

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (9): 2071.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180033
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
FANG Chao1, ZHU Hanyu1, LIU Ye1, ZHAO Waiou2, LI Yapeng1,*( ), WANG Jingyuan1
), WANG Jingyuan1
Received:2018-01-09
Online:2018-09-07
Published:2018-03-26
Contact:
LI Yapeng
E-mail:liyapeng@jlu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
FANG Chao,ZHU Hanyu,LIU Ye,ZHAO Waiou,LI Yapeng,WANG Jingyuan. Synthesis and Characterization of Nanoparticles with Hydrogen Peroxide Sensitivity, Targeting and Fluorscence for Atherosclerosis[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 2071.
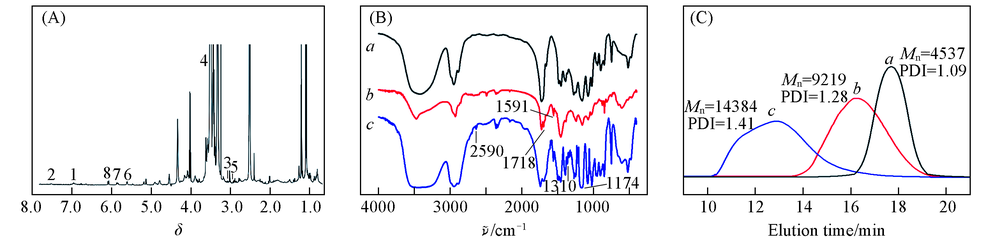
Fig.1 1H NMR spectrum(A), FTIR spectra(B) and GPC curves(C) of PSFI Peaks 1—8 are corresponding to the positions 1—8 in Scheme 2. a. PHEMA; b. PHEMA-Sim; c. PSFI.
| n(Sim)-n(FPEG) | 104 cmc/(mg·mL-1) | Size/nm | PDI | Yield/g | Yield rate(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-1 | 77.60 | 225.5±2.4 | 0.189±0.035 | 0.844 | 53.4 |
| 2-1 | 63.30 | 211.2±5.6 | 0.221±0.022 | 0.468 | 45.9 |
| 3-1 | 25.20 | 192.6±3.8 | 0.205±0.019 | 0.397 | 47.6 |
| 4-1 | 8.69 | 154.3±4.2 | 0.211±0.017 | 0.324 | 43.8 |
| 5-1 | 8.90 | 165.5±1.0 | 0.169±0.035 | 0.268 | 39.2 |
Table 1 Characteristics of PHEMA-Sim-FPEG
| n(Sim)-n(FPEG) | 104 cmc/(mg·mL-1) | Size/nm | PDI | Yield/g | Yield rate(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-1 | 77.60 | 225.5±2.4 | 0.189±0.035 | 0.844 | 53.4 |
| 2-1 | 63.30 | 211.2±5.6 | 0.221±0.022 | 0.468 | 45.9 |
| 3-1 | 25.20 | 192.6±3.8 | 0.205±0.019 | 0.397 | 47.6 |
| 4-1 | 8.69 | 154.3±4.2 | 0.211±0.017 | 0.324 | 43.8 |
| 5-1 | 8.90 | 165.5±1.0 | 0.169±0.035 | 0.268 | 39.2 |
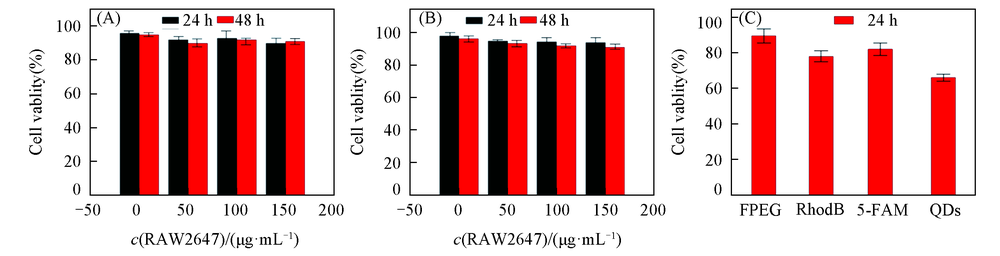
Fig.5 Cytotoxicity evaluation of PSFI in macrophages RAW264.7(A) and endothelial cells RBMEC(B) and PHEMA-Sim-FPEG, PHEMA-Sim-RhoB, PHEMA-Sim-5-FAM, PHEMA-Sim-PEG@QDs in macrophages RAW264.7 24 h(C)
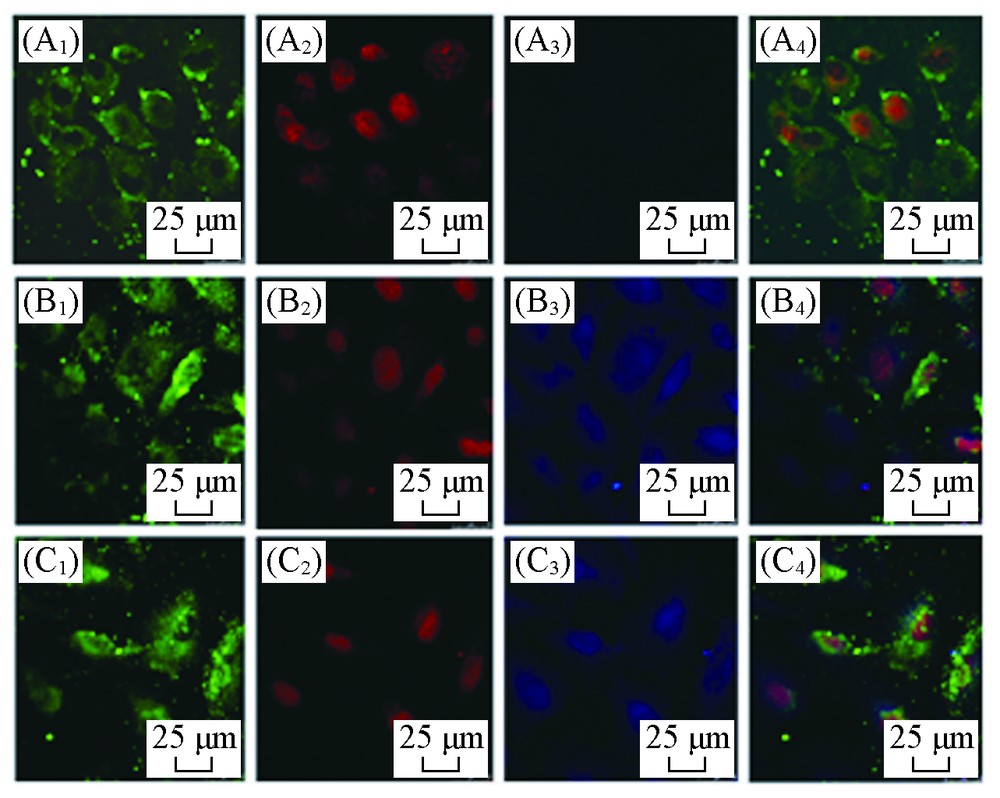
Fig.6 Confocal laser scanning microscope images of blank(A1—A4), PSF(B1—B4) and PSFI(C1—C4) in macrophages RAW264.7(A1—C1) F-actin; (A2—C2) nuclear; (A3—C3) nanoparticles; (A4—C4) merge.
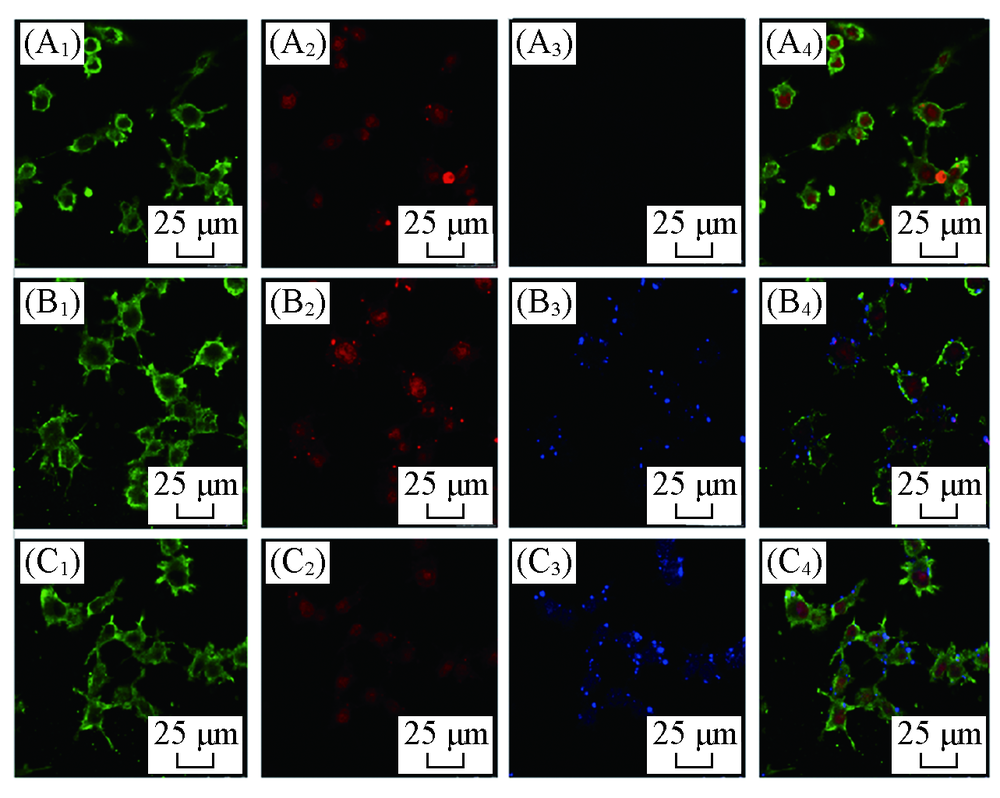
Fig.7 Confolcal laser scanning microscope images of blank(A1—A4), PSF(B1—B4) and PSFI(C1—C4) in endothelial cells RBMEC in mice(A1—C1) F-actin; (A2—C2) nuclear; (A3—C3) nanoparticles; (A4—C4) merge.
| [1] | Mark E. L., Claudia C., Antoine M., Max L. S., Francois F., Philip M. R., Sarayu R., Tina B., Maarten P., Steven S., Stephan R., Ronald E. G., Luis C. Z., Gert S., Josbert M. M., Christopher H. C., Erik S. G., Zahi A. F., Willem J. M., ACS Nano, 2015, 9(2), 1837—1847 |
| [2] | Tuttolomondo A., Di R. D., Pecoraro R., Arnao V., Pinto A., Licata G., Curr. Pharm. Design, 2012, 18(28), 4266—4288 |
| [3] | Hadeel A. Y., J. Fac. Med. Baghdad, 2014, 56(2), 186—190 |
| [4] | Yamashita T., Sasaki N., Kasahara K., Hirata K. I., J. Cardiol., 2015, 66(1), 1—8 |
| [5] | Schiener M., Hossann M., Viola J. R., Ortega-Gomez A., Weber C., Lauber K., Lindner L. H., Soehnlein O., Trends Mol. Med., 2014, 20(5), 71—81 |
| [6] | Wong B. W., Meredith A., Lin D., Mcmanus B. M., Can. J. Cardiol., 2012, 28(6), 631—641 |
| [7] | Petros R. A., De Simone J. M., Nat. Rev. Drug Discov., 2015, 9, 615—627 |
| [8] | Brannon P. L., Blanchette J. O., Adv. Drug Deliver Rev., 2004, 56(11), 1649—1659 |
| [9] | Tapeinos C., Pandit A., Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(27), 5553—5585 |
| [10] | Madamanchi N. R., Vendrov A., Runge M. S., Arterioscl. Throm. Vas., 2005, 25(1), 29—38 |
| [11] | Tong R., Tang L., Ma L., Tu C., Baumgartner R., Cheng J., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43(20), 6982—7012 |
| [12] | Zhang Y., Yu J., Bomba H. N., Zhu Y., Gu Z., Chem. Rev., 2016, 116(19), 12536—12563 |
| [13] | Sun X. C., Yang H., Wang J. Z., Ma R. J., An Y. L., Shi L. Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(7), 1570—1578 |
| (孙小成, 杨浩, 王建祖, 马如江, 安英丽, 史林启. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(7), 1570—1578) | |
| [14] | Lee S. H., Gupta M. K., Bang J. B., Bae H., Sung H. J., Adv. Healthcare Mater., 2013, 2(6), 908—915 |
| [15] | Yan Q., Yuan J. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(9), 1877—1885 |
| (闫强, 袁金颖. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(9), 1877—1885) | |
| [16] | Liu X., Xiang J. J., Zhu D. C., Jiang L. M., Zhou Z. X., Tang J. B., Liu X. R., Huang Y. Z., Shen Y. Q., Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(9), 1743—1752 |
| [17] | Xu Q. H., He C. L., Xiao C. S., Chen X. S., Macromol. Biosci., 2016, 16(5), 635—646 |
| [18] | Christos T., Abhay P., Adv. Mater., 2016, 28, 5553—5585 |
| [19] | Marian V., Dieter L., Jan M., Mark T. D., Milan M., Joshua T., Int. J. Biochem. & Cell Biology, 2007, 39, 44—84 |
| [20] | Barnes T. C., Anderson M. E., Edwards S. W., Moots R. J., Rheumatology, 2012, 51, 1166—1169 |
| [21] | Manuela C., Ileana M., Curr. Med. Chem., 2017, 24, 550—567 |
| [22] | Velasquez J. C., Weiss D., Joseph G., Landazuri N., Taylor W. R., Circulation, 2008, 118(18), S510 |
| [23] | Wang Y. L., Sun G. Y., Zhang Y., He J. J., Zheng S., Lin J. N., Mol. Med. Rep., 2016, 14, 3559—3564 |
| [24] | Guanying C., Indrajit R., Chunhui Y., Paras N.P., Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 2826—2885 |
| [25] | Mahmoud E., Gyu S., Soon-Mi L., Guorong S., Karen L.W., Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 10967—11011 |
| [26] | Karel U., Kateǐina H., Vladimir S., Aristides B., Jiǐí T., Radek Z., Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 5338—5431 |
| [27] | Calandra T., Roger T., Nat. Rev. Immunol., 2003, 3(10), 791—800 |
| [28] | Chang D., Wang Y. C., Zhang S. J., Bai Y. Y., Liu D. F., Zang F. C., Wang G. Z., Wang B. H., Ju S. H., Biomaterials, 2015, 68, 67—76 |
| [29] | Gui R. J., An X. Q., Huang W. X., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2013, 767, 134—140 |
| [30] | Gyawali D., Zhou S. Y., Tran R. T., Zhang Y., Liu C., Bai X. C., Yan. J., Adv. Healthcare Mater., 2014, 3(2), 182—186 |
| [31] | Yang J., Zhang Y., Gautam S., Liu L., Dey J., Chen W., Mason R. P., Serrano C. A., Schug K. A., Tang L. P., Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2009, 106(25), 10086—10091 |
| [32] | Cheng K. F., Al-Abed Y., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2006, 16(13), 3376—3379 |
| [33] | Gao H., Matyjaszewski K., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129(20), 6633—6639 |
| [34] | Wang J., Greszta DMatyjaszewski K., Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng., 1995, 73, 416—417 |
| [35] | Jiao Z., Liu N., Chen Z. M., Pharm. Dev. Technol., 2012, 17, 164—169 |
| [36] | Lee D., Khaja S., Velasquezcastano J. C., Madhuri D., Carrie S., John P. W., Taylor R., Niren M., Nat. Mater., 2007, 6(10), 765—769 |
| [37] | Carsten S., Stephan L. M., Martin P., Pieter A., Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. P, 2003, 30, 249—253 |
| [38] | Burak C. S., Ayse S. Ş., Exp. Therap. Med., 2014, 8, 1660—1664 |
| [39] | Calin M., Manduteanu I., Curr. Med. Chem., 2017, 24, 550—567 |
| [40] | Brown B. G., Zhao Q. X., Chait A., N. Engl. J. Med., 2001, 345(22), 1583—1592 |
| [41] | Pavia C. S., Folds J. D., Baseman J. B., Infect. Immun., 1977, 17(3), 651—654 |
| [42] | Sarala B., Atish R., Pradip K. G., Vitthal N. Y., Divya K., Anshu C., Pooja B., Shaila S., Somesh S., Ram A. V., Nilesh M. D., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2005, 19(16), 4773—4776 |
| [1] | JIANG Jing,CHEN Xiaoli,HUANG Yali,ZHANG Qilong,XU Hong,YANG Xiaosheng. Interaction Mode Between Q[8] and Feb † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 277. |
| [2] | YE Hui, LIU Yabo, JIA Yuxi. Numerical Simulation of Swelling and Drug Release Processes for Weak Polyelectrolyte Hydrogels† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(4): 817. |
| [3] | JIAN Yuhang, YAN Shifeng, LI Xing, HUANG Yanan, YIN Jingbo. Synthesis and Characterization of Injectable Hydrogels Based on Star β-CD-g-poly(L-glutamic acid) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(8): 1489. |
| [4] | ZHANG Haipeng, HAN Bing, JIA Zhizhen, DING Rongbo, XU Bin, XU Weiqing, FAN Zhimin. Fabrication of Drug Loaded Fluorescent Nanoparticles and Its Biological Application in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5): 860. |
| [5] | WANG Xiaodan, XU Dandan, LÜ Weizhong, LIU Jingyuan, LIU Qi, JING Xiaoyan, WANG Jun. Preparation and Drug Release of Anti-cancer Fe3O4@ZIF-8@PA System Loaded with Drug† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 1927. |
| [6] | LI Zhengzheng, XU Ziyang, GAO Liuyi, ZENG Wei, ZHAO Linlin. Preparation and Characterization of Thermo-sensitive N-Acetyl Glycol Chitosan Hydrogel for Sustained Drug Release† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(12): 2299. |
| [7] | HU Qi, FANG Chao, ZHAO Wai’ou, LI Yapeng, CHEN Xia, WANG Jingyuan. Synthetic of PGMA-EDA-g-PEG-g-DS@IO as a Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agent for Atherosclerosis† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(10): 2061. |
| [8] | LIU Nan, WU Yonggang, BAI Libin, WANG Yuan, HUANG Haichao, ZHAO Hongchi, BA Xinwu. Preparation of pH-Sensitive Fluorescent Poly(acryl-2-aminoethy-lammonium hydrochloride) with Porphyrin or Fluorene by One-pot Method† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(5): 1111. |
| [9] | ZHU Shoujin, LIU Faqian, WANG Jingzhao, SU Feng, LI Suming. Systhesis and Characterization of Novel Carboxymethyl Chitosan Hydrogel† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(4): 863. |
| [10] | WEI Yu, JI Ying, JI Jian. REDV/Peptide Conjugated Rapamycin-loaded Polymer Matrix for Endothelial Cells Selectivity [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(01): 193. |
| [11] | NIE Xin, QU Feng-Yu, LI Xiao-Feng, LIN Hui-Ming. Synthesis of Spherical Mesoporous SBA-15 with Abundant Carboxyl and Drug Release Profile [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(7): 1478. |
| [12] | CHEN Yang-Juan, ZHONG Shi-An*, SHI Qiong. Synthesis of Degradable Poly(polyamidoamine-methacrylamide-g-anhydride) Photocrosslinked Gels and Their Controlled Drug Release Behavior [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(5): 1194. |
| [13] | HAN Ya-Dong, XIA Jia-Liang, HE Pan, TIAN Hua-Yu, CHEN Xue-Si*, JING Xia-Bin. Poly(α,L-glutamic acid) Microspheres for Oral Insulin Delivery [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(12): 2521. |
| [14] | MAO Jing, GAN Zhi-Hua*. Synthesis and Controlled Drug Release of Amphiphilic Graft Copolymers PEO-b-PGL-g-PCL [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(11): 2291. |
| [15] | WANG Xin1, WU Zhong-Ming2, ZHANG Xin-Ge1, ZHENG Chao1, WANG Zhen1, LI Chao-Xing1*. Properties and in vitro Evaluation of Chitosan-NAC Nanoparticle for Drug Release [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29(4): 851. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||