

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (8): 1631.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170804
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
PAN Shuai1, HU Xiaobing1, SONG Runmin1, XIE Lili1,2, ZHU Zhigang1,2,*( ), ZHENG Liaoying3
), ZHENG Liaoying3
Received:2017-12-11
Online:2018-08-10
Published:2018-04-28
Contact:
ZHU Zhigang
E-mail:zgzhu@sspu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
PAN Shuai, HU Xiaobing, SONG Runmin, XIE Lili, ZHU Zhigang, ZHENG Liaoying. Ionic Liquid Assisted Synthesis of α-Fe2O3 Nanospheres Based on Potassium Acetate Solution and Their Gas-sensing Properties†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1631.
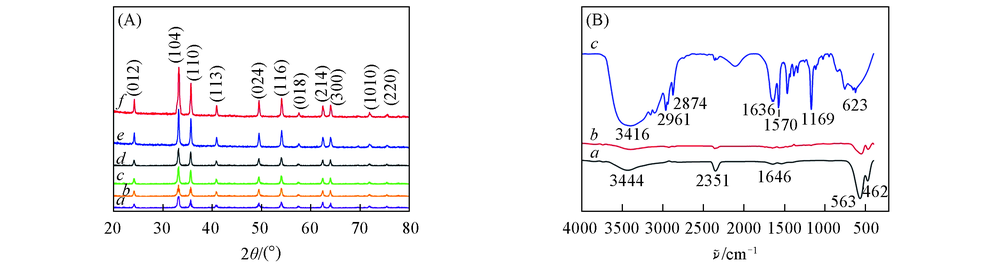
Fig.2 XRD patterns of α-Fe2O3 nanospheres prepared with different amounts of ionic liquid(A) and FTIR spectra of S-0(a), S-4(b) and [Bmim]Cl(c)(B)(A) a. S-0; b. S-1; c. S-2; d. S-3; e. S-4; f. S-5.
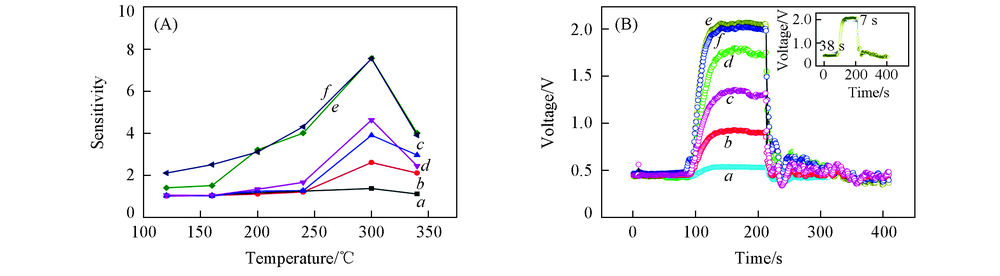
Fig.5 Temperature-dependent gas sensing response(A) and response-recovery curves(B) of different α-Fe2O3 nanospheres to 50 μL/L ethanol gasa. S-0; b. S-1; c. S-2; d. S-3; e. S-4; f. S-5. Inset of (B) shows tres and trec of S-4.
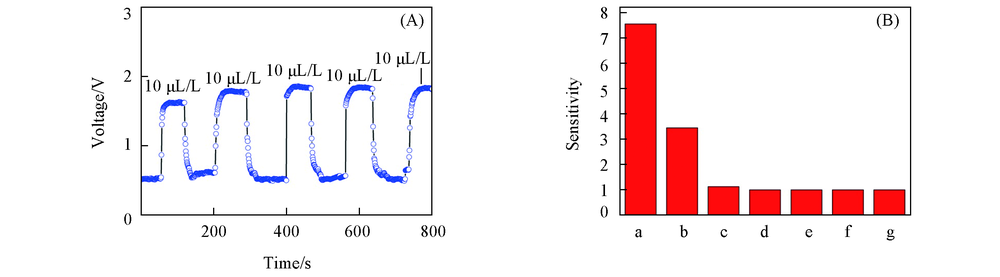
Fig.7 Stabiliity test of sample S-4 at operating temperature of 300 ℃ to 10 μL/L ethanol(A) and response sensitivity for sample S-4 to different gases at operating temperature of 300 ℃(B) (B) a. C2H5OH; b. CH3COH3; c. H2S; d. NH3; e. NO; f. Cl2; g. NO2.
| [1] | Zhu L.P., Xiao H. M., Fu S. Y., Cryst. Growth. Des., 2007, 7(2), 177—182 |
| [2] | Sun P., Zhou X., Wang C., Shimanoe K., Lu G.Y., Yamazoe N., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 2(5), 1302—1308 |
| [3] | Zhao X.L., Li Z. H., Chen C., Wu Y. H., Zhu Z. G., Zhao H. L., Lan M. B., Electroanalysis, 2017, 29, 1518—1523 |
| [4] | Zhang X.L., Huang F., Nattestad A., Wang K., Fu D, Chem. Commun., 2011, 47(16), 4808—4810 |
| [5] | Xu L., Zheng R., Liu S., Song J., Chen J., Inorg.Chem., 2012, 51(14), 7733—7740 |
| [6] | Cao J., Wang Z.Y., Wang R., Liu S., Fei T., Wang L. J., Zhang T., J. Mater. Chem. A., 2015, 3(10), 5635—5641 |
| [7] | Wang C., Cheng X., Zhou X., Sun P., Hu X., Shimanoe K., Lu G.Y., Yamazoe N., ACS Appl. Mat. Inter., 2014, 6(15), 12031—12037 |
| [8] | Li L., Chu Y., Liu Y., Dong L., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111(5), 2123—2127 |
| [9] | Chi X., Liu C.B., Liu L., Sens. Actuators B, 2014, 194, 33—37 |
| [10] | Zeng W., Liu T.M., Wang Z. C., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2012, 22, 3544—3548 |
| [11] | Navale S.T., Bandgar D. K., Nalage S. R, Ceram. Int., 2013, 39, 6453—6460 |
| [12] | Park J., Shen X., Wang G., Sens. Autuators B, 2009, 136, 494—498 |
| [13] | Ma Z., Yu J.H., Dai S., Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 261—285 |
| [14] | Li Z., Jia Z., Luan Y., Curr. Opin. Solid. St. M., 2008, 12, 1—8 |
| [15] | Taubert A., Acta Chim.Slov., 2005, 52, 183—186 |
| [16] | Welton T., Chem.Rev., 1999, 99, 2071—2083 |
| [17] | Fei Z., Oeldbach T.J., Chem. Eur. J., 2006, 12, 2122—2130 |
| [18] | Taubert A., Li Z., Dalton Trans., 2007, 7, 723—727 |
| [19] | Liu X.D., Ma J. M., Peng P., Mater. Sci. Eng. B, 2008, 150, 89—94 |
| [20] | Antonietti M., Kuang D., Smarsly B., Zhou Y., Chem. Int.Ed., 2004, 43, 4988—4992 |
| [21] | Sheldon R., Chem. Commun., 2001, 23, 2399—2407 |
| [22] | Dupont J., Suoza R.F. D., Suarez P. A. Z., Chem. Rev., 2002, 102, 3667—3692 |
| [23] | Li J., Zeng H.C., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 15839—15847 |
| [24] | Li Z.H., Li J. C., Song L. L., Gong H. Q., Niu Q., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(48), 15377—15382 |
| [25] | Li R., Du J.M., Luan Y. X., Zou H., Zhuang G. Z., Li Z. H., Cryst. Eng. Comm., 14(10), 3404—3410 |
| [26] | Wang P., Xu Y.M., Cheng X. L., Huo L. H., Sui L. L, Nat. Sci. Heilongjiang. Univ., 2014, 31(6), 778—783 |
| [27] | Hu X.B., Zhu Z. G., Chen C., Wen T. Y., Zhao X. L., Xie L. L., Sens. Autuators B, 2017, 253, 809—817 |
| [28] | Hu X.B., Zhu Z. G., Li Z. H., Xie L. L., Wu Y. H., Zheng Z. Y., Sens. Autuators B, 2018, 264, 139—149 |
| [29] | Lian J., Duan X.H., Ma J., Peng P., Kim T., Zheng W. J., ACS Nano, 2009, 3(11), 3749—3761 |
| [30] | Chu D.W., Zeng Y. P., Jiang D. L., Masuda Y., Sens. Autuators B, 2009, 137, 630—636 |
| [31] | Sun P., Cai Y.X., Du S. S., Xu X. M., You L., Ma J., Liu F. M., Liang X. H., Sun Y. F., Lu G. Y., Sens. Autuators B, 2013, 182, 336—343 |
| [32] | Zhang B., Fu W.Y., Meng X. W., Ruan A., Su P. Y., Yang H. B, Ceram. Int., 2017, 43(8), 5934—5941 |
| [33] | Shen G., Chen P.C., Ryu K., Zhou C., J. Mater. Chem., 2009, 19, 828—839 |
| [34] | Yue J., Jiang X.H., Yu A. B., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117(19), 9962—9969 |
| [1] | CUI Wei, ZHAO Deyin, BAI Wenxuan, ZHANG Xiaodong, YU Jiang. CO2 Absorption in Composite of Aprotic Solvent and Iron-based Ionic Liquid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220120. |
| [2] | PENG Kuilin, LI Guilin, JIANG Chongyang, ZENG Shaojuan, ZHANG Xiangping. Research Progress for the Role of Electrolytes in the CO2 Electrochemical Reduction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220238. |
| [3] | JI Shuangqi, JIN Zhao, GUAN Wenna, PAN Xiangyu, GUAN Tong. Preparation and Chromatographic Performance of Mixed-mode Silica Stationary Phase Modified by Double Cationic Ionic Liquid and Octadecyl Group [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220008. |
| [4] | LI Xiaohui, WEI Aijia, MU Jinping, HE Rui, ZHANG Lihui, WANG Jun, LIU Zhenfa. Effects of SmPO4 Coatingon Electrochemical Performance of High-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 Cathode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210546. |
| [5] | CHANG Sihui, CHEN Tao, ZHAO Liming, QIU Yongjun. Thermal Degradation Mechanism of Bio-based Polybutylactam Plasticized by Ionic Liquids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220353. |
| [6] | WANG Man, WANG Xin, ZHOU Jing, GAO Guohua. Efficient Synthesis of Dimethyl Carbonate via Transesterification of Methanol and Ethylene Carbonate Catalyzed by Poly(ionic liquid)s [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3701. |
| [7] | WAN Ren, SONG Fan, PENG Changjun, LIU Honglai. Group Contribution Method for Infinite Dilution Molar Conductivity of Unconventional Ions in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3672. |
| [8] | ZHOU Molin, JIANG Xin, YI Ting, YANG Xiangguang, ZHANG Yibo. Improvement of Interface Stability Between Sulfide Solid Electrolyte Li10GeP2S12 and Lithium Metal [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1810. |
| [9] | CHENG Shifu,HU Hao,CHEN Bihua,WU Haihong,GAO Guohua,HE Mingyuan. Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of Porous Carbons Prepared from Binary Ionic Liquids † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1048. |
| [10] | GAO Chong,YU Fengli,XIE Congxia,YU Shitao. Baeyer-Villiger Oxidation of Cyclic Ketones Catalyzed by Amino Alcohol Heteropoly Acid Ionic Liquid † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1101. |
| [11] | GAO Naiwei, MA Qiang, HE Yonglin, WANG Yapei. Green Electronic Devices Based on Ionic Liquids † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 901. |
| [12] | RONG Hua, WANG Chungang, ZHOU Ming. Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of FeS2 Microspheres as an Anode for Li-ion Batteries † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 447. |
| [13] | PIAO Huilan,MA Pinyi,QIN Zucheng,JIANG Yanxiao,SUN Ying,WANG Xinghua,SONG Daqian. Determination of Triazine Herbicides from Fruit Juice Samples Using Effervescence Assisted Microextraction Method Based on Acidic Ionic Liquid Packed Syringe [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 228. |
| [14] | ZHANG Li,QIAN Mingchao,LIU Xueke,Gao Shuaitao,YU Jiang,XIE Haishen,WANG Hongbin,SUN Fengjiang,SU Xianghong. Dynamic Study of Oxidative Desulfurization by Iron-based Ionic Liquids/NHD † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 317. |
| [15] | WANG Nan,YAO Kaisheng,ZHAO Chenchen,LI Tianjin,LU Weiwei. Ionic Liquid-assisted Synthesis of AuPd Nanosponges and Their Catalytic Performance † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 62. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||