

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 343.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170288
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
DI Muxin1, XIAO Guozheng1, HUANG Peng2, CAO Yihuan2, ZHU Ying1,*( )
)
Received:2017-05-05
Online:2018-02-10
Published:2018-01-08
Contact:
ZHU Ying
E-mail:zhuying@buaa.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
DI Muxin, XIAO Guozheng, HUANG Peng, CAO Yihuan, ZHU Ying. Co/N Co-doped Carbon Nanotube/Graphene Composites as Efficient Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(2): 343.
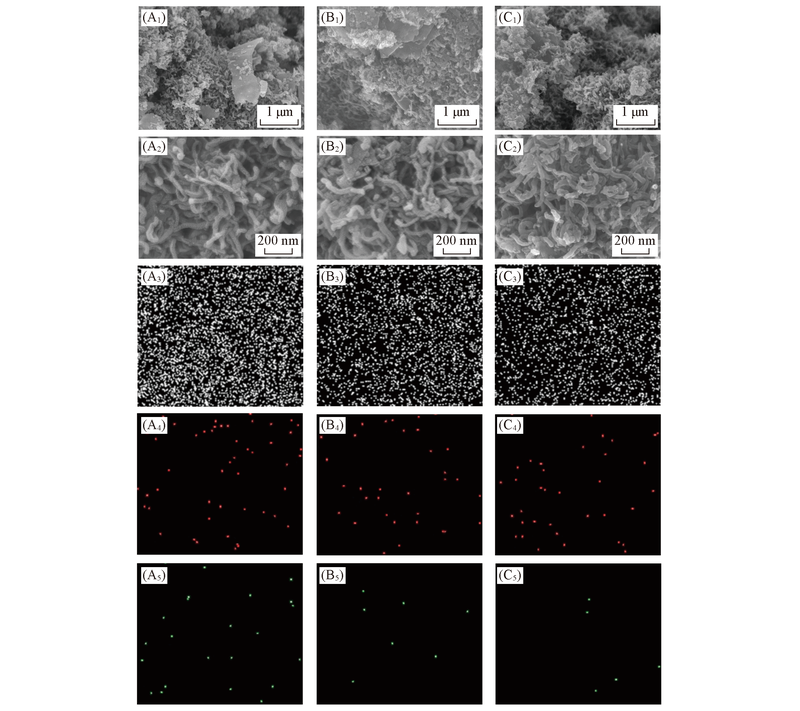
Fig.3 SEM images(A1—C1, A2—C2) and the corresponding C(A3—C3), Co(A4—C4) and N(A5—C5) elemental mappings of Co/N-CNT/Gr-800(A1—A5), Co/N-CNT/Gr-900(B1—B5) and Co/N-CNT/Gr-1000(C1—C5)
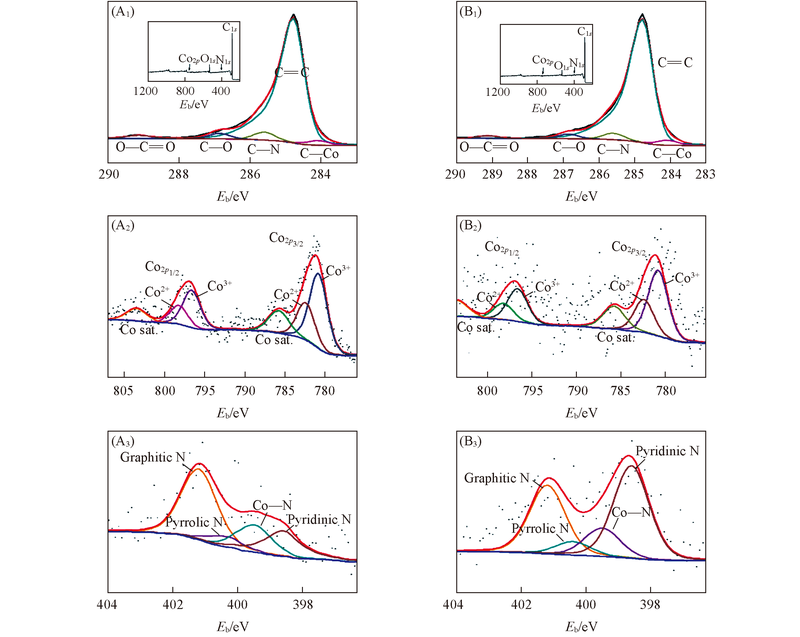
Fig.5 XPS spectra of Co-CNT/Gr(A1—A3) and Co/N-CNT/Gr-800(B1—B3) (A1), (B1) represent C1s spectra and the insets are the whole XPS spectra; (A2), (B2) and (A3), (B3) represent Co2p and N1s spectra, respectively.
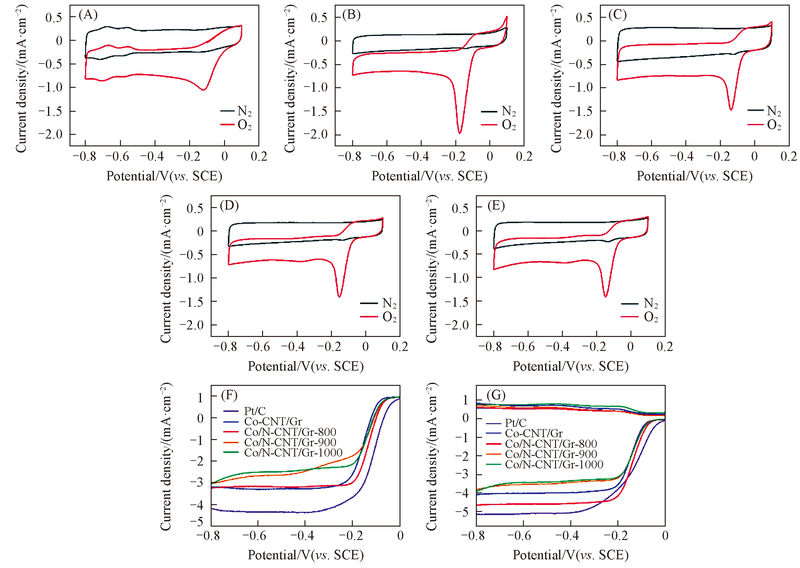
Fig.6 CV curves of Pt/C(A), Co-CNT/Gr(B), Co/N-CNT/Gr-800(C), Co/N-CNT/Gr-900(D), Co/N-CNT/Gr-1000(E), LSV(F) and RRDE(G) curves of the Co-CNT/Gr, Co/N-CNT/Gr-X(X=800, 900, 1000) and Pt/C on GC electrodes(A)—(E) In O2-saturated(solid line) and N2-saturated(dashed line) 0.1 mol/L KOH at a scan rate of 50 mV/s; (F) in O2-saturated 0.1 mol/L KOH at a scan rate of 10 mV/s and a rotation rate of 1600 r/min; (G) in O2-saturated 0.1 mol/L KOH at a scan rate of 10 mV/s and a rotation rate of 1600 r/min.
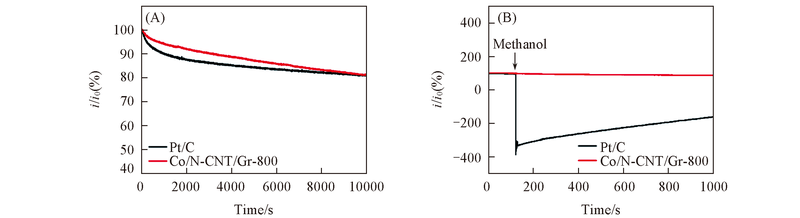
Fig.7 Current-time curves of Co/N-CNT/Gr-800 and commercial Pt/C for electrodedurability(A) and tolerance to the methanol crossover(B) (A) in O2-saturated 0.1 mol/L KOH at -0.14 V and a rotation rate of 900 r/min; (B) in O2-saturated 0.1 mol/L KOH at -0.14 V and a rotation rate of 900 r/min. The arrow in (B) indicates the addition of 5 mL methanol into the electrochemical cell after about 100 s.
| [1] | Tarasevich M., Sadkowski A., Yeager E., Oxygen Electrochemistry, Springer Boston,MA, US, 1983, 301—398 |
| [2] | Zhang J., Vukmirovic M. B., Sasaki K., Nilekar A. U., Mavrikakis M., Adzic R. R., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127(36), 12480—12481 |
| [3] | Wang J., Markovic N., Adzic R., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108(13), 4127—4133 |
| [4] | Yu X., Ye S., J. Power Sources, 2007, 172(1), 133—144 |
| [5] | Debe M. K., Nature, 2012, 486(7401), 43—51 |
| [6] | He W., Zou L. L., Zhou Y., Lu X. J., Li Y., Zhang X. G., Yang H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(1), 133—138 |
| (何卫, 邹亮亮, 周毅, 卢向军, 李媛, 张校刚, 杨辉. 高等学校化学学报, 2012,33(1), 133—138) | |
| [7] | Zheng Y., Jiao Y., Jaroniec M., Jin Y., Qiao S. Z., Small,2012, 8(23), 3550—3566 |
| [8] | Zhang L., Zhang J., Wilkinson D. P., Wang H., J. Power Sources, 2006, 156(2), 171—182 |
| [9] | Fu R. B., Yang L. Q., Feng L. Y., Guo W., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(4), 825—830 |
| (付融冰, 杨兰琴, 冯雷雨, 郭伟. 高等学校化学学报, 2014,35(4), 825—830) | |
| [10] | Gong K., Du F., Xia Z., Durstock M., Dai L., Sciencesource,2009, 323(5915), 760—764 |
| [11] | Liu J., Shen A., Wei X., Zhou K., Chen W., Chen F., Xu J., Wang S., Dai L., ACS Appl. Mater. Interf., 2015, 7(37), 20507—20512 |
| [12] | Biddinger E. J., Von Deak D., Ozkan U. S., Top. Catal., 2009, 52(11), 1566—1574 |
| [13] | Lalande G., Cote R., Guay D., Dodelet J., Weng L., Bertrand P., Electrochim. Acta, 1997, 42(9), 1379—1388 |
| [14] | Yang L., Jiang S., Zhao Y., Zhu L., Chen S., Wang X., Wu Q., Ma J., Ma Y., Hu Z., Angew. Chem., 2011, 123(31), 7270—7273 |
| [15] | Shi Q., Peng F., Liao S., Wang H., Yu H., Liu Z., Zhang B., Su D., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(47), 14853—14857 |
| [16] | Ren G., Li Y., Guo Z., Xiao G., Zhu Y., Dai L., Jiang L., Nano Res., 2015, 8(11), 3461—3471 |
| [17] | Teng C., Xie D., Wang J., Yang Z., Ren G., Zhu Y., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27(20), 1700240 |
| [18] | Bora C., Dolui S., Polymer,2012, 53(4), 923—932 |
| [19] | Collins P. G., Bradley K., Ishigami M., Zettl A., Science,2000, 287(5459), 1801—1804 |
| [20] | Li Y., Zhou W., Wang H., Xie L., Liang Y., Wei F., Idrobo J. C., Pennycook S. J., Dai H., Nat. Nanotech., 2012, 7(6), 394—400 |
| [21] | Thangasamy P., Selvakumar K., Sathish M., Kumar S. M. S., Thangamuthu R., Catal. Sci. Technol., 2017, 7(5), 1227—1234 |
| [22] | Sun Y., Gao S., Lei F., Liu J., Liang L., Xie Y., Chem. Sci., 2014, 5(10), 3976—3982 |
| [23] | Yang J., Liu H., Martens W. N., Frost R. L., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 114(1), 111—119 |
| [24] | Manivannan V., Chennabasappa M., Garrett J., Energies,2010, 3(4), 847—865 |
| [25] | Prakash D., Masuda Y., Sanjeeviraja C., Powder Technol., 2013, 235, 454—459 |
| [26] | Xia W., Qu C., Liang Z., Zhao B., Dai S., Qiu B., Jiao Y., Zhang Q., Huang X., Guo W., Nano Lett., 2017, 17(5), 2788—2795 |
| [27] | Li J., Zhou Z., Liu K., Li F., Peng Z., Tang Y., Wang H., J. Power Sources, 2017, 343, 30—38 |
| [28] | Daems N., Sheng X., Vankelecom I. F., Pescarmona P. P., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2(12), 4085—4110 |
| [29] | Wang Y., Kong A., Chen X., Lin Q., Feng P., ACS Catal., 2015, 5(6), 3887—3893 |
| [30] | Liu J., Song P., Ruan M., Xu W., Chinese J. Catal., 2016, 37(7), 1119—1126 |
| [31] | Liang Y., Li Y., Wang H., Zhou J., Wang J., Regier T., Dai H., Nat. Mater., 2011, 10(10), 780—786 |
| [1] | CHU Yuyi, LAN Chang, LUO Ergui, LIU Changpeng, GE Junjie, XING Wei. Single-atom Cerium Sites Designed for Durable Oxygen Reduction Reaction Catalyst with Weak Fenton Effect [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220294. |
| [2] | FAN Jianling, TANG Hao, QIN Fengjuan, XU Wenjing, GU Hongfei, PEI Jiajing, CEHN Wenxing. Nitrogen Doped Ultra-thin Carbon Nanosheet Composited Platinum-ruthenium Single Atom Alloy Catalyst for Promoting Electrochemical Hydrogen Evolution Process [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220366. |
| [3] | CHENG Qian, YANG Bolong, WU Wenyi, XIANG Zhonghua. S-doped Fe-N-C as Catalysts for Highly Reactive Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220341. |
| [4] | WANG Ruina, SUN Ruifen, ZHONG Tianhua, CHI Yuwu. Fabrication of a Dispersible Large-sized Graphene Quantum Dot Assemblies from Graphene Oxide and Its Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence Behaviors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220161. |
| [5] | ZHAO Runyao, JI Guipeng, LIU Zhimin. Efficient Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction over Pyrrole Nitrogen-coordinated Single-atom Copper Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220272. |
| [6] | YAN Jiasen, HAN Xianying, DANG Zhaohan, LI Jiangang, HE Xiangming. Preparation and Performance of Paraffin/Expanded Graphite/Graphene Composite Phase Change Heat Storage Material [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220054. |
| [7] | JIN Xiangyuan, ZHANG Libing, SUN Xiaofu, HAN Buxing. Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction over Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220035. |
| [8] | GU Yu, XI Baojuan, LI Jiangxiao, XIONG Shenglin. Structure Regulation of Single-atom Catalysts in Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220036. |
| [9] | WONG Honho, LU Qiuyang, SUN Mingzi, HUANG Bolong. Rational Design of Graphdiyne-based Atomic Electrocatalysts: DFT and Self-validated Machine Learning [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220042. |
| [10] | CAO Lei, CHEN Meijun, YUAN Gang, CHANG Gang, ZHANG Xiuhua, WANG Shengfu, HE Hanping. Solution-gated Graphene Field Effect Transistor Sensor Based on Crown Ether Functionalization for the Detection of Mercury Ion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210688. |
| [11] | ZHENG Xuelian, YANG Cuicui, TIAN Weiquan. The Second Order Nonlinear Optical Properties of Azulene-defect Graphene Nanosheets with Full Armchair Edge [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210806. |
| [12] | ZHANG Xiaoyu, XUE Dongping, DU Yu, JIANG Su, WEI Yifan, YAN Wenfu, XIA Huicong, ZHANG Jianan. MOF-derived Carbon-based Electrocatalysts Confinement Catalyst on O2 Reduction and CO2 Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210689. |
| [13] | GAO Jing, HE Wentao, WANG Xinxin, XIANG Yushu, LONG Lijuan, QIN Shuhao. Preparation of DOPO Derivative Modified Carbon Nanotubes and Their Effect on Flame Retardancy of Polylactic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210670. |
| [14] | ZHANG Zhibo, SHANG Han, XU Wenxuan, HAN Guangdong, CUI Jinsheng, YANG Haoran, LI Ruixin, ZHANG Shenghui, XU Huan. Self-Assembly of Graphene Oxide at Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Microparticles Toward High-performance Intercalated Nanocomposites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210566. |
| [15] | YANG Junge, GAO Chengqian, LI Boxin, YIN Dezhong. Preparation of High Thermal Conductivity Phase Change Monolithic Materials Based on Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Surface Modified Graphene Oxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210593. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||