

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 20210765.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20210765
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Yongmei1, MU Yeshu2,3, HONG Chen, LUO Wen3( ), TIAN Zhiyong2(
), TIAN Zhiyong2( )
)
Received:2021-11-08
Online:2022-03-10
Published:2022-01-13
Contact:
LUO Wen
E-mail:luowen83@163.com;tzynew@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHAO Yongmei, MU Yeshu, HONG Chen, LUO Wen, TIAN Zhiyong. Bis-naphthalimide Derivatives for Picronitric Acid Detection in Aqueous Solution[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210765.
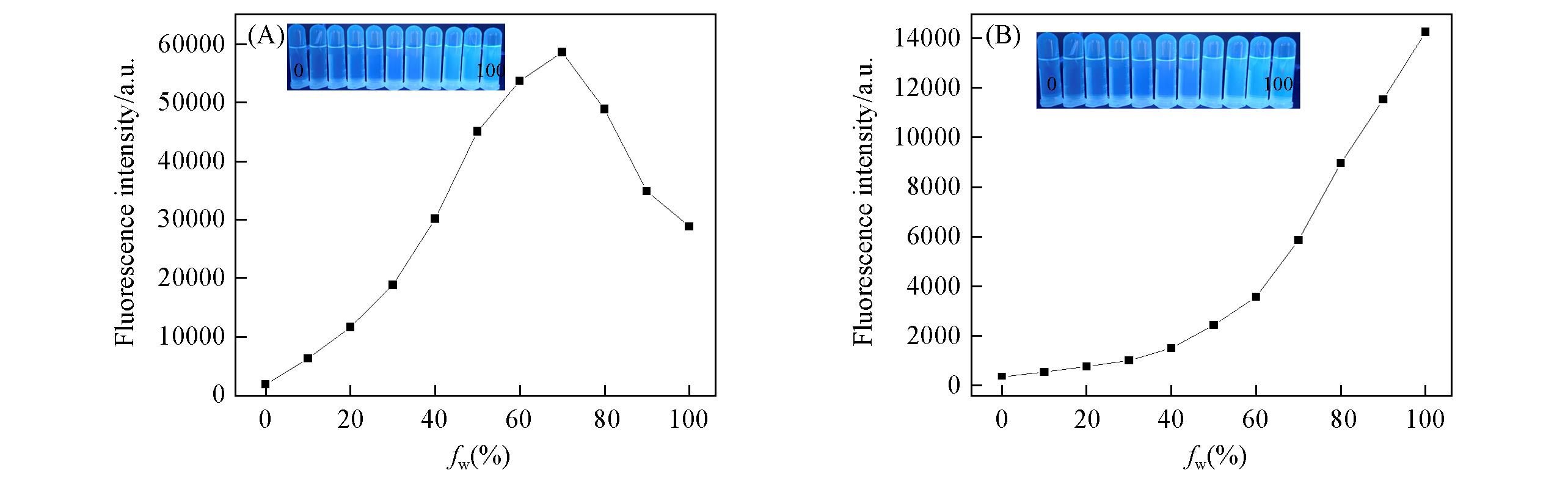
Fig.4 FL intensities of Bis?Nph(20 μmol/L) at 392 nm(A) and 490 nm(B) versus the water fraction in THF/water mixturesInsets: photographs under the illumination of a UV lamp(365 nm) at fw of 0, 10%, 20%, …… 100%.
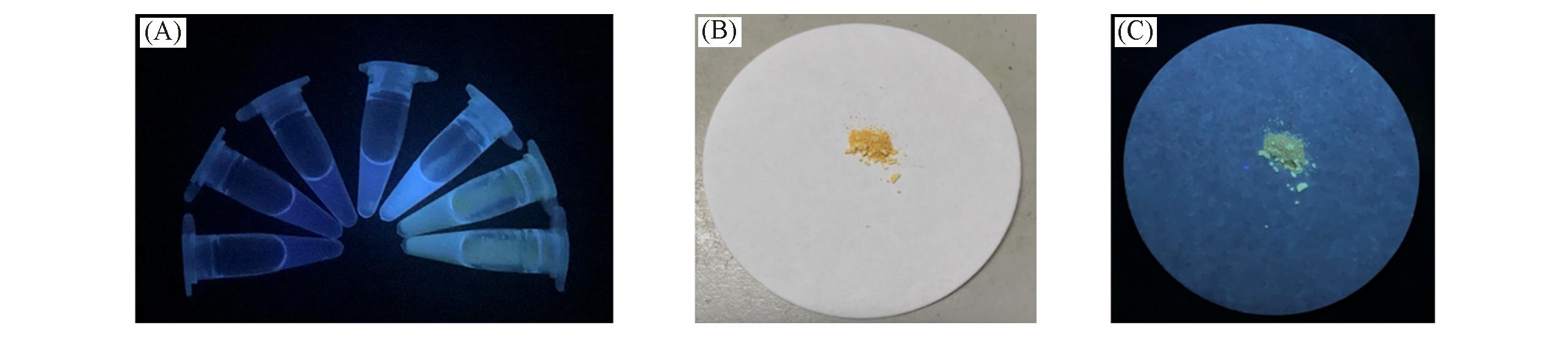
Fig.6 Photographs of Bis?Nph in THF under UV lamp(365 nm)(A), powder under the daylight(B) and UV lamp(365 nm)(C)(A) Concentrations from left to right: 1 μmol/L, 10 μmol/L, 100 μmol/L, 1 mmol/L, 10 mmol/L, 100 mmol/L, 200 mmol/L.
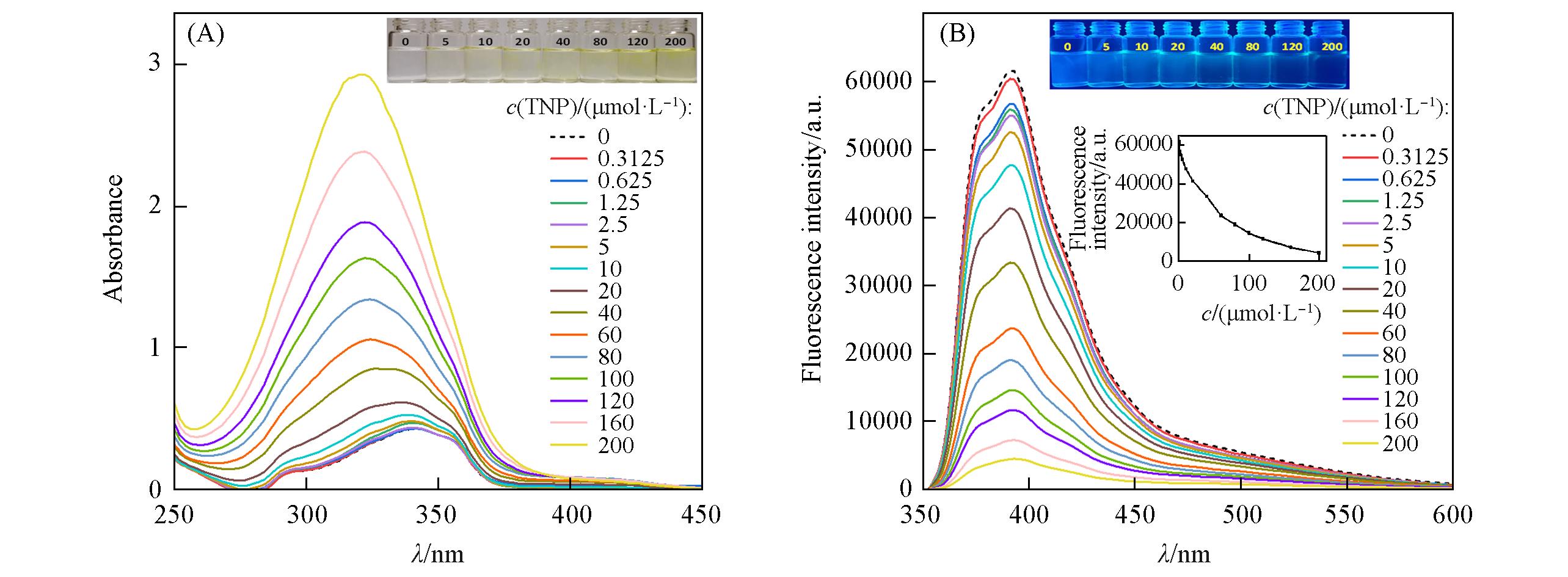
Fig.7 UV(A) and FL(B) spectra and relative photographs(insets) of Bis?Nph(20 μmol/L) with the change of TNP concentrations(0—200 μmol/L)Inset of (B): the FL intensity(391 nm) change of Bis?Nph with the increase of TNP concentration(μmol/L).
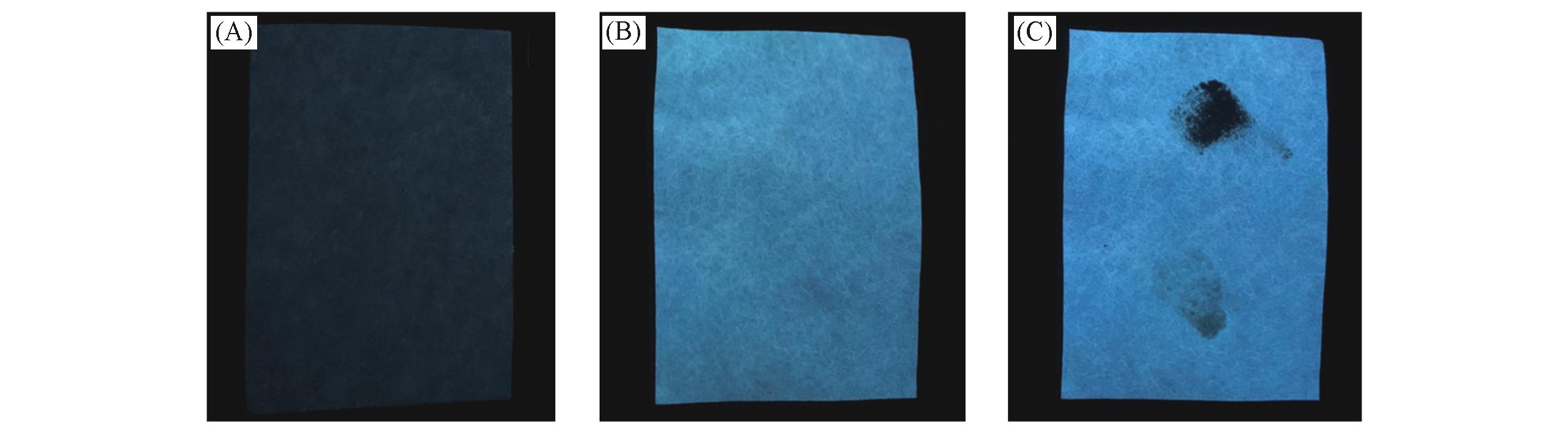
Fig.9 Photos of filter paper under UV light at 365 nm(A) Initial; (B) immersed in Bis?Nph solution(20 μmol/L) and dried; (C) rubbed (B) with TNP by human fingers.
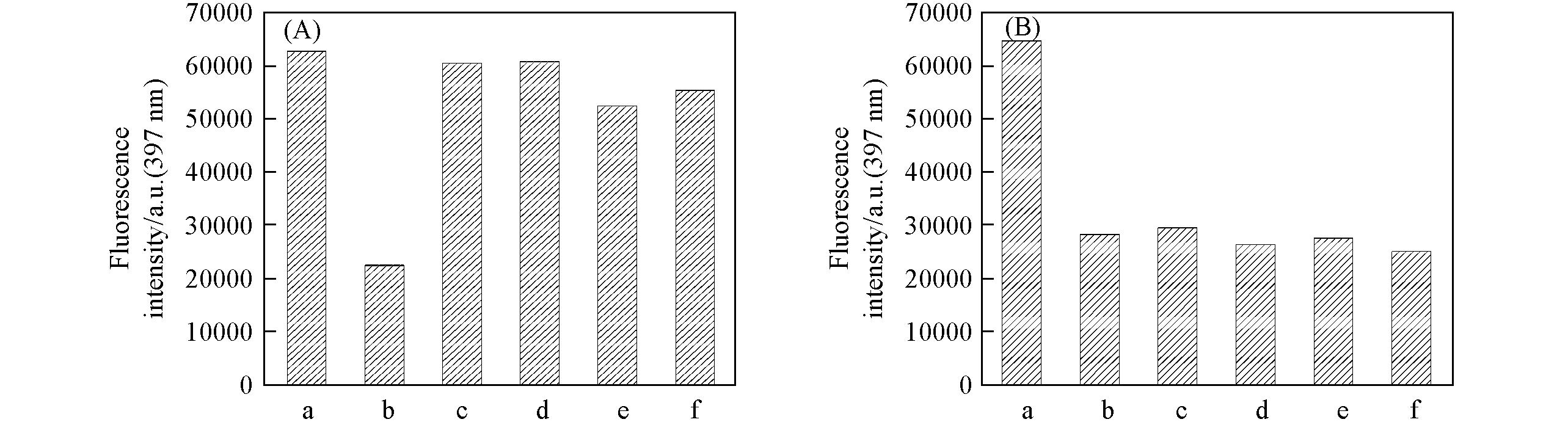
Fig.10 Selectivity(A) and anti?interference(B) of compound Bis?Nph to TNP(A) a. Blank, b. TNP, c. TNT, d. DNT, e. NB, f. NG; (B) a. blank, b. TNP, c. TNT+ TNP, d. DNT+TNP, e. NB+TNP, f. NG+TNP.
| 1 | Ma Y. X., Wang S. G., Wang L. Y., Trac⁃Trend. Anal. Chem., 2015, 65, 13—21 |
| 2 | Sun X. C., Wang Y., Lei Y., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44(22),8019—8061 |
| 3 | Germain M. E., Knapp M. J., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009, 38(9), 2543—2555 |
| 4 | Rong M., Lin L., Song X., Zhao T., Zhong Y., Yan J., Wang,Y., Chen X., Anal. Chem., 2015, 87(2), 1288—1296 |
| 5 | Qu B. H., Mu Z. Y., Liu Y., Liu Y. S., Yan R., Sun J. H., Zhang Z. S., Li P., Jing L. Q., Environ. Sci⁃Nano, 2020, 7(1), 262—271 |
| 6 | Siddique A., Pramanick A. K., Chatterjee S., Ray M., Sci. Rep., 2018, 8(1), 9770 |
| 7 | Chen B., Chai S. Q., Liu J. H., Liu C. J., Li Y. J., He J. H., Yu Z. P., Yang T., Feng C. H., Huang C. Z., Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2019, 411(11), 2291—2300 |
| 8 | Zheng Y. C., Wang S., Li R. F., Pan L., Li L. Q., Qi Z. P., Li C. J., Res. Chem. Intermed., 2021, 47(6), 2421—2431 |
| 9 | Bai L. Y., Wang P., Bose P., Li P. Z., Zou R. G., Zhao Y. L., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7(9), 5056—5060 |
| 10 | Liu J. L., Mi H. Y., Guan M. M., Huan Y. F., Fei Q., Zhang Z. Q., Feng G. D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(12), 2163—2168(刘吉林, 米红玉, 关明明, 郇延富, 费强, 张志权, 冯国栋. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(12), 2163—2168) |
| 11 | Zhang C. L., Zhang S. M., Yan Y. H., Xia F., Huang A. N., Xian Y. Z., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9(15), 13415—13421 |
| 12 | Shi J. J., Xu S., Li N., Wang X. G., Zhao X. J., Yang E. C., Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2019, 35(2), 351—360(石静静, 徐珊, 李娜, 王修光, 赵小军, 杨恩翠. 无机化学学报, 2019, 35(2), 351—360) |
| 13 | Ye J. W., Zhao L. M., Bogale R. F., Gao Y., Wang X. X., Qian X. M., Guo S., Zhao J. Z., Ning G. L., Chem. Eur. J., 2015, 21(5), 2029—2037 |
| 14 | Hu Y. L., Ding M. L., Liu X. Q., Sun L. B., Jiang H. L., Chem. Commun., 2016, 52(33), 5734—5737 |
| 15 | Wang J., Zhang L. W., Bao L., Zhou L., Liu Y. Y., Wu P. Y., Dyes Pigments, 2018, 150, 301—305 |
| 16 | Wu K., Hu J. S., Cheng X. F., Li J. X., Zhou C. H., J. Lumin., 2020, 219, 116908 |
| 17 | Li Z. Y., Yao Z. Q., Feng R., Sun M. H., Shan X. T., Su Z. H., Li W., Bu X. H., Chinese Chem. Lett., 2021, 32(10), 3095—3098 |
| 18 | Roy B., Bar A. K., Gole B., Mukherjee P. S., J. Org. Chem., 2013, 78(3), 1306—1310 |
| 19 | Xia L. X., Zhang H. C., Feng B., Yang D. Q., Bu N. S., Zhao Y. B., Yan Z. J., Li Z. N., Yuan Y., Zhao X. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12), 2456—2464(夏立新, 张红翠, 冯彬, 杨东奇, 布乃顺, 赵云, 闫卓君, 李樟楠, 元野, 赵晓君. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(12), 2456—2464) |
| 20 | Ma H. W., He C. Y., Li X. L., Ablikim O., Zhang S. T., Zhang M., Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 2016, 230, 746—752 |
| 21 | Qi J. P., Hu X. W., Dong X. C., Lu Y., Lu H. P., Zhao W. L., Wu W., Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev., 2019, 143, 206—225 |
| 22 | Hong Y., Lam J. W. Y., Tang B. Z., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40(11), 5361—5388 |
| 23 | Duke R. M., Veale E. B., Pfeffer F. M., Kruger P. E., Gunnlaugsson T., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39(10), 3936—3953 |
| 24 | Xie Z. D., Fu M. L., Yin B., Zhu Q., Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2018, 38(6), 1364—1376(谢振达, 付曼琳, 尹彪, 朱勍. 有机化学, 2018, 38(6), 1364—1376) |
| 25 | Tomczyk M. D., Walczak K. Z., Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2018, 159, 393—422 |
| 26 | Dong H. Q., Wei T. B., Ma X. Q., Yang Q. Y., Zhang Y. F., Sun Y. J., Shi B. B., Yao H., Zhang Y. M., Lin Q., J. Mater. Chem. C, 2020, 8(39), 13501—13529 |
| 27 | Stone R. M., Mazzola E., Neuberg D., Allen S. L., Pigneux A., Stuart R. K., Wetzler M., Rizzieri D., Erba H. P., Damon L., Jang J. H., Tallman M. S., Warzocha K., Masszi T., Sekeres M. A., Egyed M., Horst H. A., Selleslag D., Solomon S. R., Venugopal P., Lundberg A. S., Powell B. J., Clin. Oncol., 2015, 33(11), 1252—1257 |
| 28 | Dai F., Li Q., Wang Y., Ge C., Feng C., Xie S., He H., Xu X., Wang C., J. Med. Chem., 2017, 60(5), 2071—2083 |
| 29 | Li J., Tian R., Ge C., Chen Y., Liu X., Wang Y., Yang Y., Luo W., Dai F., Wang S., Chen S., Xie S., Wang C., J. Med. Chem., 2018, 61(15), 6814—6829 |
| 30 | Xu Z. C., Yoon J., Spring D. R., Chem. Commun., 2010, 46(15), 2563—2565 |
| 31 | Xu Y., Li B., Li W., Zhao J., Sun S., Pang Y., Chem. Commun., 2013, 49(42), 4764—4766 |
| 32 | Zheng Y., Miao M., Kemei M.C., Seshadri R., Wudl F., Isr. J. Chem., 2014, 54(5/6), 774—778 |
| 33 | Pandith A., Kumar A., Lee J. Y., Kim H. S., Tetrahedron Lett., 2015, 56(51), 7094—7099 |
| 34 | Dong M., Wang Y. W., Zhang A. J., Peng Y., Chem. Asian J., 2013, 8(6), 1321—1330 |
| [1] | YANG Jingyi, SHI Siqi, PENG Huaitao, YANG Qihao, CHEN Liang. Integration of Atomically Dispersed Ga Sites with C3N4 Nanosheets for Efficient Photo-driven CO2 Cycloaddition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220349. |
| [2] | WANG Xintian, LI Pan, CAO Yue, HONG Wenhao, GENG Zhongxuan, AN Zhiyang, WANG Haoyu, WANG Hua, SUN Bin, ZHU Wenlei, ZHOU Yang. Techno-economic Analysis and Industrial Application Prospects of Single-atom Materials in CO2 Catalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220347. |
| [3] | QIN Yongji, LUO Jun. Applications of Single-atom Catalysts in CO2 Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220300. |
| [4] | GE Yicong, NIE Wanli, SUN Guofeng, CHEN Jiaxuan, TIAN Chong. Silver-catalyzed [5+1] Cyclization of 2-Vinylanilines with Benzisoxazoles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220142. |
| [5] | YAO Yiting, LYU Jiamin, YU Shen, LIU Zhan, LI Yu, LI Xiaoyun, SU Baolian, CHEN Lihua. Preparation of Hierarchical Microporous-mesoporous Fe2O3/ZSM-5 Hollow Molecular Sieve Catalytic Materials and Their Catalytic Properties for Benzylation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220090. |
| [6] | HAN Fuchao, LI Fujin, CHEN Liang, HE Leiyi, JIANG Yunan, XU Shoudong, ZHANG Ding, QI Lu. Enhance of CoSe2/C Composites Modified Separator on Electrochemical Performance of Li-S Batteries at High Sulfur Loading [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220163. |
| [7] | HUANG Qiuhong, LI Wenjun, LI Xin. Organocatalytic Enantioselective Mannich-type Addition of 5H-Oxazol-4-ones to Isatin Derived Ketimines [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220131. |
| [8] | JIN Ruiming, MU Xiaoqing, XU Yan. Bio-chemical Synthesis of Melanin Precursor—— 5,6-Dihydroxyindole(DHI) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220134. |
| [9] | TAN Yan, YU Shen, LYU Jiamin, LIU Zhan, SUN Minghui, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. Efficient Preparation of Mesoporous γ-Al2O3 Microspheres and Performance of Pd-loaded Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220133. |
| [10] | JIANG Shenghan, CAO Changlin, XIAO Liren, YANG Tang, QIAN Qingrong, CHEN Qinghua. Preparation of Composite Semiconductor Micro-sheets with UV Shielding Performance and Its Application in Polypropylene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220071. |
| [11] | ZHOU Leilei, CHENG Haiyang, ZHAO Fengyu. Research Progress of CO2 Hydrogenation over Pd-based Heterogeneous Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220279. |
| [12] | XIA Wu, REN Yingyi, LIU Jing, WANG Feng. Chitosan Encapsulated CdSe QDs Assemblies for Visible Light-induced CO2 Reduction in an Aqueous Solution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220192. |
| [13] | WANG Zhengwen, GAO Fengxiang, CAO Han, LIU Shunjie, WANG Xianhong, WANG Fosong. Synthesis and Property of CO2 Copolymer⁃based UV-curable Polymer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220236. |
| [14] | YANG Dan, LIU Xu, DAI Yihu, ZHU Yan, YANG Yanhui. Research Progress in Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction Reaction over Gold Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220198. |
| [15] | ZHANG Xinxin, XU Di, WANG Yanqiu, HONG Xinlin, LIU Guoliang, YANG Hengquan. Effect of Mn Promoter on CuFe-based Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Higher Alcohols [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220187. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||