

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2021, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (11): 3433.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20210394
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Weiju1, CHEN Shiya2, XUE Caoye3, LIU Bo4, ZHENG Jing2( )
)
Received:2021-06-10
Online:2021-11-10
Published:2021-11-10
Contact:
ZHENG Jing
E-mail:zhengjing2013@hnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
CHEN Weiju, CHEN Shiya, XUE Caoye, LIU Bo, ZHENG Jing. Fluorescent Probe for Hypoxia-triggered Imaging and Cancer Therapy[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3433.
| Sensing moiety | Trigger | Reduction mechanism | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
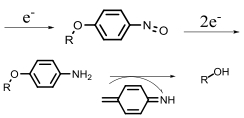
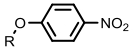 | Nitroreductase | 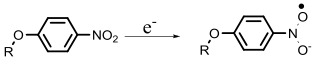 | Hypoxia?related parameter imaging, metabolic process imaging | [20, 24, 36—39, 47] |
 | Chemotherapy, photodynamic therapy | [ | ||
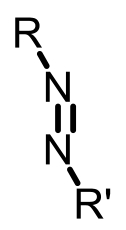 | Azoreductase | 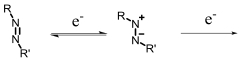 | Hypoxia?related parameter imaging,metabolic process imaging | [ |
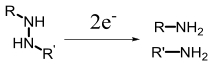 | Gene therapy, chemotherapy, photodynamic therapy, synergistic therapy | [29, 50, 55—57, 63, 65—69] | ||
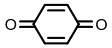 | Quinone reductase | 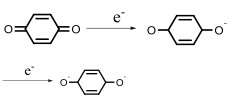 | Hypoxia?related parameter imaging, metabolic process imaging | [ |
| Sensing moiety | Trigger | Reduction mechanism | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Nitroreductase | 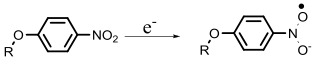 | Hypoxia?related parameter imaging, metabolic process imaging | [20, 24, 36—39, 47] |
 | Chemotherapy, photodynamic therapy | [ | ||
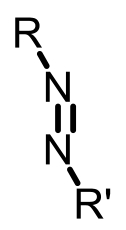 | Azoreductase |  | Hypoxia?related parameter imaging,metabolic process imaging | [ |
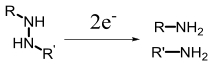 | Gene therapy, chemotherapy, photodynamic therapy, synergistic therapy | [29, 50, 55—57, 63, 65—69] | ||
 | Quinone reductase |  | Hypoxia?related parameter imaging, metabolic process imaging | [ |
| 49 | Williamson B., Nature, 1982, 298(5873), 416—418 |
| 50 | Perche F., Biswas S., Wang T., Zhu L., Torchilin V. P., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53(13), 3362—3366 |
| 51 | Li X., Kwon N., Guo T., Liu T., Yoon J., Chem. Mater., 2018, 57(36), 11522—11531 |
| 52 | Md N., Chung S. J., Kalashnikova I., Meghan L. H., Silver H., George J., Christopher H. C., Kim T., ACS Applied. Bio. Materials, 2020, 3(11), 7989—7999 |
| 53 | Liu Y. Y., Liu Y., Bu W. B., Cheng C., Zuo C. J., Xiao Q. F., Sun Y., Ni D. L., Zhang C., Liu J. N., Shi J. L., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54(28), 8105—8109 |
| 54 | Li J., Ou H.L., Dan D., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2021, 37(1), 83—89 |
| 55 | Li J., Liu W., Li Z. H., Hu Y. C., Yang J. F., Li J. S., Chem. Commun.,2021, 57(38), 4710—4713 |
| 56 | Li J. J, Meng X., Jian D., Lu D., Zhang X., Chen Y. R, Zhu J. D., Fan A. P., Ding D., Kong D. L., Wang Z., Zhao Y. J., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10(20), 17117—17128 |
| 57 | Liu J., Ding G., Chen S. Y., Xue C. Y., Chen M., Wu X., Yuan Q., Zheng J., Yang R. H., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13(8), 9681—9690 |
| 58 | Chen H. C., Bi Q. R., Yao Y. R., Tan N. H., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018, 6(26),4351—4359 |
| 59 | Sui M. H., Liu W. W., Shen Y. Q., J. Control. Release, 2011, 155(2) 227—236 |
| 60 | Hu Q. Y., Sun W. J., Wang C., Gu Z., Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2016, 98, 19—34 |
| 61 | Li M. Q., Ma H., Shi C., Zhang H., Long S., Sun W., Du J. J., Fan J. L., Peng X. J., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2021, 37(4),doi: 10.1007/s40242⁃021⁃1186⁃3 |
| 62 | Li H. L., Lei W. Y., Wu J. N., Li S. H., Zhou G. Q., Liu D. D., Yang X. J., Wang S. X., Li Z. H., Zhang J. C., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018, 6(18), 2747—2757 |
| 63 | Lee J., Oh E. T., Yoon H., Kim C. W., Han Y., Song J., Jang H., Park H. J., Kim C., Nanoscale, 2017, 9(20), 6901—6909 |
| 64 | Liu W., Liu H. T., Peng X. R., Zhou G. Q., Liu D. D., Li S. H., Zhang J. C., Wang S. X., Bioconjugate. Chem., 2018, 29(10), 3332—3343 |
| 65 | Mamnoon B., Feng L., Froberg J., Choi Y., Sathish V., Mallik S., Mol. Pharm., 2020, 17(11), 4312—4322 |
| 1 | Brown J. M., Wilson W. R., Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2004, 4(6), 437—447 |
| 2 | Harris A. L., Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2002, 2(1), 38—47 |
| 3 | Lee P., Chandel N. S., Simon M. C., Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol., 2020, 21(5), 268—283 |
| 4 | Yun J. K., McCormic T. S., Villabona C., Judware R. R., Espinosa M. B., Lapetina E. G., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., USA, 1997, 94(25),13903—13908 |
| 5 | Mazure N. M., Pouyssegur J., Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 2010, 22(2), 177—180 |
| 6 | Hu Y. L., Delay M., Jahangiri A., Molinaro A. M., Rose S. D., Carbonell W. S., Aghi M. K., Cancer Res., 2012, 72(7), 1773—1783 |
| 7 | Wilson W. R., Hay M. P., Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2011, 11(6), 393—410 |
| 8 | Sahu A., Kwon I., Tae G., Biomaterials,2020, 228, 119578 |
| 9 | Liu Y. Y., Jiang Y. Q., Zhang M., Tang Z. M., He M. Y., Bu W., Acc. Chem. Res., 2018, 51(10), 2502—2511 |
| 10 | Zbaida S., Levin W. G., Chem. Res. Toxicol., 1991, 4(1), 82—88 |
| 11 | Boddu R. S., Perumal O., K D., Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem., 2020, doi: 10.1002/bab.2073 |
| 12 | Yang Y., Zhang Y., Wu Q. Y., Cui X. L., Lin, Z. H., Liu S. P., Chen L. Y., J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res., 2014, 33, 14 |
| 13 | Thambi T., Park J. H., Lee D. S., Chem. Commun., 2016, 52(55), 8492—8500 |
| 66 | Wang W. L., Lin L., Ma X. J., Wang B., Liu S. R., Yan X. X., Li S. R., Tian H. Y., Yu X. F., Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10(23), 19398—19407 |
| 67 | Zhang X. L., Wu M., Li J., Lan S. Y., Zeng Y. Y., Liu X. L., Liu J. F., Appl. Mater. Interfaces,2018, 10(26),21909—21919 |
| 68 | Huang C. X., Zheng J., Ma D. D., Liu N., Zhu C., Li J. S., Yang R. H., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018, 6(40), 6424—6430 |
| 14 | Sanduleanu S., Wiel A., Lieverse R. I. Y., Marcus D., Ibrahim A., Primakov S., Wu G. Y., TheysJ., Yaromina A., Dubois L. J., Lambin P., Cancers, 2020, 12(5), 1322 |
| 15 | Bennani⁃Baiti B., Pinker K., Zimmermann M., Helbich T. H., Baltzer P. A., Clauser P., Kapetas P., Bago⁃Horvath Z., Stadlbauer A., Cancers, 2020, 12(8), 2024 |
| 16 | Sun X. L., Niu G., Chan N., Shen B. Z., Chen X. Y., Mol. Imaging Biol., 2011, 13(3), 399—410 |
| 17 | Gao P., Pan W., Li N., Tang B., Chem. Sci., 2019, 10(24), 6035—6071 |
| 18 | Zhang J., Liu H. W., Hu X. X., Li J., Liang L. H., Zhang X. B., Tan W. H., Anal. Chem., 2015, 87(23), 11832—11839 |
| 69 | Huang C. X., Tan W. H., Zheng J., Zhu C., Huo J., Yang R. H., Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11( 29), 25740—25749 |
| 70 | Riordan J. R., Deuchars K., Kartner N., Alon N., Trent J., Ling V., Nature, 1985, 316(6031), 817—819 |
| 19 | Munkholm C., Parkinson D. R., Walt D. R., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1990, 112( 7), 2608—2612 |
| 20 | Li Z., Li X. H., Gao X. H., Zhang Y. Y., Shi W., Ma H. M., Anal. Chem., 2013, 85(8), 3926—3932 |
| 71 | Shukla S. K., Purohit V., Mehla K., Gunda V., Chaika N. V., Vernucci E., King R. J., Abrego J., Goode G. D., Dasgupta A., Illies A. L., Gebregiworgis T., Dai B. B., Augustine J. J., Murthy D., Attri K. S., Mashadova O., Grandgenett P. M., Powers R., Ly Q. P., Lazenby A. J., Grem J. L., Yu F., Mates J. M., Asara J. M., Kim J. W., Hankins J. H., Weekes C., Hollingsworth M. A., Serkova N. J., Sasson A. R., Fleming J. B., Oliveto J. M., Lyssiotis C. A., Cantley L. C., Berim L., Singh P. K., Cancer Cell, 2017,32(3), 392 |
| 72 | Tian H., Luo Z. Y., Liu L. L., Zheng M. B., Chen Z., Ma A. Q., Liang R. J., Han Z. Q., Lu C. Y., Cai L. T., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27, 1703197 |
| 21 | Li Y. H., Wang Y. J., Yang S., Zhao Y. R., Yuan L., Zheng J., Yang R. H., Anal. Chem., 2015, 87(4), 2495—2503 |
| 22 | He X. Y., Li L. H., Fang Y., Shi W., Li X. H., Ma H. M., Chem. Sci., 2017, 5( 8), 3479—3783 |
| 23 | Yu X. Z, Xiang L., Yang S., Qu S.L., Zeng X., Zhou Y. B., Yang R. H., Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2021, 245, 118887 |
| 24 | Fan Y. S., Lu M., Yu X. A., He M. L., Zhang Y., Ma X. N., Kou J. P., Yu B.Y., Tian J. W., Anal. Chem., 2019, 91(10), 6585—6592 |
| 25 | Eom T., Yoo W., Kim S., Khan A., Biomaterials,2018, 185, 333—347 |
| 26 | Rao J., Khan A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(38), 14056—14059 |
| 27 | Kiyose K., Hanaoka K., Oushiki D., Nakamura T., Kajimura M., Suematsu M., Nishimatsu H., Yamane T., Terai T., Hirata Y., Nagano T., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(45), 15846—15848 |
| 28 | Tian Y., Li, Y. F., Jiang W. L., Zhou D. Y., Fei J. J., Li C. Y., Anal. Chem.,2019, 91(16), 10901—10907 |
| 29 | Zhao X. B., Ha W., Gao K., Shi Y. P., Anal. Chem., 2020, 92(13), 9039—9047 |
| 30 | Piao W., Tsuda S., Tanaka Y., Maeda S., Liu F. Y., Takahashi S., Kushida Y., Komatsu T., Ueno T., Terai T., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(49), 13028—13032 |
| 31 | Wendlandt A. E., Stahl S. S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2015, 54(49), 14638—14658 |
| 32 | Singh S. K., Husain S. M., ChemBioChem, 2018, 19(15), 1657—1663 |
| 33 | Sun L. L., Chen Y., Kuang S., Li G.Y., Guan R.L., Liu J. P., Ji L. N., Chao H., Chem. Eur. J., 2016, 22, 8955—8965 |
| 34 | Komatsu H., Harada H., Tanabe K., Hiraoka M., Nishimoto S., Med. Chem. Commun., 2010, 1, 50 Ch |
| 35 | Zhang P. Y., Huang H. Y., Chen Y., Wang J. Q., Ji L. N., Chao H., Biomaterials, 2015, 53, 522teri |
| 36 | Zheng A. X., Sun H. Y., Du Y. L., Wang Y. R., Wu M., Liu X. L., Zeng Y. Y., Liu J. F., Anal. Chim. Acta,2021, 1144, 76—84 |
| 37 | Fan L., Zan Q., Lin B., Wang X. D., Gong X. J., Zhao Z. H., Shuang S. M., Dong C., Wong M .S., Analyst, 2020, 145(16), 5657—5663 |
| 38 | Wang Y., Han X. Y., Zhang X., Zhang L., Chen L. X., Analyst, 2020, 145(4), 1389—1395 |
| 39 | Zhang X. Q., Zhao Q., Li Y. R., Duan X. R., Tang Y. L., Anal. Chem.,2017, 89(10), 5503—5510 |
| 40 | Lan G. X., Ni K. Y., You E., Wang M. L., Culbert A., Jiang X. M., Lin W. B., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(48), 18964—18969 |
| 41 | Pouyssegur J., Dayan F., Mazure N. M., Nature, 2006, 441(7092), 437—443 |
| 42 | Sim J., Cowburn A. S., Palazon A., Madhu B., Tyrakis P. A., Macias D., Bargiela D. M., Pietsch S., Gralla M., Evans C. E., Kittipassorn T., Chey Y. C. J., Branco C. M., Rundqvist H., Peet D. J., Johnson R. S., Cell Metab., 2018, 27(4), 898—913 |
| 43 | Liu T., Laurell C., Selivanova G., Lundeberg J., Nilsson P., Wiman K. G., Cell Death Differ., 2007, 14(3), 411—421 |
| 44 | Yadav A. K., Yadav P. K., Chaudhary G. R., Tiwari M., Gupta A., Sharma A., Pandey A. N., Pandey A. K., Chaube S. K., Cell Mol. Life Sci., 2019, 76(17), 3311—3322 |
| 45 | Li X. Y., Li Y. H., Ma H. M., Chem. Sci., 2020, 11(6), 1617—1622 |
| 46 | Ma D. D., Huang C. X., Zheng J., Zhou W. Y., Tang J. R., Chen W. J., Li J. S., Yang R. H., Anal. Chem., 2019, 91(2), 1360—1367 |
| 47 | Liu Y. C., Teng L. L., Chen L. L., Ma H. C., Liu H. W., Zhang X. B., Chem. Sci., 2018,9(24), 5347—5353 |
| 48 | Chen S. Y., Liu J., Li Y. H., Wu X., Yuan Q., Yang R. H., Zheng J., Trac⁃trend. Anal. Chem., 2020, 131, 116010 |
| [1] | LIU Suyu, DING Fei, LI Qian, FAN Chunhai, FENG Jing. Azobenzene-integrated DNA Nanomachine [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220122. |
| [2] | ZHAO Yongmei, MU Yeshu, HONG Chen, LUO Wen, TIAN Zhiyong. Bis-naphthalimide Derivatives for Picronitric Acid Detection in Aqueous Solution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210765. |
| [3] | TANG Qian, DAN Feijun, GUO Tao, LAN Haichuang. Synthesis and Application of Quinolinone-coumarin-based Colorimetric Fluorescent Probe for Recognition of Hg2+ [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210660. |
| [4] | WANG Di, ZHONG Keli, TANG Lijun, HOU Shuhua, LYU Chunxin. Synthesis of Schiff-based Covalent Organic Framework and Its Recognition of I ‒ [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220115. |
| [5] | LI Anran, ZHAO Bing, KAN Wei, SONG Tianshu, KONG Xiangdong, BU Fanqiang, SUN Li, YIN Guangming, WANG Liyan. ON-OFF-ON Double Colorimetric and Fluorescent Probes Based on Phenanthro[9,10-d]imidazole Derivatives and Their Living Cells Imaging [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2403. |
| [6] | HUANG Shan, YAO Jiandong, NING Gan, XIAO Qi, LIU Yi. Efficient Determination of Alkaline Phosphatase Activity Based on Graphene Quantum Dots Fluorescent Probes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2412. |
| [7] | YANG Xinjie, LAI Yanqiong, LI Qiuyang, ZHANG Yanli, WANG Hongbin, PANG Pengfei, YANG Wenrong. An Enzyme-free and Label-free Fluorescent Probe for Detection of Microcystin-LR Based on Circular DNA-Silver Nanoclusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3600. |
| [8] | KE Mengting, YUAN Jiangpei, ZHANG Heng, FANG Yu. Coordination Porous Polymers for Targeting Subcellular Organelles: Bio-imaging, Diagnosis and Therapy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3295. |
| [9] | WANG Mengmeng, LUAN Tianjiao, YANG Mingyan, LYU Jiajia, GAO Jie, LI Hongyu, WEI Gang, YUAN Zeli. Rhodamine Fluorescent Probe for Tumor Targeted Hypoxia-imaging as Intra-operative Navigators [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3071. |
| [10] | HUANG Jialing,LIU Fengjiao,WANG Tingting,LIU Cuie,ZHENG Fengying,WANG Zhenhong,LI Shunxing. Nitrogen and Sulfur co-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Accurate Detection of pH in Gastric Juice† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1513. |
| [11] | WU Qian, CHENG Dan, LÜ Yun, YUAN Lin, ZHANG Xiaobing. Monitoring of Peroxynitrite Variation During Liver Injury Adopting a Far Red to Near-infrared Fluorescent Probe with Large Stokes Shift [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2426. |
| [12] |
WANG Jinjin,QI Shaolong,DU Jianshi,YANG Qingbiao,SONG Yan,LI Yaoxian.
Synthesis of Benzothiazole Fluorescent Probe for Detection of N2H4·H2O and HS |
| [13] | Yong ZHANG,Cheng SHEN,Zhirong XING,Guiqi CHEN,Zi LU,Zhibing HOU,Xuemei CHEN. Benzimidazole-Derived Fluorescence Enhancement Probe for Visual Detection of HClO † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2480. |
| [14] | YANG Mei,LIU Qing,TANG Qing,WANG Chenghui,YANG Meixiang,SUN Tao,HUANG Ying,TAO Zhu. Water-soluble Supramolecular Fluorescent Probe for Sensing Carbendazim and Its Application in Living Cell Imaging† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(12): 2665. |
| [15] | HE Xiaoqin, HE Junlin, XU Hua, GUO Lei, XIE Jianwei. Active Conformation of DNA Aptamer Against Recombinant Human Erythropoietin-α† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(1): 48. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||