

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 240.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180519
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
JIA Hongliang, ZHAO Jianwei*( ), QIN Lirong, ZHAO Min
), QIN Lirong, ZHAO Min
Received:2018-07-24
Online:2019-02-10
Published:2018-11-16
Contact:
ZHAO Jianwei
E-mail:zhaojw@swu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
JIA Hongliang,ZHAO Jianwei,QIN Lirong,ZHAO Min. Uric Acid Biosensor Based on Ni Wire Modified with NiO Nanosheets†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 240.
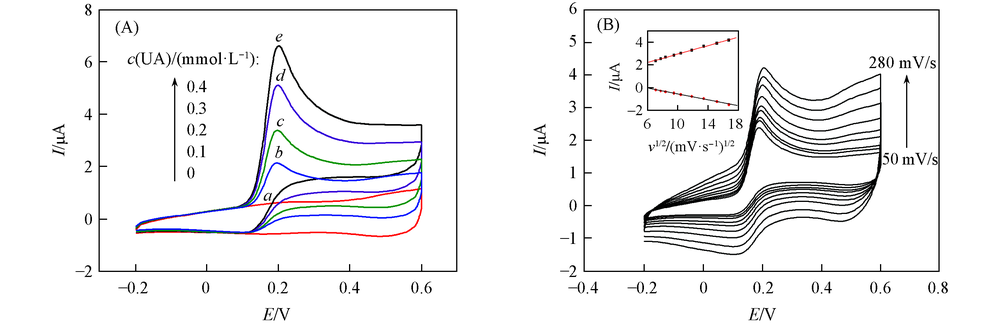
Fig.4 CV curves of the prepared electrode in the different concentration of UA(A) and typical CVs of the electrode in 0.01 mol PBS solution containing 0.2 mmol UA at different scan rates(from 50 mV/s to 280 mV/s)(B)Inset of (B): plots of peak currents vs. ν1/2.
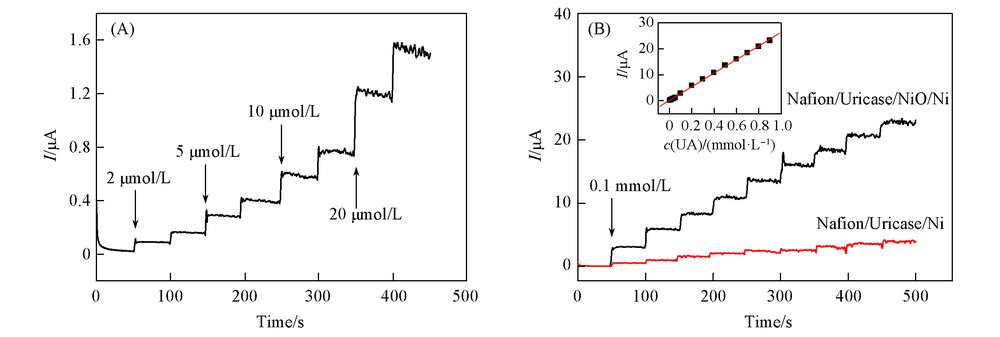
Fig.5 Typical current-time response for the prepared electrode(A) or the comparison electrode to successive additions of different concentrations of UA in a stirring PBS solution at an applied potential of 0.3 V vs. Ag/AgCl(B)Inset of (B): the linear relationship between the catalytic current and the concentration of UA.
| Type of electrode | Sensitivity/ (μA·mmol-1·cm-2) | Linear range/ (μmol·L-1) | Detection limit/(μmol·L-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uricase/Au NP/c-MWCNT/Au | 440.0 | 10—800 | 10.0 | [ |
| Uricase/CeO2-x/C/rGO/GCE | 284.5 | 49.8—1050.0 | 2.0 | [ |
| Nafion/Uricase/ZnO NSs/Ag/Si | 129.81 | 50—2000 | 0.019 | [ |
| Uricase/Ni microdiscs/NiO/ITO | 431.09 | 50—1000 | 30 | [ |
| Nafion/Uricase/ZnO/Au | 89.74 | 100—590 | 25.6 | [ |
| CoNi nanoparticles/C | 248.2 | 25—575 | 0.08 | [ |
| Nanoporous RuO2/Au | 344.2 | 20—1000 | 9.6 | [ |
| Nafion/Uricase/NiO/Ni | 821.4 | 1—900 | 0.1 | This work |
Table 1 Comparison of different electrode materials for the determination of UA
| Type of electrode | Sensitivity/ (μA·mmol-1·cm-2) | Linear range/ (μmol·L-1) | Detection limit/(μmol·L-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uricase/Au NP/c-MWCNT/Au | 440.0 | 10—800 | 10.0 | [ |
| Uricase/CeO2-x/C/rGO/GCE | 284.5 | 49.8—1050.0 | 2.0 | [ |
| Nafion/Uricase/ZnO NSs/Ag/Si | 129.81 | 50—2000 | 0.019 | [ |
| Uricase/Ni microdiscs/NiO/ITO | 431.09 | 50—1000 | 30 | [ |
| Nafion/Uricase/ZnO/Au | 89.74 | 100—590 | 25.6 | [ |
| CoNi nanoparticles/C | 248.2 | 25—575 | 0.08 | [ |
| Nanoporous RuO2/Au | 344.2 | 20—1000 | 9.6 | [ |
| Nafion/Uricase/NiO/Ni | 821.4 | 1—900 | 0.1 | This work |
| Real urine sample | Concentration of UA detected/ (μmol·L-1) | Spiked UA concentration/ (μmol·L-1) | Theoretical total UA concentration/ (μmol·L-1) | Measured total UA concentration/ (μmol·L-1) | Recovery(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 235.7 | 100 | 335.7 | 343.6 | 102.4 |
| 2 | 218.4 | 200 | 418.4 | 402.3 | 96.2 |
| 3 | 411.2 | 400 | 811.2 | 774.9 | 95.5 |
Table 2 Determination of UA in real urine samples using our biosensor(n=3)
| Real urine sample | Concentration of UA detected/ (μmol·L-1) | Spiked UA concentration/ (μmol·L-1) | Theoretical total UA concentration/ (μmol·L-1) | Measured total UA concentration/ (μmol·L-1) | Recovery(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 235.7 | 100 | 335.7 | 343.6 | 102.4 |
| 2 | 218.4 | 200 | 418.4 | 402.3 | 96.2 |
| 3 | 411.2 | 400 | 811.2 | 774.9 | 95.5 |
| [1] | Erden P. E., Kilic E., Talanta,2013, 107, 312-323 |
| [2] | Fang B., Feng Y., Wang G., Zhang C., Gu A., Liu M., Microchim. Acta,2011, 173, 27-32 |
| [3] | Ma Q. S., Wang Q., Zhao K. Z., Zhai S. B., Liu S., Liu Z. Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2013, 34(12), 2716-2720 |
| (马青山, 王茜, 赵凯姝, 翟淑波, 刘舒, 刘志强. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(12), 2716-2720) | |
| [4] | Jin D., Seo M. H., Huy B. T., Pham Q. T., Conte M. L., Thangadurai D., Lee Y. I., Biosens. Bioelectron.,2016, 77, 359-365 |
| [5] | Li X., Li G., Jiang Y., Kang D., Jin C., Shi Q., Jin T., Inoue K., Todoroki K., Toyo’oka T., Min J., J. Chromatogr. B,2015, 1002, 394-398 |
| [6] | Liu B. H., Deng J. Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,1996, 17(5), 702-706 |
| (刘宝红, 邓家祺. 高等学校化学学报, 1996, 17(5), 702-706) | |
| [7] | Dai H., Wang N., Wang D., Zhang X., Ma H., Lin M., Microchim. Acta,2016, 183, 3053-3059 |
| [8] | Hou C., Liu H., Zhang D., Yang C., Zhang M., J. Alloy. Compd.,2016, 666, 178-184 |
| [9] | KanJ. Q., Mu S. L., Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin.,1993, 9(3), 345-350 |
| (阚锦晴, 穆绍林. 物理化学学报, 1993, 9(3), 345-350) | |
| [10] | Zhao J., Mu F., Qin L., Jia X., Yang C., Mater. Chem. Phys.,2015, 166, 176-181 |
| [11] | Zhao J., Qin L., Hao Y., Guo Q., Mu F., Yan Z., Microchim. Acta,2012, 178, 439-445 |
| [12] | Suresh R., Giribabu K., Manigandan R., Stephenb A., Narayanan V., RSC Adv.,2014, 4, 17146 |
| [13] | Zhao Y., Yan X., Kang Z., Lin P., Fang X., Lei Y., Ma S., Zhang Y., Microchim. Acta,2013, 180, 759-766 |
| [14] | Ahmad R., Tripathy N., Jang N. K., Khang G., Hahn Y., Sensor. Actuat. B,2015, 206, 146-151 |
| [15] | Cheng C., Kao C. Y., Electroanal.,2016, 28, 695-703 |
| [16] | Tian K., Prestgard M., Tiwari A., Mater. Sci. Eng. C,2014, 41, 100-118 |
| [17] | Duan C., Zhao J., Qin L. Yang L., Zhou Y., Mater. Lett.,2017, 208, 65-68 |
| [18] | Chauhan N., Pundir C. S., Anal. Biochem.,2011, 413, 97-103 |
| [19] | Peng B., Cui J., Wang Y., Liu J., Zheng H., Jin L., Zhang X., Zhang Y., Wu Y., Nanoscale, 2018, 10, 1939-1945 |
| [20] | Arora K., Tomar M., Gupta V., Analyst,2014, 139, 4606-4612 |
| [21] | Singh B., Laffir F., Dickinson C., McCormac T., Dempsey E., Electroanal.,2011, 23(1), 79-89 |
| [22] | Yang Y., Jo A., Lee Y., Lee C., Sens. Actuators B,2018, 255, 316-324 |
| [1] | WANG Junyang, LIU Zheng, ZHANG Qian, SUN Chunyan, LI Hongxia. Application of DNA Silver Nanoclusters in the Fluorescence Biosensors based on Functional Nucleic Acids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220010. |
| [2] | LI Xiaohui, WEI Aijia, MU Jinping, HE Rui, ZHANG Lihui, WANG Jun, LIU Zhenfa. Effects of SmPO4 Coatingon Electrochemical Performance of High-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 Cathode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210546. |
| [3] | WEI Chuangyu, CHEN Yanli, JIANG Jianzhuang. Fabrication of Electrochemical Sensor for Dopamine and Uric Acid Based on a Novel Dimeric Phthalocyanine-involved Quintuple-decker Modified Indium Tin Oxide Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210582. |
| [4] | XU Mengyi, HUANG Xuewen, LI Xiaojie, WEI Wei, LIU Xiaoya. Fabrication of Biosensor Based on “Beads-on-a-String” Shaped Composite Nano-assembly Modified Screen Printed Electrode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1768. |
| [5] | WU Yangyi, CHEN Jianping, Ai Yijing, WANG Qingxiang, GAO Fei, GAO Feng. Synthesis of 2-(2-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-C60 and Its Application for Sensing of Cauliflower Mosaic Virus 35S Promotor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1754. |
| [6] | GAO Juan, SUN Quanhu, HUANG Changshui. Graphdiyne-based Nanostructured Materials and Their Applications in Energy Storage and Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1501. |
| [7] | WANG Yawen, LI Dong, LIANG Wenkai, SUN Yinghui, JIANG Lin. Multiplex Structures of Plasmonic Metal Nanoparticles and Their Applications [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1213. |
| [8] | GUI Chen, WANG Haolin, SHAO Baixuan, YANG Yujing, XU Guangqing. Molten-salt-assistance Synthesis and Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Performances of g-C3N4 Nanostructures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 827. |
| [9] | WANG Bodong, PAN Meichen, ZHUO Ying. Construction of Electrochemiluminescence Sensing Interface Based on Silver Nanoclusters-Silica Nanoparticles and Biomolecular Recognition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3519. |
| [10] | HU Ling, YIN Yao, KE Guoliang, ZHANG Xiaobing. Regulation of Cell-cell Interactions Based on DNA Nanostructures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3284. |
| [11] | ZHANG Jiayi, DING Zhenyao, WANG Dandan, CHEN Liping, FENG Xinjian. Fabrication of Triphase Enzyme Electrode Based on Porous Gold Substrate for High-performance Electrochemical Biosensor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3167. |
| [12] | LIAO Ni, ZHANG Jieyuan, HUANG Ziyang, ZHAO Yanxi, CHAI Yaqin, YUAN Ruo, ZHUO Ying. Construction of High Efficiency Uric Acid Sensor Based on the co-Crystal Enhanced Electrochemiluminescence from 9,10-Diphenylanthracene-perylene Microcrystals [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 1989. |
| [13] | RONG Hua, WANG Chungang, ZHOU Ming. Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of FeS2 Microspheres as an Anode for Li-ion Batteries † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 447. |
| [14] | YUAN Zhongwen, HE Lizhen, CHEN Tianfeng. Biomedical Applications of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2690. |
| [15] | SHEN Minghui, WEI Yanze, XU Nan, WANG Zumin, YANG Nailiang, YU Ranbo, WANG Dan. Construction of Hetero⁃hollow Structure Micro⁃/Nanomaterials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2561. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||