

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (5): 1063.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170444
Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Jipei, LI Yi, YANG Shenhui, ZHOU Yazhou, CHENG Xiaonong*, ZHU Jia, YANG Juan*
Received:2017-07-10
Online:2018-04-16
Published:2018-04-16
Contact:
CHENG Xiaonong,YANG Juan
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
HUANG Jipei,LI Yi,YANG Shenhui,ZHOU Yazhou,CHENG Xiaonong,ZHU Jia,YANG Juan. Synthesis of Three-dimensional Pt-Ag Aerogels and Their Electrocatalytic Performance Toward Oxygen Reduction Reaction†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(5): 1063.
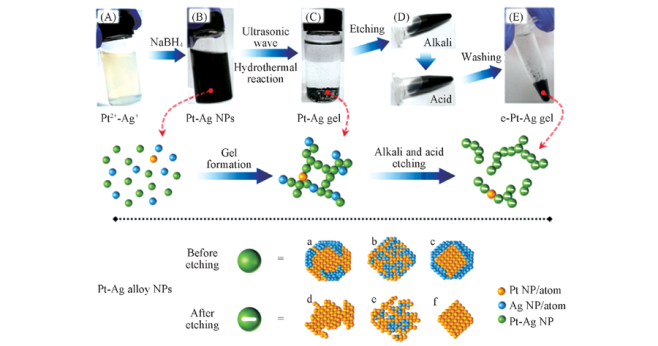
Fig.1 Preparation mechanism of catalysts Note: (A) Pt2+, Ag+ solution; (B) Pt-Ag precursor; (C) alloyed Pt-Ag gel before etching; (D) acid- and alkali-etching; (E) e-Pt-Ag gel catalyst. Possible structures of Pt-Ag bimetallic nanoparticles before and after etching: a. non-uniformly distributed structure; b. random solid solution; c. core-shell structure ordered intermetallic compound; d—f removing the Ag from surface and forming an unstructured structure.
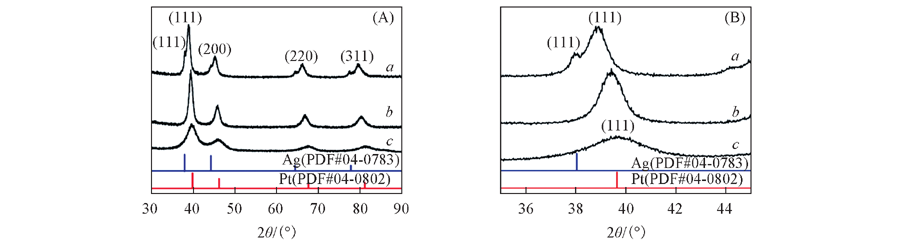
Fig.2 XRD patterns of Pt-Ag gel by two-step method before etching(a), e-Pt-Ag gel by using acid- and alkali- etching method(b) and commerical Pt/C(c)(A) and the corresponding magnification of (A)(B)
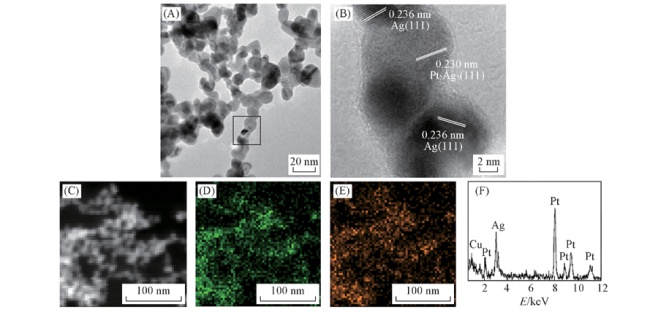
Fig.5 Representative TEM image(A), corresponding HRTEM image(B), HAADF-STEM image(C), Pt(D), Ag(E) elemental mappings and energy dispersive X-ray(EDX) spectrum of Pt-Ag gel(F)
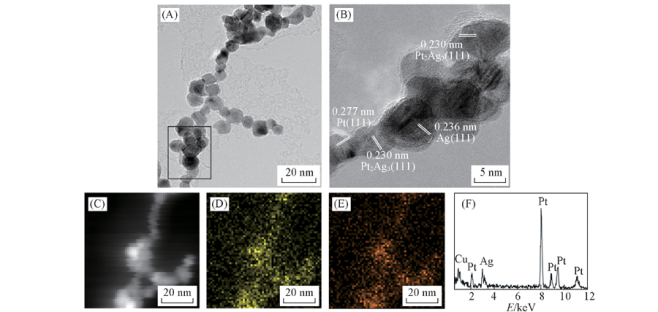
Fig.6 Representative TEM image(A) and corresponding HRTEM image(B), HAADF-STEM image(C), Pt(D), Ag(E), elemental mappings and EDX spectrum of e-Pt-Ag gel catalyst after etching(F)
| Sample | ECSA/(m2·g-1) | Onset potential/V | Half-wave potential/V | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | Initial | Final | Initial | Final | |
| e-Pt-Ag gel(deactivation) | 56.5 | 52.9 | 0.906 | 0.898 | 0.838 | 0.828 |
| Pt/C(20%)(deactivation) | 54.8 | 41.1 | 0.883 | 0.873 | 0.823 | 0.802 |
Table 1 Comparison of e-Pt-Ag gel and commercial Pt /C(20%) catalysts(before and after ADT)
| Sample | ECSA/(m2·g-1) | Onset potential/V | Half-wave potential/V | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | Initial | Final | Initial | Final | |
| e-Pt-Ag gel(deactivation) | 56.5 | 52.9 | 0.906 | 0.898 | 0.838 | 0.828 |
| Pt/C(20%)(deactivation) | 54.8 | 41.1 | 0.883 | 0.873 | 0.823 | 0.802 |
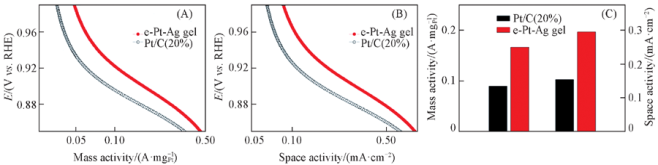
Fig.9 Electrocatalytic activity of the e-Pt-Ag gel catalyst and commercial Pt/C catalysts(A, B) and ORR-mass activities(left) and space activities(right) of catalysts measured at 0.9 V(C)
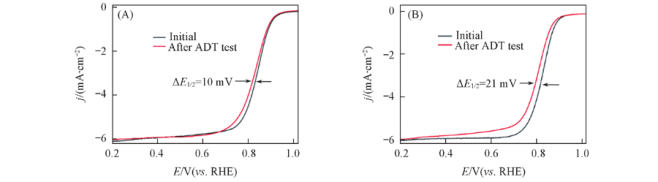
Fig.10 ORR polarization curves of e-Pt-Ag gel catalyst(A) and commercial Pt /C(B) catalysts in O2-saturated 0.1 mol/L HClO4 at room temperature before and after ADT(1600 r/min, scan rate: 10 mV/s)
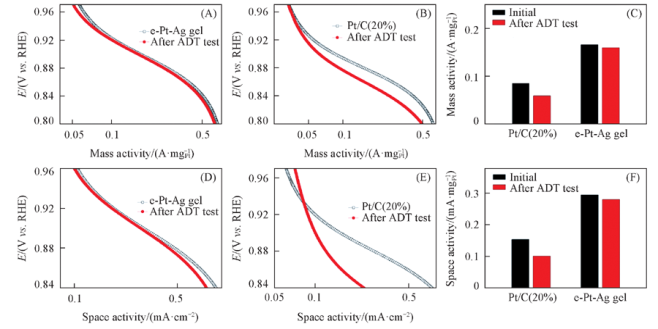
Fig.11 Tafel curves of e-Pt-Ag gel catalyst(A, D) and commercial Pt/C(B, E) and the value changes on mass activities(C) and space activities(F) of the e-Pt-Ag gel catalyst at 0.85 V before and after ADT
| [1] | Jouin M., Gouriveau R., Hissel D., Pera M.C., Zerhouni N., Int. [J]. Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(35), 15307—15317 |
| [2] | Lee K.T., Yoon H. S., Wachsman E. D., J. Mater. Research, 2012, 27(16), 2063—2078 |
| [3] | Subianto S., Pica M., Casciola M., Cojocaru P., Merlo L., Hards G., Jones D., [J]. Power Sources, 2013, 233(233), 216—230 |
| [4] | Zaidi S., Rauf M., Polymer Membranes for Fuel Cells, Springer US, NewYork, 2009, 9(7), 1—6 |
| [5] | Ehteshami S.M. M., Chan S. H., Electrochim. Acta, 2013, 93(4), 334—345 |
| [6] | Xia W., Mahmood A., Liang Z., Zou R., Guo S., Angew. Chem. Int.Ed., 2015, 55(8), 2650—2676 |
| [7] | Han B.H., Christopher E. C., Anusorn K., Ratandeep S. K., Brian R. T., Energ. Environ. Sci., 2015, 8(1), 258—266 |
| [8] | Yu S., Lou Q., Han K., Wang Z., Zhu H., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(18), 13365—13370 |
| [9] | Liu M., Chi F., Liu J., Song Y., Wang F., RSC Adv., 2016, 6(67), 62327—62335 |
| [10] | Demarconnay L., Coutanceau C., Léger J.M., Electrochim. Acta, 2004, 49(25), 4513—4521 |
| [11] | Gilroy K.D., Ruditskiy A., Peng H. C., Qin D., Xia Y., Chem. Rev., 2016, 116(18), 10414—10472 |
| [12] | Esfandiari A., Kazemeini M., Bastani D., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(45), 20720—20730 |
| [13] | Fu G.T., Ma R. G., Gao X. Q., Chen Y., Tang Y. W., Nanoscale, 2014, 6(21), 12310—12314 |
| [14] | Wen D., Herrmann A.K., Borchardt L., Simon F., Liu W., [J]. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(7), 2727—2730 |
| [15] | Qi Z., Weissmüller J., ACS Nano., 2013, 7(7), 5948—5954 |
| [16] | Yao Q., Arachchige I.U., Brock S. L., [J]. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 131(8), 2800—2801 |
| [17] | Liu X., Yu Y., Niu Y., Bao S., Hu W., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(9), 5930—5937 |
| [18] | Zhu C., Shi Q., Fu S., Bao S., Hu W., Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(39), 8779—8783 |
| [19] | Zhou Y., Yen C.H., Cheng X., Wai C. M., Yang J., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4(47), 18628—18638 |
| [20] | Peng Z., You H., Yang H., ACS Nano, 2010, 4(3), 1501—1510 |
| [21] | Xu K., Li Y., Zhao N., Du W.X., Zeng W. W., Gao S., Cheng X. N, Yang J., Chem. [J]. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(8), 1476—1484 |
| (徐凯, 李毅, 赵南, 杜文修, 曾炜炜, 高帅, 程晓农, 杨娟. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(8), 1476—1484) | |
| [22] | Guo S., Sun S., [J]. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(5), 2492—2495 |
| [1] | CHENG Qian, YANG Bolong, WU Wenyi, XIANG Zhonghua. S-doped Fe-N-C as Catalysts for Highly Reactive Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220341. |
| [2] | CHU Yuyi, LAN Chang, LUO Ergui, LIU Changpeng, GE Junjie, XING Wei. Single-atom Cerium Sites Designed for Durable Oxygen Reduction Reaction Catalyst with Weak Fenton Effect [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220294. |
| [3] | GU Yu, XI Baojuan, LI Jiangxiao, XIONG Shenglin. Structure Regulation of Single-atom Catalysts in Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220036. |
| [4] | ZHANG Xiaoyu, XUE Dongping, DU Yu, JIANG Su, WEI Yifan, YAN Wenfu, XIA Huicong, ZHANG Jianan. MOF-derived Carbon-based Electrocatalysts Confinement Catalyst on O2 Reduction and CO2 Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210689. |
| [5] | HE Yujing, LI Jiale, WANG Dongyang, WANG Fuling, XIAO Zuoxu, CHEN Yanli. Zinc-based Activated Fe/Co/N Doped Biomass Carbon Electrocatalysts with High Oxygen Reduction Activity [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220475. |
| [6] | MA Jun, ZHONG Yang, ZHANG Shanshan, HUANG Yijun, ZHANG Lipeng, LI Yaping, SUN Xiaoming, XIA Zhenhai. Design and Theoretical Calculation of Heteroatoms Doped Graphdiyne Towards Efficiently Catalyzing Oxygen Reduction and Evolution Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 624. |
| [7] | WANG Yuemin, MENG Qinglei, WANG Xian, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Enhancement of Performance of Fe-N-C Catalysts by Copper and Sulfur Doping for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1843. |
| [8] | YIN Wenjing, LIU Xiao, QIAN Huidong, ZOU Zhiqing. Preparation and Oxygen Reduction Performance of Fe, N co-Doped arbon Nanoplate with High Density of Active Sites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1480. |
| [9] | XU Zhaoquan, MA Junhong, SHI Minhui, FENG Chao, XIE Yahong, MI Hongyu. Preparation and Application of a Novel Natural Product-based Fe and N Codoped Carbon Catalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1532. |
| [10] | WANG Xiuli, HE Xingquan. Electrocatalytic Performance of Fe9S10 Nanoparticles Loaded Nitrogen and Sulphur Codoped Porous Carbon for Oxygen Reduction Reaction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1524. |
| [11] | DI Muxin, XIAO Guozheng, HUANG Peng, CAO Yihuan, ZHU Ying. Co/N Co-doped Carbon Nanotube/Graphene Composites as Efficient Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(2): 343. |
| [12] | LIU Pei, CHENG Qingqing, CHEN Chi, ZOU Liangliang, ZOU Zhiqing, YANG Hui. Preparation and Oxygen Reduction Reaction Catalytic Performance of Fe, N Co-doped Carbon Nanofibers with Encapsulated Iron Nitride† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(11): 2492. |
| [13] | KANG Huan, LI Shang, LIU Chang, GUO Wei, PAN Mu. Synthesis of Ordered Mesoporous Fe-N-C-PANI Catalyst via Self-assembly and Its Oxygen Reduction Reaction Activity in Acid Medium [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(8): 1423. |
| [14] | LI Weilun, YAO Ying, ZHANG Cunzhong. Applications of Carbon Fiber Ultra-microelectrode and Powder Microelectrode in Exploring Influences of Non-aqueous Solvents and Cathode Materials on ORR and OER† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(4): 642. |
| [15] | XU Kai,LI Yi,ZHAO Nan,DU Wenxiu,ZENG Weiwei,GAO Shuai,CHENG Xiaonong,YANG Juan. Synthesis of Hollow PtNi/Graphene Cellular Monolith Catalysts and Their Electrochemical Performance† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(8): 1476. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||