

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (12): 2364.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150464
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHI Xuanxuan, XIAO Ruijuan, WANG Zhen, ZHOU Jianping*( ), BIAN Xiaobing
), BIAN Xiaobing
Received:2015-06-12
Online:2015-12-10
Published:2015-11-17
Contact:
ZHOU Jianping
E-mail:zhoujp@snnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
SHI Xuanxuan, XIAO Ruijuan, WANG Zhen, ZHOU Jianping, BIAN Xiaobing. Effects of Magnetic Field on the Morphology and Properties of BiFeO3 Synthesized by Hydrothermal Method†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(12): 2364.
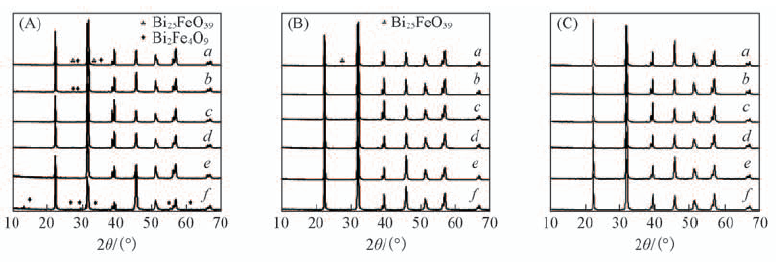
Fig.1 XRD patterns of samples synthesized at 200 ℃ for 3 h with different KOH concentrations under magnetic fields of 0(A), 120 mT(B) and 240 mT(C) c(KOH)/(mol·L-1): a. 2; b. 3; c. 4; d. 5; e. 6; f. 7.
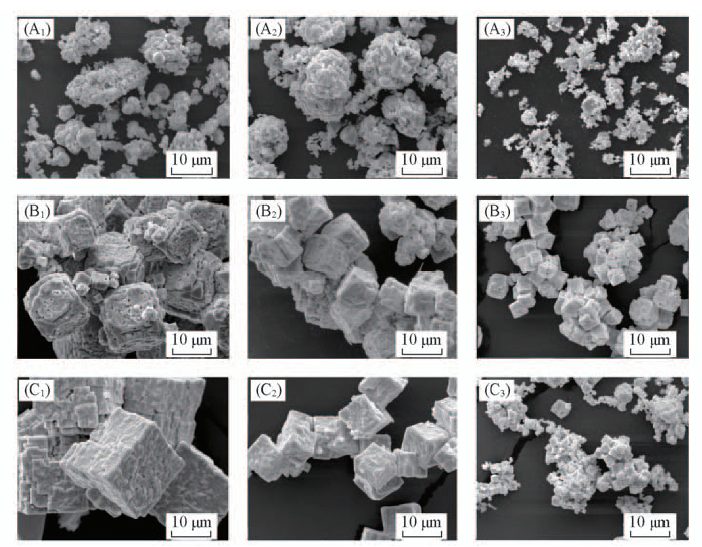
Fig.2 SEM images of samples synthesized at 200 ℃ for 3 h with c(KOH) of 4(A1—A3), 5(B1—B3) and 6 mol/L(C1—C3) under magnetic fields of 0(A1, B1, C1), 120 mT(A2, B2, B2), 240 mT(A3, B3, C3)
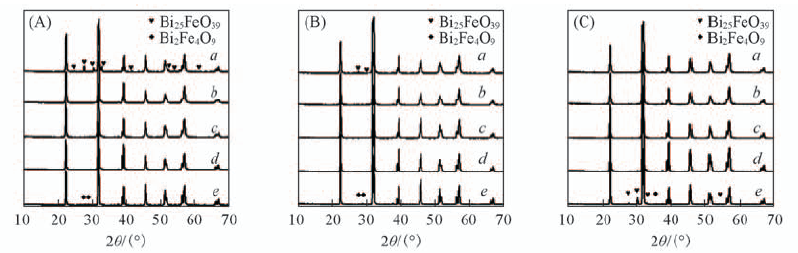
Fig.3 XRD patterns of samples synthesized at 140—220 ℃ for 3 h with c(KOH) of 4 mol/L under magnetic fields of 0(A), 120 mT(B) and 240 mT(C) Temperature/℃: a. 140; b. 150; c. 180; d. 200; e. 220.
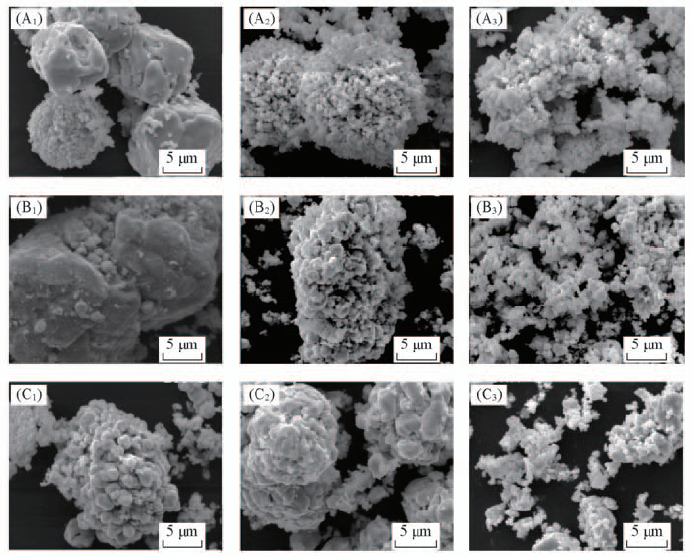

Fig.4 SEM images of samples synthesized at temperature of 150 ℃(A1—A3), 180 ℃(B1—B3) and 200 ℃(C1—C3) for 3 h with c(KOH) of 4 mol/L under 0(A1, B1, C1), 120 mT(A2, B2, C2) and 240 mT(A3, B3, C3)
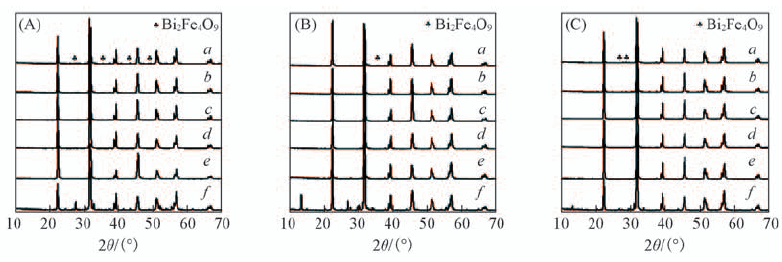
Fig.5 XRD patterns of samples synthesized at 200 ℃ with c(KOH) of 5 mol/L for different reaction time under magnetic fields of 0(A), 120 mT(B) and 240 mT(C) Reaction time/h: a. 1; b. 2; c. 3; d. 6; e. 9; f. 12.
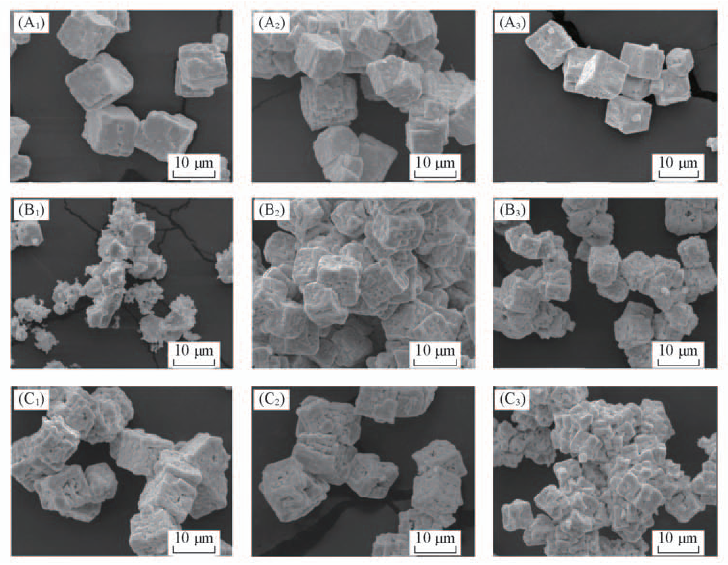
Fig.6 SEM images of samples synthesized at 200 ℃ for 2 h(A1—A3), 6 h(B1—B3) and 9 h(C1—C3) with c(KOH) of 5 mol/L under magnetic fields of 0(A1, B1, C1), 120 mT(A2, B2, C2) and 240 mT(A3, B3, C3)
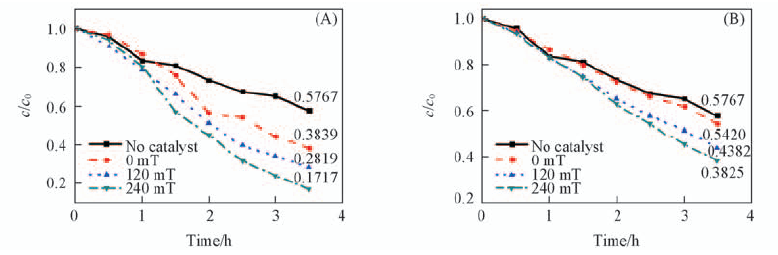
Fig.7 Photocatalytic degradation of MB over BiFeO3 powders synthesized at 200 ℃ for 3 h with c(KOH) of 4 mol/L(A) and 5 mol/L(B) under different magnetic fields
| [1] | Eerenstein W., Mathur N. D., Scott J. F., Nature, 2006, 442(7104), 759—765 |
| [2] | Ma J. , Hu J. , Li Z. , Nan C. W., Adv. Mater., 2011, 23(9), 1062—1087 |
| [3] | Wang J., Neaton J. B., Zheng H., Nagarajan V., Ogale S. B., Liu B., Viehland D., Vaithyanathan V., Schlom D. G., Waghmare U. V., Spaldin N. A., Rabe K. M., Wuttig M., Ramesh R., Science, 2003, 299(5613), 1719—1722 |
| [4] | Catalan G., Scott J. F., Adv. Mater., 2009, 21(24), 2463—2485 |
| [5] | Selbach S. M., Tybell T., Einarsrud M. A., Grande T., Adv. Mater., 2008, 20(19), 3692—3696 |
| [6] | Gao F., Yuan Y., Wang K. F., Chen X. Y., Chen F., Liu J. M., Ren Z. F., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2006, 89(10), 102506 |
| [7] | Li S., Lin Y. H., Zhang B. P., Wang Y., Nan C. W., J. Phys. Chem. C,2010, 114(7), 2903—2908 |
| [8] | Gao F., Chen X., Yin K., Dong S., Ren Z., Yuan F., Yu T., Zou Z., Liu J. M., Adv. Mater., 2007, 19(19), 2889—2892 |
| [9] | Xiao R. J., Yang R. L., Bian X. B., Zhou J. P., Wang Z., Cui J., Xie H. J., Zhang S., Liu Y. L., Journal of Shaanxi Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2013, 41(2), 39—43 |
| (肖瑞娟, 杨若琳, 边小兵, 周剑平, 王振, 崔君, 谢海江, 张栓, 刘玉龙, 刘鹏. 陕西师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 41(2), 39—43) | |
| [10] | Walker J., Bryant P., Kurusingal V., Sorrell C., Kuscer D., Drazic G., Bencan A., Nagarajan V., Rojac T.,Acta Mater., 2015, 83149—83159 |
| [11] | Koval V., Skorvanek I., Reece M., Mitoseriu L., Yan H., J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2014, 34(3), 641—651 |
| [12] | Jiang Q. H., Liu F. T., Nan C. W., Lin Y. H., Reece M. J., Yan H. X., Ning H. P., Shen Z. J., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2009, 95(1), 012909 |
| [13] | Sun W., Li J.F., Yu Q., Cheng L. Q., J. Mater. Chem. C, 2015, 3, 2115—2122 |
| [14] | Knee C. S., Tucker M. G., Manuel P., Cai S., Bielecki J., Börjesson L., Eriksson S. G., Chem. Mater., 2014, 26(2), 1180—1186 |
| [15] | Ke H., Wang W., Wang Y., Xu J., Jia D., Lu Z., Zhou Y., J. Alloy Compd., 2011, 509(5), 2192—2197 |
| [16] | Chen R., Huang K. K., Wu X. F., Si W. Z., Feng S. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2013, 34(10), 2270—2273 |
| (陈蕊, 黄科科, 吴小峰, 司文哲, 冯守华. 高等学校化学学报,2013, 34(10), 2270—2273) | |
| [17] | Sun B., Wei L., Li H., Chen P., J. Mater. Chem. C,2014, 2(36), 7547—7551 |
| [18] | Zhou J. P., Yang R. L., Xiao R. J., Chen X. M., Deng C. Y., Mater. Res. Bull., 2012, 47(11), 3630—3636 |
| [19] | Cai D., Li J., Tong T., Jin D., Yu S., Cheng J., Mater. Chem. Phys., 2012, 134(1), 139—144 |
| [20] | Zhou J. P., Xiao R. J., Zhang Y. X., Shi Z., Zhu G. Q., J. Mater. Chem. C,2015, 3(26), 6924—6931 |
| [21] | Zheng Y. Q., Tan G. Q., Miao H. Y., Xia A., Ren H. J., Mater. Lett., 2011, 65(7), 1137—1140 |
| [22] | Hou L., Zuo K. H., Sun Q. B., Ren Z. M., Zeng Y. P., Li X., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2013, 102(8), 082901 |
| [23] | Chen X. Z., Qiu Z. C., Zhou J. P., Zhu G., Bian X. B., Liu P., Mater. Chem. Phys., 2011, 126(3), 560—567 |
| [24] | Hu L., Zhang R., Chen Q., Nanoscale, 2014, 6(23), 14064—14105 |
| [25] | Xu B., Zhong Y. B., Fu X. M., Ren Z. M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2011, 32(1) , 16—22 |
| (徐斌, 钟云波, 傅小明, 任忠鸣. 高等学校化学学报,2011, 32(1), 16—22) | |
| [26] | Livesey K. L., Stamps R. L., Phys. Rev. B,2010, 81(9), 094405 |
| [27] | Park T. J., Papaefthymiou G. C., Viescas A. J., Moodenbaugh A. R., Wong S. S., Nano Lett., 2007, 7(3), 766—772 |
| [28] | Liu B., Hu B., Du Z., Chem. Commun., 2011, 47(28), 8166—8168 |
| [29] | Ramazanoglu M., Laver M., Ratcliff W., Watson S. M., Chen W. C., Jackson A., Kothapalli K., Lee S., Cheong S. W., Kiryukhin V., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2011, 107(20), 207206 |
| [30] | Haumont R., Kreisel J., Bouvier P., Hippert F., Phys. Rev. B,2006, 73(13), 132101 |
| [31] | Palai R., Schmid H., Scott J. F., Katiyar R. S., Phys. Rev. B,2010, 81(6), 064110 |
| [32] | Hermet P., Goffinet M., Kreisel J., Ghosez P., Phys. Rev. B,2007, 75(22), 220102(R) |
| [33] | Kothari D., Raghavendra Reddy V., Sathe V. G., Gupta A., Banerjee A., Awasthi A. M., J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2008, 320(3/4), 548—552 |
| [34] | Rout D., Moon K. S., Kang S. J. L., J. Raman. Spectrosc., 2009, 40(6), 618—626 |
| [35] | Suzuki N., Kamimura H., J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., 1973, 35(4), 985—995 |
| [36] | Singh M. K., Prellier W., Jang H. M., Katiyar R. S., Solid State Commun., 2009, 149(43—44), 1971—1973 |
| [37] | Luo W., Wang D., Wang F., Liu T., Cai J., Zhang L., Liu Y., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2009, 94(20), 202507 |
| [1] | LI Xiaohui, WEI Aijia, MU Jinping, HE Rui, ZHANG Lihui, WANG Jun, LIU Zhenfa. Effects of SmPO4 Coatingon Electrochemical Performance of High-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 Cathode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210546. |
| [2] | RONG Hua, WANG Chungang, ZHOU Ming. Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of FeS2 Microspheres as an Anode for Li-ion Batteries † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 447. |
| [3] | HUANG He, LI Chunguang, SHI Zhan, FENG Shouhua. Microwave-assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of Carbon Dots Based on Tyrosine and Their Application in Ion Detection and Bioimaging [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1579. |
| [4] | DONG Xiangyang,NIU Xiaoqing,WEI Jishi,XIONG Huanming. One-step Hydrothermal Synthesis of Copper Doped Carbon Dots and Their Application in White Light Devices† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1288. |
| [5] | JIA Hongliang,ZHAO Jianwei,QIN Lirong,ZHAO Min. Uric Acid Biosensor Based on Ni Wire Modified with NiO Nanosheets† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 240. |
| [6] | SUN Dawei,LI Yuejun,CAO Tieping,ZHAO Yanhui,YANG Diankai. Preparation of Dy 3+-doped YVO4/TiO2 Composite Nanofibers with Three-dimensional Net-like Structure and Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity for Hydrogen Evolution † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(11): 2348. |
| [7] | PAN Shuai, HU Xiaobing, SONG Runmin, XIE Lili, ZHU Zhigang, ZHENG Liaoying. Ionic Liquid Assisted Synthesis of α-Fe2O3 Nanospheres Based on Potassium Acetate Solution and Their Gas-sensing Properties† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1631. |
| [8] | KANG Yuanyuan, GUO Zeqing, ZHOU Jianping. Hydrothermal Preparation and Adsorption Property of MoS2/Na2Fe2Ti6O16† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1364. |
| [9] | LI Juan, ZHU Linfang, ZHAO Anting, LEI Guoming, GAO Li, XIA Wen, WANG Li. Catalytic Activity of Cucurbit[6]uril Modified Copper Flower Clusters† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(3): 422. |
| [10] | ZHANG Yiqing, LIU Jiaxiang. Hydrothermal Preparation of Cubic ITO Powder and Its Photoelectric Performance† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1110. |
| [11] | SUN Lianzhi, ZHAO Shengzhe, GAO Zhiling, CHENG Zhiqiang. Controllable Synthesis of Ag Decorated ZnO Nanofibers for Enhanced Photocatalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(6): 907. |
| [12] | HAN Yanmei, GAO Zhihua, HUANG Wei. Effects of AlOOH Structure on the Reaction of Methanol and Carbon Monoxide† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5): 823. |
| [13] | HUANG Haiping, YUE Yafeng, XU Liang, LÜ Lianlian, HU Yongmei. Glucose Biosensor Based on Dy2(MoO4)3-AuNPs Composite Nanomaterial† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(4): 554. |
| [14] | SHI Yanlong, FENG Xiaojuan, WANG Suiqian, FENG Chunchun. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Film of Co(OH)2CO3 Nanowires and Its Anticorrosion† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(3): 456. |
| [15] | ZHU Jielian, XIA Xiaofeng, ZHU Shanshan, LIU Xiang, LI Hexing. Synthesis and Photocatalytic Activity of Cr Doped TiO2 Nanowires/Reduced Graphene Oxide Composites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(10): 1833. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||