

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (9): 1866.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190106
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHENG Shan1,LIU Yang1,CHEN Piaopiao1,XING Yichen1,HUANG Chaobiao1,2,*( )
)
Received:2019-02-19
Online:2019-09-10
Published:2019-07-16
Contact:
HUANG Chaobiao
E-mail:hcb@zjnu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHENG Shan, LIU Yang, CHEN Piaopiao, XING Yichen, HUANG Chaobiao. Novel Glutathione Photoelectrochemical Sensor Based on PbS QDs/TiO2 NPs †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1866.
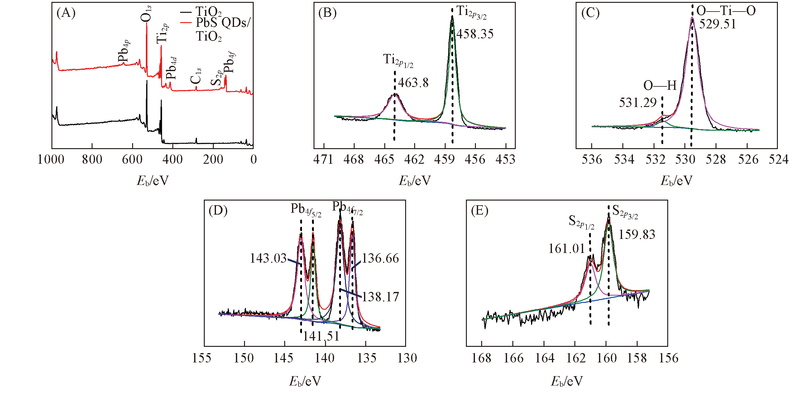
Fig.3 Full-scan XPS spectra of TiO2 NPs and PbS QDs/TiO2 NPs electrodes(A) and high-resolution XPS spectra of Ti2p(B), O1s(C), Pb4f(D) and S2p(E) of PbS QDs/TiO2 NPs electrode
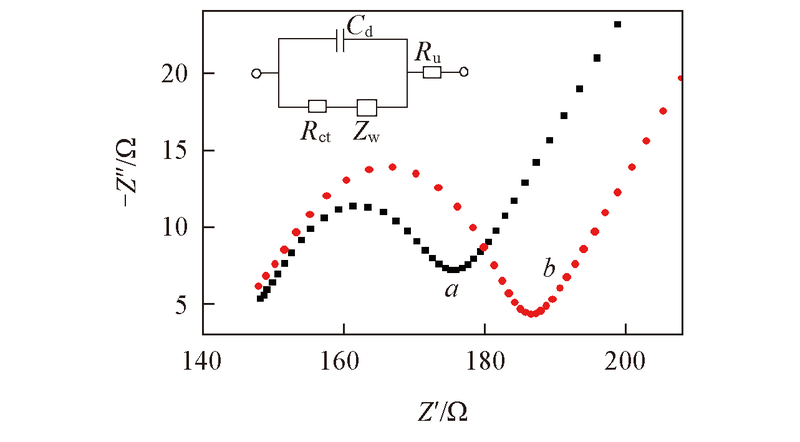
Fig.4 EIS of TiO2 NPs/ITO(a) and PbS QDs/TiO2 NPs/ITO(b) electrodes The EIS measurements are carried out in 0.1 mol/L KCl containing 5.0 mmol/L K3Fe(CN)6/K4Fe(CN)6(1∶1), The frequency range was between 0.1 and 1×105 Hz with an applied voltage of 5 mV. Inset: equivalent circuit diagram. Cd: capacitance; Rct: charge transfer resistance; Ru: ohmic resistance; Zw: diffusion resistance.
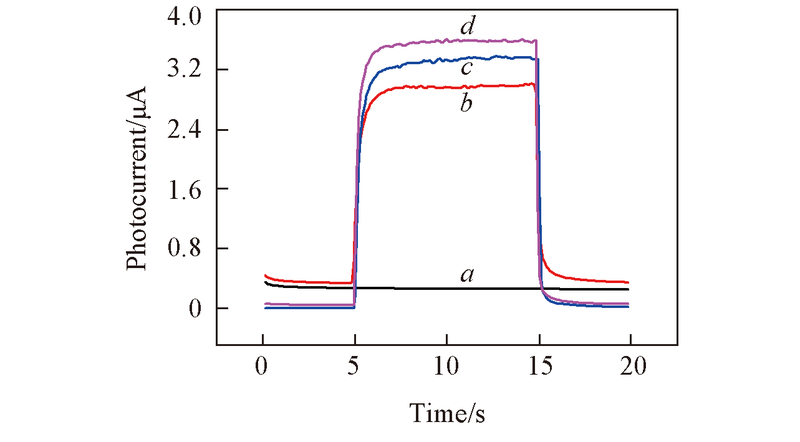
Fig.9 Photocurrent response curves of different modified ITO(a), TiO2/ITO(b), PbS QDs/TiO2/ITO(c) and QDs/TiO2/ITO(d) electrodes in 0.2 mmol/L GSH/PbS
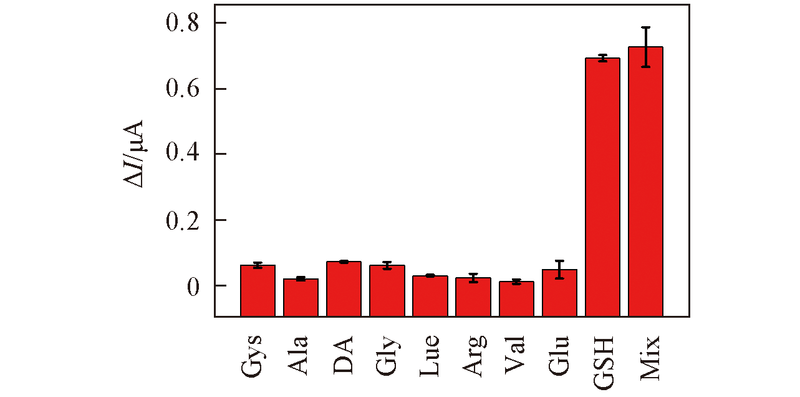
Fig.13 Photocurrent signals of the GSH sensor toward in the presence of 1 mmol/L cysteine(Cys), alanine(Ala), dopamine(DA), glycine(Gly), leucine(Lue), arginine(Arg), valine(Val), glucose(Glu) and all their mixture(Mix) and 0.2 mmol/L GSH
| [1] | Zhang X., Liu M., Liu H., Zhang S., ,. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 56, 307— 312 |
| [2] | Zhao W. W., Xu J. J., Chen H. Y., ,. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 7421— 7441 |
| [3] | Zhang X., Guo Y., Liu M., Zhang S., ,. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 2846— 2857 |
| [4] | Wu Y., Zhang B., Guo L. H., ,Anal. Chem., 2013, 85, 6908— 6914 |
| [5] | Li H., Xiao Q., Lv J. X., Lei Q., Huang Y. J., ,Anal. Biochem., 2017, 531, 48— 55 |
| [6] | Emamdoust A. S., Farjami S., ,. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 738, 432— 439 |
| [7] | Babamiri B., Hallaj R., Salimi A., ,Biosens. Bioelectron., 2018, 99, 353— 360 |
| [8] | Peng C., Wang W., Zhang W., Liang Y., Zhuo L., ,Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 420, 286— 295 |
| [9] | Subramanian A., Pan Z., Li H., Zhou L., Li W., Qiu Y., Xu Y., Hou Y., Zhang Y., ,. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 420, 631— 637 |
| [10] | Dong W., Li H., Xi J., Mu J., Huang Y., Ji Z., Wu X., ,. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 724, 280— 286 |
| [11] | Ye M., Xin X., Lin C., Lin Z., ,Nano Lett., 2011, 11, 3214— 3220 |
| [12] | Lv M., Zheng D., Ye M., Sun L., Xiao J., Guo W Lin C ., Nanoscale, 2012, 4, 5872— 5879 |
| [13] | Wang Y. J., Han C., Liu B., Yang P. D., ,. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5060— 5069 |
| [14] | Stankovich S., Dikin D. A., Piner R. D., Kohlhaas K. A., Kleinhammes A., Jia Y., Wu Y., Nguyen S. T., Ruoff R. S ., Carbon, 2007, 45, 1558— 1565 |
| [15] | Mor G K .,Varghese O. K., Paulose M., Shankar K., Grimes C. A., Sol. Energ. Mat. Sol. C, 2006, 90, 2011— 2075 |
| [16] | Podporska-Carroll J., Panaitescu E., Quilty B., Wang L., Menon L., Pillai S. C., ,. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2015, 176, 70— 75 |
| [17] | Qiu B., Xing M., Zhang J., ,J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 5852— 5855 |
| [18] | Jin L. Y., Dong Y. M., Wu X. M., Cao G. X., Wang G. L., ,Anal. Chem., 2015, 87, 10429— 10436 |
| [19] | Yu Y., Zhang K., Sun S., ,Appl. Surf. Sci., 2012, 258, 7181— 7187 |
| [20] | Li F., Huang X. T., Kong T., Liu X. Q., Qin Q. H., Li Z., ,J. Alloy. Compd., 2009, 485, 554— 560 |
| [21] | Li Y., Wu P., Xu H., Zhang H., Zhong X ., Analyst, 2011, 136, 196— 200 |
| [22] | Franco R., Panayiotidis M. I., Cidlowski J. A., ,J. Biol. Chem., 2007, 282, 30452— 30465 |
| [23] | Wang L. M., Wei M., Gu X. Q., Zhao Y. L., Qiang Y. G., ,J. Electron. Mater., 2018, 47( 11), 6540— 6550 |
| [24] | Zhang H., Xia X., Zhao H., Zhang G. H., Jiang D. Y., Xue X. Y., Zhang J., ,. Dyes Pigments 2019, 163, 183— 189 |
| [25] | Rani P. J., Vishnuvardhan C., Nimbalkar R. D., Garg P., Satheeshkumar N., ,. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 155, 320— 328 |
| [26] | Shi M., Huang Y., Zhao J. J., Li S. T., Liu Y. J., Zhao S. L ., Talanta, 2018, 179, 466— 471 |
| [27] | Wang L. M., Gu X. Q., Zhao Y. L., Wei M., Qiang Y. H., Zhao Y., ,. J. Mater. Sci-Mater. El. 2018, 29, 19278— 19286 |
| [28] | Lee H., Leventis H. C., Moon S. J., Chen P., Ito S., Haque S. A., Torres T., Nüesch F., Geiger T., Zakeeruddin S. M., Grätzel M., Nazeeruddin M. K., ,. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 2735— 2742 |
| [29] | Wang D. F., Zhao H. G., Wu N. Q., Khakani M. A. E., Ma D. L., ,. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 1030— 1035 |
| [30] | Mali S. S., Desai S. K., Kalagi S. S., Betty C. A., Bhosale P. N., Devan R. S., Ma Y. R., Patil P. S., ,. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 6130— 6136 |
| [31] | Nagaveni K., Hegde M. S., Ravishankar N., Subbanna G. N., Madras G ., Langmuir, 2004, 20, 2900— 2907 |
| [32] | Lobo A., Moller T., Nagel M., Borchert H., Hickey S.G., Weller H., ,. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 17422— 17428 |
| [33] | Wang L., Wang W., Zhang W., Chen Y., Cao W., Shi H., Cao M., ,. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 553— 560 |
| [34] | Berglund S. P., Rettie A. J., Hoang S., Mullins C. B., ,Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 14, 7065— 7075 |
| [35] | Zhao X. M., Zhou S. W., Shen Q. M., Jiang L. P., Zhu J. J ., Analyst, 2012, 137, 3697— 3704 |
| [36] | Tu W. W., Lu J., Dong Y. T., Lei J. P., Ju H. X., ,Anal. Chem., 2010, 82, 8711— 8716 |
| [37] | Xin Y. M., Li Z. Z., Wu W. L., Fu B. H., Wu H. J., Zhang Z. H., ,Biosens. Bioelectron., 2017, 87, 396— 403 |
| [38] | Zhao W. W., Xu J. J., Chen H. Y., ,Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 7421— 7441 |
| [39] | Zhuo K., Gu Y. S., Yan X. Q., Bai Z. M., Liu Y. C., ,. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 499— 504 |
| [1] | WANG Junyang, LIU Zheng, ZHANG Qian, SUN Chunyan, LI Hongxia. Application of DNA Silver Nanoclusters in the Fluorescence Biosensors based on Functional Nucleic Acids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220010. |
| [2] | LIU Jiaqi, LI Tianbao. Preparation and Photoelectrochemical Performance of BiVO4/CuBi2O4 Thin Film Photoanodes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20220017. |
| [3] | CHEN Wangsong, LUO Lan, LIU Yuguang, ZHOU Hua, KONG Xianggui, LI Zhenhua, DUAN Haohong. Recent Progress in Photoelectrochemical H2 Production Coupled with Biomass-derived Alcohol/aldehyde Oxidation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210683. |
| [4] | SHI Xiaofan, ZHU Jian, BAI Tianyu, FU Zixuan, ZHANG Jijie, BU Xianhe. Research Status and Progress of MOFs with Application in Photoelectrochemical Water-splitting [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210613. |
| [5] | TANG Ding, ZHONG Shuiping. Preparation and Photoelectrochemical Performance of Bi1-xFexVO4 Thin Film Photoanodes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2509. |
| [6] | WU Yangyi, CHEN Jianping, Ai Yijing, WANG Qingxiang, GAO Fei, GAO Feng. Synthesis of 2-(2-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-C60 and Its Application for Sensing of Cauliflower Mosaic Virus 35S Promotor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1754. |
| [7] | XU Mengyi, HUANG Xuewen, LI Xiaojie, WEI Wei, LIU Xiaoya. Fabrication of Biosensor Based on “Beads-on-a-String” Shaped Composite Nano-assembly Modified Screen Printed Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1768. |
| [8] | WANG Bodong, PAN Meichen, ZHUO Ying. Construction of Electrochemiluminescence Sensing Interface Based on Silver Nanoclusters-Silica Nanoparticles and Biomolecular Recognition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3519. |
| [9] | ZHANG Jiayi, DING Zhenyao, WANG Dandan, CHEN Liping, FENG Xinjian. Fabrication of Triphase Enzyme Electrode Based on Porous Gold Substrate for High-performance Electrochemical Biosensor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3167. |
| [10] | YUAN Zhongwen, HE Lizhen, CHEN Tianfeng. Biomedical Applications of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2690. |
| [11] | ZHANG Yimeng, ZHANG Huixin, LIU Yang. Recent Advances of Exosomes Bioanalysis and Their Clinic Applications [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2306. |
| [12] | ZHOU Yuting, TANG Yujiao, SHAO Shuang, DAI Shiyan, CHENG Guifang, HE Pingang, FANG Yuzhi. Simultaneous Detection of Mercury, Lead and Strontium Ions Based on Conformational Conversion Sensor † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1621. |
| [13] | JIA Hongliang,ZHAO Jianwei,QIN Lirong,ZHAO Min. Uric Acid Biosensor Based on Ni Wire Modified with NiO Nanosheets† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 240. |
| [14] | WANG Chunyan,JIANG Xiaoqing,ZHOU Bo. An Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Cu-TPA for Determination of Aflatoxin B1 † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(11): 2301. |
| [15] | PAN Shuai, LI Zhanhong, CHEN Yang, ZHAO Xueling, CHEN Cheng, ZHU Zhigang. Glucose Biosensor Based on Rebuilding the Surface of the Spiral-type Pt-Ir Electrode† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1163. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||