

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 706.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190584
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
FU Kefei,LIAN Huiting,WEI Xiaofeng,SUN Xiangying,LIU Bin( )
)
Received:2019-11-11
Online:2020-04-10
Published:2020-01-10
Contact:
Bin LIU
E-mail:bliu@hqu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
FU Kefei, LIAN Huiting, WEI Xiaofeng, SUN Xiangying, LIU Bin. Construction of Cyclodextrin-based Impedance Sensor for Recognition of L-Cysteine †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 706.
| Structural analogue | L-Cys | D-Cys | Hcy | L-Pen | D-Pen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔRL-Cys/ΔRother | 1 | 1.179 | 2.120 | 1.511 | 1.513 |
| Structural analogue | L-Cys | D-Cys | Hcy | L-Pen | D-Pen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔRL-Cys/ΔRother | 1 | 1.179 | 2.120 | 1.511 | 1.513 |
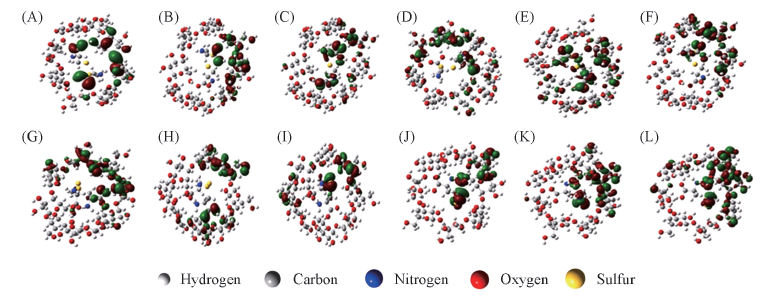
Fig.4 Molecular occupied orbitals 152(A), 369(B), 387(C), 388(D), 389(E), 391(F) for γ-CD-L-Cys and 360(G), 367(H), 390(I), 394(J), 396(K), 397(L) for γ-CD-D-Cys
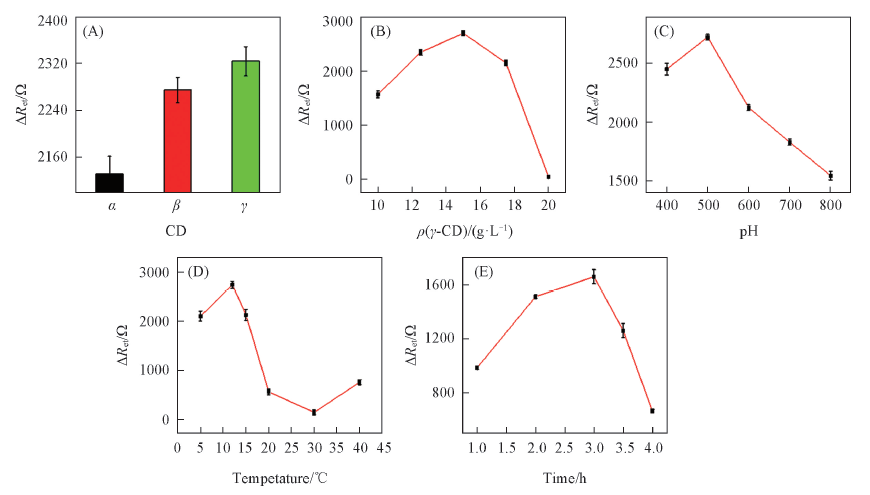
Fig.5 Effect of different types of CDs(A), concentrations of γ-CD(B), pH changing(C), temperature changing(D) and assembling time(E) on the γ-CD self-assembly on GCE
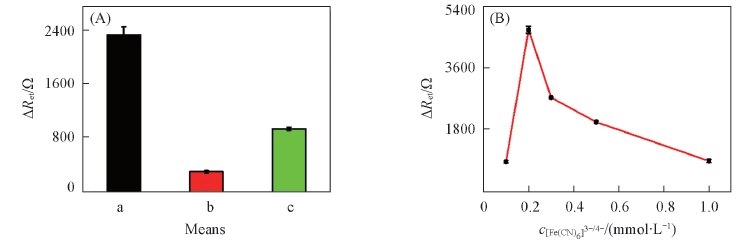
Fig.7 Effect of different means(A) and concentrations of [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-(B) on the γ-CD-based sensor (A) a. DPV, 0—1.0 V; b. stewing 65 s; c. CV, 0—1.0 V.
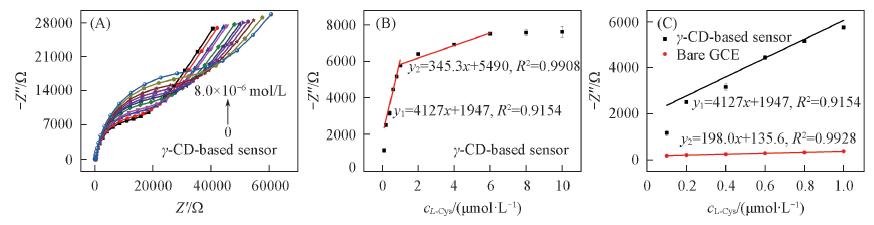
Fig.8 EIS(A) and calibration curve(B) for the detection of L-Cys with 0.1—6.0 μmol/L on γ-CD-based sensor and the comparison(C) of calibration curves for L-Cys on γ-CD-based sensor or bare GCE
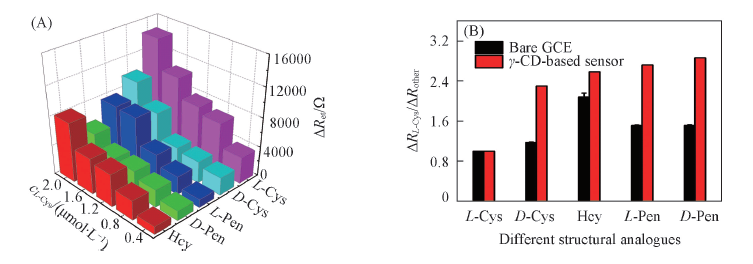
Fig.9 Impedance responses(A) of various structural analogues on γ-CD-based sensor and selectivity analysis(B) for detection of L-Cys on γ-CD-based sensor and bare GCE
| Structural analogue | L-Cys | D-Cys | Hcy | L-Pen | D-Pen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔRL-Cys/ΔRother | 1.000 | 2.301 | 2.578 | 2.724 | 2.861 |
| Structural analogue | L-Cys | D-Cys | Hcy | L-Pen | D-Pen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔRL-Cys/ΔRother | 1.000 | 2.301 | 2.578 | 2.724 | 2.861 |
| Sample | Added/(μmol·L-1) | Found/(μmol·L-1) | Recovery(%) | RSD(%)(n=3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood serum | 0 | 0.218 | | 1.0 |
| 0.300 | 0.542 | 108.0 | 0.9 | |
| 0.500 | 0.691 | 94.8 | 2.0 | |
| 0.700 | 0.910 | 98.9 | 1.5 | |
| Capsule | 0 | 0.045 | | 0.9 |
| 0.300 | 0.317 | 90.6 | 0.6 | |
| 0.500 | 0.531 | 97.2 | 0.7 | |
| 0.900 | 0.840 | 88.9 | 0.4 |
| Sample | Added/(μmol·L-1) | Found/(μmol·L-1) | Recovery(%) | RSD(%)(n=3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood serum | 0 | 0.218 | | 1.0 |
| 0.300 | 0.542 | 108.0 | 0.9 | |
| 0.500 | 0.691 | 94.8 | 2.0 | |
| 0.700 | 0.910 | 98.9 | 1.5 | |
| Capsule | 0 | 0.045 | | 0.9 |
| 0.300 | 0.317 | 90.6 | 0.6 | |
| 0.500 | 0.531 | 97.2 | 0.7 | |
| 0.900 | 0.840 | 88.9 | 0.4 |
| [1] | Wang L., Tricard S., Yue P. W., Zhao J. H., Fang J., Shen W. G., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2016, 77, 1112— 1118 |
| [2] | Zhou H. F., Ran G. X., Masson J., Wang C., Zhao Y., Song Q. J., Anal. Chem., 2018, 90( 5), 3374— 3381 |
| [3] | Deáková Z., Dura c ˙ ková Z. , Armstrong D. W., Daniel W., Lehotay J., J. Chromatogr. A, 2015, 1408, 118— 124 |
| [4] | Yang N., Song H. J., Wan X. Y., Fan X. Q., Su Y. Y., Lv Y ., Analyst, 2015, 140( 8), 2656— 2663 |
| [5] | Yan F.Y., Shi D. C., Zheng T. C., Yun K. Y., Zhou X. G., Li C., Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 2016, 224, 926— 935 |
| [6] | Abbas M. N., Saeed A. A., Singh B., Radowan A. A., Dempsey E., Anal. Methods, 2015, 7( 6), 2529— 2536 |
| [7] | Yang S L., . Li G.,Qu C.,Wang G. F., Wang D. , RSC Adv., 2017, ( 7), 35004— 35011 |
| [8] | Pandey I., Kant R., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2016, 77, 715— 724 |
| [9] | Huang Y. H., Guo D. M., Zhang Q., Guo L. J., Chen Y., Fu Y. Z., RSC Adv., 2014, 4( 63), 33457— 33461 |
| [10] | Ding S. S., Cao S. M., Zhu A. W., Shi G. Y., Anal. Chem., 2016, 88( 24), 12219— 12226 |
| [11] | Durán G. M., Abellán C., Contento A. M., Ríos A., Microchim. Acta, 2017, 184( 3), 815— 824 |
| [12] | Richardson J. J., Cui J. W., Björnmalm M., Braunger J. A., Ejima H., Caruso F., Chem. Rev., 2016, 116( 23), 14828— 14867 |
| [13] | Borges J., Mano J. F., Chem. Rev., 2014, 114( 18), 8883— 8942 |
| [14] | Liu M. H., Zhang L., Wang T. Y., Chem. Rev., 2015, 115( 15), 7304— 7397 |
| [15] | Zaidi S. A., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2017, 94, 714— 718 |
| [16] | Kannan A., Sevvel R., Mat. Sci. Eng. C, 2017, 78, 513— 519 |
| [17] | Tan S., Perry D., Unwin P. R., J. Electroanal Chem., 2018, 819, 240— 250 |
| [18] | Dey M. K., Kumar S., Satpati A. K., J. Electroanal. Chem., 2017, 807, 119— 127 |
| [19] | Abbas M. N., Saeed A. A., Singh B., Radowan A., Dempsey E., Anal. Methods, 2015, 7( 6), 2529— 2536 |
| [20] | Tang A Q.. Quantum Chemistry, Science Press, Beijing, 1982, 385— 398 |
| ( 唐敖庆. 量子化学, 北京: 科学出版社, 1982, 385— 398) | |
| [21] | Lopes J. F., Nascimento C. S., Anconi C. P. A., Santos H. F. D., Almeida B. D., J. Mol. Graph. Model., 2015, 62, 11— 17 |
| [22] | Parlak C., Spectrochim. Acta Part A, 2012, 99, 12— 17 |
| [23] | Galano A., Alvarez I., J. Comput. Chem., 2006, 27( 11), 1203— 1210 |
| [24] | Boys S., Bernardi F., Molecular Physics, 1970, 4( 19), 553— 566 |
| [25] | Alvira E., Tetrahedron Asymmetr., 2013, 24( 19), 1198— 1206 |
| [1] | LI Yulong, XIE Fating, GUAN Yan, LIU Jiali, ZHANG Guiqun, YAO Chao, YANG Tong, YANG Yunhui, HU Rong. A Ratiometric Electrochemical Sensor Based on Silver Ion Interaction with DNA for the Detection of Silver Ion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220202. |
| [2] | TAN Lejian, ZHONG Xuanshu, WANG Jin, LIU Zongjian, ZHANG Aiying, YE Lin, FENG Zengguo. Low Critical Dissolution Temperature Behavior of β⁃Cyclodextrin and Its Application in the Preparation of β⁃Cyclodextrin Sheet Crystal with Ordered Nano⁃channel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220405. |
| [3] | WEI Chuangyu, CHEN Yanli, JIANG Jianzhuang. Fabrication of Electrochemical Sensor for Dopamine and Uric Acid Based on a Novel Dimeric Phthalocyanine-involved Quintuple-decker Modified Indium Tin Oxide Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210582. |
| [4] | WEI Zheyu, WU Zhikang, RU Shi, NI Lubin, WEI Yongge. Research Progress of Polyoxometalates-Cyclodextrin Supramolecular System [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210665. |
| [5] | WANG Bodong, PAN Meichen, ZHUO Ying. Construction of Electrochemiluminescence Sensing Interface Based on Silver Nanoclusters-Silica Nanoparticles and Biomolecular Recognition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3519. |
| [6] | ZHANG Juan, HU Xinyue, WANG Hongbo, LIAN Ying, LE Jinyu, YANG Zihao. Crystal-like Hydrogels Consisting of Parallel Hexahedrons Obtained from the Self-assembly ofβ⁃Cyclodextrin/perfluorononanoic Acid Inclusion Complexes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3187. |
| [7] | PENG Yuyu,WANG Yu,YU Xinyao,ZENG Julan,XIAO Zhongliang,CAO Zhong. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of L-Cysteine Based on Mono(6-mercapto-6-deoxy)-β-cyclodextrin Modified Gold Electrode † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 268. |
| [8] | LI Botian,SHAO Wei,XIAO Da,ZHOU Xue,DONG Junwei,TANG Liming. Polypyrrole Nanowire Gels Based on Templating Fabrication and Their Energy Storage and Electrochemical Sensing Properties † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 183. |
| [9] | WU Yan,LIAN Huiting,SUN Xiangying,LIU Bin. Construction of Cyclodextrin Polymeric Membrane Sensor Based on Graphene and Potential Recognition for Histidine Enantiomer† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 230. |
| [10] | TIAN Yao,ZHANG Chunquan,WANG Wenzhe,ZHOU Yingfang,LU Yitong,ZHANG Peng,JIA Zhenfu,ZHOU Chengyu,CHEN Shilan. Preparation of Polyrotaxane Cross-linking Agent with “Pulley” Effect and Its Potential Application in Swelling Grain Used as Profile Control and Water Plugging Agent† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 2098. |
| [11] | ZHOU Min, XU Xiaoying, LONG Yuande. Enantioseparation of Seventeen Kinds of β-Lactams on Carboxymethyl-β-cyclodextrin Chiral Stationary Phase and Research on Enantioseparation Mechanism [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(6): 1164. |
| [12] | YANG Qinghua, WANG Longgang, LIU Jie, LU Yong, CHEN Tianyun. Preparation and Characterization of Star-shaped β-Cyclodextrin Based Polymer† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(4): 793. |
| [13] | LIN Musong, PENG Lei, FU Qiang, QIAN Yihua, CHEN Tiansheng, ZHANG Sheng, MA Xiaoqian. Research on Self-healing Insulating Material Based on Host-guest Cooperation† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(11): 2572. |
| [14] | CHEN Tao,HUANG Chan. β-Cyclodextrin Based Star-like Polymer for Loading Chlorambucil† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10): 2350. |
| [15] | JIAN Yuhang, YAN Shifeng, LI Xing, HUANG Yanan, YIN Jingbo. Synthesis and Characterization of Injectable Hydrogels Based on Star β-CD-g-poly(L-glutamic acid) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(8): 1489. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||