

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (6): 1311.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20131185
周晓峰1, 谢小露2, 张蕾2, 李春华2( ), 楼姣英3, 刘乃波1, 丁振山1(
), 楼姣英3, 刘乃波1, 丁振山1( )
)
收稿日期:2013-12-05
出版日期:2014-06-10
发布日期:2014-04-29
作者简介:联系人简介: 李春华, 女, 博士, 教授, 主要从事计算分子生物学与生物信息学研究. E-mail:基金资助:
ZHOU Xiaofeng1, XIE Xiaolu2, ZHANG Lei2, LI Chunhua2,*( ), LOU Jiaoying3, LIU Naibo1, DING Zhenshan1,*(
), LOU Jiaoying3, LIU Naibo1, DING Zhenshan1,*( )
)
Received:2013-12-05
Online:2014-06-10
Published:2014-04-29
Contact:
LI Chunhua,DING Zhenshan
E-mail:chunhuali@bjut.edu.cn;dzsfighting@sina.com
Supported by:摘要:
基于弹性网络模型的热力学方法, 识别出麦芽糖转运蛋白质体系中的关键残基, 探讨了麦芽糖转运蛋白内长程协同效应, 研究结果有助于更好地理解该转运体系发挥生物学功能的分子机制.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
周晓峰, 谢小露, 张蕾, 李春华, 楼姣英, 刘乃波, 丁振山. 基于弹性网络模型的麦芽糖转运蛋白功能残基的识别. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(6): 1311.
ZHOU Xiaofeng, XIE Xiaolu, ZHANG Lei, LI Chunhua, LOU Jiaoying, LIU Naibo, DING Zhenshan. Idenpngication of Functional Residues in Maltose Transporter with the Elastic Network Model†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(6): 1311.
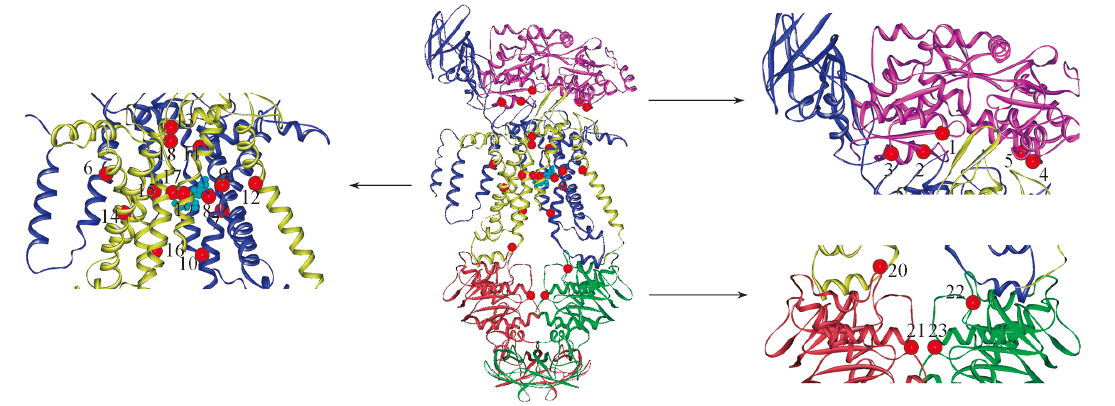
Fig.5 Key residues mapped onto the protein structureThe ball represents the location of the central residue of each residue cluster. The cluster number is the same as that in Fig.3.
| [1] | Jones P. M., George A. M., Cell Mol. Life Sci., 2004, 61(6), 682—699 |
| [2] | Rees D. C., Johnson E., Lewinson O., Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2009, 10(3), 218—227 |
| [3] | Locher K. P., Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B., 2009, 364(1514), 239—245 |
| [4] | Oldham M. L., Khare D., Quiocho F. A., Davidson A. L., Chen J., Nature, 2007, 450(7169), 515—521 |
| [5] | Oldham M. L., Chen J., Science, 2011, 332(6034), 1202—1205 |
| [6] | Oldham M. L., Chen J., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2011, 108(37), 15152—15156 |
| [7] | Hegedüs T., Gyimesi G., Gáspár M. E., Szalay K. Z., Gangal R., Csermely P., Curr. Pharm. Des., 2013, 19, 4155—4172 |
| [8] | Riordan J. R., Rommens J. M., Kerem B., Alon N., Rozmahel R., Grzelczak Z., Zielenski J., Lok S., Plavsic N., Chou J. L., Science, 1989, 245(4922), 1066—1073 |
| [9] | Mosser J., Douar A. M., Sarde C. O., Kioschis P., Feil R., Moser H., Poustka A. M., Mandel J. L., Aubourg P., Nature, 1993, 361(6414), 726—730 |
| [10] | Szakács G., Váradi A., Özvegy-Laczka C., Sarkadi B., Drug Discov. Today, 2008, 13(9/10), 379—393 |
| [11] | Dror R. O., Dirks R. M., Grossman J. P., Xu H., Shaw D. E., Annu. Rev. Biophys., 2012, 41, 429—452 |
| [12] | Isralewitz B., Gao M., Schulten K., Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 2001, 11(2), 224—230 |
| [13] | Ma J., Karplus M., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1997, 94(22), 11905—11910 |
| [14] | Sugita Y., Okamoto Y., Chem. Phys. Lett., 1999, 314, 141—151 |
| [15] | Zhang Z., Shi Y., Liu H., Biophys. J., 2003, 84(6), 3583—3593 |
| [16] | Haliloglu T., Bahar I., Erman B., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1997, 79, 3090—3093 |
| [17] | Bahar I., Rader A. J., Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 2005, 15(5), 586—592 |
| [18] | Li J. L., Geng C. Y., Bu Y. X., Chen X. H., Wang J., Huang X. R., Sun C. C., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(10), 2055—2058 |
| (李吉来, 耿彩云, 步宇翔, 陈效华, 王军, 黄旭日, 孙家锺.高等学校化学学报, 2009,30(10), 2055—2058) | |
| [19] | Atilgan C., Atilgan A. R., PLoS. Comput. Biol., 2009, 5(10), e1000544-1—e1000544-14 |
| [20] | Zheng W., Brooks B. R., Thirumalai D., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2006, 103(20), 7664—7669 |
| [21] | Ming D., Cohn J. D., Wall M. E., BMC Struct. Biol., 2008, 8, 5 |
| [22] | Su J. G., Xu X. J., Li C. H., Chen W. Z., Wang C. X., J. Chem. Phys., 2011, 135(17), 174101-1—174101-10 |
| [23] | Ehrle R., Pick C., Ulrich R., Hofmann E., Ehrmann M., J. Bacteriol., 1996, 178(8), 2255—2262 |
| [24] | Steinke A., Grau S., Davidson A., Hofmann E., Ehrmann M., J. Bacteriol., 2001, 183(1), 375—381 |
| [25] | Grote M., Polyhach Y., Jeschke G., Steinhoff H. J., Schneider E., Bordignon E., J. Biol. Chem., 2009, 284(26), 17521—17526 |
| [26] | Michael L., Oldham Jue C., Science, 2011, 332, 1202—1205 |
| [27] | Hor L. I., Shuman H. A., J. Mol. Biol., 1993, 233(4), 659—670 |
| [28] | Shilton B. H., Biochimica. et Biophysica. Acta, 2008, 1778, 1772—1780 |
| [29] | Daus M. L., Grote M., Müller P., Doebber M., Herrmann A., Steinhoff H. J., Dassa E., Schneider E., J. Biol. Chem., 2007, 282(31), 22387—22396 |
| [30] | Hunke S., Mourez M., Jéhanno M., Dassa E., Schneider E., J. Biol. Chem., 2000, 275(20), 15526—15534 |
| [31] | Loo T. W., Bartlett M. C., Clarke D. M., J. Biol. Chem., 2002, 277(44), 41303—41306 |
| [32] | UrbatschI. L., Gimi K., Wilke-Mounts S., Senior A. E., Biochemistry, 2000, 39(39), 11921—11927 |
| [33] | Dalmas O., Orelle C., Foucher A. E., Geourjon C., Crouzy S., Pietro A. D., Jault J. M., J. Biol. Chem., 2005, 280(44), 36857—36864 |
| [34] | Grote M., Bordignon E., Polyhach Y., Jeschke G., Steinhoff H. J., Schneider E., Biophys. J., 2008, 95(6), 2924—2938 |
| [35] | Oldham M. L., Khare D., Quiocho F. A., Davidson A. L., Chen J., Nature, 2007, 450, 515—521 |
| [36] | Hunke S., Landmesser H., Schneider E., J. Bacteriol., 2000, 182(5), 1432—1436 |
| [1] | 张咪, 田亚锋, 高克利, 侯华, 王宝山. 三氟甲基磺酰氟绝缘介质理化特性的分子动力学模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220424. |
| [2] | 刘洋, 李旺昌, 张竹霞, 王芳, 杨文静, 郭臻, 崔鹏. Sc3C2@C80与[12]CPP纳米环之间非共价相互作用的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220457. |
| [3] | 王思佳 侯璐 李成龙 李文翠 陆安慧. 空腔型纳米炭的制备与应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220637. |
| [4] | 武晴滢, 祝震予, 吴剑鸣, 徐昕. 泛Kennard-Stone算法的数据集代表性度量与分块采样策略[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220397. |
| [5] | 王园月, 安梭梭, 郑旭明, 赵彦英. 5-巯基-1, 3, 4-噻二唑-2-硫酮微溶剂团簇的光谱和理论计算研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220354. |
| [6] | 张伶育, 张继龙, 曲泽星. RDX分子内振动能量重分配的动力学研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220393. |
| [7] | 沈琦 陈海瑶 高登辉 赵 熹 那日松 刘佳 黄旭日. 天然产物法卡林二醇与人类 GABAA 受体的相互作用机制研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 0. |
| [8] | 陈少臣 程敏 王诗慧 吴金奎 罗磊 薛小雨 吉旭 张长春 周利. 预测金属有机骨架的甲烷和氢气输送能力的迁移学习建模[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220459. |
| [9] | 彭辛哲, 葛娇阳, 王访丽, 余国静, 冉雪芹, 周栋, 杨磊, 解令海. 一种基于苯并噻吩平面格的张力与重组能的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220313. |
| [10] | 郭程, 张威, 唐云. 有序介孔材料: 历史、 现状与发展趋势[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220167. |
| [11] | 汤乔伟 蔡小青 李江 诸颖 王丽华 田阳 樊春海 胡钧. 同步辐射X射线成像技术在脑成像研究中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220379. |
| [12] | 杨丹, 刘旭, 戴翼虎, 祝艳, 杨艳辉. 金团簇电催化二氧化碳还原反应的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220198. |
| [13] | 戴卫, 侯华, 王宝山. 七氟异丁腈负离子结构与反应活性的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220044. |
| [14] | 施耐克, 张娅, SANSON Andrea, 王蕾, 陈骏. Zn(NCN)单轴的负热膨胀性及机理研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220124. |
| [15] | 任娜娜, 薛洁, 王治钒, 姚晓霞, 王繁. 热力学数据对1, 3-丁二烯燃烧特性的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220151. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||