

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (2): 386.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140908
收稿日期:2014-10-11
出版日期:2015-02-10
发布日期:2015-01-06
作者简介:联系人简介: 苑世领, 男, 博士, 教授, 主要从事驱油体系的分子模拟研究. E-mail: 基金资助:
MA Ying, ZHANG Heng, YUAN Shiling*( )
)
Received:2014-10-11
Online:2015-02-10
Published:2015-01-06
Contact:
YUAN Shiling
E-mail:shilingyuan@sdu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
部分水解的预交联凝胶型聚丙烯酰胺在水溶液中的吸水溶胀能对油藏高渗透区域产生有效封堵, 有利于提高驱油效率. 分子模拟结果表明, 凝胶颗粒的溶胀主要归因于侧链亲水基团在水溶液中的水化作用, 这些带负电的亲水基团中心原子通过氢键和静电作用在其周围极化出一层排列规整、 有序而紧密的水化层, 并将水分子束缚其中; 同时水化层内的水分子之间依赖氢键网络促进水化层的稳定. 本文从微观结构、 动力学和氢键等方面比较了各亲水基团中心原子的水化能力, 发现—COO-官能团具有较强的束缚水分子的能力, 对水化层的稳定有重要影响.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
马莹, 张恒, 苑世领. 部分水解的预交联凝胶型聚丙烯酰胺的水化层结构. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(2): 386.
MA Ying, ZHANG Heng, YUAN Shiling. Hydration Structure of Partially Hydrolyzed Preformed Particle Gel†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(2): 386.
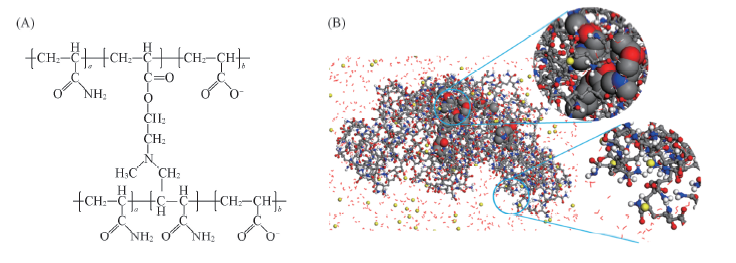
Fig.1 Scheme of cross-linked partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide and conformations of simulation (A) Scheme of cross-linked partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide; (B) initial conformation of mutually linked polymer network for molecular dynamics(MD) simulation with enlarged hydrophobic linker(in CPK model) and hydrophilic chains.
| Group | σ/nm | ε/(kJ·mol-1) | q/e |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH3 | 0.379 | 0.753 | 0 |
| CH2 | 0.395 | 0.586 | 0 |
| CH | 0.423 | 0.544 | 0 |
| C(CONH2) | 0.336 | 0.406 | 0.38 |
| O(CONH2) | 0.263 | 1.725 | -0.38 |
| N(CONH2) | 0.298 | 0.877 | -0.48 |
| H(CONH2) | 0 | 0 | 0.24 |
| C(COO-) | 0.336 | 0.406 | 0.27 |
| O(COO-) | 0.263 | 1.725 | -0.635 |
Table 1 Force field parameters for PPG used in this work*
| Group | σ/nm | ε/(kJ·mol-1) | q/e |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH3 | 0.379 | 0.753 | 0 |
| CH2 | 0.395 | 0.586 | 0 |
| CH | 0.423 | 0.544 | 0 |
| C(CONH2) | 0.336 | 0.406 | 0.38 |
| O(CONH2) | 0.263 | 1.725 | -0.38 |
| N(CONH2) | 0.298 | 0.877 | -0.48 |
| H(CONH2) | 0 | 0 | 0.24 |
| C(COO-) | 0.336 | 0.406 | 0.27 |
| O(COO-) | 0.263 | 1.725 | -0.635 |
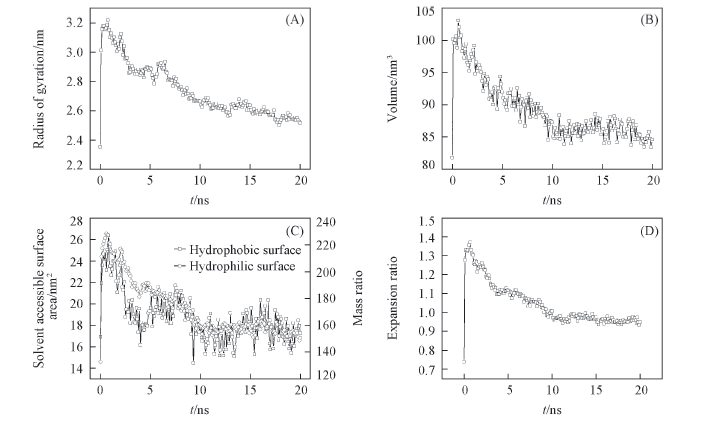
Fig.2 Conformation change of PPG during swelling (A) Radius of gyration; (B) volume; (C) hydrophilic and hydrophobic solvent access surface area; (D) expansion ratio.
| Certain atom of hydrophilic groups | 105 Diffusion coefficient, D/(cm2·s-1) | Residence time, τr/ps |
|---|---|---|
| O(COO-) | 2.95 | 13.78 |
| O(CONH2) | 3.25 | 6.58 |
| N(CONH2) | 3.50 | 10.71 |
| Bulk water[ | 3.58 | 4.40 |
Table 2 Dynamic properties of water around certain atoms of hydrophilic groups
| Certain atom of hydrophilic groups | 105 Diffusion coefficient, D/(cm2·s-1) | Residence time, τr/ps |
|---|---|---|
| O(COO-) | 2.95 | 13.78 |
| O(CONH2) | 3.25 | 6.58 |
| N(CONH2) | 3.50 | 10.71 |
| Bulk water[ | 3.58 | 4.40 |
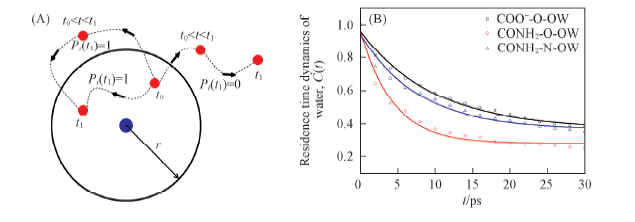
Fig.4 Residence time of water around certain atoms of hydrophilic groups (A) Illustration of definition of Pi, Pi(t1)=1 when water molecule in the first shell at t0 and t1. The location of water molecule during t0—t1 does not count; (B) time correlation functions of water around certain atoms of hydrophilic groups.
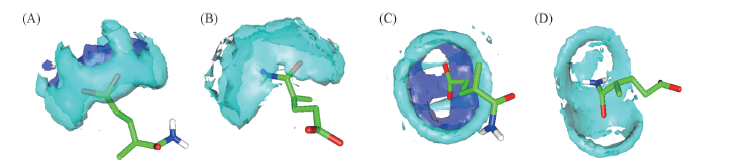
Fig.5 Spatial distributions of water and ions around certain atoms of hydrophilic groups(A, C) Spatial distribution of water and Na+ around —COO-; (B, D) spatial distribution of water around CONH2
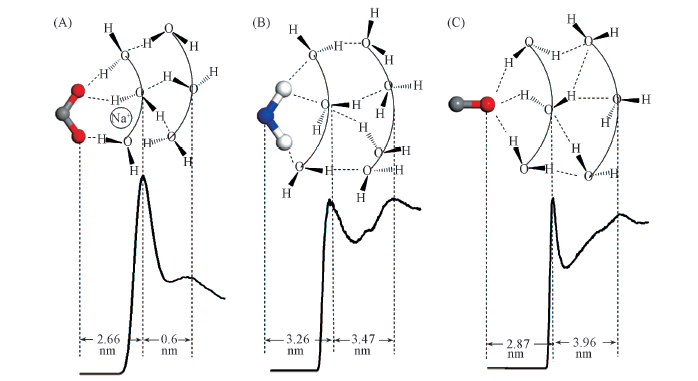
Fig.6 Radial distribution functions between certain atoms of hydrophilic groups and water molecules and scheme of hydrogen bond structure in hydration shells around them (A) gCOO-OW(r); (B) gN(CONH2)-OW(r); (C) gO(CONH2)-OW(r).
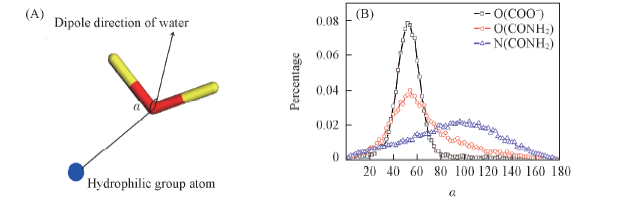
Fig.7 Definitions of α(A) and dipole orientation distribution of water molecules in the first hydration shell of certain atoms of hydrophilic groups(B)
| Certain atom of hydrophilic groups | Number of H bonds | Life time/ps | Dipole reorientation residence time, τμ/ps |
|---|---|---|---|
| O(COO-) | 1.64 | 10.20 | 6.17 |
| O(CONH2) | 1.33 | 1.75 | 4.68 |
| N(CONH2) | 1.14 | 1.11 | 4.28 |
Table 3 Hydrogen bond properties around certain atoms of hydrophilic groups
| Certain atom of hydrophilic groups | Number of H bonds | Life time/ps | Dipole reorientation residence time, τμ/ps |
|---|---|---|---|
| O(COO-) | 1.64 | 10.20 | 6.17 |
| O(CONH2) | 1.33 | 1.75 | 4.68 |
| N(CONH2) | 1.14 | 1.11 | 4.28 |
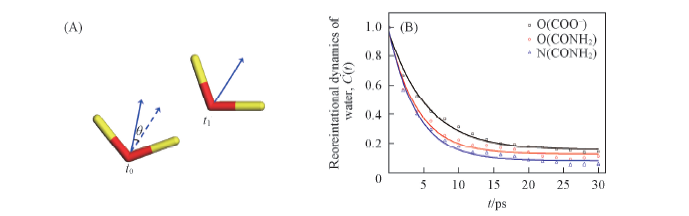
Fig.9 Illustration of angle between water dipole vectors(A) and reorientation autocorrelation functions of water around certain atoms of hydrophilic groups(B)
| [1] | Xiao L., Guo Y., Wang R., Lv S., Zhang Y. L., Luo Y. F., Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2009, 23(6), 99—102 |
| 、(肖磊, 郭艳, 王锐, 吕帅, 张伊琳, 罗艳芳. 石油地质与工程, 2009, 23(6), 99—102) | |
| [2] | Deng S. F., Wei F. L., Wu M., Liang J., Advances in Fine Petrochemicals, 2011, 12(9), 17—20 |
| 、(邓生富, 魏发林, 吴蒙, 梁杰. 精细石油化工进展, 2011, 12(9), 17—20) | |
| [3] | Zhou Y. X., Hou T. J., Guo J. H., Sun J., Li X. D., Wang X., Zhang B., Advances in Fine Petrochemicals, 2005, 5(12), 22—2 |
| 、4(周亚贤, 侯天江, 郭建华, 孙举, 李旭东, 王旭, 张滨. 精细石油化工进展, 2005, 5(12), 22—24) | |
| [4] | Liu Y. Y., Chen P. K., Luo J. H., Zhou G., Jiang B., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2010, 26(11), 2907—2914 |
| 、(刘艳艳, 陈攀科, 罗健辉, 周歌, 江波. 物理化学学报, 2010, 26(11), 2907—2914) | |
| [5] | Jia H., Pu W. F., Zhao J. Z., Liao R., Energ. Fuel., 2011, 25(2), 727—736 |
| [6] | Jia H., Ren Q., Zhao J., Energ. Fuel., 2014, 28(11), 6735—6744 |
| [7] | Jia H., Zhao J. Z., Jin F. Y., Pu W. F., Li Y. M., Li K. X., Li J. M., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2012, 51(38), 12155—12166 |
| [8] | Bai B. J., Li L. X., Liu Y. Z., Liu H., Wang Z. G., You C. M., SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng., 2007, 10(4), 415—422 |
| [9] | Bai B. J., Zhang H., SPE J., 2011, 16(2), 388—400 |
| [10] | Wang J., Liu H. Q., Wang Z. L., Xu J., Yuan D. Y., J. Petrol. Sci. Eng., 2013, 112, 248—257 |
| [11] | Ma J., Liang B., Cui P., Dai H., Huang R., Polymer, 2003, 44(4), 1281—1286 |
| [12] | Feng Y., Grassl B., Billon L., Khoukh A., François J., Polym. Int., 2002, 51(10), 939—947 |
| [13] | Wang Y. Y., Dai Y. H., Zhang L., Luo L., Chu Y. P., Zhao S., Li M. Z., Wang E. J., Yu J. Y., Macromolecules, 2004, 37(8), 2930—2937 |
| [14] | Feng Y., Billon L., Grassl B., Bastiat G., Borisov O., François J., Polymer, 2005, 46(22), 9283—9295 |
| [15] | Feng Y., Billon L., Grassl B., Khoukh A., François J., Polymer, 2002, 43(7), 2055—2064 |
| [16] | Xue W., Hamley I. W., Castelletto V., Olmsted P. D., Eur. Polym. J., 2004, 40(1), 47—56 |
| [17] | Shashkina Y. A., Zaroslov Y. D., Smirnov V., Philippova O., Khokhlov A., Pryakhina T., Churochkina N., Polymer, 2003, 44(8), 2289—2293 |
| [18] | Sheng Y. Z., Yang H., Li J. Y., Sun M., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2013, 29(4), 788—792 |
| [19] | Kong C. P., Zhang H. X., Zhao Z. X., Zhong Q. C., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2013, 29(3), 545—550 |
| [20] | Netz P. A., Dorfmüller T., J. Phys. Chem. B, 1998, 102(25), 4875—4886 |
| [21] | Chen P., Yao L., Liu Y., Luo J., Zhou G., Jiang B., J. Mol. Model., 2012, 18(7), 3153—3160 |
| [22] | Yuan R., Li Y., Li C., Fang H., Wang W., Colloid. Surface. A, 2013, 434, 16—24 |
| [23] | Wang H. X., Yao L., Ding B., Luo J. H., Zhou G., Jiang B., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(5), 1295—1302 |
| (王惠厦, 姚林, 丁彬, 罗健辉, 周歌, 江波.高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(5), 1295—1302) | |
| [24] | Schuler L. D., Daura X., van Gunsteren W. F., J. Comput. Chem., 2001, 22(11), 1205—1218 |
| [25] | Hess B., Kutzner C., van der Spoel D., Lindahl E., J. Chem. Theory Comp., 2008, 4(3), 435—477 |
| [26] | Oldiges C., Tönsing T., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2002, 4(9), 1628—1636 |
| [27] | Sulatha M. S., Natarajan U., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2011, 50(21), 11785—11796 |
| [28] | Brandsen H., Postma J., van Gunstern E., Hermans J., Pullman B., Intermolecular Force, Reidel, Dordrecht, 1981 |
| [29] | Essmann U., Perera L., Berkowitz M. L., Darden T., Lee H., Pedersen L. G., J. Chem. Phys., 1995, 103(19), 8577—8593 |
| [30] | Berendsen H. J., Postma J. P. M., van Gunsteren W. F., DiNola A., Haak J., J. Chem. Phys., 1984, 81(8), 3684—3690 |
| [31] | Hess B., Bekker H., Berendsen H. J., Fraaije J. G., J. Comput. Chem., 1997, 18(12), 1463—1472 |
| [32] | Liu S. R., Kang W. L., Bai B. J., Zhao H. Y., Meng L. W., Journal of China University of Petroleum(Natural Science), 2013, 37(2), 153—157(刘述忍, 康万利, 白宝君, 赵昊阳, 孟令伟. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 37(2), 153—157) |
| [33] | Zhang H., Wang H., Lin C.G., Wang L., Yuan S. L.,Acta Chim. Sin., 2013, (4), 649—656 |
| (张恒, 王华, 蔺存国, 王利, 苑世领. 化学学报, 2013, (4), 649—656) | |
| [34] | Shao Q., He Y., White A. D., Jiang S., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2010, 114(49), 16625—16631 |
| [35] | He Y., Hower J., Chen S., Bernards M. T., Chang Y., Jiang S., Langmuir, 2008, 24(18), 10358—10364 |
| [36] | He Y., Chang Y., Hower J. C., Zheng J., Chen S., Jiang S., Phys. Chem. Chem.Phys., 2008, 10(36), 5539—5544 |
| [37] | Hower J. C., He Y., Bernards M. T., Jiang S., J. Chem. Phys., 2006, 125(21), 214704 |
| [38] | Rasaiah J. C., Noworyta J. P., Koneshan S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2000, 122(45), 11182—11193 |
| [39] | Shao Q., Zhou J., Lu L., Lu X., Zhu Y., Jiang S., Nano Lett., 2009, 9(3), 989—994 |
| [40] | Zhou J., Lu X., Wang Y., Shi J., Fluid Phase Equilibr., 2002, 194, 257—270 |
| [41] | Shao Q., Huang L., Zhou J., Lu L., Zhang L., Lu X., Jiang S., Gubbins K. E., Shen W., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2008, 10(14), 1896—1906 |
| [42] | Bandyopadhyay S., Chakraborty S., Bagchi B., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127(47), 16660—16667 |
| [43] | Guardia E., Martí J., García-Tarrés L., Laria D., J. Mol. Liq., 2005, 117(1), 63—67 |
| (Ed.: D, Z) |
| [1] | 高志伟, 李军委, 史赛, 付强, 贾钧儒, 安海龙. 基于分子动力学模拟的TRPM8通道门控特性分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [2] | 胡波, 朱昊辰. 双层氧化石墨烯纳米体系中受限水的介电常数[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [3] | 雷晓彤, 金怡卿, 孟烜宇. 基于分子模拟方法预测PIP2在双孔钾通道TREK-1上结合位点的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2550. |
| [4] | 李聪聪, 刘明皓, 韩佳睿, 朱镜璇, 韩葳葳, 李婉南. 基于分子动力学模拟的VmoLac非特异性底物催化活性的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2518. |
| [5] | 雒春辉, 赵宇斐. 强韧抗溶胀水凝胶的简单构筑及性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 2024. |
| [6] | 曾永辉, 言天英. 质子水合结构的振动态密度分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1855. |
| [7] | 齐人睿, 李明昊, 常浩, 付学奇, 高波, 韩葳葳, 韩璐, 李婉南. 基于拉伸分子动力学模拟的黄嘌呤氧化酶抑制剂解离途径的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(3): 758. |
| [8] | 刘爱清, 徐文生, 徐晓雷, 陈继忠, 安立佳. 高分子/棒状纳米粒子复合物的分子动力学模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(3): 875. |
| [9] | 王蔓, 王鑫, 周静, 高国华. 聚离子液体催化碳酸乙烯酯与甲醇的酯交换反应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(12): 3701. |
| [10] | 瞿思颖, 徐沁. 凝血因子Xa的S4口袋部分关键残基对利伐沙班结合的不同作用机制[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(9): 1918. |
| [11] | 马玉聪, 樊保民, 王满曼, 杨彪, 郝华, 孙辉, 张慧娟. 曲唑酮的两步法制备及对碳钢的缓蚀机理[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(8): 1706. |
| [12] | 孙浩帆, 张凌怡, PATRICKNorman, 张维冰. 二芳基乙烯衍生物与DNA结合的分子动力学研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(6): 1229. |
| [13] | 张璋, 王栋, 王晓雷, 徐岩. 华根霉脂肪酶有机相酯合成活性的重塑[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(4): 747. |
| [14] | 马兰, 容婧婧, 朱有亮, 黄以能, 孙昭艳. 软胶体粒子形成束晶的动力学模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(1): 195. |
| [15] | 吴红枚, 李惠婷, 李永成, 王宏青, 王孟. 基于基团贡献法和分子动力学预测聚间苯二甲酰对苯二胺的玻璃化转变温度[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(1): 180. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||