

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (10): 1822.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170158
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
HE Jianping1, ZHANG Lei1,*( ), CHEN Lin2, YANG Zhanxu1,*(
), CHEN Lin2, YANG Zhanxu1,*( ), TONG Yufei1
), TONG Yufei1
Received:2017-03-20
Online:2017-10-10
Published:2017-09-22
Contact:
ZHANG Lei,YANG Zhanxu
E-mail:lnpuzhanglei@163.com;zhanxuy@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
HE Jianping, ZHANG Lei, CHEN Lin, YANG Zhanxu, TONG Yufei. Effect of CeO2 on Cu/Zn-Al Catalysts Derived from Hydrotalcite Precursor for Methanol Steam Reforming†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(10): 1822.
| Catalyst | Content of element(%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Zn | Al | Ce | O | |
| CZA | 9.66 | 14.60 | 36.90 | 38.84 | |
| 2%Ce/CZA | 9.43 | 14.28 | 36.11 | 1.79 | 38.39 |
| 4%Ce/CZA | 9.19 | 13.88 | 35.42 | 3.50 | 38.01 |
| 6%Ce/CZA | 9.03 | 13.24 | 34.73 | 5.37 | 37.63 |
| 8%Ce/CZA | 8.87 | 13.00 | 33.99 | 6.92 | 37.22 |
Table 1 Component contents of different catalysts
| Catalyst | Content of element(%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Zn | Al | Ce | O | |
| CZA | 9.66 | 14.60 | 36.90 | 38.84 | |
| 2%Ce/CZA | 9.43 | 14.28 | 36.11 | 1.79 | 38.39 |
| 4%Ce/CZA | 9.19 | 13.88 | 35.42 | 3.50 | 38.01 |
| 6%Ce/CZA | 9.03 | 13.24 | 34.73 | 5.37 | 37.63 |
| 8%Ce/CZA | 8.87 | 13.00 | 33.99 | 6.92 | 37.22 |
| Catalyst | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Pore volume/ (cm3·g-1) | dCuO/nm | Cu dispersionb(%) | Cu surface areac/ (m2·g-1) | (mL3·k |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CZA | 147.0 | 0.47 | 34.0 | 10.32 | 5.90 | 446.2 |
| 2%Ce/CZA | 114.1 | 0.42 | 24.4 | 10.96 | 6.17 | 786.6 |
| 4%Ce/CZA | 109.6 | 0.41 | 22.8 | 11.49 | 6.32 | 810.7 |
| 6%Ce/CZA | 106.7 | 0.38 | 26.4 | 11.44 | 6.16 | 691.2 |
| 8%Ce/CZA | 105.3 | 0.37 | 26.7 | 11.78 | 6.18 | 648.0 |
Table 2 Physical characteristics of the prepared catalysts and hydrogen production rate in methanol steam reforminga
| Catalyst | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Pore volume/ (cm3·g-1) | dCuO/nm | Cu dispersionb(%) | Cu surface areac/ (m2·g-1) | (mL3·k |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CZA | 147.0 | 0.47 | 34.0 | 10.32 | 5.90 | 446.2 |
| 2%Ce/CZA | 114.1 | 0.42 | 24.4 | 10.96 | 6.17 | 786.6 |
| 4%Ce/CZA | 109.6 | 0.41 | 22.8 | 11.49 | 6.32 | 810.7 |
| 6%Ce/CZA | 106.7 | 0.38 | 26.4 | 11.44 | 6.16 | 691.2 |
| 8%Ce/CZA | 105.3 | 0.37 | 26.7 | 11.78 | 6.18 | 648.0 |
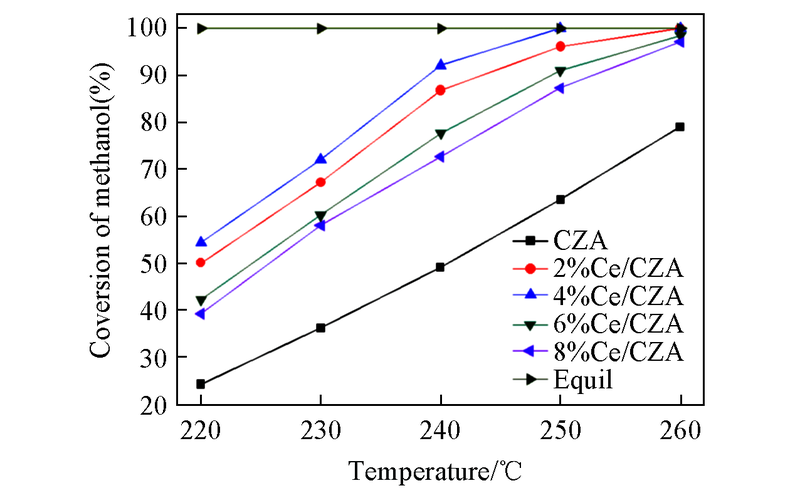
Fig.5 Profiles of the catalyst activity as a function of the reaction temperatureReaction conditions: n(water)/n(methanol)=1.2:1, GHSV=800 h-1, no carrier gas.
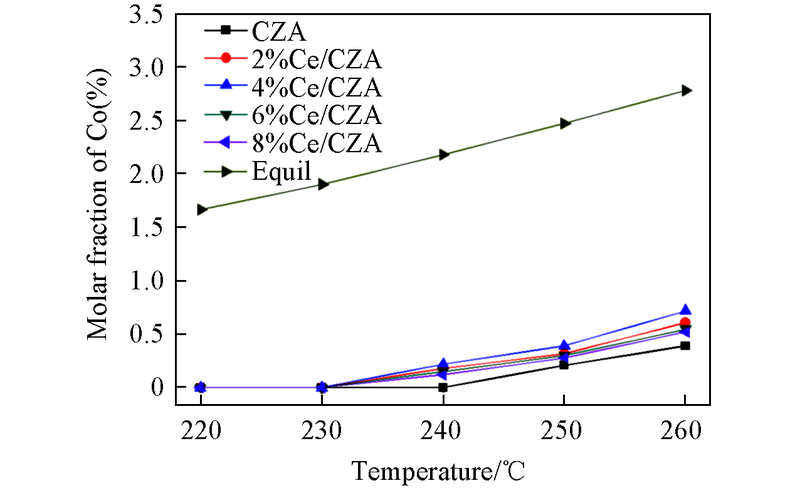
Fig.6 Profiles of the CO molar fraction as a function of the reaction temperatureReaction conditions: n(water)/n(methanol)=1.2:1, GHSV=800 h-1, no carrier gas.
| [1] | Cammack R., Michel F., CRC Press, 2015 |
| [2] | Lewis N. S., Nocera D. G., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2006, 103(43), 15729—15735 |
| [3] | Tozzini V., Pellegrini V., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, 15(1), 80—85 |
| [4] | Fihri A., Artero V., Razavet M., Baffert C., Leibl W., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2008, 47(3), 564—567 |
| [5] | Ma. Y., Guan G., Phanthong P., Li X., Cao J., Hao X., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy,2014, 39(33), 18803—18811 |
| [6] | Zhang X. R., Yao C. Z., Wang L. C., Cao Y., Wu D., Sun Y. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2005, 26(6), 1137—1139 |
| (张新荣, 姚成漳, 王路存, 曹勇, 吴东, 孙予罕. 高等学校化学学报, 2005, 26(6), 1137—1139) | |
| [7] | Zhang L., Pan L. W., Ni C. J., Zhao S. S., Wang S. D., Hu Y. K., Wang A. J., Jiang K., J. Fuel Chem. Techno., 2013, 41(1), 116—122 |
| (张磊, 潘立卫, 倪长军, 赵生生, 王树东, 胡永康, 王安杰, 蒋凯. 燃料化学学报, 2013, 41(1), 116—122) | |
| [8] | Kuc J., Neumann M., Armbrüster M., Yoon S., Zhang Y., Erni R., Matam S. K., Catal. Sci. Technol., 2016, 6(5), 1455—1468 |
| [9] | Zhou J., Zhang Y., Wu G., Mao D., Lu G., RSC. Adv., 2016, 6(36), 30176—30183 |
| [10] | Das D., Llorca J., Dominguez M., Colussi S., Trovarelli A., Gayen A., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy,2015, 40(33), 10463—10479 |
| [11] | Lytkina A. A., Zhilyaeva N. A., Ermilova M. M., Orekhova N. V., Yaroslavtsev A. B., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy,2015, 40(31), 9677—9684 |
| [12] | Zhang X. R., Wang L. C., Yao C. Z., Cao Y., Dai W. L., Fan K. N., Wu D., Sun Y. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2004, 25(11), 2125—2127 |
| (张新荣, 王路存, 姚成漳, 曹勇, 戴维林, 范康年, 吴东, 孙予罕. 高等学校化学学报, 2004, 25(11), 2125—2127) | |
| [13] | Shen J. P., Song C. S., Catal. Today,2002, 77(1), 89—98 |
| [14] | Patel S., Pant K. K., J. Porous Mater., 2006, 13(3), 373—378 |
| [15] | Yao C. Z., Wang L. C., Liu Y. M., Wu G. S., Cao Y., Dai W. L., Fan K. N., Appl. Catal. A,2006, 297(2), 151—158 |
| [16] | Busca G., Costantino U., Marmottini F., Montanari T., Patrono P., Pinzari F., Ramis G., Appl. Catal. A,2006, 310, 70—78 |
| [17] | Hammoud D., Gennequin C., Aboukaïs A., Aad E. A., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy,2015, 40(2), 1283—1297 |
| [18] | Liu Y., Hayakawa T., Tsunoda T., Suzuki K., Hamakawa S., Murata K., Shiozaki R., Lshii T., Kumagai M., Top. Catal., 2003, 22(3/4), 205—213 |
| [19] | Patel S., Pant K. K., J. Power Sources,2006, 159(1), 139—143 |
| [20] | Trovarelli A, Catal. Rev. Sci. Eng., 1996, 38(4), 439—520 |
| [21] | Xie R., Fan G., Yang L., Li F., Catal. Sci. Technol., 2015, 5(1), 540—548 |
| [22] | Zhang L., Lei J. T., Tian Y., Hu X., Bai J., Liu D., Yang Y., Pan L. W., J. Fuel Chem. Techno., 2015, 43(11), 1366—1374 |
| (张磊, 雷俊腾, 田园, 胡鑫, 白金, 刘丹, 杨义, 潘立卫. 燃料化学学报, 2015, 43(11), 1366—1374) | |
| [23] | Agarwal V., Patel S., Pant K. K., Appl. Catal. A,2005, 279(1),155—164 |
| [24] | Mateos-Pedrero C., Silva H., Tanaka D. A. P., Liguori S., Iulianelli A., Basile A., Mendes A., Appl. Catal. B,2015, 174, 67—76 |
| [25] | Zhang L., Pan L. W., Ni C. J., Sun T. J., Wang S. D., Hu Y. K., Zhao S. S., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy,2013, 38(11), 4397—4406 |
| [26] | Zhang L., Pan L. W., Ni C. J., Sun T. J., Wang S. D., Hu Y. K., Wang A. J., Zhao S. S., J. Fuel Chem. Technol., 2013, 41(7), 883—888 |
| (张磊, 潘立卫, 倪长军, 孙天军, 王树东, 胡永康, 王安杰, 赵生生. 燃料化学学报, 2013, 41(7), 883—888) | |
| [27] | Patel S., Pant K. K., Fuel Process. Technol., 2007, 88(8), 825—832 |
| [28] | Wan Y., Zhou Z. M., Cheng Z. M., Chin. J. Chem. Eng., 2016, 24(9), 1186—1194 |
| [29] | Agrell J., Birgersson H., Boutonnet M., Melian-Cabrera I., Navarro R. M., Fierro J. G., J. Catal., 2003, 219(2): 389—403 |
| [30] | Kam R., Selomulya C., Amal R., Scott J., J. Catal., 2010, 273(1), 73—81 |
| [31] | Liu Y., Hayakawa T., Suzuki K., Hamakawa S., Tsunoda T., Ishii T., Kumagai M., Appl. Catal. A,2002, 223(1), 137—145 |
| [32] | Hurst N. W., Gentry S. J., Jones A., McNicol B. D., Jones A., Catal. Reviews Sci. Eng., 1982, 24(2), 233—309 |
| [33] | Shim J. O., Na H. S., Jha A., Jang W. J., Jeong D. W., Nah I. W., Roh H. S., Chem. Eng. J., 2016, 306, 908—915 |
| [34] | Takahashi K., Takezawa N., Kobayashi H., Appl. Catal., 1982, 2(6), 363—366 |
| [1] | FAN Jianling, TANG Hao, QIN Fengjuan, XU Wenjing, GU Hongfei, PEI Jiajing, CEHN Wenxing. Nitrogen Doped Ultra-thin Carbon Nanosheet Composited Platinum-ruthenium Single Atom Alloy Catalyst for Promoting Electrochemical Hydrogen Evolution Process [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220366. |
| [2] | TANG Quanjun, LIU Yingxin, MENG Rongwei, ZHANG Ruotian, LING Guowei, ZHANG Chen. Application of Single-atom Catalysis in Marine Energy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220324. |
| [3] | LIN Gaoxin, WANG Jiacheng. Progress and Perspective on Molybdenum Disulfide with Single-atom Doping Toward Hydrogen Evolution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220321. |
| [4] | WEI Chunhong, JIANG Qian, WANG Panpan, JIANG Chengfa, LIU Yuefeng. Atomic Scale Investigation of Pt Atoms/clusters Promoted Co-catalyzed Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220074. |
| [5] | ZHOU Zixuan, YANG Haiyan, SUN Yuhan, GAO Peng. Recent Progress in Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide to Methanol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220235. |
| [6] | ZHANG Xinxin, XU Di, WANG Yanqiu, HONG Xinlin, LIU Guoliang, YANG Hengquan. Effect of Mn Promoter on CuFe-based Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Higher Alcohols [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220187. |
| [7] | ZHOU Leilei, CHENG Haiyang, ZHAO Fengyu. Research Progress of CO2 Hydrogenation over Pd-based Heterogeneous Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220279. |
| [8] | HUANG Xiaoshun, MA Haiying, LIU Shujuan, WANG Bin, WANG Hongli, QIAN Bo, CUI Xinjiang, SHI Feng. Recent Advances on Indirect Conversion of Carbon Dioxide to Chemicals [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220222. |
| [9] | DING Yang, WANG Wanhui, BAO Ming. Recent Progress in Porous Framework-immobilized Molecular Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Formic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220309. |
| [10] | MIN Jing, WANG Liyan. 1H NMR Study on the Conformation of Aromatic Amides Limited by Three-center Hydrogen Bonds [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220084. |
| [11] | SONG Youwei, AN Jiangwei, WANG Zheng, WANG Xuhui, QUAN Yanhong, REN Jun, ZHAO Jinxian. Effects of Ag,Zn,Pd-doping on Catalytic Performance of Copper Catalyst for Selective Hydrogenation of Dimethyl Oxalate [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20210842. |
| [12] | YANG Lijun, YU Yang, ZHANG Lei. Construction of Dual-functional 2D/3D Hydrid Co2P-CeO x Heterostructure Integrated Electrode for Electrocatalytic Urea Oxidation Assisted Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220082. |
| [13] | WANG Guangqi, BI Yiyang, WANG Jiabo, SHI Hongfei, LIU Qun, ZHANG Yu. Heterostructure Construction of Noble-metal-free Ternary Composite Ni(PO3)2-Ni2P/CdS NPs and Its Visible Light Efficient Catalytic Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220050. |
| [14] | CHEN Changli, MI Wanliang, LI Yujing. Research Progress of Single Atom Catalysts in Electrochemical Hydrogen Cycling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220065. |
| [15] | WANG Mingzhi, ZHENG Yanping, WENG Weizheng. Catalytic Methane Combustion over CeO2 Supported PdO and Ce1‒x Pd x O2‒δ Species [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210816. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||