

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (5): 860.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150938
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Yan, ZHENG Jing, WANG Juan, GUO Mandong*( )
)
Received:2015-12-17
Online:2016-05-10
Published:2016-04-12
Contact:
GUO Mandong
E-mail:guomd@dns.sxnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHANG Yan, ZHENG Jing, WANG Juan, GUO Mandong. Preparation and Properties of Doxorubicin Hydrochloride Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(5): 860.
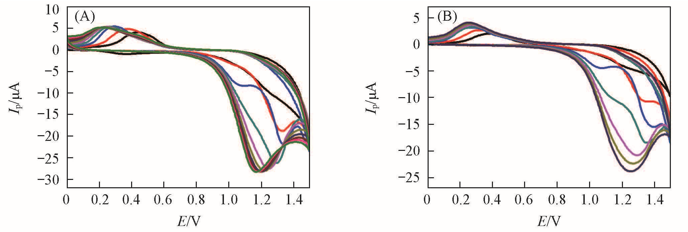
Fig.2 CV curves for the electrochemical polymerization of EDOT in the absence(A) and presence(B) of DOX in PBS Scan rate: 50 mV/s; cycling number: (A) 10; (B) 7.
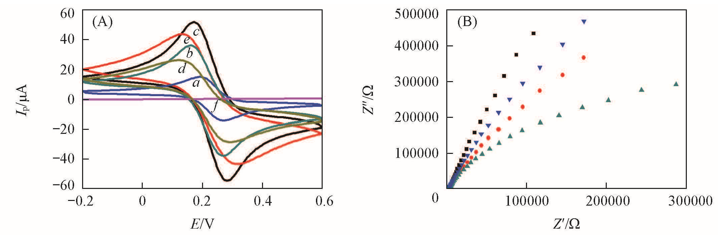
Fig.3 CV curves of the electrodes in 0.1 mol/L KCl containing 5 mmol/L K3[Fe(CN)6](A) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of the electrodes(B)(A) a. Au/CME; b. PEDOT/Au/CME; c. AuNPs-CS/PEDOT/Au/CME; d. DOX-MIPs/AuNPs-CS/PEDOT/Au/CME; e. MIPs/AuNPs-CS/PEDOT/Au/CME; f. NMIPs/AuNPs-CS/PEDOT/Au/CME. (B) ■ Au/CME;▼ DOX-MIPs/AuNPs-CS/PEDOT/Au/CME; ● PEDOT/Au/CME; ▲ AuNPs-CS/PEDOT/Au/CME.
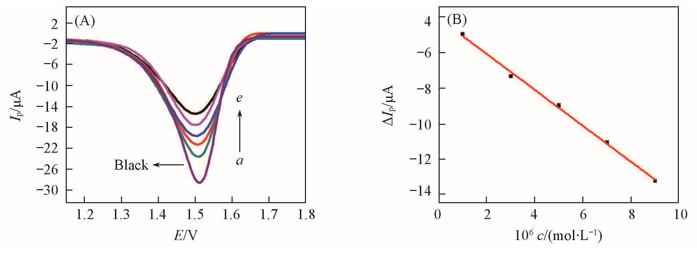
Fig.6 DPV curves of MIP/AuNPs-CS/PEDOT/Au/CME after adsorption in different concentrations of DOX(A) and linear relationship of current peak difference vs. DOX concentration on MIP/AuNPs-CS/PEDOT/Au/CME(B)
| Method | Linear range/(mol·L-1) | 108 Detection limit | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| High performance liquid chromategraphy | 1.7×10-7—1.7×10-5 | 17.0 | [1] |
| Capillary electrophoresis | 1.0×10-6—1.0×10-5 | 29.0 | [2] |
| Fluorescence spectroscopy | 7.8×10-8—5.2×10-6 | 2.3 | [3] |
| The proposed method | 6.9×10-7—4.3×10-6 | 5.0 | [4] |
| Flow injection chemilumin-escence method-escence method | 4.0×10-7—1.0×10-6 | 6.5 | This work |
Table 1 Comparison of detection results of DOX by this method and literature methods
| Method | Linear range/(mol·L-1) | 108 Detection limit | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| High performance liquid chromategraphy | 1.7×10-7—1.7×10-5 | 17.0 | [1] |
| Capillary electrophoresis | 1.0×10-6—1.0×10-5 | 29.0 | [2] |
| Fluorescence spectroscopy | 7.8×10-8—5.2×10-6 | 2.3 | [3] |
| The proposed method | 6.9×10-7—4.3×10-6 | 5.0 | [4] |
| Flow injection chemilumin-escence method-escence method | 4.0×10-7—1.0×10-6 | 6.5 | This work |
| 106 Concentration added/ (mol·L-1) | Current response/μA | 106 Concentration detected mol/L | Recovery(%) | RSD(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First | Second | Third | ||||
| 1 | -4.96 | -4.80 | -4.86 | 9.4 | 96.0 | 1.66 |
| 3 | -7.32 | -7.23 | -7.15 | 3.2 | 106.7 | 1.39 |
| 5 | -8.95 | -8.80 | -8.83 | 4.86 | 97.2 | 0.90 |
| 7 | -11.04 | -10.90 | -10.86 | 7.13 | 101.9 | 0.86 |
Table 2 Determination result of DOX in blood serum samples
| 106 Concentration added/ (mol·L-1) | Current response/μA | 106 Concentration detected mol/L | Recovery(%) | RSD(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First | Second | Third | ||||
| 1 | -4.96 | -4.80 | -4.86 | 9.4 | 96.0 | 1.66 |
| 3 | -7.32 | -7.23 | -7.15 | 3.2 | 106.7 | 1.39 |
| 5 | -8.95 | -8.80 | -8.83 | 4.86 | 97.2 | 0.90 |
| 7 | -11.04 | -10.90 | -10.86 | 7.13 | 101.9 | 0.86 |
| [1] | Chen J. H., Xia P. Y., Wang Z. Y., Wu N., Dai Q., Sun F. J., Yang B., Xiang R. F., Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy, 2010, 30(5), 353—356 |
| (陈剑鸿, 夏培元, 王章阳, 吴南, 戴青, 孙凤军, 杨波, 向荣凤. 中国医院药学杂志, 2010, 30(5), 353—356) | |
| [2] | Peng H. D., Sun Y., Mo M. F., Yang D. H., Li H. X., Journal of Guangdong PharmaCeutical University, 2011, 27(6), 587—590 |
| (彭怀东, 孙悦, 莫满芳, 杨端辉, 李海秀. 广东药学院学报, 2011, 27(6), 587—590) | |
| [3] | Hu R., Yang Q., Zhang S. R., Yang J. D., Chinese Journal ofAntibiotics, 2009, 34(7), 411—416 |
| (胡蓉, 杨琼, 张书然, 杨季冬. 中国抗生素杂志, 2009, 34(7), 411—416) | |
| [4] | Ge C., Fu H., He Y., Yi G., Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2013, 32(6), 105—107 |
| (葛闯, 付虎, 何云, 易钢. 分析试验室, 2013, 32(6), 105—107) | |
| [5] | Suryanarayanan V., Wu C. T., Ho K. C., Electroanalysis, 2010, 22(16), 1795—1811 |
| [6] | Xu W., Li X., Zhang W. Y., Ying X. G., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2012, 33(10), 2199—2204 |
| (徐雯, 李晓, 张卫英, 英晓光. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(10), 2199—2204) | |
| [7] | Malitesta C., Mazzotta E., Picca R. A., Poma A., Chianella I., Piletsky S. A., Anal. Bioanal.Chem., 2012, 402(5), 1827—1846 |
| [8] | Zhang J., Wang C. Y., Li X. P., Niu Y. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2013, 34(10), 2296—2302 |
| (张进, 王超英, 李小平, 牛延慧. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(10), 2296—2302) | |
| [9] | Spivak D. A., Shea K. J., J. Mol.Recognit., 2012, 25(6), 319 |
| [10] | Vishnuvardhan V., Prathish K. P., Naidu G. R. K., Prasada R. T., Electrochim. Acta,2007, 52(24), 6922—6928 |
| [11] | Lu C. Y., Ma X. X., He X. W., Li W. Y., Chen L. X., He H. C., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2005, 26(7), 1356—1359 |
| (卢春阳, 马向霞, 何锡文, 李文友, 陈朗星, 何海成. 高等学校化学学报, 2005, 26(7), 1356—1359) | |
| [12] | Tang K. J., Gu X. H., Zhu S., Tang J., Wang H. J., Acta Chim.Sinica, 2009, 67(7), 687—692 |
| (唐凯洁, 顾小红, 朱松, 汤坚, 王海军. 化学学报, 2009, 67(7), 687—692) | |
| [13] | Niu J., Liu Z. H., Fu L., Shi F., Ma H. W., Ozaki Y., Zhang X., Langmuir,2008, 24(20), 11988—11994 |
| [14] | Zhang N. W., Ding M. X., Liu G. Y., Song W. W., Chai C. Y., Acta Chim.Sinica, 2008, 66(7), 1961—1966 |
| (张挪威, 丁明星, 刘国艳, 宋巍巍, 柴春彦. 化学学报, 2008, 66(7), 1961—1966) | |
| [15] | Cheng Z. L., Wang E., Yang X. R., Biosens.Bioelectron, 2001, 16(3), 179—185 |
| [16] | Weetall H. H., Rogers K. R., Talanta, 2004, 62(2), 329—4107 |
| [17] | Liao H. P., Zhang Z. H., Li H., Electrochim. Acta,2004, 49, 4101 |
| [18] | HoK. C., Yeh W. M., Tung T. S., Liao J. Y., Anal. Chim.Acta, 2005, 542, 90—96 |
| [19] | Yang Z. J., Liu S. H., Ye J. N., Fang Y. Z., Chin. J. Anal.Chem., 1996, 24(4), 471—474 |
| (杨志洁, 刘盛辉, 叶建农, 方禹之. 分析化学, 1996, 24(4), 471—474) | |
| [20] | Mark S., Michael. J., Debra E. W., Sens. Actuators B:Chemical, 2015, 221, 1003—1008 |
| [21] | Song J. L., Bulletin ofBiology, 2002, 37(11), 47—49 |
| [22] | Xie C. G., Gao S., Guo Q. B., Microchim.Acta, 2010, 169(1/2), 145—152 |
| [1] | ZHANG Qingyi, CAO Jie, SHU Xiao, LIU Jianzhao. Effects of Exogenous N6-methyladenosine (m6A) Incorporation on the Expression of Cellular mRNA Transcripts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(Album-4): 20220173. |
| [2] | WENG Meiqi, SHANG Guiming, WANG Jiatai, LI Shenghua, FAN Zhi, LIN Song, GUO Minjie. Template Simulation of Organophosphorus Nerve Agent Molecularly Imprinted Polymers [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220136. |
| [3] | HUANG Qiuhong, LI Wenjun, LI Xin. Organocatalytic Enantioselective Mannich-type Addition of 5H-Oxazol-4-ones to Isatin Derived Ketimines [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220131. |
| [4] | WANG Xuebin, XUE Yuan, MAO Hua’nyu, XIANG Yanxin, BAO Chunyan. Preparation of Photo/reduction Dual-responsive Hydrogel Microspheres and Their Application in Three-dimensional Cell Culture [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220116. |
| [5] | JIN Ruiming, MU Xiaoqing, XU Yan. Bio-chemical Synthesis of Melanin Precursor—— 5,6-Dihydroxyindole(DHI) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220134. |
| [6] | TAN Yan, YU Shen, LYU Jiamin, LIU Zhan, SUN Minghui, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. Efficient Preparation of Mesoporous γ-Al2O3 Microspheres and Performance of Pd-loaded Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220133. |
| [7] | YAO Yiting, LYU Jiamin, YU Shen, LIU Zhan, LI Yu, LI Xiaoyun, SU Baolian, CHEN Lihua. Preparation of Hierarchical Microporous-mesoporous Fe2O3/ZSM-5 Hollow Molecular Sieve Catalytic Materials and Their Catalytic Properties for Benzylation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220090. |
| [8] | LI Yulong, XIE Fating, GUAN Yan, LIU Jiali, ZHANG Guiqun, YAO Chao, YANG Tong, YANG Yunhui, HU Rong. A Ratiometric Electrochemical Sensor Based on Silver Ion Interaction with DNA for the Detection of Silver Ion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220202. |
| [9] | WANG Hong, SAN Khin Nyein Ei, FANG Yun, ZHANG Xinyu, FAN Ye. Pickering Emulsion Stabilization and Interfacial Catalytic Oxidation by Janus Nano-Au [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220105. |
| [10] | LIU Xiaolei, LU Yongqiang, YOU Qi, LIU Guohui, YAO Wei, HU Riming, YAN Jixian, CUI Yu, YANG Xiaofeng, SUN Guoxin, JIANG Xuchuan. A 3-Hydroxythalidomide-based Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for the Detection of H2O2 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220070. |
| [11] | GONG Yanxi, WANG Jianbing, CHAI Buyu, HAN Yuanchun, MA Yunfei, JIA Chaomin. Preparation of Potassium Doped g-C3N4 Thin Film Photoanode and Its Application in Photoelectrocatalytic Oxidation of Diclofenac Sodium in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220005. |
| [12] | WANG Guangqi, BI Yiyang, WANG Jiabo, SHI Hongfei, LIU Qun, ZHANG Yu. Heterostructure Construction of Noble-metal-free Ternary Composite Ni(PO3)2-Ni2P/CdS NPs and Its Visible Light Efficient Catalytic Hydrogen Production [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220050. |
| [13] | JIANG Xiaokang, ZHOU Qi, ZHOU Hengwei. Synthesis and Luminescence Properties of Gd2ZnTiO6∶Dy3+, Eu3+ Single Phase White Light-emitting Phosphors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220029. |
| [14] | HUANG Yi, LYU Lingling, PAN Xiaopeng, SUN Guangdong, LI Yongqiang, YAO Juming, SHAO Jianzhong. Three-dimensional Printing of Photocrosslinked Self-supporting Silk Fibroin Hydrogels [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210841. |
| [15] | ZHAO Mengyang, HUANG Ziyang. Preparation and in vitro Bioactivity of HA/CuO/SrCO3 Gradiently Composite Coating [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210644. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||