

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (12): 20220383.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220383
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
XU Xinyu, ZHANG Letian, CAO Hui, MA Yuan, LIU Liuhui, SONG Guosheng( ), ZHANG Xiaobing(
), ZHANG Xiaobing( )
)
Received:2022-05-30
Online:2022-12-10
Published:2022-07-26
Contact:
SONG Guosheng, ZHANG Xiaobing
E-mail:songgs@hnu.edu.cn;xbzhang@hnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
XU Xinyu, ZHANG Letian, CAO Hui, MA Yuan, LIU Liuhui, SONG Guosheng, ZHANG Xiaobing. Recent Advances in Lipid-responsive Probes in the Imaging and Treatment of Atherosclerosis[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(12): 20220383.
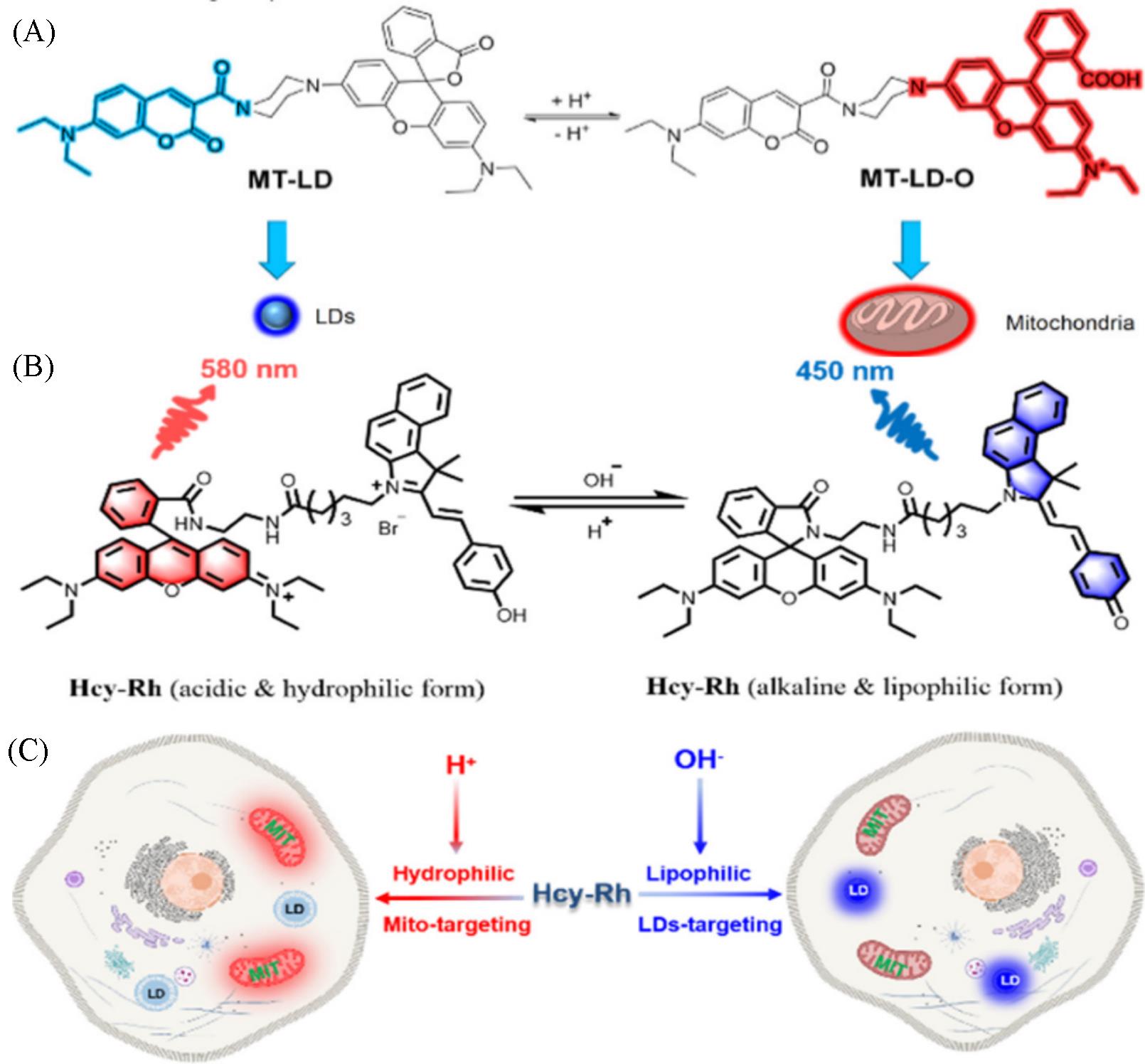
Fig.2 Chemical structure and the targeting mechanism of the probe MT⁃LD(A)[28], chemical structure of Hcy⁃Rh and the proposed polarity⁃reversible and ratiometric pH⁃sensing mechanism(B) and targeting mechanism of Hcy⁃Rh(C)[29](A) Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society; (B, C) Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society.
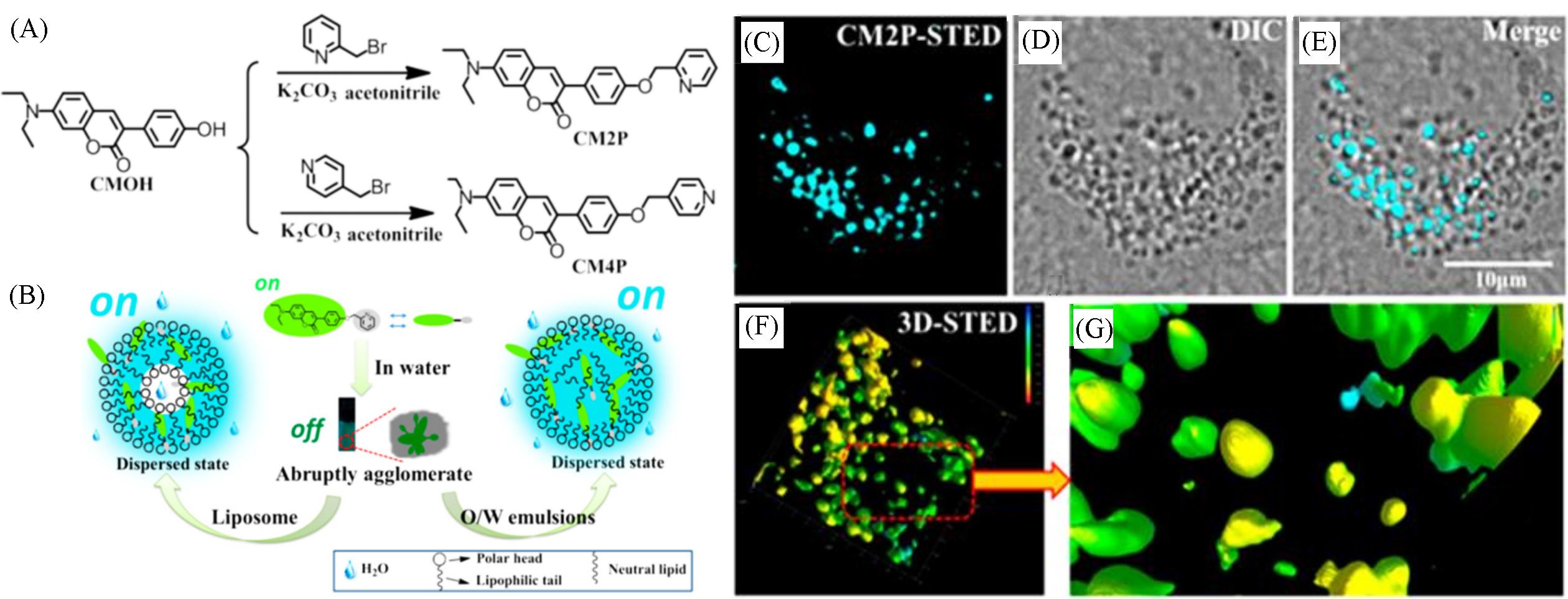
Fig.3 Synthetic route for CM2P and CM4P(A), simulation of interaction between CM2P and liposome, O/W emulsions(B), and fluorescent images of LDs stained with CM2P in live HeLa cells(C—G)[31] (C) STED image; (D) bright⁃field image; (E) merged image of (C) and (D); (F) 3D⁃STED image; (G) zoomed⁃in region from Fig.(F). Rainbow calibration bar, Z scale(0—10 μm).
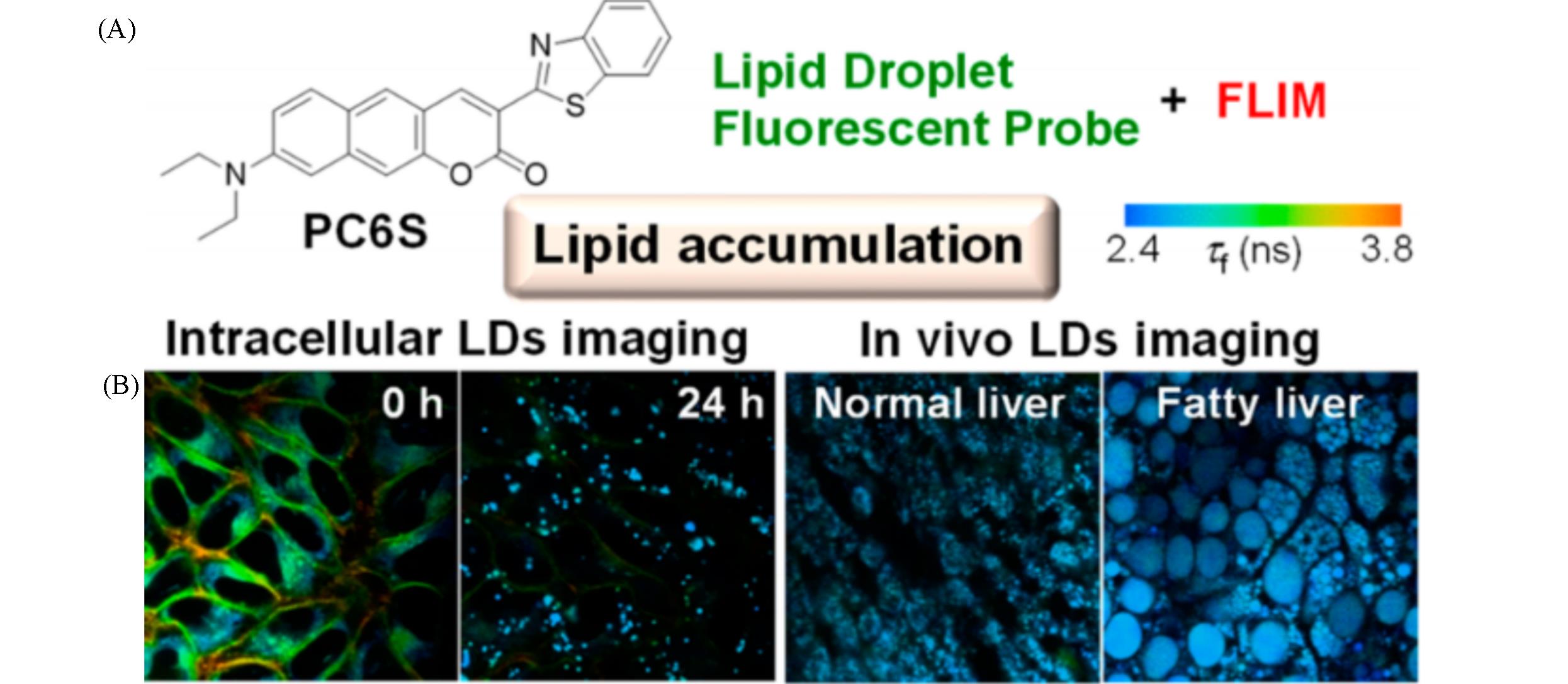
Fig.4 Chemical structure of PC6S(A) and FLIM images of HeLa cells stained with PC6S(2 μmol/L) for 30 min at 37 ℃, then treated with oleic acid(400 μmol/L) and FLIM images of the livers of living mice(B)[32](B) Excitation wavelength: 488 nm, collected emission wavelength range: 510—560 nm.
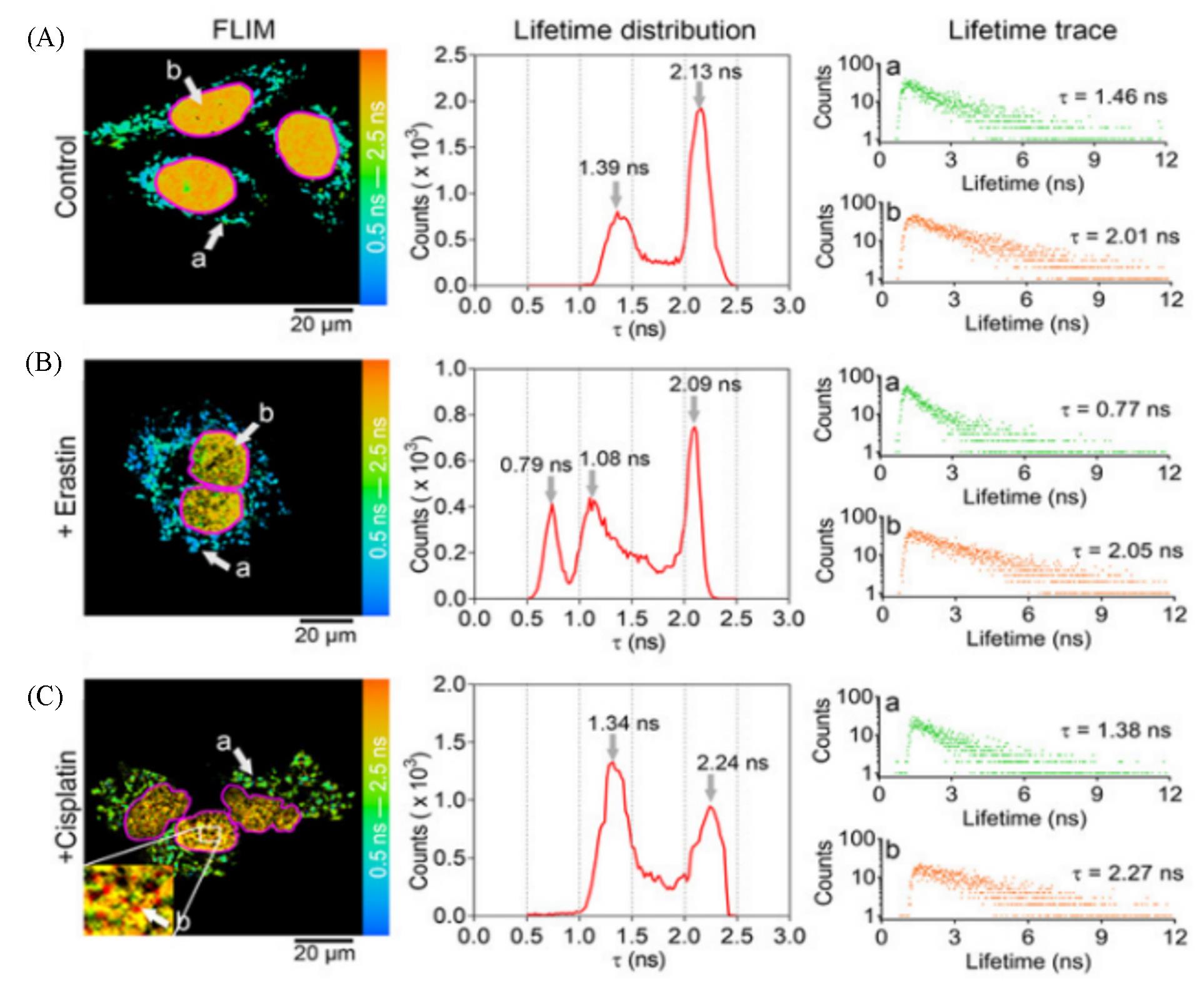
Fig.5 Application of CQPP(5 μmol/L) to monitoring the polarity changes of LDs and nucleus in living cells under different conditions by fluorescence lifetime imaging(FLIM)[33](A) HT-1080 cells under normal conditions (Control); (B) HT-1080 cells incubated with Erastin(10 μmol/L) for 6 h; (C) HT-1080 cells incubated with cisplatin(20 μmol/L) for 12 h. The solid pink line represents the shape of the nucleus. Lifetime distribution: the fluorescence lifetime(τ) distribution collected from FLIM. Lifetime trace: Fluorescence lifetime spectra of region a and b from FLIM. FLIM images were pulsed two-photon excitation at 810 nm. Images shown are representatives of replicate experiments.Copyright 2021, Wiley-VCH GmbH.
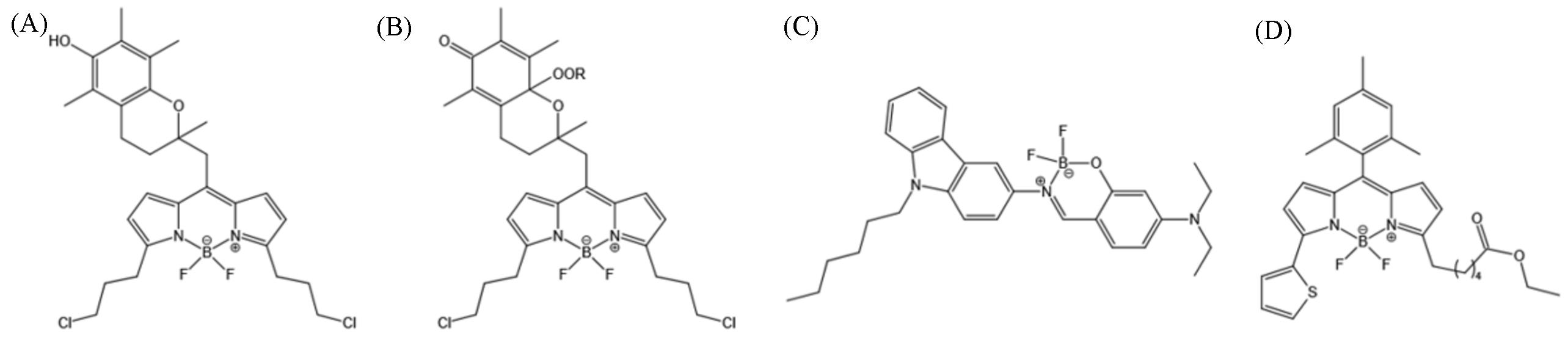
Fig.6 BODIPY⁃based LD probes(A) H4BPMHC; (B) H4BPMHCox[35]; (C) BoCz⁃Lip[36]; (D) BODIPYs 9.(A, B) Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society; (C) Copyright 2020, Elsevier B.V.;(D) Copyright 2020, the Royal Society of Chemistry.
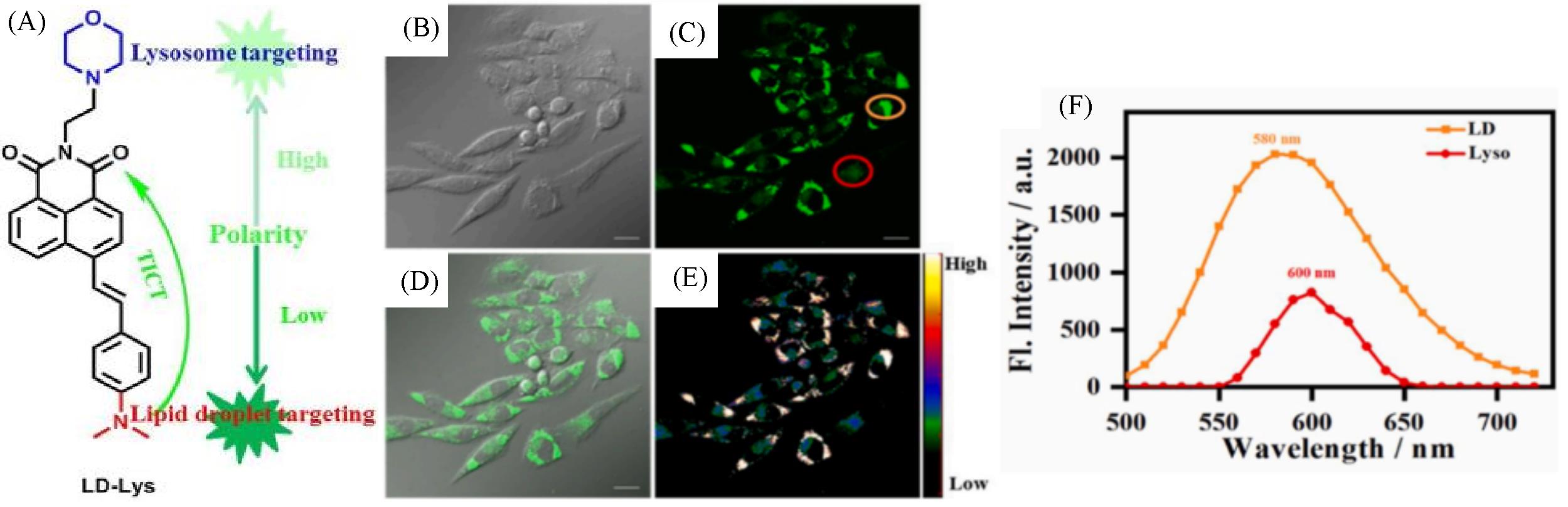
Fig.7 Molecular design and structure of LD⁃Lys(A) and fluorescent images(B—E) and spectra(F) of live SiHa cells stained with LD⁃Lys(5 μmol/L, 30 min)[39]
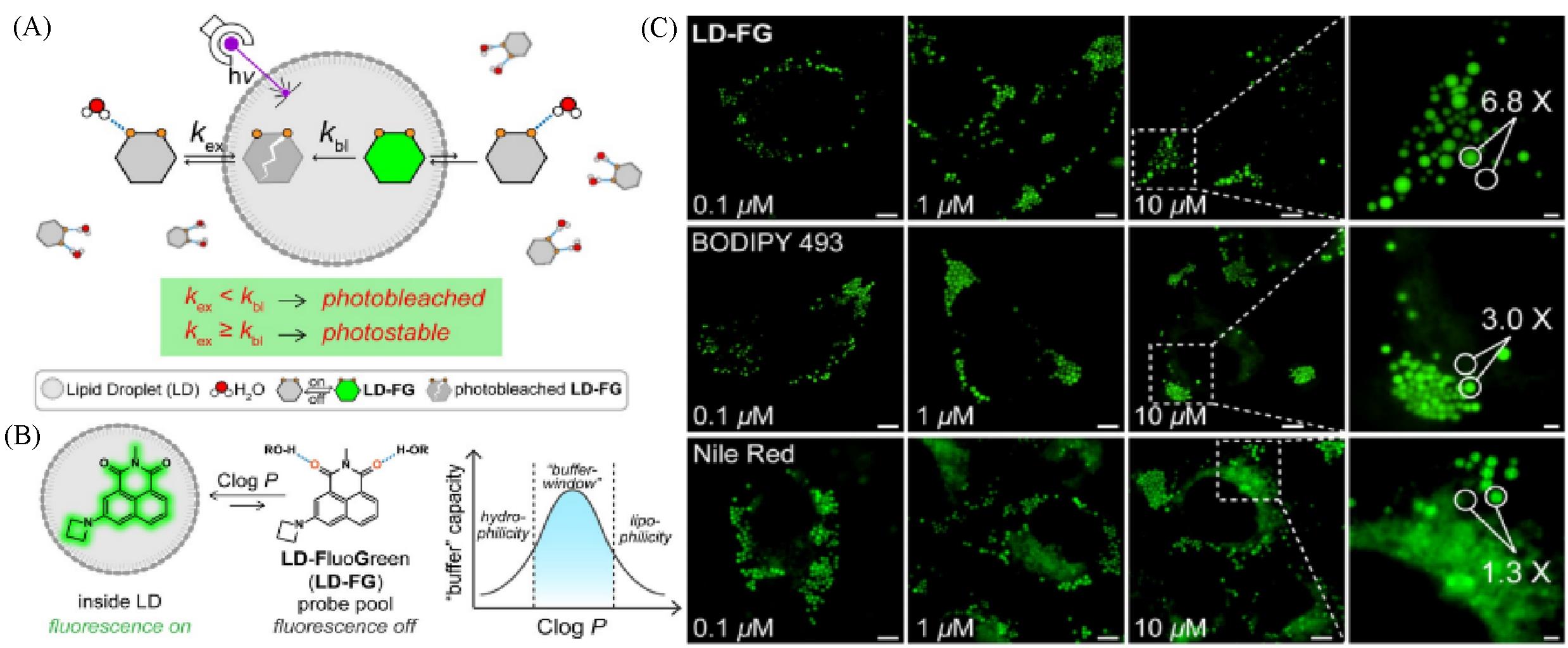
Fig.8 Super⁃resolution lipid droplet imaging probe LD⁃FG[40](A) The buffer strategy enables stable imaging of lipid droplets using LD-FG; (B) mechanism of LD-FG for LD fluorogenic and dynamic imaging; (C) fluorescent image of HeLa cells incubated with LD-FG, BODIPY 493, and Nile Red in different concentrations.Copyright 2021, Wiley-VCH GmbH.
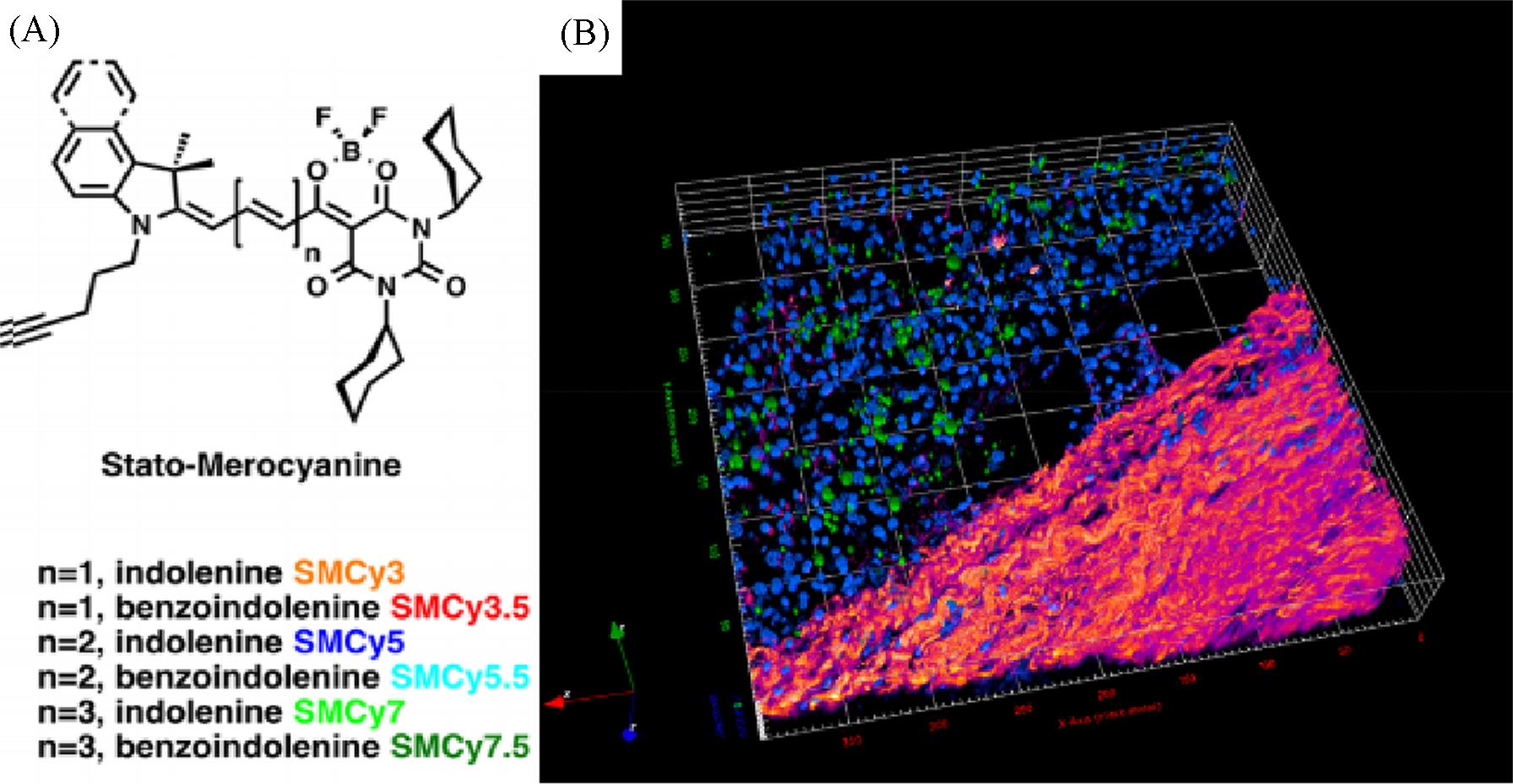
Fig.9 The six members of the StatoMerocyanines family(A) and two⁃photon excitation 3D imaging(52 μm depth) of a mouse liver slice, incubated with Hoechst(5 μg/mL) and SMCy5.5(5 μmol/L)(B)[42](B) The nuclei are displayed in blue, the lipid droplets in green, and the collagen fibers in fire color. The two⁃photon excitation wavelength was 810 nm.
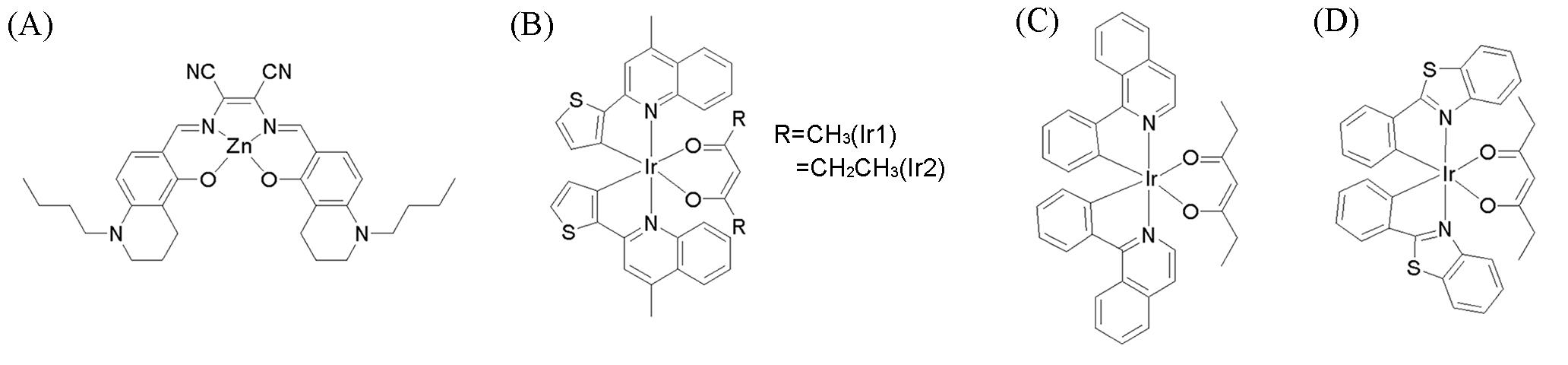
Fig.10 Chemical structures of some metal complex LD probes(A) LD⁃TPZn[43]; (B) lipophilic neutral phosphorescentIr(III) complexes(Ir1 and Ir2)[44]; (C, D) neutral cyclometalated iridium(III) complexes.(A) Copyright 2017, Wiley⁃VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA; (B) Copyright 2018, Elsevier B.V.; (C, D) Copyright 2022, Elsevier Ltd.
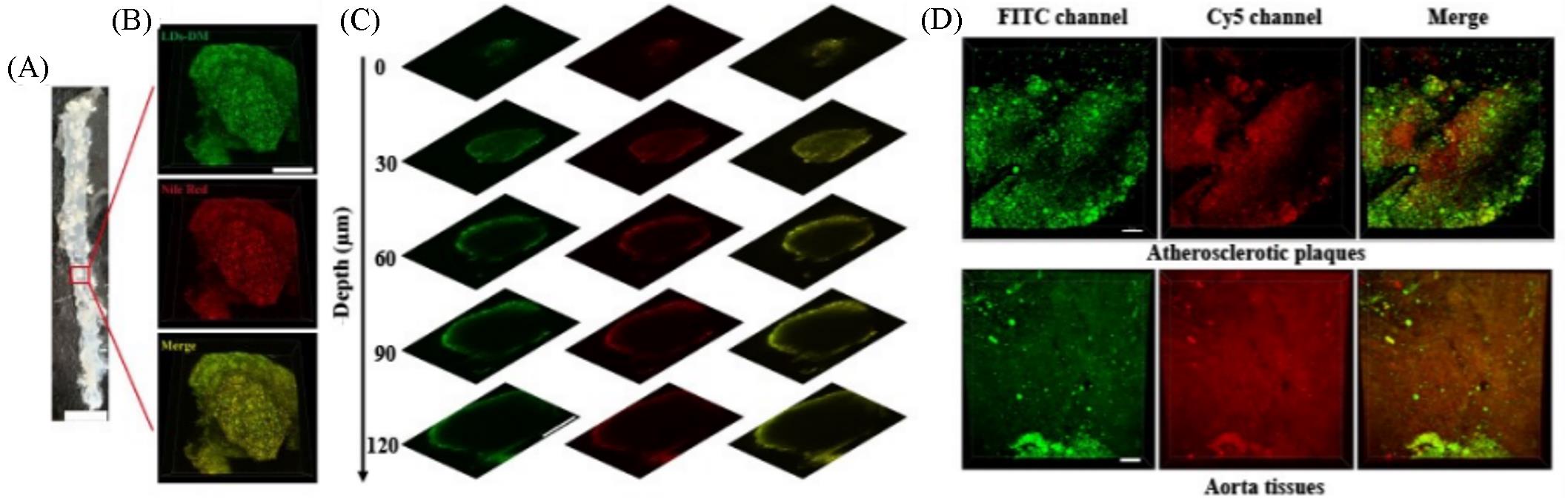
Fig.11 Simultaneous dual⁃color 3D imaging in atherosclerosis[46](A) En face photograph of the opened aorta from an ApoE-/- mouse, scale bar: 5 mm; (B) simultaneous 3D imaging of the microstructures of atherosclerotic plaques stained with LDs-DM(500 nmol/L) and Nile red (1 μmol/L), scale bar: 200 μm; (C) images of the atherosclerotic plaques stained with LDs-DM(500 nmol/L) and Nile red(1 μmol/L) at different imaging depths, scale bar: 200 μm; (D) simultaneous dual-color 3D imaging of the microstructures of atherosclerotic plaques and aorta tissue stained with 500 nmol/L LDs-DM within lumen(500—550 nm for FITC channel and 663—738 nm for Cy5 channel) under single excitation at 488 nm, scale bar: 70 μm.
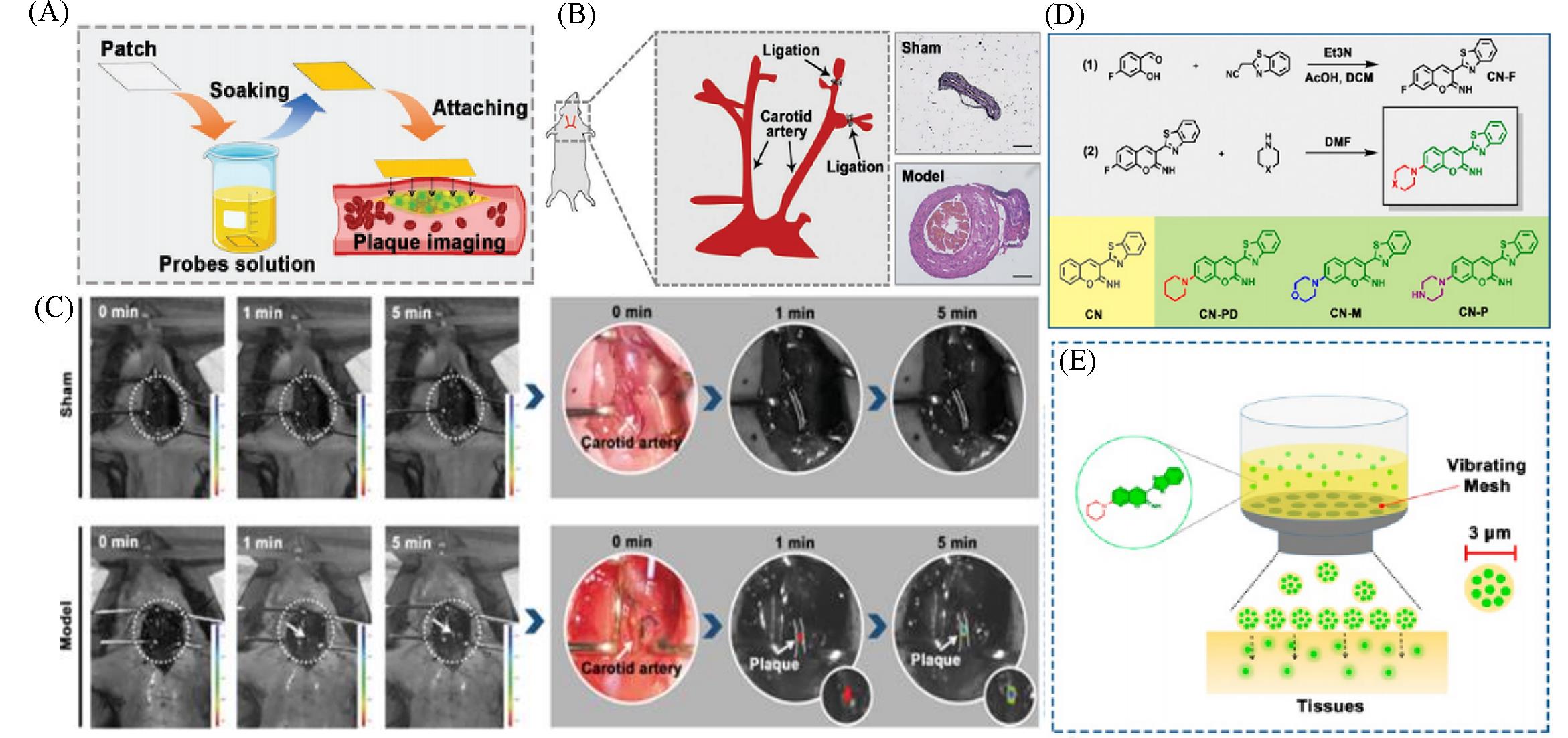
Fig.14 Lipid⁃activatable fluorescent probes for intraoperative imaging of atherosclerotic plaque(A) Schematic showing target artery surface attachment to CN-N2-soaked filter paper to realize rapid penetration of the probe into the plaque[49]; (B) Carotid ligation model of atherosclerosis illustrated using HE-stained tissue images[49]; (C) atherosclerosis model imaging procedure: the left carotid artery is exposed to CN-N2-soaked filter paper(1×10-5 mol/L) with in vivo imaging performed at 1 and 5 min[49]; (D) synthesis route, structure, and the corresponding abbreviation of the synthesized probes[50]; (E) vibrating mesh nebulized the aqueous solution of the probe into small droplets with a diameter of 3 μm to achieve rapid tissue permeation[50].(A—C) Copyright 2021, Wiley-VCH GmbH; (D, E) Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society.
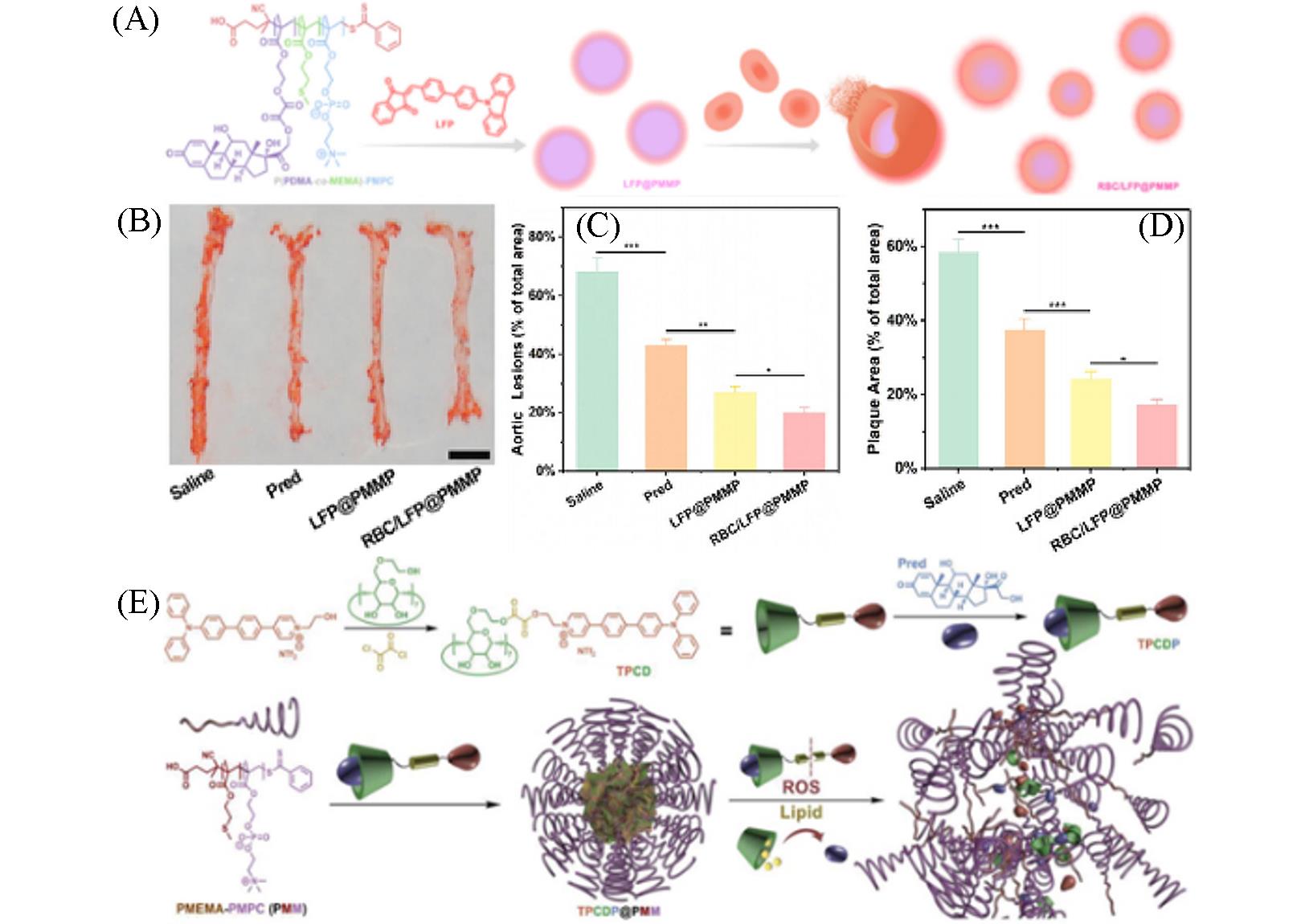
Fig.15 Nanoplatform with lipid⁃specific imaging for atherosclerosis⁃targeted therapy(A) Illustration of RBC/LFP@PMMP formation[54]; (B, C) photographs(B) and quantitative data(C) of the plaques on the en face of the aortas stained by ORO(n=6)[54], scale bar: 5 mm; (D) quantitative results of the aortic arch plaque areas[54]; (E) illustration of TPCDP@PMM preparation and its responsive behaviors under overexpressed ROS and rich lipid[55].(A—D) Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society; (E) Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH GmbH.
| 1 | Kawanishi K., Dhar C., Do R., Varki N., Gordts P., Varki A., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2019, 116(32), 16036—16045 |
| 2 | Tabas I., Garcia C. G., Owens G. K., J. Cell Biol., 2015, 209(1), 13—22 |
| 3 | Kobiyama K., Ley K., Circ. Res., 2018, 123(10), 1118—1120 |
| 4 | Ridker P. M., Circulation, 2003, 107(3), 363—369 |
| 5 | Moore K. J., Tabas I., Cell, 2011, 145(3), 341—355 |
| 6 | Soehnlein O., Drechsler M., Doring Y., Lievens D., Hartwig H., Kemmerich K., Ortega G. A., Mandl M., Vijayan S., Projahn D., Garlichs C. D., Koenen R. R., Hristov M., Lutgens E., Zernecke A., Weber C., EMBO Mol. Med., 2013, 5(3), 471—481 |
| 7 | Kojima Y., Volkmer J. P., Mckenna K., Civelek M., Lusis A. J., Miller C. L., Direnzo D., Nanda V., Ye J., Connolly A. J., Schadt E. E., Quertermous T., Betancur P., Maegdefessel L., Matic L. P., Hedin U., Weissman I. L., Leeper N. J., Nature, 2016, 536(7614), 86—90 |
| 8 | Kunjathoor V. V., Febbraio M., Podrez E. A., Moore K. J., Andersson L., Koehn S., Rhee J. S., Silverstein R., Hoff H. F., Freeman M. W., J. Biol. Chem., 2002, 277(51), 49982—49988 |
| 9 | Ji A., Meyer J. M., Cai L., Akinmusire A., de Beer M. C., Webb N. R., van der Westhuyzen D. R., Atherosclerosis, 2011, 217(1), 106—112 |
| 10 | Endemann G., Stanton L. W., Madden K. S., Bryant C. M., White R. T., Protter A. A., J. Biol. Chem., 1993, 268(16), 11811—11816 |
| 11 | Libby P., Ridker P. M., Hansson G. K., Nature, 2011, 473(7347), 317—325 |
| 12 | Thorp E., Tabas I., J. Leukoc. Biol., 2009, 86(5), 1089—1095 |
| 13 | Schrijvers D. M., de Meyer G. R., Kockx M. M., Herman A. G., Martinet W., Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 2005, 25(6), 1256—1261 |
| 14 | Thorp E., Cui D., Schrijvers D. M., Kuriakose G., Tabas I., Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 2008, 28(8), 1421—1428 |
| 15 | Beller M., Thiel K., Thul P. J., Jackle H., FEBS Lett., 2010, 584(11), 2176—2182 |
| 16 | Farese R. V. Jr., Walther T. C., Cell, 2009, 139(5), 855—860 |
| 17 | Walther T. C., Farese R. V. Jr., Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids, 2009, 1791(6), 459—466 |
| 18 | Onal G., Kutlu O., Gozuacik D., Dokmeci Emre S., Lipids Health Dis., 2017, 16(1), 128 |
| 19 | Yin J., Huang L., Wu L., Li J., James T. D., Lin W., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021, 50(21), 12098—12150 |
| 20 | Greenspan. P., Mayer. E. P., Fowler. S. D., J. Cell Biol., 1985, 100(3), 965—973 |
| 21 | Fam T. K., Klymchenko A. S., Collot M., Materials, 2018, 11(9), 1768 |
| 22 | Danylchuk D. I., Jouard P. H., Klymchenko A. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021,143(2), 912—924 |
| 23 | Zhao Y., Shi W., Li X., Ma H., Chem. Commun., 2022, 58(10), 1495—1509 |
| 24 | Rumin J., Bonnefond H., Saint⁃Jean B., Rouxel C., Sciandra A., Bernard O., Cadoret J. P., Bougaran G., Biotechnol Biofuels, 2015, 8, 42 |
| 25 | Lavis. L. D., Raines. R. T., ACS Chem. Biol., 2008, 3(3), 142—155 |
| 26 | Tian H., Sedgwick A. C., Han H.H., Sen S., Chen G.R., Zang Y., Sessler J. L., James T. D., Li J., He X. P., Coord. Chem. Rev., 2021, 427, 213577 |
| 27 | Beija M., Afonso C. A., Martinho J. M., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38(8), 2410—2433 |
| 28 | Tian M., Ge E., Dong B., Zuo Y., Zhao Y., Lin W., Anal. Chem., 2021, 93(7), 3602—3610 |
| 29 | Bai Q., Yang C., Yang M., Pei Z., Zhou X., Liu J., Ji H., Li G., Wu M., Qin Y., Wang Q., Wu L., Anal. Chem., 2022, 94(6), 2901—2911 |
| 30 | Mota A. A. R., Correa J. R., de Andrade L. P., Assumpcao J. A. F., de Souza Cintra G. A., Freitas⁃Junior L. H., Da Silva W. A., de Oliveira H. C. B., Neto B. A. D., ACS Omega, 2018, 3(4), 3874—3881 |
| 31 | Xu H., Zhang H., Liu G., Kong L., Zhu X., Tian X., Zhang Z., Zhang R., Wu Z., Tian Y., Zhou H., Anal. Chem., 2019, 91(1), 977—982 |
| 32 | Yoshihara T., Maruyama R., Shiozaki S., Yamamoto K., Kato S. I., Nakamura Y., Tobita S., Anal. Chem., 2020, 92(7), 4996—5003 |
| 33 | Wang K. N., Liu L. Y., Mao D., Xu S., Tan C. P., Cao Q., Mao Z. W., Liu B., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60(27), 15095—15100 |
| 34 | Chen S., Chen W., Shi W., Ma H., Chem. Eur. J., 2012, 18(3), 925—930 |
| 35 | Greene L. E., Lincoln R., Cosa G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(44), 15801—15811 |
| 36 | Liu X. L., Lu X., Zhu T., Du W. L., Yang Z. H., Cao H. Z., Wang S. Y., Tian Y. P., Zhang Z. P., Zhang R. L., de Souza S. C., Tian X. H., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2021, 175, 112871 |
| 37 | Tabero A., Garcia G. F., Prieto C. A., Palao E., Agarrabeitia A. R., Garcia M. I., Villanueva A., Moya S., Ortiz M. J., Chem. Commun., 2020, 56(6), 940—943 |
| 38 | Pan Y. H., Chen X. X., Dong L., Shao N., Niu L.Y., Yang Q. Z., Chin. Chem. Lett., 2021, 32(12), 3895—3898 |
| 39 | Meng F., Niu J., Zhang H., Yang R., Lu Q., Yu Y., Liu Z., Niu G., Yu X., Sens. Actuators B⁃Chem., 2021, 329, 129148 |
| 40 | Chen J., Wang C., Liu W., Qiao Q., Qi H., Zhou W., Xu N., Li J., Piao H., Tan D., Liu X., Xu Z., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60(47), 25104—25113 |
| 41 | Sun W., Guo S., Hu C., Fan J., Peng X., Chem. Rev., 2016, 116(14), 7768—7817 |
| 42 | Collot M., Fam T. K., Ashokkumar P., Faklaris O., Galli T., Danglot L., Klymchenko A. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140(16), 5401—5411 |
| 43 | Tang J., Zhang Y., Yin H. Y., Xu G., Zhang J. L., Chem. Asian J., 2017, 12(19), 2533—2538 |
| 44 | He L., Cao J. J., Zhang D. Y., Hao L., Zhang M. F., Tan C. P., Ji L. N., Mao Z. W., Sens. Actuators B Chem., 2018, 262, 313—325 |
| 45 | Pan Z. Y., Feng W. W., Liu Q. Y., He L., Yao D. H., He Z. D., Dyes Pigm., 2022, 203, 110387 |
| 46 | Zhan Z., Zhuang W., Lei Q., Li S., Mao W., Chen M., Li W., Chem. Commun., 2022, 58(25), 4020—4023 |
| 47 | Li S., Zhuang W., Chen J., Li L., Li G., Li J., Liao Y., Chen M., Wang Y., Sens. Actuators B Chem., 2021, 346, 130458 |
| 48 | Wang S., Li X., Chong S. Y., Wang X., Chen H., Chen C., Ng L. G., Wang J. W., Liu B., Adv. Mater., 2021, 33(11), 2007490 |
| 49 | Zheng J., Zhao S., Mao Y., Du Z., Li G., Sang M., Small, 2022, 18(5), 2104471 |
| 50 | Sang M., Cai B., Qin S., Zhao S., Mao Y., Wang Y., Yu X., Zheng J., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces., 2021, 13(49), 58369—58381 |
| 51 | Libby P., Bornfeldt K. E., Tall A. R., Circ. Res., 2016, 118(4), 531—534 |
| 52 | Abdel⁃Maksoud M. S., El⁃Gamal M. I., Benhalilou D. R., Ashraf S., Mohammed S. A., Oh C. H., Med. Res. Rev., 2019, 39(2), 631—664 |
| 53 | Lewis D. R., Petersen L. K., York A. W., Zablocki K. R., Joseph L. B., Kholodovych V., Prud'homme R. K., Uhrich K. E., Moghe P. V., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2015, 112(9), 2693—2698 |
| 54 | Ma B., Xu H., Wang Y., Yang L., Zhuang W., Li G., Wang Y., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13(30), 35410—35421 |
| 55 | Ma B., Xu H., Zhuang W., Wang Y., Li G., Wang Y., Small, 2020, 16(45), 2003253 |
| [1] | ZHAO Yongmei, MU Yeshu, HONG Chen, LUO Wen, TIAN Zhiyong. Bis-naphthalimide Derivatives for Picronitric Acid Detection in Aqueous Solution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210765. |
| [2] | TANG Qian, DAN Feijun, GUO Tao, LAN Haichuang. Synthesis and Application of Quinolinone-coumarin-based Colorimetric Fluorescent Probe for Recognition of Hg2+ [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210660. |
| [3] | YANG Yanling, YE Deju. Recent Advances in the Development of Molecular Probes for Targeting Carbonic Anhydrases [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(12): 20220557. |
| [4] | YAO Shankun, DING Weizhong, WU Yanping, CHEN Yuncong, GUO Zijian. Research Progress in Bioimaging and Theranostics of Thioxanthene-hemicyanine Dyes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(12): 20220568. |
| [5] | YE Zhuo, JI Moxuan, LIU Dingbin. Advances of Optical Probes in Atherosclerosis Imaging [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(12): 20220556. |
| [6] | WANG Di, ZHONG Keli, TANG Lijun, HOU Shuhua, LYU Chunxin. Synthesis of Schiff-based Covalent Organic Framework and Its Recognition of I ‒ [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220115. |
| [7] | HUANG Shan, YAO Jiandong, NING Gan, XIAO Qi, LIU Yi. Efficient Determination of Alkaline Phosphatase Activity Based on Graphene Quantum Dots Fluorescent Probes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2412. |
| [8] | LI Anran, ZHAO Bing, KAN Wei, SONG Tianshu, KONG Xiangdong, BU Fanqiang, SUN Li, YIN Guangming, WANG Liyan. ON-OFF-ON Double Colorimetric and Fluorescent Probes Based on Phenanthro[9,10-d]imidazole Derivatives and Their Living Cells Imaging [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2403. |
| [9] | YANG Xinjie, LAI Yanqiong, LI Qiuyang, ZHANG Yanli, WANG Hongbin, PANG Pengfei, YANG Wenrong. An Enzyme-free and Label-free Fluorescent Probe for Detection of Microcystin-LR Based on Circular DNA-Silver Nanoclusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3600. |
| [10] | CHEN Weiju, CHEN Shiya, XUE Caoye, LIU Bo, ZHENG Jing. Fluorescent Probe for Hypoxia-triggered Imaging and Cancer Therapy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3433. |
| [11] | HUANG Jialing,LIU Fengjiao,WANG Tingting,LIU Cuie,ZHENG Fengying,WANG Zhenhong,LI Shunxing. Nitrogen and Sulfur co-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Accurate Detection of pH in Gastric Juice† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1513. |
| [12] | WU Qian, CHENG Dan, LÜ Yun, YUAN Lin, ZHANG Xiaobing. Monitoring of Peroxynitrite Variation During Liver Injury Adopting a Far Red to Near-infrared Fluorescent Probe with Large Stokes Shift [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2426. |
| [13] |
WANG Jinjin,QI Shaolong,DU Jianshi,YANG Qingbiao,SONG Yan,LI Yaoxian.
Synthesis of Benzothiazole Fluorescent Probe for Detection of N2H4·H2O and HS |
| [14] | Yong ZHANG,Cheng SHEN,Zhirong XING,Guiqi CHEN,Zi LU,Zhibing HOU,Xuemei CHEN. Benzimidazole-Derived Fluorescence Enhancement Probe for Visual Detection of HClO † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2480. |
| [15] | FANG Chao,ZHU Hanyu,LIU Ye,ZHAO Waiou,LI Yapeng,WANG Jingyuan. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanoparticles with Hydrogen Peroxide Sensitivity, Targeting and Fluorscence for Atherosclerosis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 2071. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||