°) | Type of Si—Ob | Length of Si—Ob/nm | Bond angle of Si—Ob/(°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q2—O—Q2 | 0.166 | 168.7 | Q3—O—Q3 | 0.163 | 161.5 | ||
| Q2—O—Q2 | 0.165 | 151.1 | Q3—O—Q3 | 0.165 | 134.1 | ||
| Q2—O—Q2 | 0.166 | 134.5 | Q3—O—Q3 | 0.166 | 121.9 | ||
| Q3—O—Q3 | 0.163 | 166.1 | Q4—O—Q4 | 0.165 | 160.7 | ||
| Q3—O—Q3 | 0.163 | 161.1 | Q4—O—Q4 | 0.164 | 134.4 | ||
| Q3—O—Q3 | 0.165 | 134.2 | Q4—O—Q4 | 0.163 | 118.2 | ||
| Q3—O—Q3 | 0.166 | 120.4 |
Table 2 Bridging oxygen bond angles and length in fine structure models of binary sodium silicate optimized by 6-311G++(3df,2pd) of ab initio method
| Type of Si—Ob | Length of Si—Ob/nm | Bond angle of Si—Ob/(°) | Type of Si—Ob | Length of Si—Ob/nm | Bond angle of Si—Ob/(°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q2—O—Q2 | 0.166 | 168.7 | Q3—O—Q3 | 0.163 | 161.5 | ||
| Q2—O—Q2 | 0.165 | 151.1 | Q3—O—Q3 | 0.165 | 134.1 | ||
| Q2—O—Q2 | 0.166 | 134.5 | Q3—O—Q3 | 0.166 | 121.9 | ||
| Q3—O—Q3 | 0.163 | 166.1 | Q4—O—Q4 | 0.165 | 160.7 | ||
| Q3—O—Q3 | 0.163 | 161.1 | Q4—O—Q4 | 0.164 | 134.4 | ||
| Q3—O—Q3 | 0.165 | 134.2 | Q4—O—Q4 | 0.163 | 118.2 | ||
| Q3—O—Q3 | 0.166 | 120.4 |
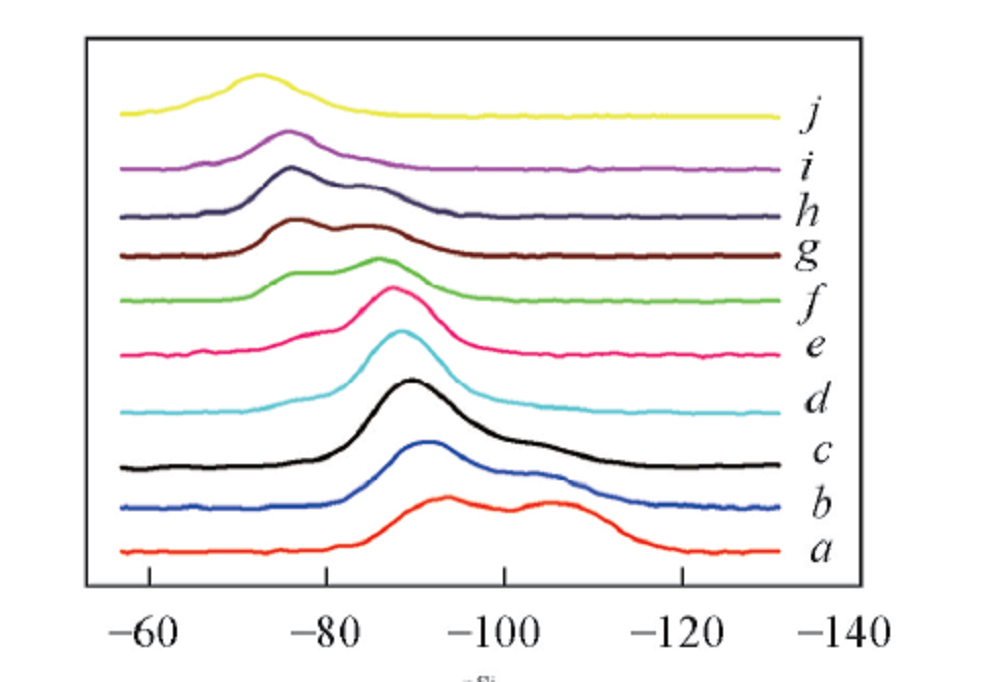
Fig.3 29Si NMR spectra of binary sodium silicate glassMolar fraction of Na2O(%): a. 20; b. 25; c. 28.6; d. 33.3; e. 36.4; f. 40; g. 42.8; h. 44.4; i. 50; j. 55.6.
| Molar fraction of Na2O(%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 25 | 28.6 | 33.3 | 36.4 | 40 | 42.8 | 44.4 | 50 | 55.6 | |
| Q0 | -59.9 | -59.0 | ||||||||
| Q1 | -67.1 | -67.1 | -67.0 | -66.8 | ||||||
| -72.6 | -72.6 | -72.6 | -72.6 | -72.6 | -72.6 | |||||
| -74.7 | -74.7 | -74.7 | -74.7 | -74.7 | -74.7 | -74.7 | ||||
| -76.7 | -76.7 | -76.7 | -76.7 | -76.7 | -76.7 | -76.7 | -76.7 | -76.7 | -76.7 | |
| -79.2 | -79.2 | -79.2 | -79.2 | -79.2 | -79.2 | -79.2 | -79.2 | -79.2 | -79.2 | |
| -82.6 | -82.6 | -82.6 | -82.6 | -82.6 | -82.6 | -82.6 | -82.6 | -82.6 | -82.6 | |
| -85.9 | -85.9 | -85.9 | -85.9 | -85.9 | -85.9 | -85.9 | -85.9 | -85.9 | -85.9 | |
| -88.1 | -88.1 | -88.1 | -88.1 | -88.1 | -88.1 | -88.1 | -88.1 | -88.1 | -88.1 | |
| -91.2 | -91.2 | -91.2 | -91.2 | -91.2 | -91.2 | -91.2 | -91.2 | -91.2 | ||
| -93.2 | -93.2 | -93.2 | -93.2 | -93.2 | -93.2 | -93.2 | -93.2 | |||
| -95.8 | -95.8 | -95.8 | -95.8 | -95.8 | -95.4 | -95.4 | -95.3 | |||
| -98.8 | -98.8 | -98.8 | -98.8 | -98.8 | -98.8 | -98.8 | -98.8 | |||
| -101.4 | -101.4 | -101.4 | -101.4 | -101.4 | ||||||
| -104.0 | -104.0 | -104.0 | -104.0 | -104.0 | ||||||
| -107.2 | -107.2 | -107.2 | -107.2 | -107.2 | ||||||
| -110.6 | -110.6 | -109.8 | ||||||||
| -113.3 | ||||||||||
Table 3 Chemical shifts of Qijklm by fitting spectra of binary sodium silicate glass
| Molar fraction of Na2O(%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 25 | 28.6 | 33.3 | 36.4 | 40 | 42.8 | 44.4 | 50 | 55.6 | |
| Q0 | -59.9 | -59.0 | ||||||||
| Q1 | -67.1 | -67.1 | -67.0 | -66.8 | ||||||
| -72.6 | -72.6 | -72.6 | -72.6 | -72.6 | -72.6 | |||||
| -74.7 | -74.7 | -74.7 | -74.7 | -74.7 | -74.7 | -74.7 | ||||
| -76.7 | -76.7 | -76.7 | -76.7 | -76.7 | -76.7 | -76.7 | -76.7 | -76.7 | -76.7 | |
| -79.2 | -79.2 | -79.2 | -79.2 | -79.2 | -79.2 | -79.2 | -79.2 | -79.2 | -79.2 | |
| -82.6 | -82.6 | -82.6 | -82.6 | -82.6 | -82.6 | -82.6 | -82.6 | -82.6 | -82.6 | |
| -85.9 | -85.9 | -85.9 | -85.9 | -85.9 | -85.9 | -85.9 | -85.9 | -85.9 | -85.9 | |
| -88.1 | -88.1 | -88.1 | -88.1 | -88.1 | -88.1 | -88.1 | -88.1 | -88.1 | -88.1 | |
| -91.2 | -91.2 | -91.2 | -91.2 | -91.2 | -91.2 | -91.2 | -91.2 | -91.2 | ||
| -93.2 | -93.2 | -93.2 | -93.2 | -93.2 | -93.2 | -93.2 | -93.2 | |||
| -95.8 | -95.8 | -95.8 | -95.8 | -95.8 | -95.4 | -95.4 | -95.3 | |||
| -98.8 | -98.8 | -98.8 | -98.8 | -98.8 | -98.8 | -98.8 | -98.8 | |||
| -101.4 | -101.4 | -101.4 | -101.4 | -101.4 | ||||||
| -104.0 | -104.0 | -104.0 | -104.0 | -104.0 | ||||||
| -107.2 | -107.2 | -107.2 | -107.2 | -107.2 | ||||||
| -110.6 | -110.6 | -109.8 | ||||||||
| -113.3 | ||||||||||
| Method | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1Q0 | 4Q0 | 8Q0 | 1Q1 | 4Q1 | 8Q1 | |
| Calculated | -36 | -57 | -58.2 | -64.0 | -66.8 | -67.9 |
| Experimental | -59 | -69 | ||||
Table 4 δisoSivalues of Q0 and Q1 species in binary sodium silicate model clusters with polymolecular structure calculated by different basis sets in ab initio method
| Method | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1Q0 | 4Q0 | 8Q0 | 1Q1 | 4Q1 | 8Q1 | |
| Calculated | -36 | -57 | -58.2 | -64.0 | -66.8 | -67.9 |
| Experimental | -59 | -69 | ||||
| [1] | Hanner M. S., Spa. Sci.Rev., Springer, Netherlands, 1999, 90(1/2), 99—108 |
| [2] | Gao H.B., Zhang Z.F., Principle of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Experimental Method(Essence), Wuhan University Press, Wuhan, 2008, 296—308 |
| (高汉宾, 张振芳. 核磁共振原理与实验方法(精), 武汉: 武汉大学出版社, 2008, 296—308) | |
| [3] | Eckert H., Prog. N. M. R. Spectro., 1992, 24(3), 159—293 |
| [4] | Sen S., Youngman R. E., J. Non-Crys. Sol.,2003, 331(1), 100—107 |
| [5] | Mahler J., Sebald A., Sol. Sta. N. M. R.,1995, 5(1), 63—64 |
| [6] | Maekawa H., Maekawa T., Kawamura K., J. Non-Crys. Sol.,1991, 127(1), 53—64 |
| [7] | Zhang P., Philip J., Stebbins J. F., J. Phys. Chem. B,1997, 101(20), 4004—4008 |
| [8] | Glock K., Hirsch O., Rehak P., J. Non-Crys. Sol.,1998, 232(10), 113—118 |
| [9] | Olivier L., Yuan X., Cormack A. N., J. Non-Crys. Sol.,2001, 293(1), 53—66 |
| [10] | Wang C. Y., You J. L., Wang Y. Y., Chinese J. Lig. Scat.,2014, 26(4), 350—355 |
| (王晨阳, 尤静林, 王媛媛. 光散射学报, 2014, 26(4), 350—355) | |
| [11] | Azizi S. N., Rostami A. A., Godarzian A., J. Phys. Soc. Jap.,2005, 74(5), 1609—1620 |
| [12] | You J. L., Jiang G. C., Hou H. Y., J. Raman Spectro.,2005, 36(3), 237—249 |
| [13] | Masanori M., Masaki A., Mol. Sim.,1991, 6(4—6), 239—244 |
| [14] | Zeng H., You J. L., Cheng H., Jiang G. C., Chinese J. Inorg.Chem.,2006, 22(6), 1023—1027 |
| (曾昊, 尤静林, 陈辉. 无机化学学报, 2006, 22(6), 1023—1027) | |
| [15] | Wang P., Pan Z.L., Weng L.B., System Mineralogy(Album), Geolog Publishing House, Beijing, 1984, 206—236 |
| (王濮, 潘兆橹, 翁玲宝. 系统矿物学(中册), 北京: 地质出版社, 1984, 206—236) | |
| [16] | Engelhardt S., Hein L., Wiesmann F., Lohse M. J., Pro. Nat. Aca. Sci.,1999, 96(12), 7059—7064 |
| [17] | Farnan I., Grandinetti P. J., Baltisberger J. H., Nature,1992, 358(6381), 31—35 |
| [18] | Charpentier T., Ispas S., Profeta M., J. Phys. Chem. B,2004, 108(13), 4147—4161 |
| [19] | Pant A. K., Cruickshank D. W. J., Acta Crys.,1968, 24(1), 13—19 |
| [20] | Pant A., Acta Crys. B, Stru. Crys. Crys. Chem., 1968, 24(8), 1077—1083 |
| [21] | Amour H., Denner W., Schulz H., Acta Crys. Sec. B: Stru. Crys. and Crys.Chem.,1979, 35(3), 550—555 |
| [22] | Takéuchi Y., Ghose S., Nowacki W., Zeit. F. Kris.,1965, 121(5), 321—348 |
| [23] | Dupree R., Holland D., McMillan P. W., Pettifer R., J. Non-Crys. Sol.,1984, 68(2), 399—410 |
| [24] | Grimmer A. R., Von Lampe F., Tarmak M., Chem. Phys. Lett., 1983, 97(2), 185—187 |
| [25] | Stebbins J. F., Zhao P., Lee S. K., Cheng X., Amer. Miner.,1999, 84(10), 1680—1684 |
| [26] | Tsvetkov E., Davydov A., Ancharov A., Yudaev I., J. Crys. Gro.,2006, 294(1), 22—28 |
| [27] | Tossell J. D., Rev. Miner. Geochem., 2001, 42(1), 437—458 |
| [28] | You J. L., Jiang G. C., Hou H. Y., Wu Y. Q., Xu K. D., Chinese Phys. Lett., 2004, 21(4), 640—641 |
| [29] | Wang W. F., Tan J., You J. L., Zhao S. R., Zhang D., Jiang G. C., J. Chinese Cer. Soc.,2003, 1(31), 41—46 |
| (王卫锋, 谭劲, 尤静林, 赵珊茸, 张德, 蒋国昌. 中国硅酸盐学会, 2003, 1(31), 41—46) |
| [1] | 赵润瑶, 纪桂鹏, 刘志敏. 吡咯氮配位单原子铜催化剂的电催化二氧化碳还原性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220272. |
| [2] | 李志光, 齐国栋, 徐君, 邓风. Sn-Al-β分子筛酸性在葡萄糖转化反应中作用的固体NMR研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220138. |
| [3] | 张伶育, 张继龙, 曲泽星. RDX分子内振动能量重分配的动力学研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220393. |
| [4] | 王美银, 黄道丰, 陈欣, 周俊夫, 任远航, 叶林, 岳斌, 贺鹤勇. 介孔磷钨酸铯盐的液相组装及酸性研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2734. |
| [5] | 张志兰, 王宁, 唐丹丹, 舒婕, 李晓虹. 固体核磁共振Multiple-CP定量技术的参数优化与应用研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(3): 784. |
| [6] | 赵淑芳, 黄骏. 分子筛材料的酸性和择形选择性的固体核磁共振研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(1): 165. |
| [7] | 叶晓栋, 齐国栋, 徐君, 邓风. Au负载SBA-15分子筛上葡萄糖氧化反应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(5): 960. |
| [8] | 肖宇情,李申慧,汤晶,徐君,邓风. 金属有机框架材料的结构、 动力学行为和主客体相互作用的固体核磁共振研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(2): 204. |
| [9] | 赵星岭, 齐国栋, 王强, 褚月英, 高伟, 李申慧, 徐君, 邓风. Ga改性Ga/ZSM-5分子筛的结构、 性质及其催化丙烷芳构化的固体核磁共振波谱研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(12): 2681. |
| [10] | 徐琰东,尤静林,王建,龚晓晔,丁雅妮,曹培明,郑少波,吴永全,余仲达. Bi4B2O9晶体及其熔体结构的高温原位拉曼光谱研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(10): 2143. |
| [11] | 顾佳丽, 张田田, 赵辉鹏, 舒婕, 李晓虹. 耗时短、 通用性强的固体核磁共振交叉极化定量检测方法[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(3): 463. |
| [12] | 方升, 刘静静, 段雪梅, 陶福明, 刘靖尧. 大气中一元酸催化亚硫酸分解反应的从头算及动力学研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(8): 1390. |
| [13] | 陈德利, 杨鹏勇, 武胜男, 何思慧, 王芳芳. 从头算分子动力学模拟Pd团簇负载UiO-66材料结构及稳定性[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(7): 1210. |
| [14] | 于泳博, 刘翠, 宫利东. 从头算和ABEEMσπ/MM对(CH3OH)n(n=3~12)和[Na(CH3OH)n]+(n=3~6)体系的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(8): 1468. |
| [15] | 仓玉萍, 陈东, 杨帆, 杨慧明. 氮化锗多形体的四方、 单斜和正交畸变的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(4): 674. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||