

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (7): 1480.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190020
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
YIN Wenjing1,2, LIU Xiao1,2, QIAN Huidong1, ZOU Zhiqing1,*( )
)
Received:2019-01-09
Online:2019-07-10
Published:2019-07-12
Contact:
ZOU Zhiqing
E-mail:zouzq@sari.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
YIN Wenjing, LIU Xiao, QIAN Huidong, ZOU Zhiqing. Preparation and Oxygen Reduction Performance of Fe, N co-Doped arbon Nanoplate with High Density of Active Sites†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1480.
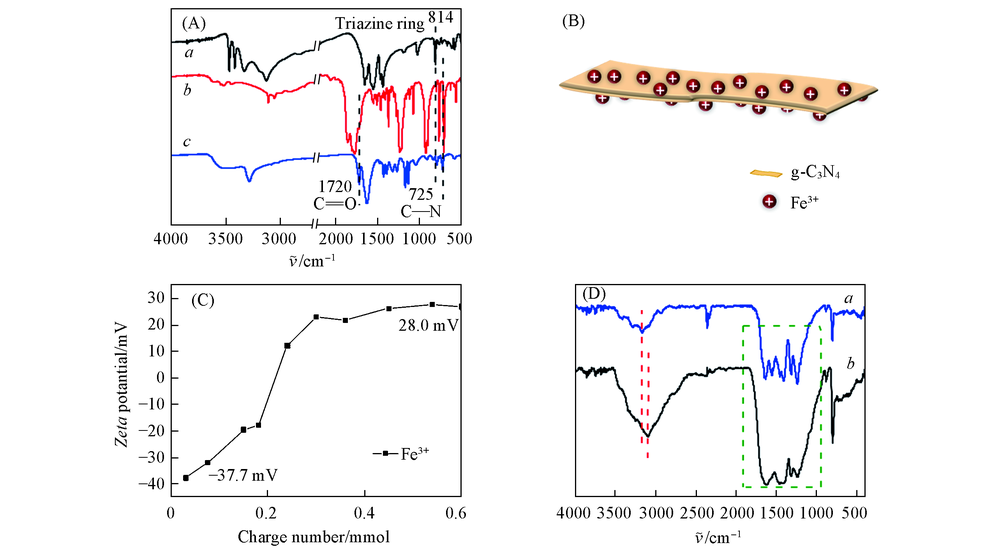
Fig.1 FTIR spectra of melamine(a), PMDA(b) and polyimide(c)(A), assembly illustration of g-C3N4 and FeCl3(B), zeta potential of g-C3N4(C) and FTIR spectra of g-C3N4(a) and g-C3N4-FeCl3(b)(D)
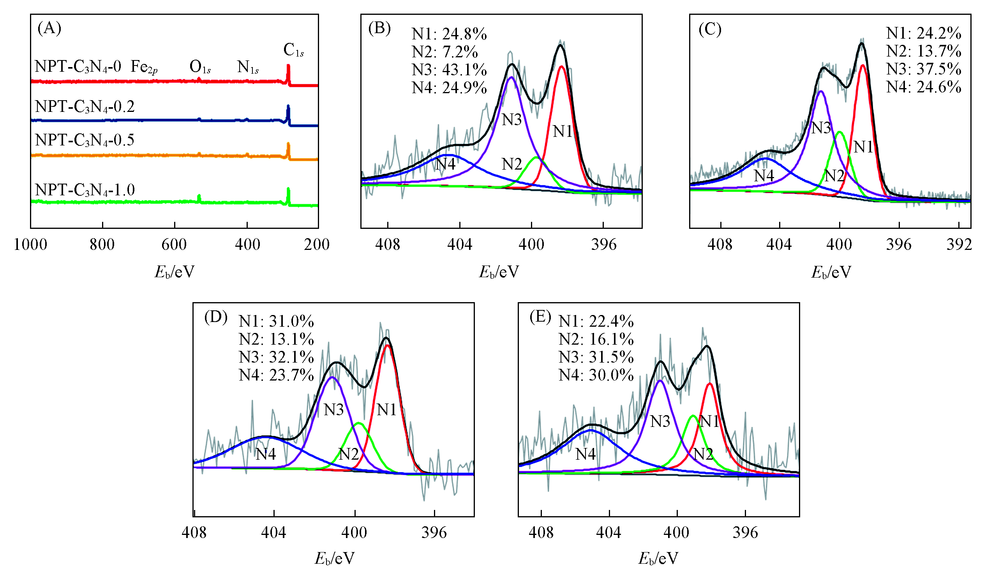
Fig.5 Survey XPS spectra(A) and high-resolution deconvoluted N1s XPS spectra of NPT-C3N4-0(B), NPT-C3N4-0.2(C), NPT-C3N4-0.5(D) and NPT-C3N4-1.0(E) N1: Pyridinic N; N2: pyrrolic N; N3: graphitic N; N4: oxidized N.
| Sample | Atomic fraction(%) | Percentage of different N(%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | N | Pyridinic N | Graphitic N | Pyrrolic N | Oxidized N | |
| NPT-C3N4-0 | 0.43 | 6.53 | 24.8 | 43.1 | 7.2 | 24.9 |
| NPT-C3N4-0.2 | 0.68 | 6.05 | 24.2 | 37.5 | 13.7 | 24.6 |
| NPT-C3N4-0.5 | 1.13 | 5.57 | 31.0 | 32.1 | 13.1 | 23.7 |
| NPT-C3N4-1.0 | 0.95 | 4.85 | 22.4 | 31.5 | 16.1 | 30.0 |
Table 1 XPS analysis of NPT-C3N4-N(N=0, 0.2, 0.5, 1.0) catalysts
| Sample | Atomic fraction(%) | Percentage of different N(%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | N | Pyridinic N | Graphitic N | Pyrrolic N | Oxidized N | |
| NPT-C3N4-0 | 0.43 | 6.53 | 24.8 | 43.1 | 7.2 | 24.9 |
| NPT-C3N4-0.2 | 0.68 | 6.05 | 24.2 | 37.5 | 13.7 | 24.6 |
| NPT-C3N4-0.5 | 1.13 | 5.57 | 31.0 | 32.1 | 13.1 | 23.7 |
| NPT-C3N4-1.0 | 0.95 | 4.85 | 22.4 | 31.5 | 16.1 | 30.0 |
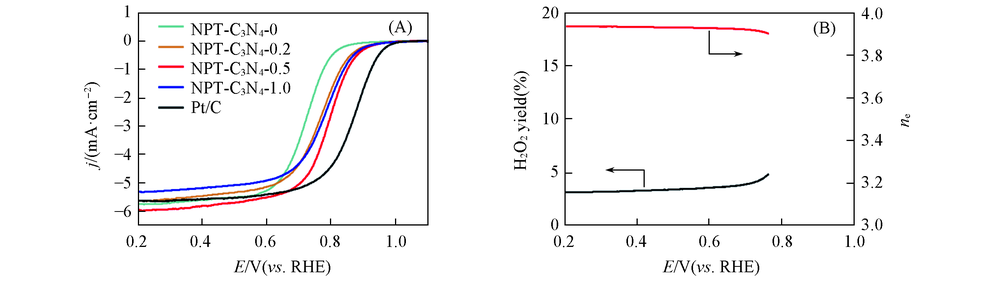
Fig.6 ORR polarization curves of NPT-C3N4-N(N=0, 0.2, 0.5, 1.0) catalysts and commercial Pt/C(20%) catalysts in 0.1 mol/L HClO4 solution at rotating rate of 1600 r/min with a scan rate of 10 mV/s(A) and H2O2 yield and average electron transfer number of NPT-C3N4-0.5(B)
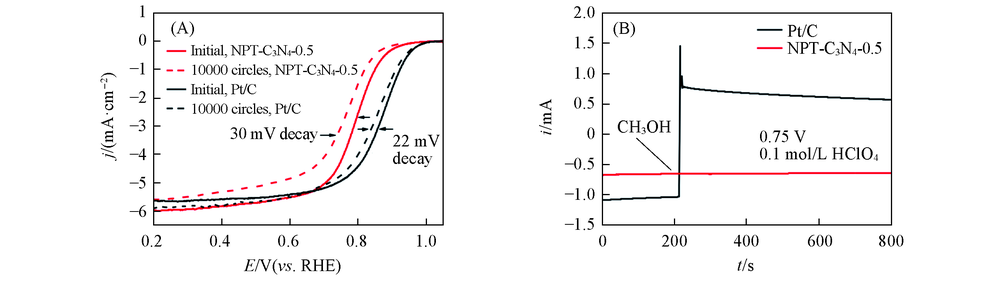
Fig.7 ORR polarization curves of NPT-C3N4-0.5 and Pt/C before and after 10000 cycles accelerated durability test(0.6—1.0 V, 50 mV/s)(A) and methanol tolerance test of NPT-C3N4-0.5 and Pt/C(B)Rotational speed: 1600 r/min; catalyst loadings: 0.6 mg/cm2 for NPT-C3N4-N(N=0, 0.2, 0.5, 1.0), 0.1 mg/cm2 for Pt/C.
| [1] | Gewirth A. A., Thorum M. S., Inorg. Chem., 2010, 49(8), 3557—3566 |
| [2] | Nie Y., Li L., Wei Z. D., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44(8), 2168—2201 |
| [3] | Wu G., Zelenay P., Accounts Chem. Res., 2013, 46(8), 1878—1889 |
| [4] | Masa J., Xia W., Muhler M., Schuhmann W., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54(35), 10102—10120 |
| [5] | Shen M. X., Wei C. T.,Ai K. L., Lu L., Nano Res., 2017, 10(5), 1449—1470 |
| [6] | Yeager E., Electrochim. Acta, 1984, 29(11), 1527—1537 |
| [7] | Proietti E., Jaouen F., Lefevre M., Larouche N., Tian J., Herranz J., Dodelet J. P., Nat. Commun., 2011, 2(1427), 1—9 |
| [8] | Zhang Z., Sun J., Wang F., Dai L., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57(29), 9038—9043 |
| [9] | Wang X. C., Chen X. F., Thomas A., Fu X.,Antonietti M., Adv. Mater., 2009, 21(16), 1609—1612 |
| [10] | Li Y.P., Gao J. Y., Zhang F., Qian Q., Liu Y., Zhang G., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6(32), 15523—15529 |
| [11] | Cao R.G., Thapa R., Kim H. J., Xu X., Kim M. G., Li Q., Park N., Liu M., Cho J., Nat. Commun., 2013, 4(3076), 1—7 |
| [12] | Cao S., Low J., Yu J., Jaroniec M., Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(13), 2150—2176 |
| [13] | Yao Y. F., You Y., Zhang G. X., Liu J.,Sun H., Zou Z., Sun S., ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2016, 8(10), 6464—6471 |
| [14] | Chu S., Wang Y., Guo Y., Zhou P., Yu H., Luo L., Kong F., Zou Z., J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22(31), 15519—15521 |
| [15] | Ekinci E., Emre F.B., Köytepe S., Seçkin T., J. Polym. Res., 2005, 12(3), 205—210 |
| [16] | Fechler N., Fellinger T. P., Antonietti M., Adv. Mater., 2013, 25(1), 75—79 |
| [17] | Zhang Y.J., Thomas A., Antonietti M., Wang X.,J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131(1), 50—51 |
| [18] | Lau V.W. H., Mesch M. B., Duppel V., Blum V., Senker J., Lotsch B. V.,J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(3), 1064—1072 |
| [19] | Lyth S.M., Nabae Y., Moriya S., Kuroki S., Kakimoto M., Ozaki J., Miyata S., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113(47), 20148—20151 |
| [20] | Li Y., Wang Z., Xia T., Ju H., Zhang K., Long R., Xu Q., Wang C., Song L., Zhu J., Jiang J., Xiong Y., Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(32), 6959—6965 |
| [21] | Xu Z. Q., Ma J. H., Shi M. H., Feng C., Xie Y. H., Mi H. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7), 1532—1539 |
| (徐朝权, 马俊红, 石旻慧, 冯超, 谢亚红, 米红宇. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(7), 1532—1539) | |
| [22] | Yu H., Shang L., Bian T., Shi R., Waterhouse G. I., Zhao Y., Zhou C., Wu L. Z.,Tung C. H., Zhang T., Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(25), 5080—5086 |
| [23] | Artyushkova K., Kiefer B., Halevi B., Knop-Gericke A., Schlogl R., Atanassov P., Chem. Commun., 2013, 49(25), 2539—2541 |
| [24] | Rao C.V., Cabrera C. R., Ishikawa Y., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2010, 1(18), 2622—2627 |
| [25] | Li S., Zhu G. W., Chen R. X., Wang J. T., Zhao W., Pan M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(8), 1782—1787 |
| (李赏, 朱广文, 陈锐鑫, 王家堂, 赵伟, 潘牧. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(8), 1782—1787) | |
| [26] | Wang X., Zhang H., Lin H., Gupta S., Wang C., Tao Z., Fu H., Wang T., Zheng J., Wu G., Li X., Nano Energy, 2016, 25, 110—119 |
| [27] | Hua X., Luo J., Shen C., Chen S., Catal. Sci. Technol., 2018, 8(7), 1945—1952 |
| [1] | JIANG Bowen, CHEN Jingxuan, CHENG Yonghua, SANG Wei, KOU Zongkui. Recent Progress of Single-atom Materials in Electrochemical Biosensing [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220334. |
| [2] | CHENG Qian, YANG Bolong, WU Wenyi, XIANG Zhonghua. S-doped Fe-N-C as Catalysts for Highly Reactive Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220341. |
| [3] | WANG Sicong, PANG Beibei, LIU Xiaokang, DING Tao, YAO Tao. Application of XAFS Technique in Single-atom Electrocatalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220487. |
| [4] | CHU Yuyi, LAN Chang, LUO Ergui, LIU Changpeng, GE Junjie, XING Wei. Single-atom Cerium Sites Designed for Durable Oxygen Reduction Reaction Catalyst with Weak Fenton Effect [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220294. |
| [5] | QIU Xinsheng, WU Qin, SHI Daxin, ZHANG Yaoyuan, CHEN Kangcheng, LI Hansheng. Preparation and High Temperature Fuel Cell Performance of Ionic Crosslinked Sulfonated Polyimides for Proton Exchange Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220140. |
| [6] | XIA Tian, WAN Jiawei, YU Ranbo. Progress of the Structure-property Correlation of Heteroatomic Coordination Structured Carbon-based Single-atom Electrocatalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220162. |
| [7] | GU Yu, XI Baojuan, LI Jiangxiao, XIONG Shenglin. Structure Regulation of Single-atom Catalysts in Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220036. |
| [8] | ZHAO Junyu, WANG Chunbo, WANG Chengyang, ZHANG Ke, CONG Bing, YANG Lan, ZHAO Xiaogang, CHEN Chunhai. Preparation and Performance of Thermally Conductive Expanded Graphite/Polyetherimide Composites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210800. |
| [9] | ZHANG Xiaoyu, XUE Dongping, DU Yu, JIANG Su, WEI Yifan, YAN Wenfu, XIA Huicong, ZHANG Jianan. MOF-derived Carbon-based Electrocatalysts Confinement Catalyst on O2 Reduction and CO2 Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210689. |
| [10] | WANG Shoubai, WU Xiuming, SHU Chen, ZHONG Min, HUANG Wei, YAN Deyue. Gas Separation Performance of Polyimide Homogeneous MembranesContaining tert-Butyl Groups [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220357. |
| [11] | HE Yujing, LI Jiale, WANG Dongyang, WANG Fuling, XIAO Zuoxu, CHEN Yanli. Zinc-based Activated Fe/Co/N Doped Biomass Carbon Electrocatalysts with High Oxygen Reduction Activity [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220475. |
| [12] | MA Jianxin, LIU Xiaodong, XU Na, LIU Guocheng, WANG Xiuli. A Multi-functional Zn(II) Coordination Polymer with Luminescence Sensing, Amperometric Sensing, and Dye Adsorption Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210585. |
| [13] | LI Weiqing, JIN Lei, YANG Jiaqiang, Wang Zhaoyun, YANG Fangzu, ZHAN Dongping, TIAN Zhongqun. Effects of Additive on the Electrodeposition and Coating Structure in a Novel System of Electronic Copper Electroplating [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2919. |
| [14] | WANG Shoubai, WU Xiuming, WU Jinming, TANG Yanfeng, SHU Chen, ZHONG Min, HUANG Wei, YAN Deyue. Synthesis and Properties of Soluble Transparent Polyimides Containing tert-Butyl and Isobutyl Groups [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2944. |
| [15] | HUANG Congcong, ZHANG Baoqing, LIU Chenyang. Predicting the Glass Transition Temperature of Polyimides: Group Additive Property Method and Assigning the Group Contributions to Unknown Groups [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2617. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||