

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (12): 2344.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170206
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
FU Ranran1, JI Xiujie1, LIU Chao2, REN Yanfei3, WANG Gang1, CHENG Bowen1,*( )
)
Received:2017-04-06
Online:2017-12-10
Published:2017-08-07
Contact:
CHENG Bowen
E-mail:bowen15@tjpu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
FU Ranran, JI Xiujie, LIU Chao, REN Yanfei, WANG Gang, CHENG Bowen. Fabrication of Cellulose/Nano Lamellar ZnO Composite Antibacterial Fibers Using Ionic Liquid†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(12): 2344.
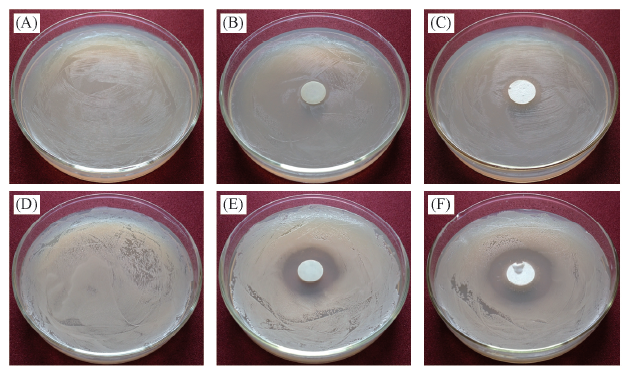
Fig.4 Digital photograph of inhibition zone for Lα-ZnO samples against E. coli(A—C) and S. aureus(D—E)(A) Control to E. coli; (B) TF-ZnO against E. coli; (C) Lα-ZnO against E. coli; (D) control to S. aureus;(E) TF-ZnO against S. aureus; (F) Lα-ZnO against S. aureus.
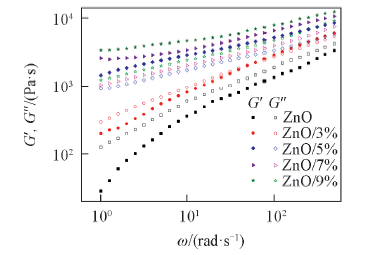
Fig.6 Changes of storage(G') and loss moduli(G″) as a function of angular frequency for the cellulose solutions with different content of nano-ZnO at 40 ℃
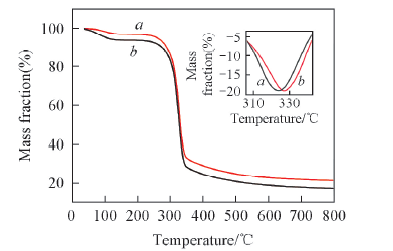
Fig.10 TGA curves of cellulose fiber(a) and cellulose composite fiber containing 7% Lα-ZnO(b) The inset displays differential thermogravimetric analysis(DTG) curves.
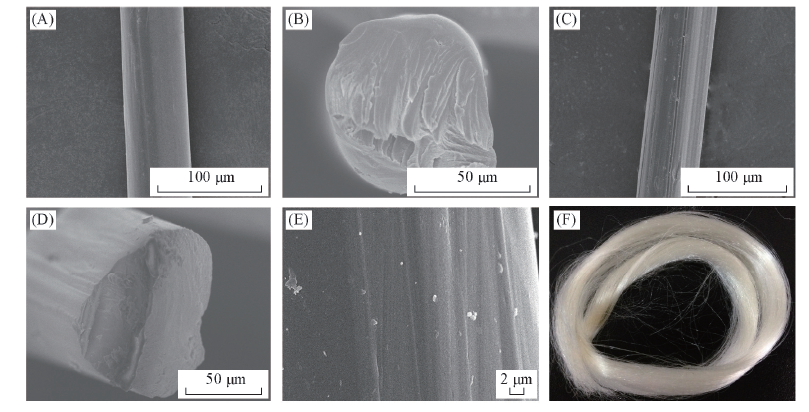
Fig.11 SEM images of side surface sections(A, C) and cross sections(B, D) of cellulose fiber(A, B) and cellulose/Lα-ZnO composite fiber(C, D)(E) Magnified image of cellulose/Lα-ZnO composite fiber; (F) digital photograph of cellulose/Lα-ZnO composite fiber.
| Sample | E. coli | S. aureus | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10-7 Microbial concentration/ (cfu·mL-1)* | Reduction in viability(%) | 10-3 Microbial concentration/ (cfu·mL-1) | Reduction in viability(%) | |
| ZnO | 8.5 | 69 | ||
| ZnO/3% | 4.2 | 50.6 | 9 | 87.0 |
| ZnO/5% | 3.2 | 62.4 | 7 | 89.9 |
| ZnO/7% | 2.4 | 71.8 | 5 | 92.8 |
| ZnO/9% | 2.1 | 75.3 | 4 | 94.2 |
Table 1 Antibacterial properties of composite fibers with different nano-ZnO content against E. coli and S. aureus
| Sample | E. coli | S. aureus | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10-7 Microbial concentration/ (cfu·mL-1)* | Reduction in viability(%) | 10-3 Microbial concentration/ (cfu·mL-1) | Reduction in viability(%) | |
| ZnO | 8.5 | 69 | ||
| ZnO/3% | 4.2 | 50.6 | 9 | 87.0 |
| ZnO/5% | 3.2 | 62.4 | 7 | 89.9 |
| ZnO/7% | 2.4 | 71.8 | 5 | 92.8 |
| ZnO/9% | 2.1 | 75.3 | 4 | 94.2 |
| [1] | Wang M. L., Zang H. J., Cai B. X., Cheng B. W., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(7), 1469—1472 |
| (王美玲, 臧洪俊, 蔡白雪, 程博闻. 高等学校化学学报 , 2009, 30(7), 1469—1472) | |
| [2] | Liu Q. B., Janssen M. H. A., Van R. F., Sheldon R. A., Green Chem., 2005, 7(1), 39—42 |
| [3] | Zhang W., Wu J., Zhang J., He J., Macromolecules,2005, 38(20), 8272—8277 |
| [4] | Mahmoudian S., Wahit M. U., Ismail A. F., Balakrishnan H., Imran M., J. Mater. Sci., 2015, 50(3), 1228—1236 |
| [5] | Zhang H., Wang Z. G., Zhang Z. N., Wu J., Zhang J., He J. S., Adv. Mater., 2007, 19(5), 698—704 |
| [6] | Song H., Luo Z., Wang C., Hao X., Gao J., Carbohyd. Polym., 2013, 98(1), 161—167 |
| [7] | Wang P., Zakeeruddin S. M., Comte P., Exnar I., Gratzel M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125(5), 1166—1167 |
| [8] | Liu X. X., Deng H., Wang Y. Y., Lu Z. W., Zeng X. Y., Wang X. X., Zou P., Rao H. B., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(10), 2156—2163 |
| (刘小霞, 邓浩, 王妍媖, 鲁志伟, 曾宪垠, 王显祥, 邹平, 饶含兵. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(10), 2156—2163) | |
| [9] | Li L., Li E. S., Gao Y., Zhao Y. H., Zhuo N., Lu L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 23(7), 1528—1533 |
| (李莉, 李恩帅, 高宇, 赵月红, 禚娜, 路露. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 23(7), 1528—1533) | |
| [10] | Gan X., Gao X., Qiu J., Li X., Appl. Surf. Sci.2008, 254(13), 3839—3844 |
| [11] | Xing L. L., Xue X. Y., Solid State Sci., 2010, 12(9), 1593—1598 |
| [12] | Qi L. M., Ma J. M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1999, 20(4), 507—510 |
| (齐利民, 马季铭. 高等学校化学学报, 1999, 20(4), 507—510) | |
| [13] | Liu C., Zhao S., Ji X., Wang B., Ma D., Mater. Chem. Phys., 2012, 133(2/3), 579—583 |
| [14] | Liu C., Ma D., Ji X., Zhao S., Li S., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, 257(9), 4529—4531 |
| [15] | Cheng G., Liu C., Mater. Chem. Phys., 2003, 77(2), 359—364 |
| [16] | Rapp G., Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst., 2002, 373(1), 201—211 |
| [17] | Lu F., Cheng B. W., Song J., Liang Y., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2012, 124(4), 3419—3425 |
| [18] | McLeish T. C. B., Allgaier J., Bick D. K., Bishko G., Biswas P., Blackwell R., Macromolecules,1999, 32(20), 6734—6758 |
| [19] | Lu X., Liu Z., Zhu Y., Jiang L., Mater. Res. Bull., 2011, 46(10), 1638—1641 |
| [20] | Zhang L., Jiang Y., Ding Y., Povey M., York D.,J. Nanopart. Res., 2007, 9(3), 479—489 |
| [1] | CUI Wei, ZHAO Deyin, BAI Wenxuan, ZHANG Xiaodong, YU Jiang. CO2 Absorption in Composite of Aprotic Solvent and Iron-based Ionic Liquid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220120. |
| [2] | PENG Kuilin, LI Guilin, JIANG Chongyang, ZENG Shaojuan, ZHANG Xiangping. Research Progress for the Role of Electrolytes in the CO2 Electrochemical Reduction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220238. |
| [3] | JI Shuangqi, JIN Zhao, GUAN Wenna, PAN Xiangyu, GUAN Tong. Preparation and Chromatographic Performance of Mixed-mode Silica Stationary Phase Modified by Double Cationic Ionic Liquid and Octadecyl Group [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220008. |
| [4] | CHANG Sihui, CHEN Tao, ZHAO Liming, QIU Yongjun. Thermal Degradation Mechanism of Bio-based Polybutylactam Plasticized by Ionic Liquids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220353. |
| [5] | HU Haocheng, LI Wenli, ZHANG Jianing, LIU Yubo. Extraction, Structure Characterization and Biological Activities of Oligosaccharides from Auricularia heimuer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2465. |
| [6] | FU Jinzhou, WANG Hanwei, LI Yingying, WANG Chao, LI Caicai, SUN Qingfeng, LI Huiqiao. Micro/Nanocellulose Functional Membranes for Energy and Environment [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1407. |
| [7] | WANG Man, WANG Xin, ZHOU Jing, GAO Guohua. Efficient Synthesis of Dimethyl Carbonate via Transesterification of Methanol and Ethylene Carbonate Catalyzed by Poly(ionic liquid)s [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3701. |
| [8] | WAN Ren, SONG Fan, PENG Changjun, LIU Honglai. Group Contribution Method for Infinite Dilution Molar Conductivity of Unconventional Ions in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3672. |
| [9] | ZHOU Molin, JIANG Xin, YI Ting, YANG Xiangguang, ZHANG Yibo. Improvement of Interface Stability Between Sulfide Solid Electrolyte Li10GeP2S12 and Lithium Metal [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1810. |
| [10] | CHENG Shifu,HU Hao,CHEN Bihua,WU Haihong,GAO Guohua,HE Mingyuan. Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of Porous Carbons Prepared from Binary Ionic Liquids † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1048. |
| [11] | GAO Chong,YU Fengli,XIE Congxia,YU Shitao. Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation of Cyclic Ketones Catalyzed by Amino Alcohol Heteropoly Acid Ionic Liquid † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1101. |
| [12] | GAO Naiwei, MA Qiang, HE Yonglin, WANG Yapei. Green Electronic Devices Based on Ionic Liquids † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 901. |
| [13] | ZHAO Ziyi,ZHENG Hongzhi,XU Yan. Multi-color Circularly Polarized Luminescence Properties of Cellulose Nanocrystal † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1120. |
| [14] | KONG Jinfeng, ZHU Yuzhang, JIN Jian. Sulfonated Cellulose Nanofibers Film Supported Nanofiltration Membrane for High-flux and High-rejection Desalination † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 690. |
| [15] | PIAO Huilan,MA Pinyi,QIN Zucheng,JIANG Yanxiao,SUN Ying,WANG Xinghua,SONG Daqian. Determination of Triazine Herbicides from Fruit Juice Samples Using Effervescence Assisted Microextraction Method Based on Acidic Ionic Liquid Packed Syringe [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 228. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||