

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 319.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170346
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
XUE Jiao, WANG Runwei*( ), ZHANG Zongtao, QIU Shilun
), ZHANG Zongtao, QIU Shilun
Received:2017-06-06
Online:2018-02-10
Published:2017-12-01
Contact:
WANG Runwei
E-mail:rwwang@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
XUE Jiao, WANG Runwei, ZHANG Zongtao, QIU Shilun. Preparation and Photocatalytic Performance of Novel Zn-doped C/Nb2O5 Nanoparticles Catalyst†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(2): 319.
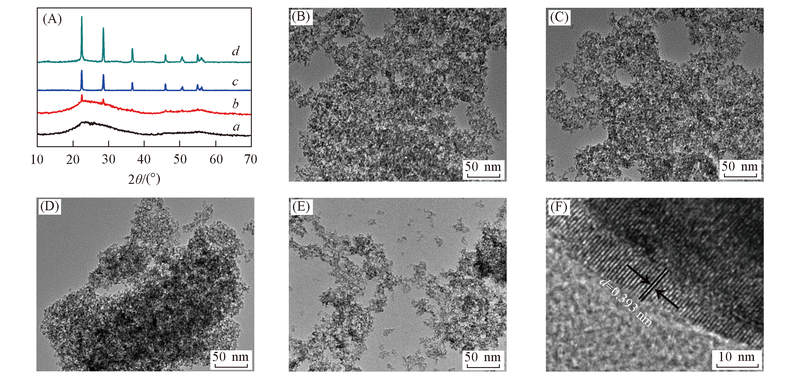
Fig.1 XRD patterns(A), TEM images of the as-prepared Zn-C/Nb2O5 samples with varying Zn/Nb molar ratios(B—E) and HRTEM image of Zn-C/Nb2O5-10(F)(A) a. C/Nb2O5; b. Zn-C/Nb2O5-5; c. Zn-C/Nb2O5-10; d. Zn-C/Nb2O5-15.(B)—(E) C/Nb2O5, Zn-C/Nb2O5-5, Zn-C/Nb2O5-10 and Zn-C/Nb2O5-15, respectively.
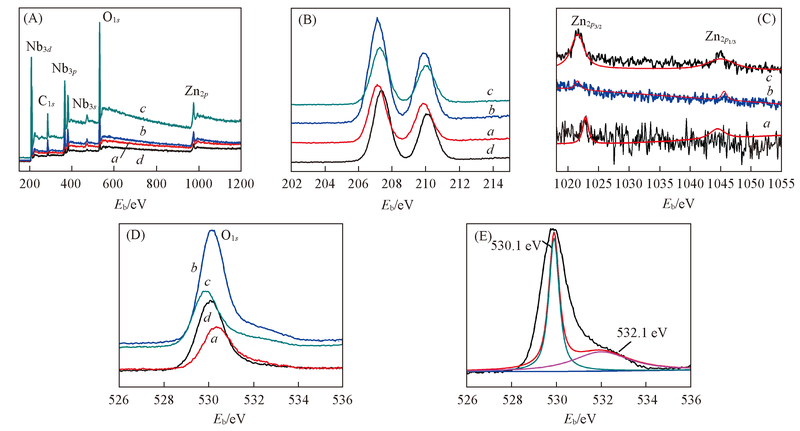
Fig.2 XPS spectra of the Zn doped C/Nb2O5(A) Full-scale; (B) Nb3d; (C) Zn2p; (D) O1s; (E) O1s fittings result for Zn-C/Nb2O5-10. (A)—(D) a. Zn-C/Nb2O5-5; b. Zn-C/Nb2O5-10; c. Zn-C/Nb2O5-15; d. C/Nb2O5.
| Sample | Lattice oxygen(OL,1s) | Surface hydroxyl(OH, 1s) | SOVs | Molar ratio(%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eb/eV | Ri(%) | Eb/eV | Ri(%) | content(%) | Zn/Nb(XPS) | Zn/Nb(ICP-AES) | |
| C/Nb2O5 | 530.3 | 58.23 | 532.0 | 41.76 | 14.0 | ||
| Zn-C/Nb2O5-5 | 530.1 | 54.49 | 532.1 | 45.41 | 18.3 | 1.40 | 0.36 |
| Zn-C/Nb2O5-10 | 530.1 | 52.90 | 532.1 | 47.10 | 19.1 | 2.43 | 0.48 |
| Zn-C/Nb2O5-15 | 530.2 | 55.86 | 532.0 | 44.14 | 16.7 | 3.22 | 0.63 |
Table 1 Calculation results for O1s XPS spectra, the content of surface oxygen vacancies(SOVs) and the Zn/Nb molar ratio from the XPS and ICP-AES of the samples
| Sample | Lattice oxygen(OL,1s) | Surface hydroxyl(OH, 1s) | SOVs | Molar ratio(%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eb/eV | Ri(%) | Eb/eV | Ri(%) | content(%) | Zn/Nb(XPS) | Zn/Nb(ICP-AES) | |
| C/Nb2O5 | 530.3 | 58.23 | 532.0 | 41.76 | 14.0 | ||
| Zn-C/Nb2O5-5 | 530.1 | 54.49 | 532.1 | 45.41 | 18.3 | 1.40 | 0.36 |
| Zn-C/Nb2O5-10 | 530.1 | 52.90 | 532.1 | 47.10 | 19.1 | 2.43 | 0.48 |
| Zn-C/Nb2O5-15 | 530.2 | 55.86 | 532.0 | 44.14 | 16.7 | 3.22 | 0.63 |
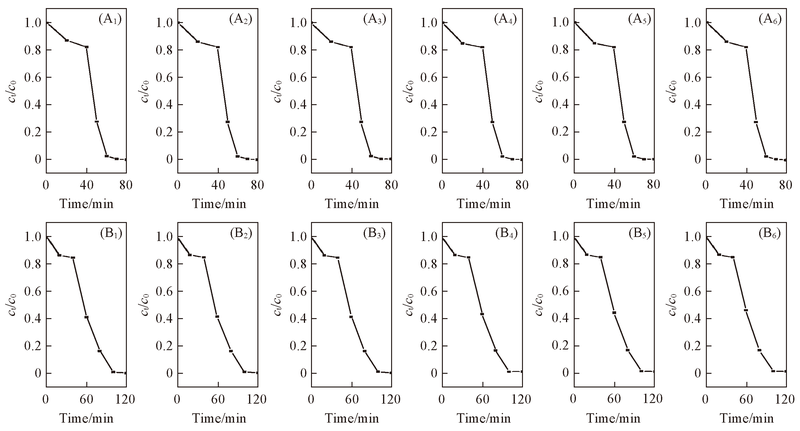
Fig.9 Cycling performance of the catalyst Zn-C/Nb2O5-10 on degradation of RhB(A1—A6) and Rh6G(B1—B6) under visible light irradiation (A1), (B1) 1st run, (A2), (B2) 2nd run, (A3), (B3) 3rd run, (A4), (B4) 4th run, (A5), (B5) 5th run, (A6), (B6) 6th run.
| [1] | Wu K., Xie Y., Zhao J., Hidaka H., J. Mol. Catal., 1999, 144, 77—84 |
| [2] | Galinado C., Jacques P., Kalt A., Chemosphere,2001, 45, 997—1005 |
| [3] | Yuan Z. H., Sun Y. C., Wang Y. H., Bie L. J., Duan Y. Q., Zhang L. D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004, 25(10), 1875—1878 |
| (袁志红, 孙永昌, 王玉红, 别利剑, 段月琴, 张立德. 高等学校化学学报, 2004,25(10), 1875—1878) | |
| [4] | Cheng K., Yang W., Wang H., Zhou J., Wu S. J., Yu T. M., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2017, 33(4), 634—647 |
| [5] | Hashemzadeh F., Rahimi R., Ghaffarinejad A., Ceram. Int., 2014, 40, 9817—9829 |
| [6] | Viet A. L., Reddy M. V., Jose R., Chowdari B. V. R., Ramarkrishna S., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, 664—671 |
| [7] | Wang Y. D., Wang L. F., Zhou Z. L., Li Y. F., Wu X. H., Matter. Lett., 2001, 49, 277—281 |
| [8] | Özer N., Chen D. G., Lampert C. M., Thin Solid Films, 1996, 277, 162—168 |
| [9] | Jose R., Thavasi V., Ramakrishna S., J. Am. Ceram., 2009, 92, 289—301 |
| [10] | Ghosh R., Brennaman M. K., Uher T., Ok M. R., Samulski E. T., McNeil L. E., Meyer T. J., Lopez R., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2011, 3, 3929—3935 |
| [11] | Prado A. G. S., Bolzon L. B., Pedroso C. P., Moura A. O., Costa L. L., Appl.Catal.,B,2008, 82, 219—224 |
| [12] | Devaiah D., Tsuzuki T., Aniz C. U., Reddy B. M., Catal. Lett., 2015, 45, 1206—1216 |
| [13] | Xie Z. G., Zhou X. X., Wu H. X., Zhao H., liu Y., Chen H. G., Catal. Lett., 2016, 146, 1355—1360 |
| [14] | Phuc N. H. H., Phuong P. T. T., Tai V. T., Huan N. M., Duy N. P. H., Loc L. C., Catal. Lett., 2016, 146, 391—397 |
| [15] | Jing L. Q., Xin B. F., Yuan F. L., Xue L. P., Wang B. Q., Fu H. G., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 17860—17865 |
| [16] | Marcì G., AugugliaroV., López-Muñoz M. J., Martín C., Palmisano L., Rives V., Schiavello M., Tilley R. D., Venezia A. M., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2001, 105, 1033—1040 |
| [17] | Zhao Y., Li C. Z., Liu X. H., Gu F., Du H.L., Shi L. Y., Appl. Catal. B, 2008, 79, 208—215 |
| [18] | Jin X. J., Liu C. L., Xu J., Wang Q. F., Chen D., RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 35546—35553 |
| [19] | Esteves A., Oliveira L. C. A., Ramalho T. C., Goncalves M., Anastacio A. S., Carvalho H. W. P., Catal. Commun., 2008, 10(3), 330—332 |
| [20] | Ce S. X., Jia H. M., Zhao H. X., Zheng Z., Zhang Z. Z., J. Mater. Chem., 2010, 20, 3052—3088 |
| [21] | Ding S., Wang R. W., Zhang Z. T., Qiu S. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(4), 695—701 |
| (丁双, 王润伟, 张宗弢, 裘式纶. 高等学校化学学报, 2014,35(4), 695—701) | |
| [22] | Xue J., Wang R. W., Zhang Z. T., Qiu S. L., Dalton Trans., 2016, 45, 16519—16525 |
| [23] | Dai Z., Dai H., Zhou Y., Liu D., Duan G., Cai W., Li Y., Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 2, 1500167—1500172 |
| [24] | Zheng Y. H., Zheng L. R., Zhan Y. Y., Lin X. Y., Zheng Q., Wei K. M., Inorg. Chem., 2007. 46, 6980—6986 |
| [25] | Sclafani A., Palmisano L., Schiarello M., J. Phys. Chem., 1990, 94, 829—832 |
| [26] | Mills A. , Holland C. E., Davies R. H., Worsley D., J. Photochem. Photobiol. A, 1994, 83, 257—264 |
| [27] | Chhor K., Bocquet J. F., Colbean-Justin C., Mater. Chem. Phys., 2004, 86, 123—131 |
| [28] | Zabek P., Eberl J., Kisch H., Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2009, 8, 264—269 |
| [29] | Jing L. Q., Sun X. J., Shang J., Cai W. M., Xu Z. L., Du Y. G., Fu H. G., Sol. Energ. Mater. Sol. Cells,2003, 79, 133—151 |
| [30] | Zhao Q. D., Xie T. F., Peng L. L., Lin Y. H., Wang P., Wang D. J., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111, 17136—17145 |
| [31] | Li H. Y., Wang D. J., Fan H. M., Wang P., Jiang T. F., Xie T. F., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2011, 354, 175—180 |
| [1] | DONG Yanhong, LU Xinhuan, YANG Lu, SUN Fanqi, DUAN Jingui, GUO Haotian, ZHANG Qinjun, ZHOU Dan, XIA Qinghua. Preparation of Bifunctional Metal-organic Framework Materials and Application in Catalytic Olefins Epoxidation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220458. |
| [2] | ZHAO Peng,ZHANG Jinteng,LIN Yanhong. Excellent Ultraviolet Photocatalytic Efficiency of Mg 2+ Doped ZnO and Analysis on Its Synergetic Effect † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 538. |
| [3] |
YANG Xiurong,ZHANG Chi,GAO Hongxu,ZHAO Fengqi,NIU Shiyao,GUO Zhaoqi,MA Haixia.
Density Functional Theory Study of NO, NO2 Adsorbed on ZnO(10 |
| [4] | ZHANG Jing,DONG Yuming,LIU Xiang,LI Hexing. Synthesis and Photocatalytic Activity of Z-Scheme Photocatalyst Sb2WO6/g-C3N4 † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 123. |
| [5] | WANG Fuxiang,CHEN Ziyu,YANG Weiting,LIU Lijuan,REN Guojian,LIU Yanfeng,PAN Qinhe. Preparation and Adsorption Performance for U(Ⅵ) of ZnO@ZIF-8 Core@Shell Microspheres† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 24. |
| [6] | HUANG Yuting,YING Zuping,ZHENG Jixing,ZHUANG Sigeng,LIU Lu,FENG Wei. Hierarchical Porous ZnO Nanomaterial Synthesized with Corn Straw as Biological Templates and Its Photocatalytic Performance† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 2031. |
| [7] |
WANG Bin,WU Yingga,LIU Zhelin,WANG Xiaohong,AN Zhihua,ZENG Jun,YANG Peng,LIU Zongrui.
Photocatalytic Activity of Keggin Type Polyoxometalates XW12 |
| [8] | HAN Zhiying, LI Youji, LIN Xiao, WANG Ziyu, LI Ziqin, WANG Hao. Preparation and Photoelectrocatalytic Performance of Fe2O3/ZnO Composite Electrode Loading on Conductive Glass† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(4): 771. |
| [9] | HU Qian, DING Yadan, PAN Ying, HONG Xia. Effect of Substrate Surface Wettability on the Adsorption of Magnetic Carrier/Protein Nanocomposites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(1): 124. |
| [10] | SI Wenyan, ZHANG Hongdi, LIU Yanjie, ZHAO Aijing, ZHANG Zhiguang, GONG Maogang, ZHANG Juncheng, LONG Yunze. Fabrication and Pressure Sensing Analysis of ZnO/PVDF Composite Microfiber Arrays by Low-voltage Near-field Electrospinning [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(6): 997. |
| [11] | SUN Lianzhi, ZHAO Shengzhe, GAO Zhiling, CHENG Zhiqiang. Controllable Synthesis of Ag Decorated ZnO Nanofibers for Enhanced Photocatalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(6): 907. |
| [12] | CHEN Yu, WANG Lei, WANG Bo. Study on Robust Icephobicity of Tape Surface† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(4): 631. |
| [13] | LI Ru, YU Liangmin, YAN Xuefeng, JIANG Tao. Morphology-controlled Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Cu2O/ZnO Microstructures† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(2): 267. |
| [14] | FU Ranran, JI Xiujie, LIU Chao, REN Yanfei, WANG Gang, CHENG Bowen. Fabrication of Cellulose/Nano Lamellar ZnO Composite Antibacterial Fibers Using Ionic Liquid† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(12): 2344. |
| [15] | LIU Jiaxin, SONG Yian, HUANG Yudong. PdZn Alloy Nanoparticles Epitaxial Growth on ZnO Nanowires for Methanol Steam Reforming† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(7): 1372. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||