

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 115.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180551
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LUO Wei1, FANG Lei1, MENG Yue2, XUE Jilong1, CHEN Tao1, XIA Shengjie1,*, NI Zheming1,*( )
)
Received:2018-08-03
Online:2019-01-10
Published:2018-12-06
Contact:
XIA Shengjie,NI Zheming
E-mail:xiasj@zjut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LUO Wei,FANG Lei,MENG Yue,XUE Jilong,CHEN Tao,XIA Shengjie,NI Zheming. Theoretical Study on Adsorption of α,β-Unsaturated Aldehydes on Ni-Pt(111) Surface†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 115.
| Molecule | ΔE/(kJ·mol-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-(s)-trans | E-(s)-cis | Z-(s)-trans | Z-(s)-cis | |
| Crotonaldehyde | 0 | 8.46 | 10.73 | 14.92 |
| Cinnamaldehyde | 0 | 7.82 | 18.64 | 23.07 |
Table 1 Relative energy of unsaturated aldehyde models
| Molecule | ΔE/(kJ·mol-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-(s)-trans | E-(s)-cis | Z-(s)-trans | Z-(s)-cis | |
| Crotonaldehyde | 0 | 8.46 | 10.73 | 14.92 |
| Cinnamaldehyde | 0 | 7.82 | 18.64 | 23.07 |
| Species | Adsorption site | Eads /(kJ·mol-1) | Species | Adsorption site | Eads /(kJ·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crotonaldehyde | Cinnamaldehyde | Crotonaldehyde | Cinnamaldehyde | ||||
| O | top | 47.15 | 69.70 | C=O, C=C | top-hcp | 61.58 | 98.80 |
| bri | 44.81 | 75.99 | top-fcc | 61.37 | 98.52 | ||
| hcp | 44.52 | 85.77 | bri-top | 61.92 | 99.21 | ||
| fcc | 45.20 | 76.33 | bri-bri | 61.50 | 98.82 | ||
| C=C | top | 60.59 | 96.81 | bri-hcp | 58.57 | 98.72 | |
| bri | 61.86 | 98.42 | bri-fcc | 61.92 | 98.61 | ||
| hcp | 61.43 | 97.76 | hcp-top | 61.94 | 99.10 | ||
| fcc | 60.70 | 97.93 | hcp-bri | 61.86 | 98.93 | ||
| C=O | top | 60.96 | 97.81 | hcp-hcp | 61.66 | 98.79 | |
| bri | 61.78 | 96.16 | hcp-fcc | 61.68 | 98.60 | ||
| hcp | 61.60 | 98.54 | fcc-top | 61.60 | 98.70 | ||
| fcc | 60.19 | 97.93 | fcc-bri | 61.71 | 98.80 | ||
| C=O, C=C | top-top | 60.98 | 98.24 | fcc-hcp | 62.32 | 98.38 | |
| top-bri | 61.84 | 98.56 | fcc-fcc | 59.49 | 99.85 | ||
Table 2 Adsorption energy(Eads) of unsaturated aldehyde molecules on Ni-Pt(111) surface
| Species | Adsorption site | Eads /(kJ·mol-1) | Species | Adsorption site | Eads /(kJ·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crotonaldehyde | Cinnamaldehyde | Crotonaldehyde | Cinnamaldehyde | ||||
| O | top | 47.15 | 69.70 | C=O, C=C | top-hcp | 61.58 | 98.80 |
| bri | 44.81 | 75.99 | top-fcc | 61.37 | 98.52 | ||
| hcp | 44.52 | 85.77 | bri-top | 61.92 | 99.21 | ||
| fcc | 45.20 | 76.33 | bri-bri | 61.50 | 98.82 | ||
| C=C | top | 60.59 | 96.81 | bri-hcp | 58.57 | 98.72 | |
| bri | 61.86 | 98.42 | bri-fcc | 61.92 | 98.61 | ||
| hcp | 61.43 | 97.76 | hcp-top | 61.94 | 99.10 | ||
| fcc | 60.70 | 97.93 | hcp-bri | 61.86 | 98.93 | ||
| C=O | top | 60.96 | 97.81 | hcp-hcp | 61.66 | 98.79 | |
| bri | 61.78 | 96.16 | hcp-fcc | 61.68 | 98.60 | ||
| hcp | 61.60 | 98.54 | fcc-top | 61.60 | 98.70 | ||
| fcc | 60.19 | 97.93 | fcc-bri | 61.71 | 98.80 | ||
| C=O, C=C | top-top | 60.98 | 98.24 | fcc-hcp | 62.32 | 98.38 | |
| top-bri | 61.84 | 98.56 | fcc-fcc | 59.49 | 99.85 | ||
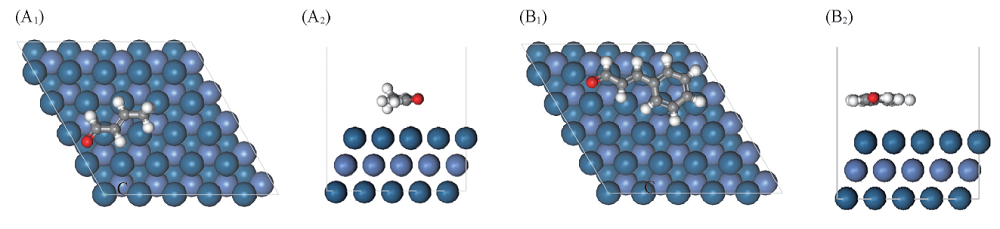
Fig.3 Top(A1, B1) and side(A2, B2) views of the most stable adsorption configuration for crotonaldehyde(A1, A2) and cinnamaldehyde(B1, B2) on Ni-Pt(111) surface
| Crotonaldehyde | d1/nm | d2/nm | d3/nm | d4/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | 0.1271 | 0.1429 | 0.1393 | 0.1481 |
| fcc-hcp | 0.1269 | 0.1435 | 0.1396 | 0.1480 |
| Δd/nm | 0.0002 | 0.0006 | 0.0003 | 0.0001 |
Table 3 Structure parameters of crotonaldehyde for the most stable adsorption configuration*
| Crotonaldehyde | d1/nm | d2/nm | d3/nm | d4/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | 0.1271 | 0.1429 | 0.1393 | 0.1481 |
| fcc-hcp | 0.1269 | 0.1435 | 0.1396 | 0.1480 |
| Δd/nm | 0.0002 | 0.0006 | 0.0003 | 0.0001 |
| Cinnamaldehyde | d1/nm | d2/nm | d3/nm | d4/nm | d5/nm | d6/nm | d7/nm | d8/nm | d9/nm | d10/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | 0.1272 | 0.1425 | 0.1404 | 0.1430 | 0.1433 | 0.1407 | 0.1414 | 0.1414 | 0.1408 | 0.1432 |
| fcc-fcc | 0.1270 | 0.1431 | 0.1406 | 0.1434 | 0.1436 | 0.1411 | 0.1416 | 0.1416 | 0.1412 | 0.1434 |
| Δd/nm | 0.0002 | 0.0006 | 0.0002 | 0.0004 | 0.0003 | 0.0004 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.0004 | 0.0002 |
Table 4 Structure parameters of cinnamaldehyde for the most stable adsorption configuration*
| Cinnamaldehyde | d1/nm | d2/nm | d3/nm | d4/nm | d5/nm | d6/nm | d7/nm | d8/nm | d9/nm | d10/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | 0.1272 | 0.1425 | 0.1404 | 0.1430 | 0.1433 | 0.1407 | 0.1414 | 0.1414 | 0.1408 | 0.1432 |
| fcc-fcc | 0.1270 | 0.1431 | 0.1406 | 0.1434 | 0.1436 | 0.1411 | 0.1416 | 0.1416 | 0.1412 | 0.1434 |
| Δd/nm | 0.0002 | 0.0006 | 0.0002 | 0.0004 | 0.0003 | 0.0004 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.0004 | 0.0002 |
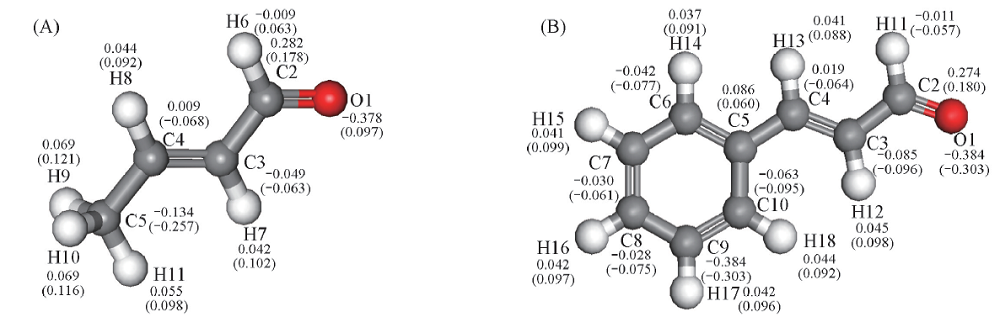
Fig.4 Mulliken charge populations of crotonaldehyde(A) and cinnamaldehyde(B)The values outside the parentheses are the amount of charge of each atom for free molecules. The values in parentheses are the amount of charge of the atom after the adsorption, and the adsorption configuration modes are shown in Fig.3.
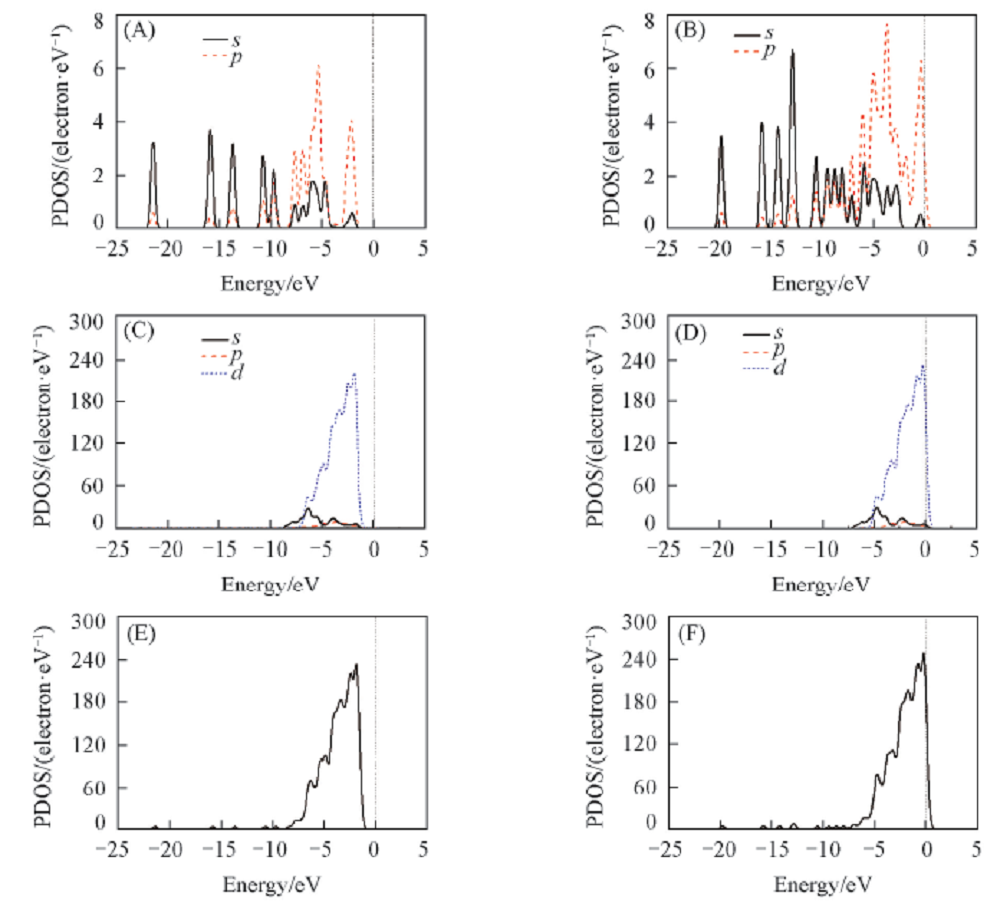
Fig.6 Densities of states of crotonaldehyde(A, C, E) and cinnamaldehyde(B, D, F) for the most stable adsorption configuration(A), (B) Represent the electron density of molecule after adsorption; (C), (D) represent electron density of of Pt-Ni-Pt(111) surface after adsorption; (E), (F) represent total DOS most stable adsorption configuration.
| [1] | Concepción P., Pérez Y., Hernández-Garrido J. C., Fajardo M., Calvino J. J., Corma A., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.,2013,15, 12048—12055 |
| [2] | Haubrich J., Loffreda D., Delbecq F., Sautet P., Krupski A., Becker C., Wandelt K., J. Phys. Chem. C,2009, 113, 13947—13967 |
| [3] | Mohr C., Hofmeister H., Radnik J., Claus P., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 1905—1911 |
| [4] | Raj K. J. A., Prakash M. G., Elangovan T., Viswanathan B., Catal. Lett.,2012, 142, 87—94 |
| [5] | Esan D. A., Ren Y., Feng X., Trenary M., J. Phys. Chem. C,2017, 121, 4384—4392 |
| [6] | Luo Q. Q., Wang T., Beller R., Jiao H. J., J. Phys. Chem. C,2013, 117, 12715—12724 |
| [7] | Cao Y. Y., Jiang J. H., Ni Z. M., Xia S. J., Qian M. D., Xue J. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2016, 37(7), 1342—1350 |
| (曹勇勇, 蒋军辉, 倪哲明, 夏盛杰, 钱梦丹, 薛继龙. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(7), 1342—1350) | |
| [8] | Myint M. N., Yan Y., Chen J. G., J. Phys. Chem. C,2014, 118, 11340—11349 |
| [9] | Esan D.A., Trenary M.,Top. Catal., 2017, 1—10 |
| [10] | Zanella R., Louis C., Giorgio S., Touroude R., J. Catal.,2004, 223, 328—339 |
| [11] | Ide M. S., Hao B., Neurick M., Davis R. J., ACS Catal.,2012, 2, 671—683 |
| [12] | Liu J., Fan X. F., Sun C. Q., Zhu W. G., Appl. Surf. Sci.,2018, 441, 23—28 |
| [13] | Wang X. J., Li X. J., Liao S. J., Li B. T., Comp. Mater. Sci.,2018, 149, 107—114 |
| [14] | Chen J. G., Menning C. A., Zellner M. B., Surf. Sci. Rep.,2008, 63, 201—254 |
| [15] | Zheng R., Zhu Y., Chen J. G., Chem. Cat. Chem.,2015, 3, 578—581 |
| [16] | Zheng R., Humbert M. P., Zhu Y., Chen J. G., Catalysis Science & Technology,2011, 1, 638—643 |
| [17] | Li X. D., Wan W. M., Kattel S., Chen J. G., Wang T. F., J. Catal.,2016, 344, 148—156 |
| [18] | Murillo L. E., Menning C. A., Chen J. G., J. Catal.,2009, 268, 335—342 |
| [19] | Murillo L. E., Goda A. M., Chen J. G., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2007, 129, 7101—7105 |
| [20] | Humbert M. P., Chen J. G., J. Catal.,2008, 257, 297—306 |
| [21] | Delbecq F., Sautet P., J. Catal.,2003, 220, 115—126 |
| [22] | Delbecq F., Sautet P., J. Catal.,1995, 152, 217—236 |
| [23] | Liu H. Y., Mei Q. Q., Li S. P., Yang Y. D., Wang Y. Y., Liu H. Z., Zheng L. R., An P. F., Zhang J., Han B. X., Chem. Commun.,2018, 54, 908—911 |
| [24] | Liu C., Luo W., Liu J. H., Sun L., Yang Y., Liu G., Wang F., Zhong W., Guild C., Suib S. L., Catal. Lett.,2018, 148, 1—9 |
| [25] | Perdew J. P., Wang Y., Physical Review B,1992, 45, 13244—13249 |
| [26] | Vigné F., Haubrich J., Loffreda D., Sautet P., Delbecq F., J. Catal.,2010, 275, 129—139 |
| [27] | Qian M. D., Luo W., Ni Z. M., Xia S. J., Xue J. L., Jiang J. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2017, 38(9), 1611—1618 |
| (钱梦丹, 罗伟, 倪哲明, 夏盛杰, 薛继龙, 蒋军辉. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(9), 1611—1618) | |
| [28] | Ni Z.M., Xia M. Y., Shi W., Qian P. P., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2013, 29, 1916—1922 |
| (倪哲明, 夏明玉, 施炜, 钱萍萍. 物理化学学报, 2013, 29, 1916—1922) | |
| [29] | Kang G. J., Ma J., Chen Z. X., Catal. Lett.,2012, 142, 287—293 |
| [30] | Durig J. R., Brown S. C., Kalasinsky V. F., George W. O., Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular Spectoscopy,1976, 32, 807—813 |
| [31] | Groot M. S. D., Lamb J., Proc. Roy. Soc. A,1957, 242, 36—56 |
| [32] | Haubrich J., Loffreda D., Delbecq F., Sautet P., Krupski A., Becker C., Wandelt K., J. Phys. Chem. C,2009, 113, 13947—13967 |
| [33] | Tao J., Yao Z.J., Xue F., Fundamentals of Material Science, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2006, 50—51 |
| (陶杰, 姚正军, 薛烽. 北京:化学工业出版社, 2006, 50—51) | |
| [34] | Liu R. Q., Comput. Theor. Chem., 2013, 1019, 141—145 |
| [1] | HE Hongrui, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Density-functional Theoretical Study on the Interaction of Indium Oxyhydroxide Clusters with Carbon Dioxide and Methane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [2] | JIANG Hongbin, DAI Wenchen, ZHANG Rao, XU Xiaochen, CHEN Jie, YANG Guang, YANG Fenglin. Research on Co3O4/UiO-66@α-Al2O3 Ceramic Membrane Separation and Catalytic Spraying Industry VOCs Waste Gas [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220025. |
| [3] | HAO Honglei, MENG Fanyu, LI Ruoyu, LI Yingqiu, JIA Mingjun, ZHANG Wenxiang, YUAN Xiaoling. Biomass Derived Nitrogen Doped Porous Carbon Materials as Adsorbents for Removal of Methylene Blue in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220055. |
| [4] | WONG Honho, LU Qiuyang, SUN Mingzi, HUANG Bolong. Rational Design of Graphdiyne-based Atomic Electrocatalysts: DFT and Self-validated Machine Learning [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220042. |
| [5] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, QING Jiang, MA Tengzhou, JIANG Wei, HUANG Weiqiu, CHEN Ruoyu. Activation of Biochar from Cattail and the VOCs Adsorption Application [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210824. |
| [6] | CHEN Xiaolu, YUAN Zhenyan, ZHONG Yingchun, REN Hao. Preparation of Triphenylamine Based PAF-106s via Mechanical Ball Milling and C2 Hydrocarbons Adsorption Property [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210771. |
| [7] | MENG Xianglong, YANG Ge, GUO Hailing, LIU Chenguang, CHAI Yongming, WANG Chunzheng, GUO Yongmei. Synthesis of Nano-zeolite and Its Adsorption Performance for Hydrogen Sulfide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210687. |
| [8] | TAN Lejian, ZHONG Xuanshu, WANG Jin, LIU Zongjian, ZHANG Aiying, YE Lin, FENG Zengguo. Low Critical Dissolution Temperature Behavior of β⁃Cyclodextrin and Its Application in the Preparation of β⁃Cyclodextrin Sheet Crystal with Ordered Nano⁃channel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220405. |
| [9] | LIU Yang, LI Wangchang, ZHANG Zhuxia, WANG Fang, YANG Wenjing, GUO Zhen, CUI Peng. Theoretical Exploration of Noncovalent Interactions Between Sc3C2@C80 and [12]Cycloparaphenylene Nanoring [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220457. |
| [10] | ZHENG Meiqi, MAO Fangqi, KONG Xianggui, DUAN Xue. Layered Double Hydroxides as Sorbent for Remediation of Radioactive Wastewater [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220456. |
| [11] | TIAN Xiaokang, ZHANG Qingsong, YANG Shulin, BAI Jie, CHEN Bingjie, PAN Jie, CHEN Li, WEI Yen. Porous Materials Inspired by Microbial Fermentation: Preparation Method and Application [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220216. |
| [12] | CHENG Yuanyuan, XI Biying. Theoretical Study on the Fragmentation Mechanism of CH3SSCH3 Radical Cation Initiated by OH Radical [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220271. |
| [13] | WANG Yuanyue, AN Suosuo, ZHENG Xuming, ZHAO Yanying. Spectroscopic and Theoretical Studies on 5-Mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thione Microsolvation Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220354. |
| [14] | ZHOU Chengsi, ZHAO Yuanjin, HAN Meichen, YANG Xia, LIU Chenguang, HE Aihua. Regulation of Silanes as External Electron Donors on Propylene/butene Sequential Polymerization [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220290. |
| [15] | MA Jianxin, LIU Xiaodong, XU Na, LIU Guocheng, WANG Xiuli. A Multi-functional Zn(II) Coordination Polymer with Luminescence Sensing, Amperometric Sensing, and Dye Adsorption Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210585. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||